Some people experience pain in the stomach area a couple of times, while others accompany it throughout their lives, periodically reminding themselves. There are many reasons for this condition: from ordinary overeating to serious pathology.
And if in the first case it is enough to simply normalize the diet by limiting yourself in food, then the disease requires a comprehensive examination and serious treatment. If stomach pain has become habitual, it is necessary to identify the cause of its occurrence and carry out adequate therapy. What to do if your stomach hurts and feels nauseous?
Main causes of stomach pain
Dyspepsia - stomach pain and nausea
If the patient complains of pain in the upper abdominal region, accompanied by nausea, we can talk about gastric dyspepsia. The nature of pain is important in diagnosis. Occasional discomfort caused by excessive consumption of heavy food should not frighten a person.
This is a temporary digestive disorder that goes away without any medication. You just need to reduce the amount of food you eat and eliminate harmful foods.
If pain appears quite often, its occurrence is associated with any meal or with a feeling of hunger, you should seek help from a doctor. A comprehensive examination and properly prescribed therapy will help improve the quality of life and maintain health. Delay and self-medication can lead to the most disastrous results.
Basically, the described symptoms indicate gastrointestinal diseases. Sometimes nausea and abdominal pain are a manifestation of neurological pathology. This condition cannot be ignored; it cannot be done without the help of specialists. Another reason for the appearance of these signs is infectious diseases.
In children, viral and infectious diseases are often accompanied by dyspeptic syndrome.
Headache, gastritis and immunodeficiency
Headache, gastritis and immunodeficiency... You were probably surprised by this combination of diseases, but they have more in common than it might seem. They write everything on the Internet about the causes of headaches: increased intracranial pressure, cervical osteochondrosis, brain tumors, problems with blood vessels, and even intolerance to cheeses or nitrates. In fact, these are probably the rarest causes of its occurrence.
The accumulation of excess fluid around the brain is a potentially dangerous condition, and it occurs in no more than 0.01% of people. Pain with increased intracranial pressure is daily and intensifies in a lying position; it does not creep up suddenly, and there is no need to think about it during periodic discomfort.
Hernias and protrusions of the spine create pain only in 4% of cases, and even if you have them, this is not a reason to blame them for the pain. It has been unequivocally proven that people who have them and those who do not have headaches equally often.
The notorious osteochondrosis is not even a disease, but a manifestation of the natural decline of the body, and over time (by the age of forty) it appears in everyone. But not all of the older half of people in the world are tormented by their heads.
Brain tumors do not hurt, except in the final stages, when they begin to put pressure on something. But by this time, many other symptoms will appear (impaired perception, gait, speech), so you should not think about cancer with a headache at all, unless you are an elderly person who has suddenly lost a lot of weight.
All that can be said about vascular disorders is that obstruction of blood supply to the brain does not lead to pain, at most to fainting and decreased mental abilities. The only exception is a hemorrhagic stroke (including from a ruptured aneurysm), but here it is not the headache that will alert you, but the lack of coordination of movements and slurred speech.
Recently, it has become fashionable to attribute headaches as a cause to food intolerance. The list of possible provocateurs included all the most delicious things: from cheese and fruit to olives and bacon. Of course, there are individual food allergic reactions, but then the cause is still gastritis itself, and not the allergy itself.
And now we get to the more common, although less “obvious,” causes of headaches, including gastritis, dehydration, infections, eyestrain and emotional stress.
Gastritis With gastritis, 27% of people, even without stomach complaints, experience headaches, especially if they forget to eat on time. Sometimes a headache is the only symptom indicating an ulcer. When digestion is disrupted, the stomach triggers a mechanism aimed at searching for food. The signals amplified by inflammation “overstrain” the brain, and the head begins to hurt. By the way, hunger itself (low blood sugar) can cause headaches through the same mechanism. The paradox is that elevated sugar levels can create similar inconveniences for a person due to increased adrenaline and noradrenaline after a heavy meal. In general, eat in moderation.
