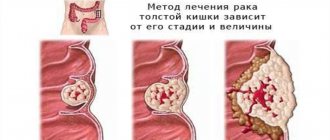
The article discusses the main stool disorders in malignant neoplasms of the gastrointestinal tract.
The color of stool in case of intestinal cancer is quite informative, although not the only sign. It is important to know that gastrointestinal cancer may not manifest itself for a long time, even if the tumor is quite large. Or maybe, with minimal damage to the mucous membrane, force you to see a doctor. It all depends on the localization of the malignancy, the presence of concomitant diseases, the extent of the process and damage to neighboring organs. And a chair can tell you a lot of this.
Main signs of colorectal cancer
The most common sign of pathology is pain , but this symptom is not an early one. When it appears, the tumor grows to a fairly large size and disrupts peristaltic functions or extends beyond the boundaries of the affected organ and spreads to the peritoneum. Intense pain is also accompanied by partial or complete intestinal obstruction. If, at the time of the onset of pain, an examination has not yet been carried out in the clinic, then this must be done urgently. If cancer is detected, you can undergo treatment for colorectal cancer in Moscow.
Colorectal cancer pain is usually short-lived and varies in intensity, so people often mistake it for stomach discomfort. If fecal retention occurs, the patient’s stomach becomes bloated, appetite decreases, and he is bothered by nausea and constant belching.
A pronounced sign of the development of intestinal obstruction is vomiting with the smell of feces .
If an unstable alternation of constipation and diarrhea , while the stool has a foul odor and mucus is present in it, then the rectum and left side of the colon are most likely affected. If the right parts of the colon are affected, the patient is bothered by constipation. When a cancer tumor is localized in the rectum, patients are often bothered by the feeling of incomplete emptying .
In the later stages of the disease, signs of intoxication appear, which are caused by the active process of decay and the absorption of toxins into the blood. The patient feels constant weakness and gets tired quickly. Cancer pathology destroys the walls of blood vessels, causing constant bleeding, which leads to anemia.
Signs of colorectal cancer are unstable and varied, so the disease is difficult to diagnose at the initial stage. Any disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract cannot be ignored, even if they are minor, because cancer can masquerade as many diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. After diagnosis, you can organize treatment in Moscow, in a modern clinic equipped with the latest generation equipment.
Black color of stool
Black stool in colorectal cancer indicates bleeding in the upper gastrointestinal tract. This is the small intestine or stomach. But, since oncology in the small intestine develops extremely rarely, problems begin to be looked for in the latter. A tumor is a neoplasm that grows in the gastric mucosa, or an ulcer prone to necrotic changes. In any case, it damages the vessels, which begin to bleed. Hemoglobin in the blood mixes with hydrochloric acid in the stomach, resulting in the formation of black hemin. Next, the blood passes through the intestines, mixing with feces. The resulting stool is not formed and has a characteristic name - tarry. This is an important diagnostic sign that helps to distinguish actual bleeding from stool that has turned black as a result, for example, of the use of iron supplements, which is not a pathology.
The first symptoms of colorectal cancer
Despite the atypicality of the early signs of cancer, it can be suspected by such early manifestations as:
- frequent urge to urinate or constipation;
- constant alternation of constipation and diarrhea;
- visible mucus and blood in the stool (stool turns black due to the presence of fresh blood);
- intense noises in the intestines, bloating (such signs occur in many people and are often not associated with oncology, but if these symptoms appear constantly, then you should pay attention to them);
- feeling of fullness in the intestines;
- spasmodic pain in the stomach;
- pain during bowel movements.
Secondary symptoms of bowel cancer
The appearance of secondary signs of cancer indicates that the formation has increased significantly. The clinical picture develops against the background of narrowing of the intestinal lumen and limited mobility of the intestinal walls.
When the upper intestine is affected, intestinal obstruction of varying severity develops, and complete obstruction is possible. First, the process of moving feces through the intestines is disrupted, which leads to bloating, constipation, and rumbling. If the disease is advanced, then spasmodic pain occurs in the abdominal area.
