Neurosis of the stomach and intestines is a sign of a psychological disorder. Many people confuse it with a gastroenterological disease. But in the absence of any problems with the gastrointestinal tract, men and women may experience strange phenomena in the abdominal area. For example, a feeling of fullness and bloating in the gastrointestinal tract even after one sip of water.
Unfortunately, gastric neurosis must be treated under the supervision of qualified doctors. Symptoms and their causes do not go away on their own, but often progress with age, complicating life activities.
Why does it appear?
Due to a busy daily routine, problems at school or work, and stress, every third person has encountered neurosis. And such a disease as neurosis of the stomach and intestines has its own causes. Among them are:
- poor nutrition. This is the root cause of all diseases, in particular neurosis. Frequent consumption of fast food and processed foods instead of natural food, as well as untimely nutrition can lead to stomach problems;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, for example, ulcers, tumors and gastritis;
- mental disorders and stress. They are the cause of many neuroses and lead not only to problems with the nervous system, but also to problems with the body as a whole;
- diseases of the digestive organs: pancreatitis, cholecystitis, colic. Because of them, a reflex reaction of the stomach occurs;
- external influence on the stomach. This includes poisoning from spoiled food, as well as exposure to chemicals that enter the body through the respiratory tract. Most often, gastric neurosis occurs in people over 35 years of age.
What is irritable bowel syndrome and how to live with it
They occur frequently, but are not usually discussed - irritable bowel syndrome is just one of these diseases. It affects up to 25 percent of the world's population. How IBS manifests itself, is diagnosed and treated, explained Vera Serezhina, a medical expert at the LabQuest personalized medicine laboratory.
Symptoms: how does it manifest itself?
Although irritable bowel syndrome is common, it is not known exactly what causes the condition. Each patient with IBS has his own history of the onset of the disease, but it almost always involves stress factors - social, psychological, biological, etc. In addition, periods of exacerbation are also associated with stress. The work of the intestines is subject to nervous regulation, and constant stress leads, among other things, to disruption of its motor function.
It is believed that the main symptom of IBS is diarrhea, but rare bowel movements are another option. There is also a mixed option, when a person is bothered by both. Other symptoms include bloating, the association of intestinal symptoms with certain foods that either make you feel better or worse, a feeling of incomplete bowel movements, and sudden urges that force you to literally run to the toilet. In some cases, patients cannot leave the house because of this. There are manifestations that have nothing to do with the intestines: for example, insomnia, migraines, muscle pain, discomfort during sexual intercourse in women. By the way, women suffer from IBS much more often than men.
There are so-called Roman diagnostic criteria for IBS. This disease is characterized by recurrent abdominal pain that has occurred at least once a week over the past 3 months and has been associated with at least two of the following: associated with defecation, a change in stool frequency, and/or a change in stool shape.
A special feature of IBS is the morning ritual: every morning at a certain moment (for example, after breakfast), the patient begins to experience discomfort in the abdomen, and then the need to visit the toilet. The discomfort after this usually goes away until the next morning. The morning ritual does not happen in all cases of IBS; unfortunately, it is often much more difficult for patients and irritable bowels remind themselves not only in the morning.
Examination: what tests are needed
Often, patients with IBS manage to take control of the disease or adapt to it, learn to coexist with it, but this is not a solution, because the very situation with a chronic intestinal disorder, be it diarrhea or constipation, leads to impaired absorption of nutrients from food, and ultimately affects the functioning of the entire body. Therefore, it is better not to get used to IBS, but to be examined and, if the problem is really irritable bowel, to fight the cause.
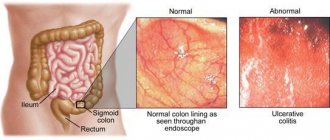
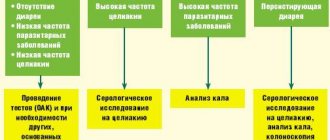
Irritable bowel syndrome is a diagnosis of exclusion. It is diagnosed only after all other possible causes have been excluded: infectious and diseases of the endocrine system (thyroid and pancreas), food intolerance, autoimmune and oncological processes, etc. There are so-called “red flags” - symptoms that are in no way cases that cannot be ignored and require mandatory consultation with a doctor: weight loss, nighttime abdominal pain, the appearance of discomfort and pain in old age, cases of autoimmune diseases or intestinal cancer in the family, fever, blood in the stool.
Before a doctor makes a diagnosis of IBS, he must refer the patient for an examination, which includes several stages.
* Clinical and biochemical blood test. This will help identify anemia and
diseases of internal organs (diabetes mellitus, etc.)
