Fibrogastroscopy is an informative examination method that helps to identify many pathologies of the digestive system in the initial stages. This allows the doctor to make an accurate diagnosis and develop a treatment strategy. Therefore, it is so important to carefully prepare for the procedure so as not to miss areas of pathology.
Gastroscopy is a responsible procedure for which you need to prepare. It is especially important to follow all the rules on the eve of the examination. The informativeness and usefulness of the diagnosis depends on how physically and psychologically prepared a person is. In the article you will find complete information on how to prepare for the procedure.
Preparation for fibrogastroduodenoscopy (FGDS)
- Alcohol should be avoided 2-3 days before the test.
- 12 hours (minimum 8 hours) before the test, you must avoid eating.
- 8 hours before the test, it is necessary to minimize fluid intake (pure still water). 4 hours before the test, you must completely stop drinking liquids.
- On the eve of the procedure, you need to eat light food (exclude fatty, fried, smoked, spicy, pickled foods, fresh fruits and vegetables).
- Discuss in advance with your doctor the possibility of using anesthesia, the need and regimen for taking medications on the day of the FGDS.
- Brush your teeth no later than 2 hours before the test.
- Stop smoking at least 2 hours before the test.
Experts recommend paying attention to your psycho-emotional mood. If you strictly follow the preparation rules, the procedure will go quickly and with minimal discomfort. During the examination, you need to listen carefully to the doctor and follow his recommendations.
Features of preparation for the procedure scheduled for the first half of the day
If gastroscopy is scheduled in the morning, prepare in the evening.
Dinner includes foods that are easy to digest. Have dinner no later than 4 hours before bedtime: at night, the secretory activity of the stomach decreases, and food is less easily digested.
It is better to eat food that takes longer to digest (for example, meat) for lunch. Fresh vegetable salads are not recommended to be eaten in the evening. If a gastroenterologist has given you a preliminary diagnosis of gastritis, gastroduodenitis or a stomach ulcer, then the diet will become more strict, with mechanical treatment. Drinks for dinner should avoid gas formation. Herbal teas are preferable, for example, chamomile, which relieves inflammation, or green tea.
Lunch and breakfast on the eve of FGS should also consist of easily digestible dishes with maximum sparing of the gastric mucosa.
In the morning, any food is prohibited. If the procedure is performed under local anesthesia, drink no more than 150 ml of drinking water within 3-4 hours. You should not drink any tea or decoction at this time. If you are planning to undergo anesthesia, you should not drink at all. You can only take a few sips of water to wash down the pills prescribed by your doctor.
You cannot smoke on this day so as not to cause secretory activity of the stomach.
Choose from four breakfast options:
Option I
Breakfast
- Steamed protein omelette 200 g.
- Low-fat kefir 250 ml.
II option
Breakfast
- Low-fat yogurt 200 ml.
- Berry tea 250 ml.
III option
Breakfast
- Low-fat cottage cheese 250 ml.
- Rose hip decoction 250 ml.
IV option
Breakfast
- Curd casserole 200 g.
- Green tea 250 ml.
Breakfast, lunch and dinner on the eve of FGS should consist of easily digestible foods
How long should you fast?
The examination of the stomach is carried out strictly on an empty stomach. To do this, you need to organize complete rest for the digestive tract for 12 hours (minimum 8 hours).
-If FGDS takes place in the morning or afternoon (before 15:00) , a light dinner is allowed in the evening before the study. Next, you need to refrain from eating.
-If FGDS is scheduled for the afternoon (after 15:00) , the rules for preparing for the study change somewhat. To avoid feeling unwell, the patient can arrange a light snack in the morning. It is important that breakfast takes place no later than 8 hours before the start of the procedure. You can eat low-fat yogurt, drink herbal tea with honey.
Violation of this rule is fraught with severe nausea during the study, vomiting and extremely unpleasant sensations. Also, the information content of the study is sharply reduced.
