: Reading time:
Irritable bowel syndrome is regular pain and discomfort in the abdomen, a painful desire to go to the toilet, which visits a person much more often than he would like. What is irritable bowel syndrome, its symptoms, causes and methods of treating IBS is explained by psychiatrist, psychotherapist, specialist in psychosomatic disorders at the “Pain Clinic” CELT Lyubov Konstantinovna Myasnikova.
The diagnosis of irritable bowel syndrome or IBS is quite common.
We cannot say for sure what leads to irritable bowel in each specific case, everything is individual. Sometimes this is an intestinal infection or poisoning. Sometimes the cause of IBS is stress, when a person first experiences an urgent need to go to the toilet, for example, while traveling. Next, the patient’s attention is fixed on the problem, “looping.” A process is launched that does not depend on external factors, but is tied to an internal cause: having experienced the discomfort associated with a strong urge to go to the toilet, a person begins to be afraid of being in such a situation again with these unpleasant, shameful, difficult-to-bear sensations. The “fear of fear” begins - the disease begins to take on a life of its own. As you can see, it is not always possible to say exactly what causes irritable bowel syndrome.
According to the Rome III criteria, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is defined as a functional disorder in which abdominal pain or discomfort occurs on at least 3 days per month over the past 3 months, with a total duration of complaints of at least 6 months. The diagnosis of IBS is established based on the compliance of the patient's symptoms with the Rome criteria of the third revision in the absence of organic causes for their occurrence.
The disease can be cured. And not just to suppress the symptoms or put the patient into remission, but to cure IBS without subsequent relapses.
The problem is that a person with IBS does not always reach a psychotherapist or psychiatrist. Patients naturally start with a gastroenterologist and proctologist. They should be contacted to rule out Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis and other organic diseases. But the root of IBS lies in the field of psychosomatics; it is a psychiatrist with a specialization in psychosomatic disorders who knows how to treat irritable bowel syndrome. Therefore, if other diagnoses are excluded and the gastroenterologist diagnoses “irritable bowel syndrome,” you should definitely consult a psychiatrist.
What are the symptoms of IBS?
A patient may suspect signs of IBS if his intestinal problems are associated with a psychogenic factor, that is, they include a reaction to a change in emotional state - excitement, anxiety, frustration. Often, symptoms can be triggered by stress before an important event or while traveling long distances - when the intestines stop working according to the usual pattern while traveling.
Sometimes the disease can manifest itself in the form of a so-called “refusal reaction.” A student begins to have severe stomach pain before an exam, which he is afraid of failing. In a person with symptoms of social phobia, with a fear of speaking in public, the attack is triggered by the looming need to make a report, when the imagination begins to paint pictures of failure or shame. In principle, such a reaction can occur several times in life in many people, but in patients with IBS it is consolidated, becomes rigid, that is, the body’s usual way of reacting: severe stress has already passed, but the stomach continues to bother every little thing.
Often, symptoms can be triggered by stress before an important event or while traveling long distances - when the intestines stop working according to the usual pattern while traveling.
IBS can occur in conjunction with panic disorder. There are people who, during a panic attack, experience a sudden strong urge to defecate. This is a separate type of panic attack.
An excess of exciting, stimulating substances in the blood (adrenaline, serotonin and other neurotransmitters) causes anxiety, fear, palpitations, a feeling of lack of air and other unpleasant bodily sensations, including excessive urination or loose stools. An attack, as a rule, develops quickly - within ten minutes, and lasts approximately twenty to thirty minutes. A person is overwhelmed by inexplicable horror. After experiencing a crisis, a feeling of depression, hopelessness, and self-pity appears. Having attacks several times gives rise to fear of repetition and “anxiety of anticipation.” Hence the fear of IBS sufferers to travel on public transport, go to theaters, cinema, and on dates.
What is the cause of IBS disease?
IBS is a somatoform disorder, the main feature of which is that patients present somatic symptoms simultaneously with persistent demands for medical examinations, despite their negative results and doctors’ assurances that the symptoms are not of a somatic nature (ICD-10).
Even if a person has any physical illnesses, they do not explain the nature and severity of the patient's symptoms or suffering or complaints. IBS implies a mental origin of somatic phenomena.
According to the psychopathological model of somatoform disorders by A. B. Smulevich and his students, developed at the Scientific Center for Mental Health of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, “disorders of the body that imitate bodily pathology are paired lesions of two levels of organization of the psyche: associated with the neuropsychic system itself and with the way in the body is reflected in the psyche (that is, how our brain interprets the signals it receives from the internal organs).”