What does a person with a headache do? He takes painkillers, which, unfortunately, themselves cause gastritis. Paracetamol, analgin, ibuprofen, celecoxib, ketanol, diclofenac, nimesulide - they all irritate the gastric mucosa and increase acid production, although ibuprofen is the most relatively safe in this matter. And here you can encounter another paradox: taking painkillers can cause pain in the head (this is in the instructions). This happens because this closes the vicious circle “headache - painkiller - gastritis - headache”.
Dehydration Those who don't drink coffee at work drink tea. And he does the right thing. Coffee is a diuretic drink, but we perceive it as a consumed liquid and do not notice the creeping dehydration. Although it would be worth wondering why in many cafes they immediately bring you a glass of water along with the espresso. The same goes for beer, after which everyone knows about the need to go to the restroom. In addition, most of the working population snacks on something fatty (sandwiches with cheese or sausage, nuts, chocolate), and more water is required to break down fats. And it’s not even about the sensational “need for 2 liters per day” - it actually varies not only for different people, but also for the same person on different days. It's a matter of the ratio of moisture consumed and wasted. When breathing and sweating in a dry climate (as in our apartments during the heating season), more water is required than on a cool summer evening on the seashore. It’s curious that you always want to drink after taking a shower, where the humidity seems to be okay. It’s just that in hot water we still sweat a lot, but the sweat is immediately washed off and does not help the body cool down; the body tries to produce more and more sweat, losing more and more moisture, leading to dehydration and a “post-bath” headache.
Infections If it hurts in the back, everyone will suspect the neck, and if it hurts in the front, it’s logical to think about the nose. More precisely, the sinuses of the nose are the frontal (in the forehead), the maxillary (under the eyes) and the ethmoid (in the depths behind the nose). When the mucous membrane of the sinuses swells, the outflow from them worsens, and this is felt as a bursting pain in the head. In this case, there may be no runny nose at all, as well as other manifestations of a cold. An ear infection begins in the same way - only a headache, although hearing loss or congestion, as on an airplane, may occur with swelling of the Eustachian tube. But it’s not just about swelling of the sinuses or ear canals. An infection that is chronically lodged in your nasal appendages or any other place is bacteria and viruses, particles of which are toxins for us. As a result, any chronic infectious disease is a source of constant intoxication, and it causes headaches.
Overstrain of eyesight All of us have been told by our mothers since childhood: “Don’t sit in front of the screen for a long time, you’ll damage your eyesight.” And then at work, most people got monitors that require them to look at for a long time. Eye strain has become less obvious due to the daily use of smartphones, tablets and laptops. It is difficult for the brain to imagine that something permanent can be harmful (as with the atmospheric air that we breathe, usually without thinking about the exhaust gases in it). And constant stress on the eye muscles without refocusing leads to eye pain, which we can perceive as a headache. Of course, in the process of peering into the depths of the screen, we do not notice overstrain of the neck muscles, but true neck pain occurs in only 1% of cases and it is associated with vertebral subluxation, and this is a completely different story.
Surprisingly, not all people with poor vision are aware of its inferiority and not everyone starts wearing glasses in time. The principle of headaches with uncorrected myopia or suddenly creeping farsightedness is the same: overstrain of the eye muscles. It is also worth visiting an ophthalmologist to rule out glaucoma, a disease with increased intraocular pressure, which also makes you reach for painkillers.
Emotional stress “This whole situation is already giving me a headache” is a typical expression. Yes, stress is the favorite cause of headaches and tension pain. The mechanisms of chronic headache in anxiety-depressive disorder, which manifests itself to varying degrees in half of the people in the Western world, have long been described. (Where to go, the price to pay for the race of progress with its frantic pace of life, constant lack of sleep, scandalous bosses and deadlines). In short, stress is excess arousal circulating in a circle in a certain area of the brain. This zone is constantly active and cannot “rest”; the neurons do not have time to get rid of decay products and send a signal for help in the form of pain and anxiety. If stress becomes chronic, then a restructuring of receptors on nerve cells occurs, as a result of which the exchange of neurotransmitters is disrupted and depression develops. And one of the masks of depression (link to my “why it hurts”) is just a headache.
