Pain in the rectum causes people a lot of inconvenience. After all, she just has to endure pain, but also put up with stool disturbances, pathological discharge, itching, and swelling.
The general condition of the body worsens, patients suffer from weakness, irritability, and other manifestations of intoxication. It is impossible to clearly determine pain in the rectum by its location: it can be felt in one place or spread throughout the entire perineum, often radiating to neighboring organs.
Rectum: anatomical features
The length of the rectum is 15 cm.
This part of the intestine is located in the small pelvis, in its lower part. The rectum extends into the back of the perineum.
The length of this intestine is 15 cm, and the diameter varies from 4 to 7.5 cm depending on the area of the intestine.
Feces cannot come out of it voluntarily, thanks to 2 sphincters (external, internal). These are special circular muscles that close and diverge at the right moment.
Another important part is the hemorrhoidal zone, which is essentially loose tissue in the mucosa; almost all of its space is filled by the venous plexus. This is where hemorrhoids form.
The very name of the rectum has no physiological basis. This part of the intestine has 2 bends: back - in the sacrum area, forward - near the coccyx. The organs located near the rectum differ by gender. For men it is the prostate gland, for women it is the uterus and vagina.
Since defecation is a complex process that takes place under the total control of the brain, there are many nerve endings in the rectum.
Diagnosis of pathologies
To identify the cause of the disease and prescribe the correct treatment, it is necessary to undergo a comprehensive examination. It will include several stages that must be completed:
Lower abdominal pain and discharge
- barium enema;
- blood, urine and stool tests;
- CT scan;
- sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy;
- Ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs;
- X-ray of the abdominal cavity.
Sometimes doctors may order laparoscopy to visualize the pelvic organs. It also helps to carry out surgical treatment without extensive intervention. Contraindications for manipulation are intestinal obstruction and hypovolemic shock.
Causes of pain
A rectal fissure causes pain in the anus.
It is difficult to make an accurate diagnosis based only on pain in the rectum. This can be a manifestation of any pathology.
Moreover, the severity of pain does not correspond to the severity of the disease. Even minor pathology can lead to severe pain.
Conversely, a serious illness may not manifest itself for a long time or may cause insignificant pain. The main diseases that lead to pain in the rectum:
- fissures in the anus;
- thrombosis of nodes;
- prostatitis;
- proctitis, paraproctitis;
- appendicitis;
- neoplasms;
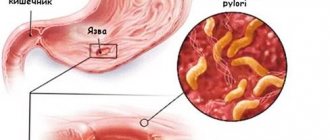
- ulcer;
- gynecological pathology.
You need to know that such a pathology as proctalgia causes pain in the rectum without any reason at all. Some experts believe that pain begins at the moment when spasms begin in the muscles of the anus.
It is not known exactly why these spasms occur. However, it has been noted that this disorder is typical for anxious, suspicious women who nervously perceive everything around them. The disease most often develops after operations, injuries, or against the background of immersion in stress. Secondary proctalgia is a consequence of diseases of the rectum.
Anal fissure is the most common cause of pain. They appear most often on the front or back walls. They are extremely rare on the right and left sides. You can find out about a crack both by sharp, severe pain and by bloody discharge.
Cracks can provoke constipation, because defecation becomes a painful process, and a person involuntarily tries to avoid timely bowel movements. As a result, the situation only gets worse: stress during defecation intensifies the lesion and does not heal for a long time.
Paraproctitis is an inflammation of the perianal tissue of a purulent nature. With this disease, pain is accompanied by a feverish state. The pain itself is also quite peculiar: it is throbbing. The disease can be determined by palpation.
A lump with fluctuation can be felt on the side of the anal sphincter. Touching this area causes severe pain, which radiates to the rectum. With simple proctitis, pain is accompanied by burning and itching. All symptoms become more pronounced with defecation. Although with proctitis, tenisms are also possible, when there is a urge to defecate, but the bowel movement itself does not occur.
Like
Social buttons
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT EMAIL: This email address is being protected from spambots. You must have JavaScript enabled to view it.
Rectal pain
Pain in the rectum manifests itself in quite a variety of ways, in some cases it is blurry and unclearly expressed. Discomfort in the anal canal is often accompanied by constipation or diarrhea, bloating, the sensation of a foreign body in the anus, bloody, purulent or mucous discharge, itching in the perineum, general weakness, symptoms of intoxication, anemia, and a false urge to defecate.
