What should you do before endoscopy?
FGS is not a rare study. It is often prescribed to patients in order to examine the stomach, its mucous membrane and take a biopsy for analysis. Endoscopy is performed for 5 to 20 minutes. All steps have been worked out by doctors, there is an action plan for unforeseen situations, so no need to worry.
The main task of preparation is to follow all the doctor’s instructions.
Preparation for EGD of the stomach has several important recommendations, which consist of the following stages:
- Home preparation.
- Morning preparation before endoscopy.
- Moral attitude.
You should not ignore any of the above stages, as the consequences may be unfavorable.
What does a gastroenterologist treat?
The doctor’s competence extends to the diagnosis, therapy and prevention of the following diseases and disorders:
- Acute and chronic gastritis;
- Duodenitis;
- Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum;
- Colitis, enterocolitis, irritable bowel syndrome, dysbacteriosis;
- Hernias (in particular, hiatal hernias);
- Inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis), its cystic neoplasms;
- Hepatitis (infectious and non-infectious);
- Cirrhosis of the liver;
- Hepatosis;
- Cholelithiasis;
- Biliary dyskinesia;
- Cholecystitis.
Our specialists also help their patients heal the negative consequences of surgical interventions (including on the stomach) and select the most effective preventive measures against relapses when chronic forms of diseases are established.
until 03/31/2022 Check Up promotion: Healthy liver Comprehensive diagnosis of liver diseases, the study includes an appointment with a specialist doctor, ultrasound diagnostics and laboratory tests.
How to prepare at home?
Preparing for FGS of the stomach at home involves proper nutrition. A well-structured diet will help prepare the stomach cavity for examination.
It is best for an adult to prepare a week before the scheduled procedure. To do this, you should exclude the following foods from your diet:
- bread and flour products, including pasta;
- fatty and fried foods;
- semi-finished products;
- fish and fatty meat;
- smoked meats;
- spicy and canned foods;
- mayonnaise, ketchup and other sauces;
- alcoholic drinks.
If the examination is scheduled for tomorrow, then it will be enough to exclude dinner at a later time and eat your last meal 12 hours before the procedure. During this time, the stomach will have time to digest the food that has entered it. Digestion takes 8 hours, but since human metabolism slows down at night, foods are also digested more slowly. It is for this reason that the difference between food intake and examination should be at least 12 hours.
If this recommendation is not followed, then the remaining food in the stomach will interfere and may regurgitate during the procedure.
To make dinner easily digestible and nutritious, you can prepare the following dishes:
- buckwheat porridge;
- steamed or boiled vegetables;
- steamed cutlets;
- lean meat, such as chicken, rabbit or fish;
- mashed potatoes.
Do not eat too hot or cold food; it is recommended to exclude raw vegetables and fruits. It is also not recommended to eat chocolate the day before the test.
Indications and contraindications for gastroscopy
Gastroscopy is an informative diagnostic method
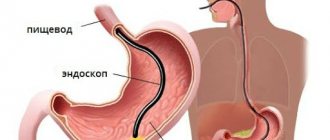
Gastroscopy, otherwise known as esophagogastroduodenoscopy, is a medical procedure that is performed to examine the upper parts of the human digestive system. As a result, the following can be examined:
- esophagus
- stomach
- duodenum
This procedure is prescribed by a doctor if it is necessary to confirm a particular disease. In some situations, the results of gastroscopy determine the rational therapy of the detected diseases.
To carry out the examination, a special device is used - an endoscope. Depending on the examination methods chosen by the specialist, different types of endoscopes are used. Modern devices are particularly versatile and efficient.
Indications for gastroscopy can be for a variety of reasons. First of all, these are various diseases of the digestive system. In their case, examination is mandatory. In situations where an urgent examination of the patient is necessary, for example, in the event of heavy internal bleeding, the procedure is mandatory.
In some cases, it is resorted to even in case of myocardial infarction. An examination may be prescribed in the following situations:
- patient complaints of pain in the epigastric region that occurs after eating
- if the patient experiences frequent heartburn
- when he vomits blood
- if you suspect various diseases of the digestive system
Routine gastroscopy may have some contraindications. Thus, a very serious condition of the patient, in some cases, serves as a reason to postpone the examination for an indefinite period. For example, gastroscopy cannot be performed when the patient is in a dying state.
