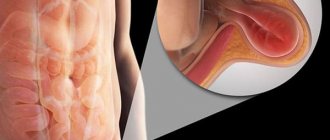
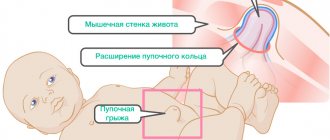
Any hernia, as an anatomical formation, always represents a failure of muscle protection in a certain place, when it becomes possible for the insides to escape under the skin. With a hernia of the linea alba, the weak area is the junction of the rectus and oblique muscles of the abdominal wall.
It is more often observed in young men aged 20–35 years. They account for 60% of cases. But it also happens to women, children, and the elderly. The most typical localization is in the epigastric region (5% of all possible abdominal hernias). The disease can only be treated surgically. Other methods provide slight temporary relief, but are not able to eliminate the hernia.
Features of the anatomy of the zone
The linea alba is a powerful fusion of muscle tendons that runs from the lower end of the sternum to the pubic bone. It is not visible on the surface of the abdomen. Projected along the midline. The bilateral oblique muscles carry a constant load and provide position and movement of the body. Their tendons converge in front and represent a relatively thin formation (1–2 mm), poorly supplied with blood supply and nerve endings.
The width of the fusion is individual, varying from 20 to 30 mm. The fibers of the aponeurosis (the dense membrane of the muscle) are capable of twisting and forming cracks in the form of diamonds. In terms of quantity, they are maximally located in the upper and middle parts of the line. Normally, they are filled with adipose tissue from the anterior peritoneal tissue (preperitoneal) and are capable of stretching.
How is implantation carried out?
There are 4 ways to install a mesh in the hernial orifice:
- Onlay . The mesh is sewn onto the aponeurosis of the rectus or external oblique abdominal muscles, directly contacting the subcutaneous fatty tissue.
- Inlay . The mesh is installed on the rectus or external oblique muscle, separated from the subcutaneous fat layer by the same aponeuroses.
- Underlay . The mesh is placed behind the muscle layer, usually separated from the abdominal cavity by the transversus abdominis muscle and transversalis fascia.
- Sublay . The mesh is located in the preperitoneal tissue, separated by the peritoneum from the abdominal organs.
The surgeon individually selects the appropriate implantation method for each patient.
In this case, it is necessary to follow the rules for installing mesh endoprostheses:
- the hernia mesh is installed only within the aponeurotic and muscle tissues;
- multifilament threads cannot be used to secure the endoprosthesis;
- For mixed truncation, a non-absorbable type of mesh endoprosthesis cannot be used.
What happens when a hernia forms?
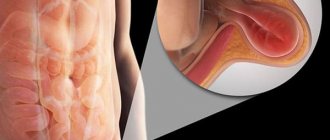
The hernial canal in the linea alba forms gradually. The tendon fibers diverge over a distance of up to 12 cm. A hernial orifice is formed, resembling a circle, oval or diamond. There are stages of development. A hernia begins with stretching of the cracks in the fibers of the aponeurosis and the release of fatty tissue under the skin. It forms preperitoneal lipomas. The holes are still small.
With further expansion, an anatomical hernial orifice appears, into which the peritoneum protrudes in addition to the tissue. Normally, the role of the peritoneum is to cover and protect the inside of the abdominal wall and the outside of the abdominal organs. Here it forms the shell of the hernial sac.
At the stage of complete formation, the disease has all the classic signs:
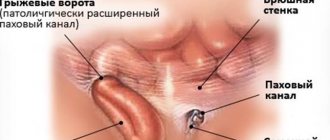
- hernial orifice - represented by an opening where organs protrude;
- peritoneal sac;
- components of the hernial sac are the intestinal loop, omentum, stomach wall, ligaments of internal organs.
Trauma to the contents of the sac causes swelling. The hernial orifice becomes narrow for self-reduction of the prolapsed omentum, pinching occurs with all the negative consequences.
Diagnostics
The primary diagnosis can be made based on an external examination of the patient; additional examinations are required to accurately determine the condition.
- Ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity. The condition of the internal organs is checked.
- X-ray examination of the hernial sac. Before the examination, the patient is given a barium preparation to increase the contrast of the image.
- Multislice tomography. Used in the most difficult cases, it allows you to completely eliminate errors during diagnosis and assessment of the current condition.
Why does a hernia form?