With inflammation and malignant formations, metabolic processes and the functioning of the genital organs are disrupted. To differentiate symptoms, a clinical and biochemical analysis of blood and feces, x-rays, anoscopy, sigmoidoscopy, fibrocolonoscopy, and palpation of the posterior part of the intestinal canal are performed.
Causes of pain in the rectum
1. A fissure in the anus is one of the most common causes of pain in the rectum. With this pathology, intense pain, cramping, and bloody discharge in the stool are noted. In some cases, constipation occurs, less often - diarrhea. To establish a diagnosis, an examination of the anal canal is performed. The damage can be localized on the posterior or anterior wall of the anal canal. As therapy in the acute phase of the disease, medicinal baths are prescribed three times a day. For chronic cracks, surgery may be performed.
2. Paraproctitis. This disease is characterized by an inflammatory process of the anal glands located in the rectal sinuses. The main symptom is a painful throbbing in the posterior part of the intestinal canal, often accompanied by fever. A dense or fluctuating formation is felt to the touch in the perineum or rectal canal. Treatment is carried out surgically.
3. Damage to hemorrhoids. Painful sensations occur if the internal hemorrhoid falls out and becomes pinched or thrombosis of the external hemorrhoid forms. In the latter case, the pain syndrome is much stronger. A painful tightness is felt in the area of the anal canal, and diarrhea or constipation occurs. If the internal node falls out, its reduction is indicated using local anesthesia. The doctor manually adjusts the node, after which he prescribes additional therapeutic procedures.
4. Proctalgia. This type of pain can occur from time to time without organic damage to the posterior intestinal canal. The presumable cause of this disorder is spasm of the anal muscles. The pathogenesis of the disease is practically unknown, which significantly complicates its treatment. The clinical picture of the disease includes symptoms such as severe aching pain or sudden pain in the rectum, accompanied by contractions. If the patient is standing, the pain is usually less pronounced. This pathology is preceded by injury or surgery on the pelvic organs. Treatment of the disease is individual in each case and requires consultation with specialists such as a psychotherapist, therapist, and surgeon.
5. Coccydynia. Injury to the coccyx can contribute to the development of this disease. Pain is usually felt when the patient is sitting, or during bowel movements. Treatment for such conditions is carried out using conservative methods for six months.
6. Perianal hematoma. With this disease, a neoplasm appears in the area of the anus, which occurs due to damage to the anal vein and is accompanied by painful sensations of varying intensity. As a rule, the disease goes away on its own within a few days.
7. Ulcerative formation in the anal canal. In addition to pain, this pathology is characterized by a sensation of a volumetric formation in the posterior part of the intestinal canal, problems with bowel movements, blood and mucous discharge from the rectum. The disease mainly affects young people. For treatment, nutritional correction is mainly prescribed.
8. Prostatitis in men. With this disease, pain can radiate to the rectum, accompanied by painful sensations when urinating, frequent urge to empty the bladder, and fever. Treatment is prescribed by a urologist in accordance with the general picture of the disease.
9. Ovarian cyst, inflammation of the pelvic organs in women. In females, diseases such as ovarian cysts or inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs can cause pain to radiate to the rectum. Elimination of discomfort and pain is carried out after a preliminary examination by the treating gynecologist.
Symptoms of pain in the rectum
Pain in the rectum and its accompanying symptoms are quite varied and may indicate various diseases. When pain in the rectum occurs, constipation or diarrhea, flatulence, bloating, abdominal pain, sensation of a foreign body and discharge from the anus of a bloody or mucous consistency, etc.
The nature of the pain is quite varied - from aching and pressing to sharp and intense. If pain in the rectum is accompanied by exhaustion of the body, metabolic disorders, and the functioning of the genital organs, this may be a symptom of the development of a tumor. If pain in the rectum is combined with painful cramping sensations in the abdomen, this may indicate Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis. If pain in the abdomen is constant, we may be talking about the development of diverticulosis or diverticulitis, irritable bowel syndrome, or ulcerative colitis. Often pain in the rectum is combined with pain in the anus or perineum. Such pain can intensify significantly after bowel movement and be a sign of thrombosis of hemorrhoids, acute paraproctitis or a fissure in the anal canal. Such a symptom as the discharge of mucus or purulent masses from the anus during the act of defecation can occur with proctitis, fistulas of the posterior part of the intestinal canal, and tumor formations. Mucus in the stool is present in irritable bowel syndrome. Bloody discharge in the stool is observed with hemorrhoids and rectal fissures, Crohn's disease, colitis, and diverticulosis. Such a symptom as regular false urge to empty the bowel, accompanied by the release of mucous or bloody impurities, can lead to the formation of cracks or erosions and are the result of inflammatory processes of the mucous membrane.