* Stool analysis to identify intestinal pathogens (Shigella, Salmonella,
Yersinia), toxins A and B of Clostridium difficile.
* Study of the level of thyroid hormones to identify its hyperfunction.
* Stool analysis to detect hidden blood during an ulcerative process in the wall
intestines.
* Study of antibodies to tissue transglutaminase IgA or IgG in patients with
diarrheal and mixed variants of the disease if celiac disease is suspected.
* Determination of calprotectin level in feces. It will show the degree of inflammation in the wall
intestines.
* Ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs.
* Endoscopy with duodenal biopsy to exclude celiac disease. Biopsy
performed when antibodies to transglutaminase are detected in the diagnostic titer.
* Colonoscopy with biopsy.
Treatment: which doctor to go to and is it possible to forget about this disease?
IBS is the most common gastrointestinal disease. However, according to statistics, only one patient out of three goes to the doctor. The rest are left without help for various reasons. For some, IBS does not particularly interfere with life - there are quite a few of them, up to 40 percent of all patients. Another scenario: a person finds out that he “just” has irritable bowel syndrome, and not Crohn’s disease or intestinal cancer, calms down and lives from relapse to relapse. Often people with IBS go for help only to gastroenterologists and see diet as treatment. Eliminating certain foods - coffee, fatty foods, grains, spicy seasonings, etc. - can really give a noticeable result, as it can reduce the discomfort that causes flatulence. Only this is not enough. As soon as the patient experiences stress, irritable bowel syndrome makes itself felt again. The correct approach to treating this problem for many people with IBS involves the joint work of a gastroenterologist and a psychotherapist. The first one selects proper nutrition, antispasmodics, antidiarrheal or laxative drugs and other therapy, the second one helps to solve the underlying problems that lead to IBS, for example, to cope with increased anxiety. For some patients, talking with a psychotherapist is enough to understand the causes of the illness; others require a course of antidepressants. With intestinal diseases, a situation of amino acid deficiency arises in the body for the synthesis of the neurotransmitter serotonin, which is also called the hormone of happiness. Therefore, patients with IBS need to replenish this hormone and antidepressants have good therapeutic effects.
Stomach neurosis: symptoms
The clinical signs of this disease are:
- discomfort in the stomach. The patient feels either fullness or emptiness in the abdomen. This may be accompanied by pain;
- aversion to food. Nausea occurs at the smell or sight of it. There may be vomiting. Very often the symptom is confused with a sign of anorexia or bulimia;
- hunger. This feeling persists even after a person has recently eaten;
- cardiopalmus. With neurosis, the patient often has pain in the heart and heaviness in the chest;
- unhealthy sleep. Another symptom of this disease. Many people have disrupted sleep patterns and are unable to fall asleep or wake up on time. Insomnia may develop, and as a result, severe headaches;
- heartburn. Unlike the usual one, not associated with neurosis, it does not go away after following a special diet;
- aerophagia or belching. Appears after swallowing a large amount of air. With neuroses, a person may make strange loud sounds while belching;
- aggressiveness. This symptom accompanies all problems with the nervous system. With gastric neurosis, the patient's irritability can also develop into panic attacks and various phobias. At the first symptoms, it is advisable to consult a doctor.
Treatment of gastric neurosis: the most effective and proven methods
So, treatment of gastric neurosis is a rather long process, the course of which must be monitored by a doctor. It is necessary to start it as early as possible, because in a very advanced form this pathology leads to much more serious complications and even other diseases - problems with the esophagus and stomach.
The very first advice that can be given to a patient is to visit a competent psychotherapist. He will give all the necessary advice on avoiding emotional stress and worries, and will also prescribe certain physical activities.
Diet therapy plays a certain role. It should be selected depending on the general acidity of the patient’s stomach. The peculiarity of diet therapy is that the transition from dietary food to a regular diet occurs smoothly and also covers a long period of time. You will need to abstain from hot, spicy and salty foods during treatment. It is also necessary to completely exclude from the diet foods that are prone to fairly rapid fermentation.
The patient will benefit from baths with the addition of mint, essential oils, and any medicinal herbs. It is necessary to take herbal infusions that have a strong sedative effect. Such as infusions of oregano, motherwort and valerian. Such plants perfectly normalize the state of mind and help overcome neurosis.
In what forms does it appear?
For a faster diagnosis, it is recommended to first learn about the form in which this disease may manifest itself. Each type of manifestation is dangerous, and therefore it is necessary to quickly make a correct diagnosis and begin therapy.
The main forms of manifestation of the disease are:
- Uncontrollable vomiting. As a rule, it occurs without a preliminary feeling of nausea or urge.
- Belching, caused by a reflexive swallowing of a large amount of air.