The expansion of the white line in men is often determined by a discrepancy between the development of muscle tissue and its aponeurosis. Abdominal hernias in women occur due to weakening of the abdominal wall due to frequent repeated pregnancies. The causes of the pathology are conventionally divided by nature: into factors that increase intra-abdominal pressure, contributing to the weakening of the tendons of the abdominal muscles.
The first include:
- heavy physical work, weight lifting for weightlifters;
- the passion of teenagers, young men and girls for bodybuilding, the desire to “pump up the abs”;
- enlarged abdomen due to abdominal fat in obesity, ascites due to fluid accumulation caused by venous blood retention (portal hypertension in liver cirrhosis, circulatory failure);
- diseases leading to prolonged constipation;
- suffered complicated pregnancies and childbirths;
- diseases that cause prolonged severe coughing and vomiting;
- pathology of the genitourinary system, contributing to urinary retention (prostatitis, malignant and benign tumors of the prostate, bladder, urolithiasis);
- babies cry for various reasons.
Weakness of the aponeurosis and tendons can be caused by sudden weight loss
Postoperative scars in the white line area lead to tendon weakness. Such hernias are called ventral. Many abdominal surgeries require an incision along the linea alba (laparotomy). This improves access to the required area, provides more opportunity to examine the entire abdominal cavity, ligate vessels and eliminate bleeding during the recovery period. However, there is an increased risk of postoperative hernia.
Traumatic injuries to the abdomen are most common among athletes; closed and open types occur from bruises, falls from a height, during road accidents, gunshot and knife wounds. There may be a hereditary predisposition caused by impaired collagen synthesis in connective tissue.
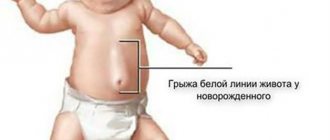
Most often, the reasons are mixed. But finding out the main factors is important for deciding on the treatment of a particular person and preventing relapse. You can learn more about the causes of linea alba hernia in newborns from this article.
Causes
Factors that provoke the development of the disease are divided into 2 categories: causes arising from weakness of the white line, and factors caused by increased pressure inside the peritoneum.
The reasons belonging to the first group act as prerequisites for the occurrence of a hernia. This:
- Genetic predisposition If you have relatives with this diagnosis, the risk of the disease increases.
- Excess weight Due to a thick layer of subcutaneous fat, the anterior abdominal wall becomes weak and the linea alba begins to stretch.
- Scars formed as a result of surgical interventions Each of them is a vulnerable place where a hernia can bulge.
- Injuries Any injury to the abdomen makes the anterior abdominal wall weaker.
- Pregnancy During this period, the abdominal muscles weaken and the abdominal wall stretches.
Factors included in the second group are direct provocateurs of the disease. These include:
- strong and prolonged crying in children;
- difficult birth, large baby;
- diseases occurring against the background of problems with urination;
- great physical activity;
- constipation;
- diseases of the abdominal cavity occurring against the background of a severe cough.
Surgical classification
In surgery, hernias of the white line of the abdomen are distinguished by location and relation to the navel:
- from above - epigastric (supra-umbilical);
- in the navel area - paraumbilical;
- below.
The upper localization is the most common. Due to the thinnest structure. Below the navel, the fusion of the aponeurosis is much stronger, thicker, and there are few gaps in them, so hernias rarely occur here.
It is possible for one person to develop several hernias at different stages at once; they are located on the white line in the form of floors
Characteristic signs
Symptoms of a hernia of the linea alba can be noticed by the patient himself already at the lipoma stage by a formation protruding along the midline in an upright position of the body. Some people are immediately sure that they have a tumor. But unlike a neoplasm, it is painless, soft, and “goes” inward when lying down. The skin over the area of the hernial sac does not change.
As the hernia forms, it becomes clear that:
- the formation has a clear localization along the midline and does not spread anywhere;
- elastic to the touch, painless;
- diameter ranges from 1 to 12 cm;
- if a loop of intestine enters the hernial sac, rumbling is felt;
- the skin is no different from other areas;
- characterized by an increase with straining.
Abdominal hernias may not bother a person and may be asymptomatic. The doctor identifies them only during a preventive examination or concomitant diseases.
Other patients complain of moderate pain with exercise. Less commonly, belching, heartburn, nausea, a feeling of heaviness in the upper abdomen. Such cases require additional examination to exclude diseases of the stomach, biliary tract, liver and other digestive organs.
