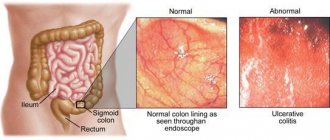
Inflammation of the large intestine is a collective name used to designate painful processes occurring in one or more parts of the mentioned organ. Developing for various reasons, this condition occurs equally often in people of both sexes and all ages. Moreover, due to the complexity of the disease, its treatment must be selected for each individual patient individually, and always by specialists.
For what reasons does inflammation occur in the large intestine? How does this disease manifest itself? Is it possible to diagnose such a disease at an early stage and, most importantly, how and with what to treat it? Our article will answer these and other equally important questions related to inflammatory processes in the intestines.
Why does inflammation occur?
Inflammation is the death of mucosal cells.
Before answering this question, you need to understand how this painful process generally proceeds.
From a medical point of view, any inflammation is the death of cells of the mucous membranes, accompanied by abundant blood supply to the affected area.
This process is accompanied by inevitable disruptions in the functioning of the “injured” organ and, as a consequence, pain.
The role of the factor that provokes the problem, as a rule, is various harmful organisms. When it comes to intestinal inflammation, it is usually:
- worms and other parasites;
- pathogens (viruses and microbes);
- other pathogenic flora.
Of course, other negative factors can also be the cause of the violation. Among them are:
- autoimmune diseases leading to spontaneous rejection of cells from the mucous membrane of the large intestine;
- genetic predisposition, in other words, an inherited lack of digestive enzymes, causing problems with the gastrointestinal tract;
- poor nutrition, which provokes chemical and mechanical damage to the mucous membranes of the organs involved in the digestive process (usually through the consumption of excessively spicy or fatty foods);
- atherosclerotic abnormalities, due to vasoconstriction, inevitably leading to disruption of the blood supply to the intestinal walls.
The following video will tell you about the symptoms and treatment of colitis:
IBD in children: growth and development of the body is at risk
Ulcerative colitis in children can appear even before the age of one year and very quickly lead to total damage to the colon. If left untreated, the disease can result in a serious disruption of the physiological process of development of the child’s body: growth retardation or retardation in physical development. If endocrine pathology is not detected, a good pediatrician will definitely prescribe a gastrointestinal tract diagnosis for the child. In addition, this pathology causes serious psychological problems in both children and schoolchildren.
Classification of diseases
Duodenitis is a disorder of the function of the duodenum.
Depending on the location of the source of inflammation, painful processes in the intestines are usually classified as follows:
- Enteritis. This term refers to inflammation of the small intestine (both all at once and any individual section).
- Duodenitis. This name refers to dysfunction of the duodenum.
- Mesadenitis. In such diseases, inflammation affects only the lymph nodes located in the intestines (the painful process itself, as a rule, is caused by infection).
- Colitis. This general term is usually used to describe inflammatory processes in the large intestine. Moreover, either the entire organ or only its lower section can be affected. Colitis is also commonly called inflammation of the mucous membrane of the rest of the intestine.
Colitis
Chronic colitis during an exacerbation period is advisable to treat in a hospital, in the proctology department. Colitis of an infectious nature is treated in specialized infectious diseases departments. A significant element in the treatment of chronic colitis is adherence to a therapeutic diet. At the same time, all products that can mechanically or chemically irritate the intestinal mucosa are excluded from the diet; food is consumed pureed, with a frequency of at least 4-5 times a day. In addition, to eliminate lactic acid fermentation, patients are advised to give up milk; in order to reduce gas formation, they limit cabbage and legumes.
Dried unsweetened wheat bread is allowed for baked goods. It is advisable to consume low-fat meat and fish steamed. When severe clinical symptoms subside, the diet is gradually expanded. To combat constipation, it is recommended to include boiled vegetables, fruit purees (jelly), and bran bread in the diet. Vegetable oil and a sufficient amount of fluid consumed per day contribute to improving the passage of intestinal masses. It is undesirable to consume fruits and vegetables raw during the acute period of the disease. You should also avoid chilled foods, dairy products and foods high in acid. To regulate fluid secretion in the intestines, limit the use of table salt.