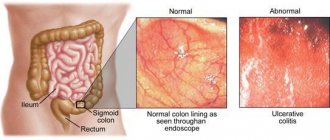
Sometimes in the complaints of patients with somatoform disorder there is a certain “pretentiousness” or “strangeness” of sensations, which is usually not used to describe the pain experience in people with organic lesions (Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis). This can help a competent gastroenterologist suspect the psychosomatic nature of diarrhea and promptly involve a psychiatrist in the treatment process. Alas, some gastroenterologists will persist in treating “superficial gastroenteritis” rather than irritable bowel syndrome. But in some cases, symptoms of IBS will appear, and patients will report them in the same way as with somatic pathology. Then the signal that it is time to see a psychiatrist will be the absence of positive dynamics in treatment with gastroenterological drugs.
A signal that it is time to see a psychiatrist will be the absence of positive dynamics in treatment with gastroenterological drugs.
Non-pharmacological therapy
In combination with drug treatment of the disease, additional methods and techniques are recommended that speed up the healing process:
- physical activity within acceptable limits (for example, yoga). If you are overweight, it is also necessary to use programs to reduce your body mass index;
- dietary nutrition that excludes the use of poorly digestible substances, but includes foods enriched with soluble dietary fiber. In addition, it is necessary to exclude the use of products that cause gas formation;
- psychological consultations, stress management training programs.
Who gets IBS?
In many articles on the topic, there is an assumption that women are more likely to suffer from the disease. But according to the observations of doctors at our clinic, this is not confirmed. Quite the contrary: we see patients of both sexes in approximately equal proportions, but men are more likely to come with severe forms of the disease.
There are also certain personality types that are, in principle, predisposed to this disease. For example, individuals with the so-called anancast structure. They are prone to hypochondriacal disorders of various types. In the case of IBS, such patients are especially attentive to bowel movements, which in some cases becomes a certain element of obsession.
Anancastic personality disorder is a mental disorder that is characterized by an increased tendency to doubt, absolute absorption in details, suspiciousness and perfectionism, as well as manifestations of stubbornness and recurrent obsessions and/or compulsions. Anankastic personality disorder is a diagnosis included in the ICD-10.
Another possible feature of IBS disease is its association with mysophobia. Such people often pay special attention to the cleanliness of the toilet. Do not use public toilets, wait until home or office.
Mysophobia is an obsessive fear of contamination or infection, the desire to avoid contact with surrounding objects.
In rare cases, the diagnosis may also be influenced by the patient’s mother’s excessive focus on potty training during childhood. There are mothers who try, relatively speaking, “in every incomprehensible situation” to put their child on the potty. As a result, for the child it becomes a super idea. He begins to fear the process.
The following personal qualities also become favorable conditions for the development of irritable bowel disease:
- adherence to rules and routines,
- increased anxiety,
- need to control oneself and others,
- perfectionism.
We can also observe a certain degree of social phobia in such patients. They gravitate towards solitude themselves and are afraid to disturb the comfort of others.
The listed personal characteristics significantly worsen a person’s quality of life and become fertile ground for the development of diseases such as IBS. Perhaps the patient should simultaneously visit a psychologist - go to group therapy to develop communication skills or work with self-esteem. Only a medical specialist knows how long it takes to treat irritable bowel syndrome.
Danger and complications
IBS with a predominance of constipation reduces a person’s quality of life. A prolonged absence of stool can cause chronic intoxication of the body, depletion of defenses, exacerbation of dermatological diseases and allergies. Pain contributes to a reduced emotional background, can limit social activity, and cause irritability and nervousness.
In the long term, persistent constipation can be a risk factor for the development of cancer of the digestive system, atherosclerosis, thrombosis, heart attacks, and strokes. Stagnation of feces leads to overstretching of the intestinal walls and accompanying structural changes and inflammatory processes.
How is IBS treated?
Ideally, three specialists should provide assistance to the patient: a psychiatrist, a gastroenterologist (he will advise what to take for intestinal disorders) and a psychotherapist. It is better if the psychiatrist and psychotherapist are the same doctor, who is a psychiatrist by training and has the right to prescribe medications, and has additionally completed training in psychotherapy. In our clinic, almost all psychiatrists are proficient in various methods of psychotherapy, without which work in the field of psychosomatics is almost impossible.