A separate conversation about migraine, a severe one-sided pulsating headache, accompanied by nausea, intolerance to bright light and strong odors, preceded by a migraine aura (repeated unusual visual effects). Migraine attacks disable performance and should be treated by a neurologist without any self-medication.
What NOT to do for headaches (unless, of course, you have been referred by a neurologist):
- MRI of the brain - completely different symptoms indicate cancer, and not pain at all, so what should we look for there?
- MRI of the neck - even if protrusions and hernias are found, this will not say anything about the cause of the pain and will not affect treatment in any way.
- Ultrasound of the neck vessels is not necessary if you do not faint. This study is prescribed by cardiologists to assess atherosclerosis; headache has nothing to do with it.
- EEG is an old method that is only effective for detecting epilepsy. It is popular only because of its price, when you need to “prescribe something”.
How to get examined if your head often bothers you:
- Go to a neurologist: he is the “chief in pain”; during the examination, he will immediately (usually even without additional examinations) tell you about the causes of your illness and prescribe treatment.
- Go to an ophthalmologist: glaucoma and blurred vision are common causes of headaches. It will also eliminate swelling of the fundus, and you will be sure that everything is in order with your intracranial pressure.
- Do an FGDS (gastroscopy): almost everyone has digestive problems, and if treated in time, they will not create complications, which include headaches.
- Donate blood for a clinical test, check your immunity and do cultures from the intestines, tonsils and reproductive system to rule out chronic infections.
- Blood pressure control: a cardiologist or therapist will help you with this, and if necessary, refer you for daily blood pressure monitoring.
- Consult a psychotherapist: if stress is constant and has already begun to affect your health, it is better not to delay it and learn to cope with it in time before it develops into something more serious.
- You also need to exclude the simplest possible causes - your neighbor’s irritating perfume, an uncomfortable sofa for sleeping, or even clips pressing on your ears. Sometimes it happens, “but the box just opened.”
Pain is an important signal, and despite the fact that in 9 out of 10 cases the headache hurts “on its own”, from overexertion, in 10% of cases pain can indicate the presence of a problem that can be dangerous to ignore.
Get examined and treated on time, and be healthy!
Nausea is a physiological reaction
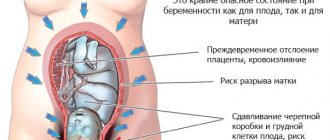
Pregnancy is a common cause of nausea
Every time you encounter abdominal pain or nausea, you need to analyze the events that preceded this condition. There are 2 conditions in which pain begins: either a full stomach or a hungry one. It is imperative to determine whether there is pain at night.
If your stomach starts to hurt only after alcohol or after an acute illness, you can conclude that you have a simple stomach disorder. This disorder is considered a physiological reaction of the body to the intake of heavy food. This is evidence of the health of the gastrointestinal tract, which simply cannot work in such an increased mode.
When are symptoms considered physiological?
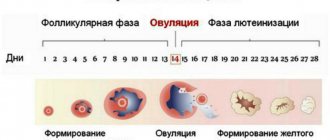
Physiological changes are always temporary, quickly appear and also disappear. An example is the condition of women during pregnancy or menstruation. A similar process in irritable bowel syndrome has been little studied. So far, the most acceptable opinion of scientists is that it is caused by dyskinesia of muscle contractions.
This is expressed in short-term cramping pain along the intestines, including in the lower abdomen, diarrhea, and nausea. The condition is observed with nervous tension and stress in emotional young people. It goes away on its own.
Stress is one of the causes of pathology
You should not hope for recovery without treatment for any pain syndrome. The area below the navel is associated with the work of all body systems, and therefore requires careful determination of the cause of the lesion.
Nausea is a sign of illness
Unfortunately, nausea often becomes a signal of the presence of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Defeating these diseases is not so easy. Often people have to follow the doctor’s recommendations and be under the supervision of a specialist for the rest of their lives, because most diseases in this area are chronic. These are gastritis and ulcers, cholecystitis and pancreatitis. But not all diseases are chronic. There are also acute conditions. For example, appendicitis, intestinal adhesions, tumors. These pathologies require surgical intervention.