In the case of the infectious nature of colitis and to suppress the pathogenic bacterial flora that has developed as a result of dysbacteriosis, short courses of antibiotic therapy are prescribed (drugs ciprofloxacin, Nifuroxazide, rifaximin). Prescriptions of medications are made only by a specialist. Detection of worm eggs is an indication for the prescription of anthelmintic drugs. To relieve pain, antispasmodics (drotaverine, papaverine) are prescribed.
In the treatment of proctosigmoiditis, local therapy is useful: microenemas with decoctions of chamomile, calendula, tannin or protargol. For proctitis, rectal suppositories with belladonna, anesthesin to relieve severe pain, and astringents (zinc oxide, xeroform) are prescribed. For diarrhea, astringents and enveloping agents are prescribed orally (tannin + albumin, bismuth nitrate, white clay, oak bark decoction, other decoctions and infusions of herbs containing tanning components). For constipation, colon hydrotherapy is indicated. Severe spasms during colitis may be an indication for the prescription of anticholinergic drugs.
In addition to the above remedies, enterosorbents (to combat flatulence), enzyme preparations (for digestive disorders as a result of enzyme deficiencies), and eubiotics (to correct dysbiosis) can be prescribed for colitis. A good effect in the treatment of chronic colitis is achieved by regular spa treatment and balneotherapy.
Typical symptoms
Bloating indicates a lack of digestive enzymes.
Symptoms that appear during inflammatory processes in the intestines can vary greatly depending on the location of the problem.
However, some of the characteristic manifestations of such ailments can be considered common.
It is on them that doctors rely when making a preliminary diagnosis of “inflammation of the intestines.” Among these specific features, the following can be particularly highlighted:
- pain of a bursting or compressive nature, the main source of which, as a rule, is not possible to determine;
- nausea and vomiting syndrome, usually worsening after eating and subsiding after cleansing the stomach;
- bloating and other symptoms indicating a lack of digestive enzymes;
- unstable stool (from constipation to diarrhea);
- anemia (anemia occurs as a result of a lack of iron, inevitable with intestinal damage);
- increased temperature (a reaction typical of any inflammatory process).
Symptoms of intestinal diseases: when should you see a doctor?
The disease often manifests itself with intimate symptoms, which the majority of patients try to fight on their own, without rushing to a paid appointment with a proctologist or gastroenterologist. In addition, intestinal inflammation is often accompanied by “masking” symptoms: for example, only stomatitis, as in Crohn's disease, or only inflammation around the anus - perianal dermatitis, or lesions of the eyes or joints. Therefore, the patient often comes to the doctor with a severe form, when the path to recovery turns out to be both longer and more financially expensive.
The following signs should alert anyone:
- frequent diarrhea - up to 15–20 times a day;
- pain and/or cramping in the abdominal area;
- weakness, increased fatigue;
- loss of appetite and noticeable weight loss;
- temperature increase;
- the appearance of traces of blood in the stool.
The likelihood of damage to the large and small intestines is increased in people who regularly and in large quantities consume dark varieties of meat and processed products (sausages, sausage, ham, bacon, etc.). But you should know that adherence to a diet with a predominance of vegetables, fruits, and foods made from whole grains is not a panacea.
A genetic factor plays a certain role: the tendency to intestinal inflammation can be inherited. Among the sick people, people who abuse smoking predominate. Also important are the lack of vitamin D in the body and frequent and uncontrolled self-administration of antipyretic medications.
An appointment with a proctologist in Moscow is recommended not only for people with unstable stools. In order not to fill the army of colorectal cancer patients, even a generally healthy person after 45 years of age should visit a doctor at least once every five years for preventive purposes. The absence of visible signs of inflammation does not exclude the possibility of a hidden disease. Symptoms of intestinal cancer detected at an early stage allow doctors to save the patient and achieve stable remission.
