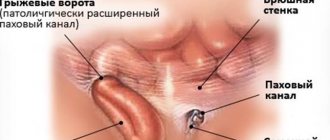
An inguinal hernia is the protrusion of internal organs covered by peritoneum through the inguinal canal.
Causes
The causes of inguinal hernias can be divided into two groups:
- predisposing factors - gender, age, body type, anatomical weakness of the walls of the inguinal canal, etc.;
- producing - conditions that contribute to an increase in intra-abdominal pressure: heavy physical labor, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, leading to a slowdown in bowel movements, etc.
Lipoma of the spermatic cord, which occurs in 32.4-72.5% of healthy individuals, is also a risk factor for the occurrence of inguinal hernia. As the size of the lipoma increases, the inguinal ring stretches, the lipoma puts pressure on the lower edges of the internal oblique and transverse abdominal muscles, which contributes to an increase in the height of the inguinal space.
In women, a common cause of hernia development is pregnancy.
Types of inguinal hernias
In patients with an inguinal hernia, the inguinal canal becomes a “weak spot” of the anterior abdominal wall, as a result of which, with an increase in intra-abdominal pressure, the abdominal organs gradually begin to exit through the inguinal canal with the formation of a hernial protrusion.
Inguinal hernias can be congenital (as a result of non-fusion of the vaginal process of the peritoneum; such a hernia is always oblique) and acquired (arise as a result of “destruction” of the walls of the inguinal canal).
An acquired hernia can be:
- oblique (lateral) - passes through the elements of the spermatic cord;
- straight (medial) - passes outside the elements of the spermatic cord in the area of the posterior wall.
If a hernia occurs for the first time, then it is called primary ; if a hernia appears after surgical treatment, this hernia will be recurrent .
The contents can be easily pushed back into the abdominal cavity - this is a reducible inguinal hernia . But the hernial orifice may narrow, in which case a strangulated inguinal hernia .
Inguinal hernias are more often observed in men, which is explained by the structural features of the inguinal canal (the deep inguinal ring is larger, the inguinal space is higher, etc.). In common parlance, such a hernia is often called a “male hernia.”
Photo: inguinal hernia in men
Inguinal hernia code according to ICD-10
K40.0 Bilateral inguinal hernia with obstruction without gangrene.
K40.1 Bilateral inguinal hernia with gangrene.
K40.2 Bilateral inguinal hernia without obstruction or gangrene.
K40.3 Unilateral or unspecified inguinal hernia with obstruction without gangrene.
K40.4 Unilateral or unspecified inguinal hernia with gangrene.
K40.9 Unilateral or unspecified inguinal hernia without obstruction or gangrene.
Classification of inguinal hernias according to ESH
In 2014, the classification of the International Congress of EHS (35th International Congress of the European Hernia Society) was presented. It makes it possible to fairly accurately determine the type of hernia and, when studying various types of hernioplasty (hernia repair operations), to objectively evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of each method depending on the type of hernia.
Classification
Umbilical hernias can be reducible or unreducible. The protrusion can be reduced in the initial stages - to do this, it is enough to simply press on it with your fingers or take a horizontal position. Gradually, the situation becomes more complicated with adhesions and progressive muscle relaxation; the intestinal loops in the hernial sac cannot be returned inside the peritoneum and the disease moves to the next stage.
An irreducible umbilical hernia occurs when the tissues of the hernial opening fusion with the hernia itself due to fibrinous strands - adhesions. This is a dangerous complication, although painless in the early stages. After physical work, pinching may occur and the patient will require urgent surgery.
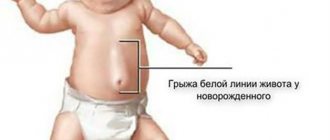
Congenital pathology is determined immediately after birth or after the navel heals. Doctors do not consider this a hernia, since the situation in a child under 3–5 years of age can change when the umbilical ring is fully formed. Such a hernia is called a false hernia.
Acquired or true hernial neoplasm appears at the age of 5–6 years. There are direct and indirect hernias. Straight ones appear from the umbilical opening itself. Oblique - above or below it. Passing through the opening between the linea alba and the transversalis fascia, the hernia exits through the umbilical opening.
Symptoms and diagnosis
The main symptom of an inguinal hernia is the identification of a tumor-like formation of soft elastic consistency in the groin area (or groin areas). This formation is reduced into the abdominal cavity and changes its size when the patient is in an upright position, during physical activity, coughing, or the Valsalva maneuver.
The symptom of a “cough shock” is considered unambiguous - bulging of the formation during cough shocks. Pain or discomfort in the area of the hernial protrusion appears or intensifies with straining, heavy lifting, chronic or acute cough, with ascites, obesity, and pregnancy.