What is FGS
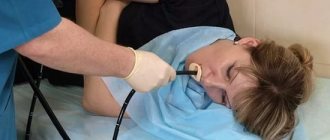
FGS is not a very pleasant procedure
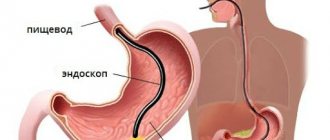
One of the most reliable studies of the stomach, as mentioned above, is FGS. FGS stands for fibrogastroendoscopy, during which an endoscope, or as it is also called a gastroscope, is inserted into the patient’s stomach, with which you can clearly examine the stomach, its mucous membrane, and also take a biopsy for analysis.
The procedure consists of several stages:
- First stage. The doctor administers local anesthesia, which in most cases involves treating the root of the patient’s tongue with lidocaine
- Second phase. The patient is placed on his left side
- Third stage. After the anesthesia has begun to take effect, which is about 5 or 10 minutes, a plastic ring is inserted into the person’s mouth, which must be clamped with the teeth.
- Fourth stage. Then, the doctor will insert the endoscope through this ring. When the endoscope is inserted, the person will be asked to swallow
- Fifth stage. After a couple of seconds, the endoscope will be in the stomach, the doctor will pump air into it so that the stomach straightens and begin the examination
- Sixth stage. In a few minutes the doctor will take out the endoscope
Typically, gastric FGS is prescribed if:
- There is suspicion of inflammation of the upper digestive tract
- Peptic ulcer present
- There is bleeding
- There is a suspicion of a tumor
FGS is a very serious study, for which you need to carefully prepare in order to avoid unpleasant sensations and for the result to be reliable.
How to deal with bad habits?
To effectively prepare for an FGDS of the stomach, it is better for an adult to give up bad habits. Alcohol consumption should be avoided at least 2 days before the test.
Doctors give separate recommendations to smokers: you need to stop smoking at least 2 hours before the test. The fact is that nicotine stimulates the secretion of gastric juice and peristalsis of the gastrointestinal tract. The activity of the digestive system can cause additional discomfort for the patient. To avoid such symptoms, you should avoid smoking for a while.
general information
Gastroscopy is prescribed for almost any pathology of the stomach or suspicion of it: gastritis, tumors, erosions, ulcers, reflux disease. This examination makes it possible not only to examine the mucous membrane, but also to carry out other diagnostic and therapeutic procedures:
- study of gastric motility;
- determination of the level of gastric secretion (pH-metry);
- taking mucosal samples for biopsy;
- stopping bleeding;
- administration of drugs for local action;
- removal of benign tumors;
- removal of foreign bodies.
The preparation plan for it depends on the purpose of the procedure.
Note. Gastroscopy is also called FGDS, since its full name is fibrogastroduodenoscopy. This term implies the study of not only the stomach cavity, but also the duodenum.
What should people who take medications do?
For some adults, the question of how to prepare for gastroscopy of the stomach is relevant if you need to take medications at a certain time. We can talk about antihypertensive drugs, hormone replacement therapy, etc. It is better to coordinate this point in advance with the doctor who prescribes a stomach examination. It is impossible to skip taking medications, as this can adversely affect the well-being and general condition of the patient during medical manipulation.
At the same time, you need to comply with the requirements regarding hunger and fluid restriction. In most cases, the solution is to take medications on an empty stomach, 4 hours before the test with a small amount of water. If the procedure is scheduled for the morning, it is better for the patient to set an alarm clock and wake up early in order to take the medications at the right time.
Other types of training
Moral attitude is very important before research. Usually, the doctor himself tells the patient everything. Feel free to ask questions that interest you. The answers you receive will make you feel better.
If an adult has a predominant feeling of panic or increased excitability, the doctor may prescribe sedatives.
In case of cardiovascular pathologies, for example, hypertension, respiratory failure, their premature correction is important.