If pain and nausea become commonplace, it is most likely inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract. Here it is necessary to distinguish between ordinary gastritis and ulcers. These diseases have much in common, but if the ulcer is not detected in time, you can quickly ruin your life. The fundamental difference is the time of onset of pain. Gastritis gives pain that goes away half an hour after eating.
With an ulcer, pain appears an hour and a half after eating and greatly torments a person at night. Nausea is a common occurrence for those suffering from pancreatitis. Only the pain will spread throughout the abdomen or hit the right hypochondrium.
Cholecystitis has a distinctive feature - a bitter taste, which is difficult to get rid of.
Diseases with right-sided localization
On the right in the iliac region in women, similar unilateral inflammations of the genital organs are possible, as on the left side. Here in persons of both sexes there is a vermiform appendix, the confluence of the jejunum and the cecum. Accordingly, according to the localization of inflammation, the diseases are called appendicitis and ileocolitis.
If everyone has heard enough about an attack of appendicitis, then ileocolitis is less common, but most affects the intestinal area in Crohn's disease. An attack of appendicitis begins with nausea, single vomiting, epigastric pain, and short-term diarrhea.
Gradually they move to the right lower abdomen and grow. A pulsating character, chills, and a rise in temperature indicate the formation of an abscess and a phlegmonous-gangrenous form.
With ileocolitis, inflammation covers the entire depth of the intestinal wall and breaks into the peritoneum or neighboring organs. The pain is very intense. The formation of local peritonitis, adhesions, and fistula tracts is possible. Intoxication causes nausea and fever.
Diagnostic Basics
Stomach hurts and nausea even after drinking
The first stage of diagnosis is a conversation with the patient. Only by learning from the person the time of onset of pain, their nature, frequency and other features, will the doctor be able to navigate the problem. Next you need an inspection. In addition to an external examination, an instrumental examination will be required; such an examination gives a complete picture of what is happening.
Therefore, it is impossible to do without FGDS. This examination allows you to examine the stomach cavity, identify areas of inflammation, and even take a fragment of the inflamed area for analysis. Ultrasound of the abdominal organs allows you to identify foci of inflammation, neoplasms in the liver, gallbladder and pancreas.
Survey
Nausea after eating most often indicates the presence of diseases of the digestive system, so the examination is carried out by a gastroenterologist, and the diagnostic search involves a comprehensive study of the morphological and functional characteristics of the patient’s gastrointestinal tract. When making a diagnosis, modern laboratory and instrumental methods are used, of which the most informative are:
- Sonography
. Abdominal ultrasound is prescribed as a screening method for all patients with long-term dyspeptic disorders. Ultrasound examination allows to identify nonspecific signs of ulcerative-destructive and inflammatory processes. If necessary, targeted ultrasound of individual organs is performed. - Gastrointestinal endoscopy
. Endoscopy is the most informative method for diagnosing diseases of the upper digestive tract, which are accompanied by nausea. According to indications, the study is supplemented with a biopsy. If it is necessary to visualize the entire length of the small intestine, video capsule endoscopy is used. - Radiography
. X-ray examination with contrast with a barium mixture is effective in detecting ulcerative-destructive processes in the digestive tract. The method is not specific enough for the diagnosis of inflammatory pathologies, so it is advisable to use it in combination with gastrointestinal endoscopy. - Study of gastric secretion
. Nausea associated with food may indicate disturbances in the acid-producing function of the stomach, so 24-hour pH testing is prescribed. The amount of total and free hydrochloric acid on an empty stomach and after the administration of drugs that stimulate secretion are also assessed. - Stool analysis
. A standard coprogram allows one to suspect malabsorption of food and various inflammatory processes in the intestines, which are accompanied by dyspeptic symptoms. Additionally, bacteriological culture of stool and analysis for helminth eggs are performed to exclude an infectious etiology of the process.
A biochemical blood test is necessary to exclude biliary and hepatic pathologies that cause nausea after eating. If a patient has a general infectious syndrome, specific serological tests are carried out to search for antibodies to pathogenic microorganisms. Intraesophageal manometry is prescribed to assess the motor function of the organ and the coherence of the sphincter apparatus.