By what signs can one suspect infringement?
Before pinching, something usually happens to the person that sharply increases intra-abdominal pressure (for example, lifting something heavy, severe coughing) and muscle tension. A strangulated hernia of the white line of the abdomen is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- the protrusion becomes painful, the pain increases with palpation if you ask the patient to breathe with his stomach;
- nausea and vomiting;
- bloating caused by delayed passage of gases;
- constipation;
- deterioration (weakness, palpitations, blood pressure fluctuations).
The peculiarity of the course of a hernia of the white line is the possible long pain-free period. But a person usually knows about his illness and no matter how hard he tries to protect himself, he can provoke a situation of infringement. Therefore, surgeons insist on timely suturing of the hernial orifice before serious plastic surgery is needed to close a significant area of the opening and combat the consequences of strangulation.
The most severe complication of a hernia is necrosis of the wall of the organ entering the hernial sac, with the development of inflammation of the peritoneum (peritonitis)
Indications and contraindications
Installation of mesh endoprostheses is indicated:
- for hernias repaired surgically;
- with injuries to the chest wall;
- with damage to the diaphragm;
- for soft tissue defects;
- to strengthen traumatic and surgical wounds.
The use of surgical mesh for hernia is contraindicated:
- during pregnancy;
- when the patient is under 5 years of age;
- for disorders of the cardiovascular system;
- after a stroke;
- for respiratory disorders;
- during exacerbations of chronic diseases.
In order to find out exactly whether a mesh endoprosthesis is indicated or contraindicated, it is necessary to consult with a surgeon, providing him with full information about the disease, health status, current and past diseases.
What is needed to make a diagnosis?
Diagnosis begins with clarifying complaints, how long ago the disease was, and examining a doctor. It is necessary to establish the degree of muscle divergence and which organs are included in the hernial sac. The following methods are used for this:
Gastric hernia
- Ultrasound diagnostics - the study is carried out with the patient standing, allows you to identify adhesions;
- fluoroscopy of the stomach and intestines with preliminary administration of a contrasting barium suspension;
- computed tomography in multispiral mode.
Patients should remember that the appearance of any formation, even a painless one, on the body is a serious reason to consult a doctor. A hernia must be distinguished from diastasis (widening) of the central junction of the rectus abdominis muscles. It forms after childbirth in women in the second or third month. The reason is the special physiological looseness of the connective tissue, which ensures normal contractions.
If you start early training to correct your abdomen, diastasis appears. In men, this phenomenon can occur under heavy loads and obesity. In appearance, diastasis differs from the hernial sac in a roller-like stripe along the white line; it manifests itself when the muscles are tense. The symptoms do not differ from hernia-like ones.
Advantages and disadvantages of hernia meshes
Advantages of mesh endoprostheses:
- are not rejected by the body;
- low probability of recurrence of a hernia;
- does not interfere with the patient after surgery and does not cause discomfort;
- short rehabilitation period;
- fuses with connective tissue and reliably fixes the hernial orifice.
Disadvantages of mesh endoprostheses:
- slight inflammation, as the body’s reaction to a foreign body, which quickly passes.
Is treatment possible without surgery?
You cannot listen to the advice of strangers and try to cure a hernia yourself using folk remedies. There is only one method of radical treatment - surgery. Other treatment options temporarily relieve unpleasant symptoms (pain, increased gas formation), but do not stop the process that has begun, and even stretch the hernial opening even more.
Advertised “hernia exercises” lead to increased growth of the hernia sac. They are good for prevention, but not at the stage of an already formed hernia. Conservative therapy is indicated for the period of preparation of the patient for planned surgical treatment, for patients with severe general diseases.
Complete tissue restoration occurs only by the end of the year after childbirth.
Temporary measures include the following:
- We recommend wearing a special bandage belt. It should be clearly understood that no bandage can replace the muscular frame. Its purpose is to reduce the risk of prolapse and strangulation of the hernial sac and damage to internal organs. Surgeons believe that long-term use of a bandage reduces muscle tone, promotes the process of atrophy, and reduces strength and elasticity.
- Medicines with antispasmodic and analgesic effects. Indeed, good analgesics and antispasmodics can relieve pain. But at the same time, the patient is blocked from all pain sensitivity. Signs of infringement can be blurred and difficult to diagnose. This prevents doctors from assessing symptoms and making the right treatment decisions.