A characteristic symptom of this condition is the alternation of periodic diarrhea with persistent constipation. This happens due to a significant narrowing of the lumen of the rectum, through which dense feces do not pass. Against the background of this disorder, water absorption decreases, while secretory activity and intestinal motility increase.
Part of the feces is retained in the colon, in front of the tumor canal. If this condition is not eliminated in time, obstructive intestinal obstruction, end-to-end disruption of the intestinal wall above the tumor and fecal peritonitis develops. In such cases, cancer treatment abroad must be urgent.
If the ampullary part of the rectum is affected, then complete obstruction occurs very rarely, which is due to the wide lumen in this part of the intestine. More often, partial intestinal obstruction is diagnosed, while the patient has a feeling of incomplete emptying due to the fact that a tumor is developing in the intestine.
A tumor developing in the lower part of the rectum causes significant narrowing and painful, frequent urge to defecate, up to 15 times during the day. When trying to empty the intestines, a small amount of liquid feces is released from the rectum, which contains pathological impurities, or nothing is released at all. The presence of a tumor in the intestine is perceived by the body as a foreign body, and the defecation reflex is triggered, but solid feces do not pass through the areas of the intestine that are narrowed. The prognosis of intestinal cancer in this case will depend on how quickly and efficiently the treatment is completed. The prognosis is also affected by the presence of metastases, for example, if a patient is undergoing treatment for bone cancer abroad, then the prognosis of intestinal cancer takes into account the success of all treatment measures.
Signs of colorectal cancer depending on location
When colorectal cancer develops, the tumor can have different locations, which determine the nature of the symptoms.
Symptoms of colon damage
The early stages of such a tumor are rarely accompanied by any symptoms. But as the tumor process spreads, characteristic symptoms of the pathology appear:
- aching pain in the abdomen; if a person takes a certain body position, the pain may intensify;
- disruption of the digestive process (stomach is bloated, stool is constantly disrupted, intestinal patency is impaired, nausea and vomiting are constantly present);
- ascites develops (an abnormal amount of fluid accumulates in the abdominal cavity);
- Intra-abdominal hypertension develops.
Signs of damage to the small intestine
The later stages of this pathology are associated with a complex treatment regimen, so treatment of stomach cancer abroad should not be delayed. In order to detect a malignant disease in time, you need to contact the clinic if the following signs appear:
- stool becomes dark in color and contains blood;
- bothered by sudden attacks of acute cramping pain in the abdomen;
- there is a sudden dislike for certain foods;
- a metallic taste appears in the mouth;
- Nausea, vomiting, bitterness in the mouth bothers me.
Signs of colorectal cancer in women
With the development of cancer pathology in women, the bladder is affected, and a rectovaginal fistula develops (the straight passage through which the rectum connects to the vagina). As a result, feces and gases enter the vagina.
Other specific symptoms of colorectal cancer in women:
- disruptions of the menstrual cycle;
- signs of blood in the urine;
- sudden weight loss;
- unreasonable dislike for fatty and fried foods.
How to find out if you have bowel cancer? General symptoms
Signs of bowel cancer vary. Their manifestation is affected by the size of the formation and its location in the organ. It is difficult to accurately recognize cancer from early manifestations of pathology, since they are nonspecific.
The first thing a patient may notice is signs of damage to the organ mucosa. This clinical picture is called toxic-anemic and occurs when lesions form on the intestinal mucosa. Through them, toxic substances penetrate into the tissues, then they enter the bloodstream through the disturbed structure of the capillaries and general intoxication develops.
The general clinical picture is expressed:
rapid fatigue;- headaches;
- anemia;
- loss of interest in food;
- joint pain;
- pale skin;
- signs of blood in the stool.
The listed symptoms are difficult to attribute to a specific disease, since they are characteristic of many diseases. But it is at this stage that treatment of intestinal cancer abroad shows the best results, so early diagnosis and prevention measures must be given special attention.
Further development of the formation leads to inflammation of large areas of the intestinal mucosa.
In addition to the above symptoms, signs of intestinal dysfunction are added:
- flatulence;
- body temperature rises to 38 degrees and above;
- stool contains mucus, blood, and pus.
But even at this stage, many patients are in no hurry to seek help, so treatment of intestinal cancer often begins at an advanced stage, when treatment of stomach cancer abroad or other organs affected by metastases is already required.