When does pain radiate to the rectum?
In cases where pain radiates to the rectum, this can be a sign of a variety of pathologies. For example, with cystitis, painful sensations arising from inflammation of the bladder often radiate to the anus, while its exact location is not always clearly defined. A disease such as inflammation of the sigmoid colon can also provoke cases where pain radiates to the rectum. The sigmoid colon is actively involved in the process of digesting food; when it becomes inflamed, intense cramp-like pain occurs in the ileum, constipation, diarrhea, bloating, rumbling, nausea, and the pain can radiate to the rectum. Pain can also radiate to the rectum when the appendix is inflamed, which is why if appendicitis is suspected, a rectal examination is performed. In women, pain radiates to the rectum with ovarian cysts or inflammatory processes of the pelvic organs. In men, irradiation of pain into the anal canal can occur with prostatitis.
Pain in the rectum at night
Pain in the rectum at night often occurs with proctalgia, a disorder that manifests itself against the background of unfavorable emotional states and is caused by spasms in the rectum; the disease most often affects middle-aged men. With proctalgia, painful sensations can occur at night and last from several minutes to half an hour, disturbing the patient’s sleep and peace; repeated attacks can occur repeatedly during the night, provoking pain of varying degrees of intensity. As a treatment, psychocorrection of the patient’s condition is carried out; it is also possible to prescribe the drug salbutamol strictly according to the indications and recommendation of the doctor. Pain in the rectum at night can occur when the anal canal prolapses and can be quite intense. Associated symptoms include bloating, chills, diarrhea or constipation, and increased sweating after the attack subsides.
Sharp pain in the rectum
Sharp pain in the rectum often occurs when a crack forms in it. Such painful sensations can appear both in the morning and at night; in the acute stage, it increases during bowel movements, and when the chronic form develops, it increases after defecation. Pain from a fissure of the anal canal causes very sharp and long-lasting pain, and may be accompanied by pain in the sacrum and perineum, disruption of the menstrual cycle, heart pain, and difficulty emptying the bladder. The prognosis for the outcome of the disease is usually favorable, the symptoms of the disease disappear, but complete recovery occurs rarely. Attacks of sharp pain in the rectum can also occur with proctalgia. Typically, pain occurs spontaneously and is accompanied by a sensation of spasm. Pain during proctalgia is not associated with the process of defecation, it radiates to the coccyx, anus, perineum, etc. It is believed that a strong emotional stress or stress can provoke an attack of exacerbation of the disease. Sometimes sharp painful sensations occur with hemorrhoids when the disease worsens. During this period, there is an increase in hemorrhoids, their swelling and redness. Sharp pain in the rectum is also characteristic of diseases such as proctitis, paraproctitis, and when the anal canal prolapses, it leads to shock. Sharp pain in the rectum occurs in many of its pathologies, depending on the severity of the disease. Thus, sharp pain in the rectum can be disturbing due to anal fissure, thrombosis of hemorrhoids, development of an abscess, prolapse or prolapse of the anal canal, etc.
If you experience sharp pain in the rectum, this is a good reason to see a doctor. Only a qualified proctologist, using digital examination and auxiliary diagnostic methods, will be able to determine the causes of the disease and prescribe the necessary therapeutic procedures.
Throbbing pain in the rectum
Throbbing pain in the rectum is characteristic of paraproctitis, which can be acute or chronic. In the acute phase of the disease, an inflammatory process occurs in the peri-rectal tissue, accompanied by the formation of pus. The patient's body temperature rises, swelling and redness in the anus are observed. Constipation, diarrhea, physical activity, poor diet, alcohol abuse, and hypothermia can provoke infection into the fiber. At the location of the anal crypts, a small hole is formed through which the infection penetrates, and, as a result, an inflammatory process develops. Throbbing pain is also observed with perirectal abscess. With this disease, it is difficult for the patient to sit in a sitting position due to the formation of a hard swelling. The inflammatory process leading to the development of an abscess usually occurs due to damage to the mucous membrane of the anal canal, which subsequently becomes infected. To treat a perirectal abscess, it is opened and drained using anesthetic and antibacterial agents.