- Laxative medications that reduce gas formation and constipation. If the intestines begin to work hard, then, on the one hand, this reduces intra-abdominal pressure and protrusion of the hernial sac, on the other hand, motor activity contributes to the intestinal wall entering the formed formation. And, of course, medications do not matter for closing the hernial orifice.
The folk remedies recommended by healers are selected according to the principle of action of the described drugs. Decoctions of plants are used (chamomile, immortelle, Alexandria leaf, wormwood, senna). They are not capable of causing fusion of the hernial orifice into tendon tissue, but they facilitate bowel function and relieve bloating.
If a patient has an asymptomatic preperitoneal lipoma, he is informed about the initial stage of hernia formation and is offered observation. Treatment in such cases is not indicated.
Types of mesh for hernia
According to the degree of resorption, medical meshes for hernia treatment are:
- Absorbable . Over a certain period of time they dissolve in the human body. When using these endoprostheses, it is necessary to take into account that the time for complete wound healing and patient recovery is less than the time for resorption of the mesh endoprosthesis. There is a risk of relapse after complex operations.
- Non-absorbable . They do not dissolve in the human body at all. Such an endoprosthesis stays in the human body all his life and does not interfere with it in any way. Over time, they become overgrown with muscle tissue, as they have sufficient porosity. Most commonly used in medicine. The most reliable, with minimal risk of re-development of the hernia. They are produced, for example, by the Volot company.
- Partially absorbable . After muscle tissue builds up, it is partially resorbed in the body.
By form:
- Simple one-dimensional ones . They represent a grid that is in the same plane.
- Complex three-dimensional . A mesh consisting of 3 flaps located in different planes. The structure of the three-dimensional mesh is such that one flap is applied on the inside of the hernial orifice, and the other on the outside, and they are connected by a flap rolled into a cylinder, which fills the hole itself.
By coverage:
- Drug coated . Coated with a substance that prevents infection and promotes rapid wound healing.
- No drug coverage . No drug coverage.
By thickness:
- Lungs . Meshes with a thickness of 0.32-0.44 mm with a monofilament diameter of 0.09±0.01 mm. Intended for reconstructive surgical plastic surgery after removal of hernias of various locations, in cases where the tissues do not experience increased stress and/or their own tissues are in satisfactory condition, as well as for strengthening wounds.
- Classic . Meshes with a thickness of 0.45-0.70 mm with a monofilament diameter of 0.12±0.01 mm. Intended for reconstructive plastic surgery of the anterior abdominal wall after removal of a hernia, for damage to the diaphragm and chest wall, for soft tissue defects, as well as for strengthening traumatic and surgical wounds.
- Heavy . Meshes with a thickness of 0.65-0.99 mm with a monofilament diameter of 0.14±0.02 mm. Used to treat giant ventral hernias. They are used on areas of soft tissue that have greater mobility and are subject to increased stress.
- Superheavy . Meshes with a thickness of 0.65-0.99 mm with a monofilament diameter of 0.16±0.02 mm. Used in the most severe cases when the highest strength is required.
Do I need a special diet?
The purpose of the diet for patients with a hernia of the linea alba is to prevent bloating of intestinal loops and stagnation of feces (coprostasis). Both processes make it possible to slow down the formation of the hernial sac. Nutritional recommendations are applied both before and after surgery until the integrity of the abdominal wall is completely restored.
The following are excluded from the diet:
- nuts;
- legumes;
- white cabbage, asparagus;
- tomatoes;
- animal fats and butter;
- all fried foods;
- canned food;
- fresh baked goods and culinary products;
- fast food;
- chocolate;
- coffee;
- carbonated drinks;
- hot sauces and seasonings;
- fresh apples.
The patient needs to eat 6–7 times a day, in small portions, not to overeat, and drink a lot of water (1.5–2 l).
Allowed:
- porridge;
- milk if well tolerated;
- low-fat meat and fish dishes;
- fresh fruit juices;
- carrots, beets, cucumbers;
- kefir;
- cheese;
- low-fat cottage cheese;
- boiled sausage;
- eggs no more than two per week;
- broccoli;
- citrus fruit;
- apricots, dried apricots, prunes;
- dried white bread.
Methods of surgical treatment
The general opinion of doctors is that it is impossible to treat a hernia of the white line of the abdomen without surgery. After the examination, the patient is prepared for planned surgery. The volume of the operation is related to the size of the hernial sac, the strength of the aponeurosis in the intervention area, combination with diastasis of the rectus muscles, concomitant pathology, and the age of the patient.