How is intestinal inflammation diagnosed?
A blood test will determine the degree of inflammation.
In the case of inflammation of any part of the intestine, laboratory diagnosis of the disease is a necessary step before prescribing treatment.
It is this that makes it possible to establish the source of the disease process, and therefore to identify its causes. Without such procedures, developing an adequate strategy for treating inflammation would simply be impossible.
What examinations will a patient have to undergo if he suspects intestinal problems? Today, the following laboratory and instrumental methods for diagnosing diseases of the gastrointestinal tract are especially popular (due to their effectiveness):
- bacteriological examination of stool (used to detect the presence of pathogenic microbes in the body);
- general blood test (allows you to determine the number of active leukocytes in the body, and therefore the degree of development of inflammation);
- FEGDS, colonoscopy or video capsule endoscopy (visual examination of the intestines and stomach allows you to accurately identify the source of inflammation and, moreover, obtain the biomaterial necessary for further laboratory tests, for example, biopsy);
- coprogram (a more detailed study of stool is necessary to determine the lack of digestive enzymes).
Folk remedies for treating inflammation symptoms
Chamomile infusion will help with increased acidity.
Medicinal plants are successfully used to combat the symptoms of many serious diseases. Inflammation in the intestines was no exception.
Today, remedies to alleviate the symptoms of this disease can be found in any pharmacy. Let us list the most effective of them:
- To combat bloating and stabilize stool, mix fennel fruits, caraway seeds and chamomile flowers in equal proportions. The resulting mass is poured with boiling water. The liquid is filtered and taken after meals (maximum three times a day).
- In case of increased acidity in the stomach, prepare a tincture from pharmaceutical preparations of chamomile, elecampane, valerian, yarrow, cucumber, alder, calendula, licorice and marshmallow. The listed ingredients are mixed, poured with boiling water and placed in a water bath for 5 minutes. The finished liquid is filtered and drunk half a glass at a time before each main meal (that is, three times a day).
- For low acidity, other herbs are used. In this case, the tincture is prepared from collections of linden, marshmallow, chamomile, fennel and elecampane. The ingredients are mixed and placed in boiling water. The liquid is infused and filtered. They do not drink the drug regularly, but as a pain reliever (in other words, only during exacerbations of the disease).
- Plantain juice and honey will help reduce inflammation in the intestines. The mentioned components are mixed in a ratio of 2 to 1 and drunk three times a day (a tablespoon at least an hour before a major meal).
- Enemas based on a 3% solution of boric acid and calendula also help well with inflammation. For one session, take a tablespoon of each component. It is best to give such an enema before bedtime.
Colonoscopy of the intestine: are patients’ fears justified?
An illness diagnosed at an early stage creates the least amount of problems for the patient. Therefore, highly informative screening colonoscopy is included in government programs to combat colon cancer in the USA, Israel and European countries. Citizens of developed countries are constantly informed about the need for regular examinations for the prevention and early diagnosis of colorectal cancer.
The specifics of such an intimate procedure do not evoke the most positive emotions among Russians. Pain is a major deterrent even for those people who are fully aware of the need for testing. But is it possible to compare the sensations that arise during a colonoscopy with the torment experienced by patients suffering from already developed oncology!
It should be understood that gentle diagnostic technology, which can be performed under anesthesia, will allow you to avoid dangerous symptoms, frightening diagnoses and a solid set of diagnostic procedures in the future.
Preventive measures
You should always wash your hands before eating.
Like any disease of the gastrointestinal tract, intestinal inflammation can be easily avoided if you follow simple hygiene rules from childhood.
For example, keep your hands clean and wash food before eating. However, in practice, adherence to the banal principles of proper nutrition is no less important. What are they?
If the patient is already aware of the tendency of his intestines to inflammation, it would not be superfluous for him to completely review his diet in order to prevent the disease from becoming chronic. The most rational steps in this sense would be a complete rejection of any exotic food and reasonable restrictions on the use of spicy seasonings.