- Bulimia is the consumption of excessive amounts of food.
- Anorexia is a refusal to eat food. Both this and the previous forms of the disease can cause death.
- Heartburn that does not go away even with a diet.
Causes and predisposing factors
Gastric neurosis, that is, inflammation of the gastric mucosa not associated with Helicobacter pylori bacteria, is considered by many experts to be a borderline somatoform disorder that requires complex gastroenterological and psychotherapeutic correction. The disease can occur at any age.
Groups of people most susceptible to gastroneurosis
The maximum risk group includes women, as the most vulnerable category of patients in terms of emotional lability. The second category at risk is children of primary preschool and school age, who often experience stress due to difficulties with social adaptation when entering kindergartens and schools.
Chronic neurotic dysfunctions of the stomach in most cases occur in individuals with various types of psychopathologies. Such patients often experience feelings of irritation, anger, and sudden attacks of aggression.
In children, risk factors include asthenic syndromes, autism, and various neurotic disorders. In infancy, possible manifestations of gastroneurosis can be provoked by the syndrome of traumatic shaking of the child.
Important in treatment: continue to leave the house
A very important indicator of the prognosis is how involved a person is in his usual life; this will determine how long irritable bowel syndrome will last. If gradually the theme of the disease crowds out everything else and the structure of life begins to obey the schedule of the intestines, this is a serious bell.
In psychosomatics there is such a concept: narrowing the focus of attention. The patient's attention is narrowed to the disease, and other interests in life gradually begin to disappear. Metaphorically speaking, our mental energy is a limited resource. If you direct it all towards your illness, then it will only flourish in this nourishment and focus of light.
Protective techniques promote fixation. There is no need to quit work, study, lock yourself at home and cancel dates. This will only make the situation worse. In this way, you contribute to the consolidation of symptoms and throw yourself overboard from an active, interesting life. Live your life to the fullest and do everything you did before you got sick.
There are patients with IBS who even have to issue certificates in order to be allowed to reschedule, for example, exams to later hours due to a psychosomatic disorder. This is better than giving up exits altogether.
Live your life to the fullest and do everything you did before you got sick.
If you start to dread riding the subway, keep riding! You can carry an anti-anxiety medication with you to quickly relieve an attack (it is usually prescribed by psychiatrists).
The patient’s task is to gradually break out of the vicious circle “stimulus - attack of illness.” That is, with drug therapy and psychotherapy, you “get out of the habit” of giving a pathological reaction to certain circumstances. We say to such a patient: “Look, you can get on the transport or sit through the lecture by taking the drug? This means the process can be controlled.” The thought “Yesterday I left the house and my stomach didn’t hurt” is fixed in his mind. Then, when the body has already “reconsidered” its reaction and has lost the habit of “wanting to go to the toilet” in any situation, we gradually begin to reduce the dose of medication. And we continue to train the skill of switching attention from the problem.
Whatever one may say, an attack of pain and urge as a reaction to certain conditions (a trip in transport, going on a visit, a date) is triggered by the “head” and not the “stomach”. Often, when the patient gets out of an exciting situation, the urge and discomfort stop.
Who gets IBS?
In many articles on the topic, there is an assumption that women are more likely to suffer from the disease. But according to the observations of doctors at our clinic, this is not confirmed. Quite the contrary: we see patients of both sexes in approximately equal proportions, but men are more likely to come with severe forms of the disease.
There are also certain personality types that are, in principle, predisposed to this disease. For example, individuals with the so-called anancast structure. They are prone to hypochondriacal disorders of various types. In the case of IBS, such patients are especially attentive to bowel movements, which in some cases becomes a certain element of obsession.
Anancastic personality disorder is a mental disorder that is characterized by an increased tendency to doubt, absolute absorption in details, suspiciousness and perfectionism, as well as manifestations of stubbornness and recurrent obsessions and/or compulsions. Anankastic personality disorder is a diagnosis included in the ICD-10.
Another possible feature of IBS disease is its association with mysophobia. Such people often pay special attention to the cleanliness of the toilet. Do not use public toilets, wait until home or office.
Mysophobia is an obsessive fear of contamination or infection, the desire to avoid contact with surrounding objects.
In rare cases, the diagnosis may also be influenced by the patient’s mother’s excessive focus on potty training during childhood. There are mothers who try, relatively speaking, “in every incomprehensible situation” to put their child on the potty. As a result, for the child it becomes a super idea. He begins to fear the process.
The following personal qualities also become favorable conditions for the development of irritable bowel disease:
- adherence to rules and routines,
- increased anxiety,
- need to control oneself and others,
- perfectionism.