In general, the following possible contraindications for canceling planned gastroscopy can be noted:
Preparation on the day of the examination
On the day of the FGDS, you should also prepare. One of the important recommendations is to temporarily refuse water on the day of the procedure. The examination is usually carried out in the morning, so this rule will not affect the general condition in any way. If you still need to take regular medication or are very thirsty, you are allowed to drink water at least 3 hours before the examination, but not more than half a glass.
Smoking is also prohibited when preparing for FGS.
Nicotine can increase salivation, which affects the results of the study. In this regard, in the morning it is advised to breathe more fresh air and not smoke.
Here are some more important recommendations:
- Clothing should be comfortable and loose, without tight belts.
- Breathe correctly through your mouth. Inhalation and exhalation should not be sharp, but smooth.
- Try not to worry.
Gastroscopy of the stomach is an unpleasant but safe procedure. Proper breathing will reduce discomfort, and loose-fitting clothing will relieve panic attacks.
Alcohol after gastroscopy
After diagnosis, you should not drink alcohol for at least 24 hours. This is the minimum period, if you do not take into account the presumptive diagnosis, to confirm which FGDS is performed.
Firstly, during the procedure the mucous membrane of the larynx and esophagus may be slightly injured. The irritating effect of alcohol solutions and general dehydration of the body after taking them can significantly aggravate the condition.
Secondly, sedatives or anesthesia are often used to prepare for the procedure. Their simultaneous use with alcohol can have serious consequences, even irreversible.
Gastroscopy is not compatible with alcoholic beverages!
Other types of training
Moral attitude is very important before research. Usually, the doctor himself tells the patient everything. Feel free to ask questions that interest you. The answers you receive will make you feel better.
If an adult has a predominant feeling of panic or increased excitability, the doctor may prescribe sedatives.
In case of cardiovascular pathologies, for example, hypertension, respiratory failure, their premature correction is important.
This is due to the fact that during the FGS process complications may arise on their part. The patient will have to prepare for endoscopy in the hospital. Before FGDS, local preparation is carried out, which includes the following points:
- The skin and mucous membrane of the patient's oral cavity are examined in order to exclude tonsillitis, jams or cracks. If such problems are identified, then the FGS is postponed.
- To reduce foaming in the stomach and intestines, the doctor prescribes the drug Espumisan, which should be drunk 5 minutes before the start of the test.
- To reduce pain during insertion of the endoscope, the patient is given local anesthesia. To do this, the throat is treated with lidocaine in the form of a spray.
Local preparation takes place under the guidance of a physician. Do not forget to inform your doctor about the presence of chronic diseases.
FGDS (gastroscopy). How it is carried out, methods of preparation.
Gastroscopy with biopsy allows you to take samples of the juice of the digestive organs and mucous membranes for analysis. This collection helps to identify abnormalities that were not noticed with x-rays and ultrasound.
What should a specialist know about the patient in advance?
Before examination with an endoscope, the patient is required to report recent operations or treatment of the gastrointestinal tract with medications. In such cases, the mucous membrane may become very vulnerable to external irritants and a recovery period is first indicated before the examination.
The choice of anesthetic is greatly influenced by pregnancy, so this should also be reported to the doctor. During the procedure, Lidocaine is usually used in the form of a spray. It is safe even for pregnant women and the fetus, but if a person is intolerant to it, the session is carried out without an anesthetic at all.
The doctor must be informed about the presence of a heart valve, defibrillator, or pacemaker. The patient should report dental crowns (if he has them), a tendency to bleed after injury, and poor blood clotting. The doctor must be notified if a person has previously had endocarditis.
How to prepare for the procedure?
How to prepare for gastroscopy of the stomach? The examination is performed only on an empty stomach. The last meal is allowed 12 hours before the procedure. If a person is tormented by severe thirst, then you can only drink water in small quantities. A few hours before the procedure, brush your teeth, prohibit smoking, spraying cologne or perfume.