This is due to the fact that during the FGS process complications may arise on their part. The patient will have to prepare for endoscopy in the hospital. Before FGDS, local preparation is carried out, which includes the following points:
- The skin and mucous membrane of the patient's oral cavity are examined in order to exclude tonsillitis, jams or cracks. If such problems are identified, then the FGS is postponed.
- To reduce foaming in the stomach and intestines, the doctor prescribes the drug Espumisan, which should be drunk 5 minutes before the start of the test.
- To reduce pain during insertion of the endoscope, the patient is given local anesthesia. To do this, the throat is treated with lidocaine in the form of a spray.
Local preparation takes place under the guidance of a physician. Do not forget to inform your doctor about the presence of chronic diseases.
How to prepare if a biopsy is performed?
When identifying ulcerative defects of the mucous membrane, neoplasms, foci of inflammation, gastroscopy is combined with a biopsy. Manipulation involves sampling suspicious areas of the mucosa in several places for the purpose of histological analysis. A biopsy can be prescribed in advance or directly during an endoscopic examination of the stomach and duodenum. Preparation for the procedure coincides with standard preparation for FGDS. That is, additional organizational measures are not needed.
What does FGDS of the stomach show?
Gastroscopy allows you to obtain the most accurate information about the condition of organs and tissues, the presence of erosions and various formations. Using FGDS, the following problems can be identified:
- stomach and duodenal ulcers;
- benign and malignant neoplasms;
- gastrointestinal bleeding;
- gastroesophageal reflux disease;
- gastritis and duodenitis;
- esophagitis.
What symptoms may indicate that you should make an appointment with a gastroenterologist and, possibly, do an FGDS:
- vomiting and feeling of nausea;
- swallowing disorder;
- decreased appetite;
- bloating;
- chronic cough;
- pain in the epigastrium;
- feeling of heaviness in the stomach after eating;
- heartburn;
- belching;
- weight loss for no reason.
Rules for preparing for FGDS under anesthesia
The use of general anesthesia allows the patient to be relieved of any discomfort during gastroscopy. Anesthesia ensures immersion in sleep and complete relaxation of the muscles, which simplifies the diagnosis in general. However, medicated sleep requires additional preparation from the patient.
To conduct FGDS under anesthesia, patients over 45 years of age must provide an ECG to the anesthesiologist (expiration date - 1 month), as well as permission from the general practitioner (in the presence of pathologies: diabetes mellitus, heart disease, etc.).
Since preparation for gastroscopy involves refusing to eat and drink, additional restrictions are not necessary. The need to use or discontinue medications on the day of the study is agreed with the attending physician.
Preparation for FGS on the day of the study
After waking up in the morning, the patient is prohibited from brushing his teeth and smoking, as this can cause the production of mucus in the stomach, which will delay the examination process.
When you go to the hospital, you need to take with you a referral from your attending physician for FGS, a passport and medical insurance policy (and sometimes an insurance pension certificate), as well as a towel. In order to ensure the most comfortable procedure, it is best to:
- Unbutton the top button on your clothing, especially on the neck, if there is one.
- Unfasten the belt on trousers or jeans, as there may be a feeling of constriction
- Warn the doctor who will perform the procedure about allergic reactions to medications
- Relax, although it will be difficult to do this, since few people take FGS calmly
- Breathe evenly, deeply and slowly, preferably through your mouth
- Try not to swallow, although this will be very difficult
- Think about something good. This will help you take your mind off
In some cases, examinations may be performed under general anesthesia. This is done when a person is intolerant to lidocaine or is in such a state that FGS with local anesthesia can cause any problems, in particular, a dangerous increase in blood pressure, a panic attack, etc. Also, in people with a low pain threshold, FGS is indicated only under general anesthesia.
Sometimes fibrogastroendoscopy is prescribed for the afternoon. Here it will be much more difficult to follow the doctor’s recommendations, but it still needs to be done.
It is also necessary not to eat anything for 8 or 10 hours, not to smoke before the procedure, etc. In general, follow all of the above points.