Signs of colorectal cancer in men
With the development of colorectal cancer and the lack of treatment in its early stages in men, the prostate gland is affected, and characteristic clinical manifestations arise:
- disturbance of the urination process (pain, false urge to empty the bowel, abnormal color of urine);
- low-grade body temperature that persists for a long time:
- decreased sexual activity;
- abdominal pain;
- signs characteristic of digestive problems.
Early detection of colorectal cancer
One of the most common malignant tumors in economically developed countries of the world is colorectal cancer.
The term colorectal cancer (colon cancer) is used to define tumors of the colon and rectum. Anatomically, the colon is divided into the cecum with appendix, ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon, sigmoid colon and rectum. The rectum ends in the anal canal. The transition of the ascending colon to the transverse colon is called the hepatic flexure, and the transition of the transverse colon to the descending colon is called the splenic flexure.
CAUSES OF COLORECTAL CANCER AND FACTORS THAT INCREASE THE RISK OF ITS DEVELOPMENT
The risk of developing colorectal cancer is associated with age. Less than 2% of cases occur in people under 40 years of age. The risk of colorectal cancer increases sharply after age 50. It is believed that most colorectal tumors develop from adenomatous polyps. It has been established that the time for malignancy of polyps is at least 5 years, on average - from 10 to 15 years. Mortality from colorectal cancer is low if the disease is detected in its early stages.
Factors that increase the risk of developing colorectal cancer include:
- Age over 50 years.
- Family history: familial diffuse polyposis, Peutz-Jeghers syndrome, Gardner syndrome, Turco's disease, hereditary adenocarcinoma (Lynch syndrome), colorectal cancer in family members.
- Tumors of other localizations, previously treated: previously suffered cancer of the female genitalia, breast.
- Precancerous diseases of the colon: single and multiple adenomas (polyps) of the colon, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease.
- Poor diet: According to the World Health Organization, the risk of colorectal cancer is increased by excessive consumption of animal fats, consumption of foods with insufficient plant fiber, excessive alcohol consumption, smoking, obesity, and, as some studies have shown, a sedentary lifestyle.
Reduce the risk of colorectal cancer: consumption of vegetables and fruits (high content of plant fiber), according to some studies - consumption of fermented milk products, vitamins A, E and C, calcium supplements.
IS IT POSSIBLE TO DETECT COLORECTAL CANCER IN THE EARLY STAGES?
Modern advances in science and technology and diagnostic methods make it possible to detect colorectal cancer at the earliest stages of its occurrence.
Seeking medical help - a doctor can only help you if you contact him. You should be alert to an unmotivated deterioration in your health, a change in the rhythm of bowel movements, or any unexplained symptoms that do not disappear on their own or after the treatment prescribed to you. In this case, sometimes you need to consult a doctor again. The presence of blood in the stool can be explained by hemorrhoids only after examining the intestines with a probe.
Colorectal cancer screening is an examination of asymptomatic individuals who are at risk for colorectal cancer, which allows not only to detect tumors at an early stage, but also to identify and remove polyps that may eventually turn into cancer. There are several methods for screening for colorectal cancer:
- Fecal occult blood test. The blood vessels on the surface of the tumor are fragile and are easily damaged by advancing feces. Damaged blood vessels usually release small amounts of blood into the intestinal lumen.
- Digital rectal examination. Digital examination is a mandatory method for diagnosing diseases of the rectum, pelvis and abdominal organs. It always precedes instrumental research.
- Colonoscopy. The examination is carried out using a colonoscope (a thin, flexible tube equipped with a light bulb). The study has the greatest accuracy and allows you to perform a biopsy.
- Examination using barium enema and air contrast. Barium sulfate, a chalky substance, is used to partially fill and dilate the colon. This test is better tolerated by patients than a colonoscopy, but may not detect small polyps and tumors.
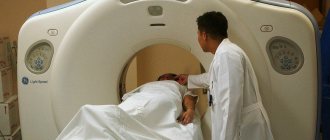
- Virtual colonoscopy. This method does not use a contrast agent. Only air is introduced to expand the colon. Spiral computed tomography is then used. This test cannot biopsy or remove polyps or detect lesions smaller than 5 mm.