Dull pain in the rectum
Dull pain in the rectum is caused by the development of an abscess - a red, swollen formation near the anus. Painful sensations increase when the patient sits, sneezes or coughs. Dull pain in the rectum may be accompanied by the discharge of purulent masses, constipation or diarrhea. Rectal swelling can also cause a dull, painful sensation that radiates to the lumbar region. In this case, blood and mucus are released from the anus, a feeling of bloating, fullness and squeezing in the anus occurs, and stool retention or diarrhea is noted.
Severe pain in the rectum
Severe pain in the rectum can appear with any of its pathologies, in particular with anal fissure, paraproctitis, node thrombosis, proctitis, prolapse or prolapse of the anal canal. With such a pathological process as anal fissure, intense painful sensations are combined with spasms of the anal sphincter, bloody discharge in the stool, constipation, the occurrence of perianal eczema, and itching. Severe and excruciating pain occurs when the anal canal prolapses. The reasons for the development of this pathology include frequent straining, stool retention, injury to the anal muscles, as well as their changes associated with age-related factors, and surgical interventions in the pelvic area. As the disease develops, spontaneous passage of gases and liquid feces occurs, mucous and bloody discharge appears, and itching in the anal area. The development of proctitis, which affects the intestinal mucosa and causes severe pain, can be associated with alcohol abuse, constipation, stagnation of blood in the pelvis, helminthic infestation, hypothermia, inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs, and hemorrhoids.
Bursting pain in the rectum
Bursting pain in the rectum occurs due to thrombosis of hemorrhoids, while a sensation of a foreign body appears in the anus. Painful sensations are accompanied by pulsation and increase with sudden movements, during coughing, bowel movements, and also with palpation of nodes. Bursting pain in the rectum can occur with the development of malignant tumors. Blood appears in the stool, the process of defecation also becomes painful, and a foreign body is felt in the anus. Accompanying symptoms of malignant neoplasms also include the development of anemia, sudden loss of body weight, bloating and constipation. The pain radiates to the hips, lower abdomen, and genitals. The disease often develops in older people. Painful sensations of a bursting and aching nature in the rectum in women can be a symptom of an ovarian cyst. The discomfort is combined with a disruption of the monthly cycle, nagging pain in the lower abdomen, which becomes stronger during sexual intercourse, uterine bleeding, nausea and vomiting.
Nagging pain in the rectum
Nagging pain in the rectum is most characteristic of inflammation of the peri-rectal tissues. With this pathology, there is a false urge to defecate, general malaise, pain in the perineum and pelvic region. Depending on a number of accompanying symptoms, painful sensations can be of varying degrees of intensity - from moderate to severe. In women, nagging and bursting pain in the rectum can occur due to the formation of ovarian cysts and various inflammatory diseases of the pelvic region. In men, nagging pain in the rectum can occur with prostatitis. A disorder such as proctalgia, associated with muscle spasm of the anus, can also provoke nagging pain in the rectum. The etiology of this disease remains unclear. An attack of pain lasts from several minutes to half an hour, the pain radiates to the tailbone, perineum, and hip area. Painkillers for this disease are usually ineffective. Nervous strain, stress, and physical overload can provoke the development of proctalgia.
Pain due to rectal cancer
Pain in rectal cancer is accompanied by bloody and purulent discharge in the stool, pain in the anus during bowel emptying, itching, false urge to defecate, and can cause sensations of varying intensity and nature. As the disease progresses, the pain syndrome covers the lower abdomen and iliac region. The intensity of pain in rectal cancer does not depend on the stage of the disease and can be very strong in the presence of a small tumor or, conversely, moderate in cases of severe disorders. Pain in rectal cancer usually occurs when the tumor grows locally, especially when it moves to nearby tissues and organs. However, if the tumor is localized in the anorectal region, pain occurs already at an early stage of the disease. Pain from rectal cancer is combined with a state of powerlessness, rapid fatigue, anemia, weight loss, and pale skin color.
Who to contact?