Ultrasound of the abdominal organs
Basic recommendations for stomach pain and nausea
If stomach pain has become habitual, you should urgently go to the doctor. Only the observation of a specialist and competently prescribed treatment will help normalize the situation. If the pain occurs suddenly and it is possible to assume that this is ordinary poisoning, then there is no need to rush to the doctor. Standard measures are sufficient: prevention of dehydration, activated carbon to neutralize toxins, symptomatic treatment.
If you are worried about nausea while expecting a baby, you can use folk remedies such as seeds, crackers, and a small amount of water in the morning, literally a couple of sips. You should try not to be in places where unpleasant odors are common.
How are gastrointestinal diseases treated?
My stomach hurts and I feel nauseous - it’s time to see a gastroenterologist!
Self-medication for diseases of the gastrointestinal tract is very dangerous. The course of treatment is prescribed by a specialist. Properly prescribed modern medications can quickly stabilize the situation. De-nol, Omeprazole, Famotidine are drugs for correcting stomach conditions.
Eliminate nausea with home remedies
If you suffer from an acute attack of pain and nausea, you can assume ordinary poisoning. Then a solution of calcium permanganate and activated carbon will help. You should definitely keep these simple drugs on hand; they will definitely help in a difficult situation. Tea with lemon, citrus juice, even simple dry cookies help eliminate nausea after a portion of fatty foods.
Rest also helps relieve nausea. Of course, you should try to stay away from sources of unpleasant odors. Ginger tea and sour candies are common home remedies for nausea and are not dangerous at all.
Causes of food poisoning
Poisoning can be due to various reasons. There are toxic infections and toxic poisonings.
Foodborne toxic infection occurs as a result of pathogenic microorganisms entering the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) with food. As a rule, the causative agent is pathogenic bacteria that multiply in products if they are improperly stored or get into ready-made food if it is not properly processed.
Toxic poisoning can be caused by various poisons - chemicals or natural toxins found in poisonous berries, mushrooms and many other foods.
The greatest danger from the point of view of food poisoning is represented by perishable foods: fish, meat, milk, salads, etc. Also, eggs, home-canned food, fruits and vegetables with a high content of nitrates, poisonous mushrooms and berries, raw beans, sprouted green potatoes and insufficiently washed raw vegetables and fruits can lead to food poisoning.
It is not recommended to consume products that have expired, are in swollen jars, are in damaged original packaging, or have an unusual appearance, smell, consistency and color.
Prevention of dyspepsia attacks
Problems with the gastrointestinal tract due to poor nutrition!
If the gastrointestinal tract is in a healthy state, then following a proper diet will help you never encounter dyspeptic syndrome. You also need to remember to maintain hygiene and prepare food responsibly.
Giving up bad habits is another opportunity to maintain your health and avoid the appearance of dyspeptic syndrome. If you have a disease, you need to be careful during periods of exacerbation. In particular, you need to remember about seasonal exacerbations and not leave your body without the supervision of a specialist.
It is better to visit the clinic in advance and get the necessary recommendations. Caution is needed even when you feel good. If you wait for pain to appear, then correcting the condition will be even more difficult. Much more useful is periodic examination and timely measures taken.
Symptomatic therapy
Episodic nausea after errors in diet or overeating does not require drug treatment. To relieve unpleasant symptoms, you can drink ginger or mint tea and slowly eat a slice of lemon. To prevent nausea, you need to normalize your diet: eat 4-5 times a day, avoid eating dry food. If you have a food allergy, it is important to completely exclude certain foods from your diet and limit the consumption of peanuts and strawberries, which can cause severe systemic reactions.
If nausea after eating does not go away on its own within a few days and is not associated with physiological causes, you should contact a medical facility for a comprehensive diagnosis. Before the clinical diagnosis is verified, prokinetics that improve motility and prevent antiperistaltic contractions, antihistamines, and sedatives can be used to reduce unpleasant symptoms. If poisoning is suspected, sorbents are recommended.