Morning preparation for examination
Preparation for gastroscopy of the stomach begins in the morning by avoiding taking any medications. This is agreed upon with the doctor in advance. In case of internal bleeding, gastric lavage is performed. If the session is scheduled for the morning, it means that food intake stops in the evening.
Preparation for inspection in the 2nd half of the day
If the study will be carried out in the afternoon, a light breakfast is allowed. You can only eat until 6:00. For breakfast, you are allowed to eat low-fat yogurt with a piece of bread. For drinks, you can allow tea or mineral water, but stop taking liquids 3 hours before the process.
You must arrive 10-15 minutes in advance for the procedure, as some preparation is required. If a person is very nervous, he is given a sedative. After examination, it is not recommended to eat or drink for 30 minutes until sensitivity returns to the mucous membrane.
Diet features
Preparation for gastroscopy of the stomach necessarily includes a mandatory diet. The diet is adjusted 3 days before the session. The procedure is done only on an empty stomach. Eating ends 12 hours before the examination. Fasting almost eliminates the digestive organs’ rejection of the endoscope and the occurrence of vomiting. The diet changes three days before the examination. During this period, the gastrointestinal tract is completely cleansed.
General recommendations for the diet:
- 5 meals a day;
- food is consumed in small portions;
- Dishes that cause increased gas formation are excluded from the diet;
- You need to drink at least 2 liters of plain water per day.
If a person is prone to flatulence, then for 3 days before gastroscopy one should take medications prescribed by the doctor. After the biopsy, a strict diet is followed for a day.
It is formulated in such a way as to spare the mucous membranes of the digestive organs as much as possible. Any mechanical, chemical, thermal effects on the gastrointestinal tract are excluded. You can only eat and drink non-acidic fruit juices, pureed soups, and milk. Spicy, hot food is prohibited. Any rough food is completely excluded.
What and when can you drink before FGDS?
Before the study, you can only allow weak tea, plain or mineral still water. For 8-10 hours, it is advisable to completely abandon liquids. In case of severe thirst, you can drink only half a glass, the last time - 3 hours before the start of the procedure. If a person takes pills and it is not recommended to skip them, then the medicine is washed down with plain water, but in a couple of sips.
What and when can you eat before FGDS?
During the preparation period, one day before the examination, the following is allowed:
- white poultry meat;
- compotes;
- dietary vegetable soups;
- green or other weak tea;
- boiled fish;
- skim cheese;
- fruits and vegetables (baked);
- still mineral water.
It is necessary to reduce sweet, flour products, and salt to a minimum. If the patient is not recommended to fast, then within 12 hours (at most, within an hour you can eat some white crackers, buckwheat porridge, stewed vegetables or apples baked in the oven.
Methodology for conducting FGDS
FGDS is mainly carried out in the morning, before lunch. Immediately before the procedure, dental crowns and glasses are removed in the office. The belt does not need to be removed if it does not compress the stomach. The person lies on his side on the couch, facing the apparatus. The doctor treats the patient's throat and mouth with an anesthetic. Most often, Lidocaine is used for these purposes in the form of a spray.
This anesthetic dulls the discomfort from insertion of the probe and reduces nausea. A mouthpiece is placed in the mouth, then a thin hose is inserted through the esophagus, at the end of which there is a mini-camera. It drops first to the middle. Then it is slowly pushed into the stomach. Its walls are examined within a few minutes.
The image from the camera is sent to a computer monitor, which immediately allows you to assess the condition of the organ being examined. If necessary, samples of the internal fluid are taken. The duration of such a study takes only a couple of minutes. To avoid unpleasant sensations and to minimize the urge to feel sick, the patient must completely relax.
The endoscope easily slides into the esophagus during a sigh. Then the person being examined needs to breathe exclusively through the nose. In some cases, gastroscopy can be performed under local or general anesthesia. For example, with severe bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract. The total duration of the procedure from the moment the probe enters the esophagus until its removal is from 5 to 15 minutes. This time may increase slightly if the person is under anesthesia.
What should you take with you?