Proctologist
Treatment of pain in the rectum
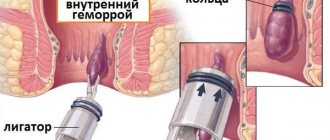
To eliminate such a symptom as pain in the rectum, treatment is prescribed primarily based on the causes and type of disease. Thus, when treating the internal form of hemorrhoids, the ligation method with latex rings is used, with the help of which the blood flow to the hemorrhoids is blocked, as a result of which they dry out and are neutralized. When treating external hemorrhoids, the drug “Surgitron” is used. The walls of the hemorrhoidal node are exposed to a flow of thermal energy, which leads to sclerosis of the node.
For rectal fissures, ointments and suppositories are used at the initial stage of the disease. Anuzole suppositories are administered rectally, one piece two to three times a day. The drug relieves itching, spasm and inflammation, has a drying and antiseptic effect. For cracks and hemorrhoids, hemorrhoid suppositories are used, preferably after emptying the intestines. It is recommended to administer the drug one suppository at night, in severe forms of the disease - two or three suppositories throughout the day. The course of treatment is no more than seven days. Bezornil ointment for anal fissures and internal hemorrhoids is injected into the anus using a special tip twice a day, as well as after each bowel movement. The duration of treatment is two weeks. Anestezol suppositories are administered rectally after cleansing the intestines naturally or using an enema. The drug is used once or twice a day, one suppository.
In case of inflammation of the mucous membrane, a therapeutic diet, antibacterial therapy, enemas with collargol and chamomile are indicated. When the condition improves, oil enemas are given and sitz baths with potassium permanganate are prescribed.
When treating proctalgia, the patient’s psycho-emotional state is corrected, sedatives are prescribed, novocaine blockades are prescribed during exacerbations, oil microenemas with anesthetics are given, UHF therapy, diathermy are performed, and massage procedures are prescribed for spasms of the anal canal.
For paraproctitis, surgical intervention is performed, during which the abscess is opened and the internal opening of the fistula is neutralized.
When treating anal ulcers, a therapeutic diet and laxatives are prescribed. If conservative treatment is ineffective, surgery is prescribed.
Treatment of coccydynia is carried out using physiotherapy methods, prescribing paraffin baths, the use of therapeutic mud, etc. For pronounced pain syndrome, novocaine or lidocaine blockades and massage of the rectal muscles are indicated.
Nature of pain
Itching in the anus causes discomfort.
It is impossible to speak precisely about the nature of pain in the rectum. The nature and intensity vary depending on the cause.
Sometimes they are pulling, aching, sometimes sharp, sharp. The pain may be felt more strongly at certain times of the day, and is often accompanied by other symptoms.
If the pain is caused by a disease of the rectum, then it intensifies during defecation, and after it weakens, sometimes it goes away completely for a while.
Often pain in this area is caused by diseases of other systems located in the immediate vicinity. However, the pain that appears cannot be attributed to already known diseases. Every time you need to be examined and find out the cause of the condition.
It should be taken into account that intestinal disease can cause pain that radiates to neighboring organs. Therefore, one cannot judge a disease by pain alone. An in-depth examination is required.
What to do if you have bloating?
If, after the examination, it turns out that the source of systematic problems with the gastrointestinal tract is poor nutrition, you need to contact a nutritionist who will help you eliminate harmful foods in each individual case and choose the correct portion composition. When complex diseases are detected, it is necessary to influence their root cause. Treatment is adjusted based on the severity of the pathology and includes both drug and instrumental therapy. If tumor or adhesive processes are detected, the issue of surgical intervention is decided.
After the treatment and rehabilitation period, it is necessary to undergo a second hardware examination. The nuclear resonance scanner does not have a harmful effect on the body’s cells, immune and nervous systems, so diagnostics can be performed as many times as required for clinical purposes.
Prevention
In order to minimize the risk of developing diseases that cause pain in the lower abdomen and pain in the anus, it is necessary to follow simple measures. To prevent diseases of the genitourinary system:
- Adhere to the rules of personal hygiene.
- Try to prevent hypothermia.
- Take vitamin complexes and harden yourself, thereby keeping your immune system in good shape.
- Regularly drink at least 1.5–2 liters of liquid per day.
To prevent intestinal diseases:
- Adhere to a proper and healthy diet and monitor your lifestyle.
- Monitor the state of the intestinal microflora.
- Play sports, even in the smallest quantities (for example, walking).
Remember! It is much easier to prevent the development of unpleasant symptoms and pathologies than to treat them later.