What to take with you
Take things with you to the hospital that may be needed during the diagnosis:
- sheet;
- towel;
- napkins;
- medical insurance policy;
- referral from a doctor;
- an outpatient card or the results of previous examinations of the digestive tract.
In many clinics, at the reception desk, patients are given instructions containing information about proper preparation and a list of necessary things.
Will there be any discomfort during the procedure?
During gastroscopy, air is supplied to the stomach, so a feeling of bloating may occur; some patients regurgitate air. Pain syndrome is usually not observed.
After the procedure, slight bloating and discomfort in the throat may persist for a short time.
Irrigation of the pharynx with lidocaine solution is used as a local anesthesia, which helps reduce the gag reflex (in the absence of contraindications). It is performed before insertion of the endoscope.
If EGDS is performed by an experienced specialist, the procedure takes place without any particular difficulties for the patient. However, it cannot be called pleasant, so we recommend conducting the examination under anesthesia - this is a more gentle option. Some people, especially older people, are prejudiced against anesthesia and prefer to “be patient a little.” We believe that general anesthesia, which is used today for endoscopy (light sleep), is absolutely justified. It relieves the patient from anxiety and discomfort, and gives the doctor the opportunity to do his job carefully and obtain maximum information, which significantly increases the effectiveness of the intervention.
We also note that during endoscopy without anesthesia, intra-abdominal pressure increases in all patients without exception, and the load on the heart and lungs increases.
At a minimum, in severe patients, we use anesthesiological monitoring, and the anesthesiologist himself decides whether to administer any drugs or not, depending on the functioning of all the vital systems of the body.
We are confident in the modern and safe anesthetic agents we use, and our medical staff is highly qualified. During the procedure, constant monitoring of the patient’s cardiovascular and respiratory systems is carried out.
Indications for the study
Gastroscopy is performed for peptic ulcers.
Gastroscopy is a high-tech method for studying the digestive system. It helps make a diagnosis:
- Cancer;
- Chronic gastritis;
- Peptic ulcer;
- Polypov.
This diagnosis is carried out if there is a need to accurately determine the source of gastric bleeding. The procedure is prescribed if the appearance of malignant neoplasms is suspected.
If an X-ray examination of the stomach has negative results, and the patient complains of gastric discomfort, then the procedure is indicated for him. Gastroscopy is performed if it is necessary to diagnose other diseases with an assessment of the condition of the mucous membranes of the stomach.
If a person has no appetite and begins to rapidly lose weight, then this requires this diagnostic method. If signs of poor food passage during swallowing appear, this research method is also prescribed.
The indication for diagnosis is pain in the upper parts of the stomach. Regular occurrence of vomiting and heartburn requires the use of this research method.
Indications for gastroscopy are quite varied. This research method is widely used in the presence of diseases of the digestive tract.
Question answer
Olga: (2020.02.20)
How to behave correctly during FGS so that it goes away painlessly?
Expert answer:
Olga, hello.
What is the right question to ask: a lot depends on the patient’s behavior during this study. We have prepared a detailed article on this matter and posted it on our center’s website. You will find detailed recommendations in it, including how to properly prepare for the study. Link to article: VIDEOGASTROSCOPY (FGS)
Excerpts from an article on the question asked:
How is Videogastroscopy (FGS, FGDS, EGDS) performed?
During the procedure, the patient lies on his left side with his knees bent. To reduce discomfort during therapy, the patient's nasopharynx is irrigated with a ten percent lidocaine solution. The flexible endoscope is inserted into the oral cavity through a plastic mouthpiece fixed between the teeth. After introducing the gastroscope into the oral cavity, the patient needs to make a swallowing movement to facilitate the advancement of the device into the esophagus. Relaxation and calm breathing help suppress the gag reflex that occurs during the procedure, which also makes the entire procedure easier for both the doctor and the patient.