We can also observe a certain degree of social phobia in such patients. They gravitate towards solitude themselves and are afraid to disturb the comfort of others.
The listed personal characteristics significantly worsen a person’s quality of life and become fertile ground for the development of diseases such as IBS. Perhaps the patient should simultaneously visit a psychologist - go to group therapy to develop communication skills or work with self-esteem. Only a medical specialist knows how long it takes to treat irritable bowel syndrome.
Medical therapy
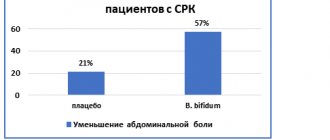
Since the mechanisms of development of the disease have been poorly studied, the choice of treatment methods depends on the current symptoms and individual characteristics of the patient’s body. There is no single generally accepted method, but placebo has been found to be highly effective in treatment. This indicates the significant role of psychological factors in the course of the disease.
Diet for irritable bowel syndrome is one of the most important factors affecting the patient’s well-being. It is recommended to select products on an individual basis: the patient should keep notes in a food diary and note the body’s reaction to certain foods. Regular meals without quick snacks are recommended. For diarrhea, avoiding foods with gluten or lactose may be beneficial. Frequent constipation is relieved by increasing the amount of fiber-rich foods: vegetables, whole grain cereals, bran, fruits.
It is equally important to normalize the functions of the patient’s nervous system. A good means for this is moderate physical activity: walking, swimming in the pool, fitness, yoga, etc. If necessary, psychotherapy sessions and taking psychotropic drugs are prescribed.
Clinical recommendations for irritable bowel syndrome include drug therapy, including:
- gastroenteroprotectors;
- antispasmodics;
- means that normalize peristalsis;
- for constipation - laxatives with lactulose;
- probiotic preparations;
- tricyclic antidepressants or serotonin reuptake inhibitors.
The effectiveness of therapy depends on the general condition of the patient and the severity of disorders of the nervous system.
general information
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a disorder of the digestive tract, localized in the large intestine, associated with changes in the nature of peristalsis and the digestive process. It is characterized by an irregular, wave-like course, lack of progression of symptoms and a connection between the appearance of pain and stressful situations, emotional tension. In this case, pronounced organic pathologies of the digestive tract are, as a rule, absent.
The disease develops in people of all age categories, but representatives of the active age group from 25 to 40 years are most susceptible to it. Women get sick two to three times more often than men, and in general, according to various estimates, IBS occurs in 5-10% of the population.
Treatment
Drug treatment for IBS should be prescribed by a doctor. Non-drug methods include:
- diet,
- psychotherapy.
The use of medications is determined by the form of the syndrome. If constipation predominates, the following groups of medications can be used:
- modern antispasmodics that do not affect the functioning of the cardiovascular system;
- bulk laxatives;
- gastroprokinetics, which stimulate intestinal motility.
Among bulk laxatives, psyllium is of particular importance. Herbal preparations have been developed on its basis. Psyllium is obtained from plantain seeds. Psyllium retains water in the intestines, increases the volume of intestinal contents and softens stool, resulting in a mild laxative effect. As a rule, such products are approved for long-term use.
Symptomatic treatment of IBS with constipation may include the use of osmotic laxatives as indicated, but it is better to avoid taking them regularly. As a rule, such funds are used in preparation for endoscopic diagnosis. They cause the so-called drastic effect, frequent and profuse, watery stools, and can also increase pain.
A separate method of treatment is the prescription of anti-anxiety medications and antidepressants. But such means should be used with caution. Doctors usually prescribe them in short courses lasting up to 14 days, mainly during periods of severe stress. For example, this may be appropriate for a patient going through divorce proceedings or a student who is about to start a session.
Long-term use of anxiolytics, or anti-anxiety drugs, leads to a decrease in their effectiveness and the development of addiction. Antidepressants are also prescribed strictly according to indications, but the paradox is that they can cause constipation - many drugs in this group have such a side effect. Therefore, it is better to weigh everything and discuss this approach in detail with your doctor. In some cases, it is advisable to get by with a course of psychotherapy.
The development of a diet should be based on the individual characteristics of a person’s health status and the leading symptoms of the syndrome. If additional fiber may be contraindicated in IBS with diarrhea, then constipation is a reason to reconsider the diet. Products with coarse fiber will help cope with the symptom.
The incidence of lactase deficiency in people with IBS is the same as in healthy individuals. But eliminating dairy products from your diet can be helpful. Sheptulin explained this in detail: “It should be borne in mind that in a number of patients with IBS, diarrhea may be a manifestation of individual intolerance to any food products. In such cases, elimination diets can have a good effect” (Sheptulin A. A., 1999, p. 8).