In general, making a diagnosis is not difficult.
However, in obese patients it may be difficult to identify a hernial protrusion. In some cases, this requires additional examination (ultrasound of soft tissues, MSCT of the anterior abdominal wall) in order to confirm the diagnosis or exclude it.
In addition, difficulties in clinical diagnosis may arise in the initial stage of hernia formation, which may be accompanied by pain. During palpation, in most clinical observations it is possible to identify a defect in the anterior abdominal wall, through which a small soft elastic formation emerges when intra-abdominal pressure increases.
To make an accurate diagnosis, it is important to exclude other possible diseases with similar symptoms. Differential diagnosis of hernias is carried out with lymphadenitis and lymphadenopathy, soft tissue neoplasms, inflammatory infiltrate and abscess, endometrioid cyst, aneurysm, varicose veins and ectopia of organs.
Symptoms of a strangulated umbilical hernia in adults
An umbilical hernia is often almost asymptomatic, but can also be strangulated.
When the contents of the hernial sac are compressed in the hernial orifice, signs of strangulation of the umbilical hernia appear. Strangulation can begin with a hernia of any size after severe physical stress, for example, after lifting something heavy. The patient's excess weight contributes to the injury. Usually the loops of the small intestine are strangulated, and symptoms of acute intestinal obstruction appear. Rapid compression of internal organs causes poor circulation and necrosis (death) of their tissues. In the case when the compression of tissues does not occur too sharply, only the veins are compressed and venous stagnation occurs, and then the arteries are gradually compressed. In this case, tissue necrosis occurs more slowly and the patient’s condition is not so severe.
Symptoms of strangulated umbilical hernia are sharp, sudden pain in the hernia area, its non-reducibility (even if it was previously reducible freely), nausea and vomiting. After some time, an area of redness with a bluish tint appears near the navel.
Inguinal hernia treatment
The main method of treating hernias is surgical. Conservative treatment leads only to temporary results.
The rate of postoperative relapses is 2-20% with traditional techniques with local tissue plastic surgery and 1-5% with the use of mesh prostheses.
Surgical treatment of inguinal hernia (hernioplasty) is carried out using various methods. Currently, tension-free Lichtenstein plastic surgery using polypropylene mesh is most often used. There are laparoscopic hernioplasty techniques that use video endoscopic minimally invasive technologies. The choice of the preferred treatment method and type of operation will be determined by the attending surgeon, depending on the characteristics of the disease.
Operations for inguinal hernia ⇒
Therapy methods
To prevent strangulation, the hernia begins to be treated immediately after diagnosis. Conservative methods are used if the patient has any contraindications to surgery: acute pancreatitis, renal or heart failure, in which anesthetics cannot be used. Late pregnant women also do not undergo surgery.
Conservative methods include a bandage. It must be worn until the patient is cured of concomitant diseases or the body is strong enough to endure the operation. If you refuse hernioplasty, the bandage is worn constantly.
Massage procedures do not help narrow the umbilical ring. Massage is prescribed for children under 3 years of age to speed up the formation of a scar in the navel area. In adults, the body's regenerative abilities are much lower.
There is a misconception that you need to pump up your abs and your muscles will become stronger. It is not right. Treatment of umbilical hernia in men involved in strength sports is complicated by increased loads. Strong abdominal muscles can aggravate the situation when pinched, so the only way is hernioplasty.
A method that allows you to forget about problems with a hernia forever is surgical suturing of the umbilical ring and closing the hernial orifice. There are several surgical techniques:
- Laparoscopic using implants. In this case, instruments are inserted into the cavity through small punctures to visualize the peritoneum and perform surgical procedures. A special mesh is placed on the umbilical ring and secured with threads. Over time, the implant becomes overgrown with the body’s own tissues and firmly holds the intestinal loops.
- Open abdominal surgery. For overweight patients, this is the best way, since surgeons have access to the subcutaneous fatty tissue and remove it along with areas of skin, then suturing it. The hernial orifice is closed in two ways - with your own tissue or with a synthetic mesh.
The laparoscopic method allows you to reduce the time spent in the clinic; there are practically no postoperative complications after it, but it is not suitable for all patients and is more expensive.
After abdominal surgery, the patient takes longer to recover; there is a danger that the weakened body will not cope with the infection and internal inflammation will begin, therefore, after surgery, therapy with antibiotics and restorative drugs is indicated.
Complications
The main complication of a hernia of various locations and sizes is its strangulation.