A few words about “unpleasant sensations” . When performing an endoscopy, the patient experiences the following “indescribable” sensations:
- Nausea and gag reflex (The same sensations occur when examining the throat with a spatula or the handle of a spoon);
- Feeling of a “lump” in the throat (As if you chewed something poorly and choked when trying to swallow it. Very reminiscent of a piece of kebab that got stuck for a while);
- In rare cases, there may be pain as a result of spasm of the upper esophageal sphincter and pharyngeal muscles;
- Distension, bloating and heaviness in the abdomen are a consequence of insufflation (filling) of the stomach with air;
- There may be sensations of movement or movement inside the abdomen (Arise when advancing and manipulating the endoscope);
- Sometimes there is a feeling of lack of air - these sensations are of a subjective nature (the endoscope does not block the airways and air flows freely into the lungs).
No other sensations arise during EGDS. The whole range of sensations is strictly individual and depends on many factors. But if you behave correctly, listen to the prompts of the medical staff and prepare well for the examination, then the procedure takes place with the minimum necessary amount of time and a minimum of discomfort.
!!!How should you behave during EGDS:
1. Prepare well for your research. The procedure is carried out strictly on an empty stomach, the last meal is possible 6-8 hours before the examination, this will allow the endoscopist to examine the entire surface of the mucous membrane as efficiently and quickly as possible. At the same time, detect even minimal changes on it. An empty stomach also reduces the gag reflex and nausea. 2. When passing the endoscope through the mouth and throat, try not to touch it with your tongue. 3. Try to breathe deeply and evenly through your mouth, do not freeze or stop breathing: deep and even breathing calms and reduces nausea. This is the main technique to facilitate research. It is better to breathe directly through the mouth, since during the examination itself it is difficult to switch breathing, and when breathing through the nose, reflex swelling of the mucous membrane and mucus secretion occurs, as a result of which the nose becomes stuffy and breathing becomes difficult. 4. Hug your stomach tightly, do not swing your arms. This will help you focus on breathing and will not interfere with the endoscopist conducting the examination. 5. Try not to resist the endoscope or interfere with medical personnel. Thus, you will significantly reduce the procedure time and improve its quality. Also try not to burp air: the time for insufflation will decrease, and therefore the entire procedure. 6. Only point 1 concerns everyone who performs endoscopy under anesthesia: an empty stomach will help avoid vomiting and aspiration, and will also significantly improve the quality of the examination.
IMPORTANT: Preparation for the study
1) Video gastroscopy is performed on an empty stomach (12 hours of fasting before the procedure is recommended, minimum 8 hours).
2) There is no special diet before the procedure. It is recommended not to eat heavy foods (fried, fatty, spicy), foods that cause bloating (cabbage, legumes, etc.) the evening before the procedure.
3) It is advisable not to smoke at least 2 hours before gastroscopy, since smoking provokes the formation of gastric juice and can increase discomfort.
4) If the patient needs to take medications, this can be done no later than 4 hours before the procedure, with a small amount of water. You must inform your endoscopist about taking the drug.
You can sign up for the FGS on this website in the “Make an Appointment” section (you leave a request and phone number, the registrars will contact you and offer to choose a convenient time) or at the reception desk of the medical appointment department by phone 8 (3902) 242-008, 242- 048.
We are waiting for you at the address: Abakan, st. Taras Shevchenko, 85.
What to do after gastroscopy
After removing the gastroscope, you should not stand up suddenly. You need to lie down or sit for 15 minutes. You are allowed to leave the medical facility no earlier than 1.5 hours later to make sure that no complications have arisen.
It is not recommended to smoke within an hour after the examination, and drink and eat for 2-3 hours. For a couple of days after gastroscopy, you need to eat easily digestible foods: oatmeal, fermented milk products, lean fish, vegetable soups. Then the patient gradually returns to his usual diet and lifestyle.
Gastroscopy is one of the most informative diagnostic methods for stomach diseases. However, improper preparation can distort the results and complicate the procedure. You need to take medical recommendations carefully, and clarify all unclear points in advance. After completing the study, monitor your health so as not to miss dangerous complications: perforation of the esophagus or stomach, bleeding, inflammatory process.