The best models of the bandage have a reinforcement plate sewn into the front
An uncomplicated operation is performed under general anesthesia. Pain relief is provided for the entire period of the operation. The abdominal cavity is opened with incisions. Inspect the contents of the hernial sac. It is necessary to exclude damage caused by partial or complete infringement.
If there is no damage, then the omentum and intestinal loop are reduced into the abdominal cavity. If altered tissues are detected, they are removed. The hernial orifice is eliminated using suturing. For medium and large hernias, combined with significant diastasis (up to 5–7 cm), various hernioplasty methods are used. So, it is called the closure and strengthening of a defect in the abdominal wall.
Among the methods developed are strengthening the aponeurosis with its own tissues with two rows of sutures and the use of polypropylene mesh. With the usual tightening of the edges of the hole, patients experience relapses with a frequency of 20–40% according to different authors. The use of a reinforcing mesh eliminates tissue tension, and the number of relapses is significantly lower (about 7%).
A promising method is considered to be a combination of suturing the opening of the hernial sac through a small incision and installing a mesh using modern laparoscopic techniques.
Surgery to remove a hernia of the linea alba
A hernia can only be treated surgically in an inpatient setting. An operation aimed at removing a hernia is called hernioplasty. To date, about 300 surgical methods have been developed for the treatment of hernias of the anterior abdominal wall. Both simple techniques using the patient’s own tissues and complex reconstructive interventions using artificial materials are used.
The following types of operations are distinguished:
- Plastic surgery using local tissues (open surgery with tension plastic surgery). The defect is sutured with a non-absorbable thread to eliminate possible divergence of the rectus muscles. Due to the weakness of the connective tissue and the significant load on the postoperative sutures, in 25-40% of cases, a relapse of the disease occurs after the intervention, so this method is used infrequently. Another disadvantage is that the long incision leaves a large scar.
- Plastic surgery using synthetic prostheses and meshes (open surgery with tension-free plastic surgery). To close the defect after eliminating the diastasis, a mesh made of allomaterial is installed. Dentures and meshes provide a strong frame, so the likelihood of recurrence of the disease is low. This is a minimally invasive technique; during the operation, a small incision is made in the umbilical area. Through this incision, not only the hernia formation is removed, but also a prosthesis is installed. The mesh can be installed under the aponeurosis (tendon plate), as well as in its lumen and inside the abdominal cavity. Over time, the allomaterial grows with connective tissue, and it becomes impossible to distinguish it from its own tissues. External seams remain invisible.
- Laparoscopic intervention. With the advent of high-tech devices, this technique in the treatment of white line hernia is becoming increasingly popular. In this case, no incision is made. Instead, the surgeon makes several holes through which the formation is removed and a mesh prosthesis is inserted. Laparoscopic surgery minimizes the risk of recurrence of the disease and is less traumatic in general. The recovery period after laparoscopy is reduced to ten days (compared to other techniques). After this, the patient can return to normal life. This operation is not suitable for patients with heart and lung diseases. Also, its implementation is impossible in the absence of the necessary equipment and qualified specialists.
- Paraperitoneal intervention. In this case, several punctures are also performed, but unlike laparoscopy, the peritoneum is not pierced and instruments are not inserted into the cavity. A special balloon is placed between the peritoneum and adjacent tissues. Due to its inflation, a space is formed that provides access to the hernial formation. The advantages of this method are the same as those of laparoscopy, but the intervention is somewhat more complicated. Because of this, the mesh prosthesis cannot be securely fixed.
The peculiarity of radical treatment of white line hernia is that removal of the formation alone is not enough. It is necessary to eliminate the discrepancy of the rectus muscles.
The operation can be performed as planned. The surgeon examines the patient, conducts an examination, makes an accurate diagnosis and sets a date for surgery.
As noted above, now mainly non-tension techniques are used to eliminate white line hernia and eliminate diastasis.
The advantages of such an operation are as follows:
- Reliability, minimal risk of re-development of the disease;
- Simplified intervention technique, which allows it to be used in outpatient practice;
- Possibility of using minimally invasive techniques with the introduction of synthetic implants;
- Slight tissue trauma, due to which the patient experiences less pain in the postoperative period;
- Reducing the rehabilitation period and temporary disability;
- Good cosmetic effect.
How is the operation performed?