However, a strangulated umbilical hernia, along with a femoral or identical defect of the white line of the abdomen, is much less common than an inguinal hernia, which has a maximum prevalence among the adult population. In most cases, unilateral infringement is noted , which somewhat reduces the rate of increase in the symptoms of gangrene and general intoxication.
Save the link, or share useful information on social media. networks
Diagnosis with code K42 includes 3 clarifying diagnoses (ICD-10 subheadings):
Chain in classification:
The diagnosis also includes: peri-umbilical hernia
The diagnosis does not include: – omphalocele (Q79.2)
mkb10.su - International classification of diseases, 10th revision. Online version 2022 with disease search by code and decoding.
General information
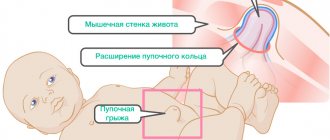
Umbilical hernia is the most common surgical pathology in pediatrics, which is diagnosed in 20% of full-term and 30% of premature children. Among adults, umbilical hernia is more common in women over 40 years of age, accounting for 5-12% of hernias of the anterior abdominal wall. In operative gastroenterology, an umbilical hernia is understood as a condition accompanied by the release of internal organs (part of the intestine and the greater omentum) through the expanded umbilical ring beyond the anterior abdominal wall.
Complications
The main complication of a hernia of various locations and sizes is its strangulation.
However, a strangulated umbilical hernia, along with a femoral or identical defect of the white line of the abdomen, is much less common than an inguinal hernia, which has a maximum prevalence among the adult population. In most cases, unilateral infringement is noted , which somewhat reduces the rate of increase in the symptoms of gangrene and general intoxication.
Forecast and prevention of umbilical hernia
For children, surgery for an umbilical hernia is easily tolerated; as a rule, it is not complicated by relapses and allows one to achieve a good cosmetic effect. If left untreated, an umbilical hernia can take a complicated course - become unreducible, strangulated, etc.
Measures to prevent umbilical hernia include: prevention of situations associated with straining of an infant (excessive screaming and crying, bloating, constipation, etc.), rational feeding, preventive massage and gymnastics aimed at strengthening the abdominal wall, treatment of intestinal dysbiosis, wearing prenatal bandage
Causes of the disease
For an umbilical hernia to form, several factors must combine. This is an innate factor and acquired during life. The congenital factor is associated with a certain anatomical structure of the navel area. And acquired factors include an increase in intra-abdominal pressure, which causes the abdominal organs to protrude.
Factors that are considered congenital are:
- weak umbilical ring;
- congenital anatomical defect;
- connective tissue dysplasia;
- weak muscles of the anterior abdominal wall.
Factors that arise during a person’s life may be:
- cough (this especially applies to cough that occurs with chronic bronchitis or in those who smoke);
- constipation;
- some types of professions (for example, musicians who play wind instruments);
- persons engaged in heavy physical labor.
Diagnosing the presence of an umbilical hernia is not so difficult. To do this, you should conduct a particularly thorough examination, for which you will need to visit a specialist.
All other diagnostic measures are aimed at excluding possible complications of such a disease. To understand whether a patient has this formation, he needs to undergo a series of diagnostic procedures, such as:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs.
- X-ray examination. It is also necessary to add x-rays using contrast agents.
- General urine analysis. Such a study can show the inflammatory process that occurs against the background of strangulation of the umbilical hernia.
If treatment is untimely, there is a possibility that various complications may arise, such as:
- the appearance of intestinal obstruction;
- peritonitis;
- infectious-toxic or painful shock;
- coma state.
All this suggests that treatment should not be delayed under any circumstances. At the slightest suspicion of an umbilical hernia, the patient should immediately consult a doctor and undergo the necessary examinations.
Possible consequences and complications
Complications of an umbilical hernia include:
- rupture of the hernial sac;
- infringement;
- relapse of the disease.
In up to 20% of cases after tension-free hernioplasty, hernia recurrences occur. This technique does not use a synthetic mesh, and the sutured tissues diverge, reopening the hernial orifice. In this case, a repeat operation is scheduled as planned.
A strangulated hernia is the most dangerous complication. When intestinal loops get into the hernial sac, the movement of feces stops, and the tissue gradually dies. Surgical intervention is carried out urgently, as the person’s condition is rapidly deteriorating.
Rupture of the hernial sac can occur when the peritoneum and omentum adhere to the hernia itself. When trying to straighten the protrusion, the patient makes efforts and the thin tissues cannot withstand it. Loops of intestines become trapped under the skin. Sometimes, along with the layers of the peritoneum, the intestinal wall is damaged and its contents leak into the cavity. In such a situation, urgent surgery and disinfection of internal organs are necessary. If there is delay, the person develops peritonitis.