- Biopsy. The only method that allows us to reliably state whether there is cancer in a given case or not (examination of tissues, cells, organs taken intravitally from the body using special dyes and a microscope).
All other methods: ultrasound, CT, MRI, laparoscopy, determination of CEA, Ca19-9 and other markers are additional research methods and are used for special indications in specialized institutions to clarify the extent of the tumor process.
WHAT SYMPTOMS SHOULD ALERT A PATIENT AND MAKE HIM CONSULT A DOCTOR
According to the clinical course of colorectal cancer, it is convenient to distinguish cancer of the right half of the colon, cancer of the left half of the colon, cancer of the rectum and anal canal.
Cancer of the right half of the colon (cecum, ascending colon, hepatic flexure) is characterized by the following symptoms:
- hyperthermic reaction (low-grade fever and higher);
- weakness, anemia, weight loss;
- the presence of a palpable tumor in the abdominal cavity.
For cancer of the left half of the colon (splenic flexure, descending colon, sigmoid colon) other signs are characteristic:
- the presence of pathological discharge from the anus (bloody, mucous, purulent);
- the presence of intestinal disorders (tenesmus, constipation, diarrhea or their alternation);
- intestinal obstruction (chronic or acute obstructive intestinal obstruction).
Cancer of the rectum and anal canal is characterized by pathological discharge from the anus.
- Bleeding from the anus is observed in 75–90% of patients. Blood is discharged more often with feces during bowel movements. Less common are mucus and pus in the stool.
- Intestinal dysfunction: constipation, diarrhea or their alternation.
- Tenesmus is a frequent false urge to lower oneself, up to 15–20 times a day.
- Pain in the anus during defecation, and in advanced stages - constantly.
- General manifestations: anemia, weight loss, poor appetite, weakness, sallow skin color - these are rare in the initial stages of rectal cancer and are characteristic of already advanced forms.
DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF COLORECTAL CANCER
The examination algorithm for colorectal cancer includes the following research methods and in the following sequence:
- Finger examination. It allows you to identify up to 90% of all rectal carcinomas and determine the extent of their local spread.
- Colonoscopy. With a flexible endoscope it is possible to examine all parts of the colon. In this case, a biopsy of pathological formations is possible for the purpose of their morphological examination.
The only radical treatment for colorectal cancer is surgery. Chemotherapy and radiation therapy are also used to improve long-term treatment results.
PREVENTION AND PROTECTION MEASURES
Awareness of the patient Every person should monitor their health, if they have any diseases, read the available scientific literature in order to reasonably and consciously follow the doctor’s recommendations.
To reduce the risk of developing colorectal cancer, you must adhere to the following recommendations.
- If you have first-degree relatives (parents, brothers or sisters) with colorectal cancer, you should be screened at age 50.
- Exercise and maintain a normal weight.
- Eat more vegetables, fruits and other fiber-rich foods.
- Avoid fatty foods.
- Do not smoke or drink strong alcohol.
- Monitor regular bowel function.
- Fight chronic constipation.
- Do not ignore diseases such as chronic colitis, anal fissures, polyps in the colon.
- Be sure to consult a doctor if there is mucus or blood in the stool, a feeling of discomfort or pain in the anus, frequent urge to urinate, or a change in the rhythm of bowel movements.
Remember! Detection of colorectal cancer in the earliest stages guarantees its complete cure!
Author: Rolevich I.I. – surgeon-oncologist
Common signs of colorectal cancer
Regardless of the type of tumor and its location, as well as the gender of the patient, colorectal cancer is accompanied by the following general symptoms:
- the ability to work decreases, a person quickly gets tired while performing the usual amount of work;
- there is constant weakness and low-grade fever;
- weight decreases for no reason, and the process of losing weight is constantly progressing;
- stool visually changes (becomes dark, there is mucus and blood in it);
- the skin and mucous membranes turn pale.
The listed signs are not specific manifestations of colorectal cancer. They are not typical for any other oncological pathology, and these symptoms often accompany a malignant disease. If at least one of the listed disorders occurs, you must consult a doctor and undergo an examination.