Clothes should not restrict movement, be loose and light. This preparation will help the subject to relax. Be sure to bring napkins (without alcohol) or a collar for clothes.
During the procedure, the patient experiences strong salivation and severe belching, so clothing must be covered. If the person being examined is insulin dependent or takes antihypertensive drugs, then they may be useful after the end of the process. Additionally, you need to have a 0.5 bottle of still water with you.
The process of gastroscopy of the stomach is completely safe. It is performed only by doctors of certain qualifications. It is not recommended to be nervous during the procedure; you need to relax. FGDS is an unpleasant study, but necessary for a correct diagnosis.
Necessary things
Before going to the hospital you should have with you:
- a medical record containing all the necessary tests and x-rays;
- sheet (for the couch);
- wet wipes and a towel (needed for heavy salivation or belching);
- replacement shoes or shoe covers.
You should also take with you the medications that you regularly take, as you may need them later.
After completing the FGDS, eating is prohibited for another 2 hours, so take drinking still water with you.
Examinations of the internal state of the stomach, intestines and duodenum can be done either free of charge in the hospital at the place of registration, or for a fee in private clinics. But this does not change the preparation process in any way. All preparatory steps must be followed equally. Before starting the procedure, be sure to remove anything that might get in your way, such as glasses or dentures. Lie down comfortably on the couch in a side position, relax and mentally tune up.
Information for the doctor
Before FGDS, it is important to talk with your doctor about early diseases, symptoms that worry you, and allergic reactions, if any. This will ensure that the medical staff prepares you correctly for the endoscopy. For example:
- If the patient is prone to allergies, be sure to tell the doctor about it. FGS involves treating the pharynx with an anesthetic. If the patient is prone to allergies, you will need to select a drug that will not be sensitive to the body.
- Chronic pathologies are not a contraindication for FGS, but the doctor needs to be aware of them. During a biopsy, this information will help to avoid unnecessary trauma to the mucous membrane, so as not to provoke a relapse of this disease.
- During pregnancy, in the 1st and 2nd trimester, it is not recommended to use an anesthetic. As a rule, lidocaine is safe, but still, if there are contraindications, the procedure can be performed without anesthesia.
- If you have previously had surgery, taken a biopsy, or treated your stomach with medications, it is important to mention this to your doctor. This is due to the fact that the gastric mucosa in such situations becomes vulnerable to irritation during FGDS. A recovery period will be required for the study results to be accurate.
It is necessary to prepare for endoscopy carefully and ahead of time. Dietary nutrition, necessary tests and positive emotions will help you go through this procedure quickly and without problems.
How is an appointment with a gastroenterologist?
Any visit to a gastroenterologist begins with his objective assessment of your complaints. The doctor conducts a physical examination and clarifies the features of your diet and lifestyle. If necessary, the specialist will clarify the presence of certain diseases in your closest relatives (family history). If a specialist suspects a specific pathology, you will be prescribed certain tests to rule out or confirm the diagnosis.
%PROMO_3836%
Our specialists use a wide range of ultrasound, radiological, endoscopic and functional measures.
A visit to a gastroenterologist includes the following steps:
- An objective consultation with a specialist, during which he will ask you about current complaints, previous diseases (in particular, related ones, not related to diseases of the gastrointestinal tract), assess your lifestyle and nutritional pattern, review the results of previous studies, and refer you for appropriate tests and will conduct a traditional inspection;
- Prescribing a specific treatment regimen after analyzing the results of an in-person survey and additional studies;
- Providing personal recommendations regarding diet correction (diet therapy), lifestyle, and taking certain medications.
If no gastroenterology problems are identified, the specialist will refer you to a general practitioner. To diagnose a specific disease, our clinic uses the following measures:
- Clinical/biochemical blood/urine analysis;
- Test for Helicobacter Pylori infection;
- Blood test for gastropanel;
- Coprogram;
- Examination of stool for dysbacteriosis;
- Endoscopic examinations (fibrogastroscopy and fibrocolonoscopy);
- Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the abdominal organs;
- Computed tomography (CT);
- X-ray of the peritoneal organs.
After your disease has been thoroughly studied, you will be offered certain methods of treating it.