Before the intervention, the patient undergoes a series of tests:
- Blood and urine for general analysis;
- Blood biochemistry;
- Tests for hepatitis, syphilis and HIV;
- He undergoes an electrocardiogram.
During the intervention, the surgeon separates the hernial sac, opens it, assesses the condition of the organs inside and places them in the abdominal cavity. The hernial sac is bandaged and cut off, its base is sutured. After this, diastasis is eliminated and the white line is strengthened.
In case of a strangulated hernia, surgery is performed on an emergency basis. The surgeon opens the sac and evaluates the part of the intestine that has fallen into it. If it has died, it is excised. In some cases, a significant area of the intestine dies - then the incision is enlarged and all dead tissue is removed.
The intervention is performed under general anesthesia, the operation lasts about an hour (if there are no complications). If a planned operation is performed, the patient leaves the clinic the next day. Dressings are carried out twice a week. The sutures are removed on days 10-12.
Recovery after surgery
In case of exacerbation of the disease, surgical intervention is inevitable, but the scope of resection in this case can be expanded. If the formation has already formed, there is no point in wearing a bandage, since this will only aggravate the situation (squeezing the protrusion is highly not recommended).
Bandages are worn in two cases: to prevent the development of the disease and in the period after surgery to maintain the integrity of the sutures and support weakened abdominal muscles.
After surgery, you should also not strain the site of the removed hernia. Lifting heavy objects is prohibited and physical activity should be avoided in general. After two to three months, when the body has fully recovered after the intervention, on the contrary, special exercises aimed at strengthening the abdominal muscles are recommended. You should not create a complex on your own; to do this, you need to consult a doctor who will recommend an effective restorative set of exercises.
After the intervention, you must follow a special diet. Consumption of foods that cause gas formation and stool retention is prohibited. The diet should be as gentle as possible in order to maintain the integrity of postoperative sutures and not injure the operated areas. Food should be eaten in small portions. Consumption of liquid meals and cereals is recommended.
If you have problems with weight, to eliminate the risk of re-development of the hernia, you need to normalize your body weight and strengthen your muscle corset.
Prognosis after surgery. After open interventions with tension methods, the likelihood of relapses is high: in 25-40% of patients, the hernia occurs again. With tension-free, minimally invasive techniques, the risk of relapse is low.
In general, the likelihood of a relapse depends on how conscientiously the patient follows the surgeon’s recommendations in the postoperative period.
Features of the postoperative period
After the operation, the patient is observed and wound infection is prevented (a course of antibiotics, dressings with disinfectants). Men often have difficulty urinating. Walking is allowed on the second day. It is recommended to wear a bandage.
They are discharged home on days 8–10, immediately after the stitches are removed, but complete restoration of the tissue and wound will occur only after several months. At home, it is recommended to treat the wound with brilliant green. Dieting. Showering is allowed after two weeks. The doctor may prescribe physical therapy.
Prevention
In order to prevent the formation of a hernia, it is recommended to adhere to the following rules:
- Train your abdominal muscles.
- Organize a proper diet to avoid constipation and diarrhea.
- Maintain your weight at an optimal level.
- Try not to lift heavy objects.
- During pregnancy you need to wear a bandage.
As for the occurrence of recurrent hernias after their repair, the likelihood of relapse will be determined by the method of hernioplasty, the age of the patient and the condition of the tissues of the abdominal wall. The best results are achieved when strengthening the abdominal wall with synthetic materials in young patients.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
What to pay attention to during rehabilitation?
To ensure a sufficiently strong fusion during the rehabilitation period, restrictions are established. They concern:
- ability to carry heavy loads - 2 months, not more than two kg;
- playing sports and training - only from the third month with the permission of a doctor;
- food - only boiled, light dishes, milk porridges, juices, low-fat soups, kefir, cottage cheese (the rest is in accordance with the above dietary requirements).
The photo shows a neat postoperative suture on days 2–3
Prices for hernia meshes
On average, mesh endoprostheses can cost:
- Absorbable - 5,000 - 17,000 rubles;
- Partially absorbable - 3000 - 10,000 rubles;
- Non-absorbable - 1000 - 5000 rubles;
- Three-dimensional - from 10,000 rubles.
You can purchase from us non-absorbable Endoprol mesh endoprostheses in the following options:
- Lungs;
- Classic;
- Heavy;
- Super heavy.
These are our products, which have long been successfully used in many Russian medical institutions.