In exceptional cases, patients are lucky to find a specialist who works at the intersection of gastroenterology and psychiatry. But there are few such specialists, so a gastroenterologist is usually involved separately.
Three specialists must provide assistance to the patient: a psychiatrist, a gastroenterologist and a psychotherapist.
There are three stages of treatment for IBS.
The first stage is the selection of medications for irritable bowel syndrome. At the first stage, we select the so-called target symptoms (for example, anxiety) and select drugs to relieve them. We create scales with symptoms from 10 to 0. The patient monitors his condition, keeps a diary and evaluates the level of anxiety that bothers him at the moment on a scale from 0 to 10. When the symptoms reach 0, we move to the second stage of treatment. Typically the first stage lasts from two weeks to three months.
The second stage is psychotherapy. At the second stage, work on developing the skill of distraction comes to the fore. We use cognitive behavioral techniques and acceptance of responsibility therapy.
Acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT) is a model of behavioral psychotherapy that aims to increase psychological flexibility to improve quality of life. Used for a wide range of problems such as anxiety disorders, depression, PTSD, chronic pain, eating disorders.
The stage usually lasts from two to six months depending on how long the disease has progressed. If the patient has been sick for three months, the stage will last approximately two months. If the disease lasts for years, the stage will take at least six months.
The third stage is anti-relapse therapy. We begin to discontinue the medications, carefully and gradually reducing the dose to the minimum (this should always be done under the supervision of a doctor). The main criterion for the effectiveness of treatment is that dose reduction does not lead to a resumption of symptoms.
I repeat, the duration of taking medications depends on the duration of the disease itself. Doctors have a special schedule according to which we calculate the duration of psychopharmacotherapy. We show it to patients, explaining why their treatment will take the amount of time it does and explaining how long it actually lasts. It is important that the patient does not stop treatment at the first signs of improvement, otherwise we may get the so-called “ricochet effect”, when a rapid deterioration of the condition develops after abruptly stopping the medication. The effect of treatment must be “consolidated”; the body must get used to working according to the correct pattern.
Patients with IBS and panic attacks need psychotherapy sessions with relaxation, immersion in pleasant memories, hypnotic and meditative techniques, and calming art therapy. Sometimes we offer massage of acupuncture points. In this way, we try to influence different senses, causing pleasant sensations, diverting attention from the discomfort in the stomach. Sometimes it helps them to carry a bottle of essential oil with a pleasant smell.
Modern hypnosis
An individual approach is important. Patients try different relaxation options and keep a diary - what helps better, what worse. One patient came up with his own life hack, distracting himself during a panic attack by looking at beautiful girls (despite the fact that he himself was absolutely faithful to his wife).
Important in treatment: continue to leave the house
A very important indicator of the prognosis is how involved a person is in his usual life; this will determine how long irritable bowel syndrome will last. If gradually the theme of the disease crowds out everything else and the structure of life begins to obey the schedule of the intestines, this is a serious bell.
In psychosomatics there is such a concept: narrowing the focus of attention. The patient's attention is narrowed to the disease, and other interests in life gradually begin to disappear. Metaphorically speaking, our mental energy is a limited resource. If you direct it all towards your illness, then it will only flourish in this nourishment and focus of light.
Protective techniques promote fixation. There is no need to quit work, study, lock yourself at home and cancel dates. This will only make the situation worse. In this way, you contribute to the consolidation of symptoms and throw yourself overboard from an active, interesting life. Live your life to the fullest and do everything you did before you got sick.
There are patients with IBS who even have to issue certificates in order to be allowed to reschedule, for example, exams to later hours due to a psychosomatic disorder. This is better than giving up exits altogether.
Live your life to the fullest and do everything you did before you got sick.
If you start to dread riding the subway, keep riding! You can carry an anti-anxiety medication with you to quickly relieve an attack (it is usually prescribed by psychiatrists).
The patient’s task is to gradually break out of the vicious circle “stimulus - attack of illness.” That is, with drug therapy and psychotherapy, you “get out of the habit” of giving a pathological reaction to certain circumstances. We say to such a patient: “Look, you can get on the transport or sit through the lecture by taking the drug? This means the process can be controlled.” The thought “Yesterday I left the house and my stomach didn’t hurt” is fixed in his mind. Then, when the body has already “reconsidered” its reaction and has lost the habit of “wanting to go to the toilet” in any situation, we gradually begin to reduce the dose of medication. And we continue to train the skill of switching attention from the problem.
Whatever one may say, an attack of pain and urge as a reaction to certain conditions (a trip in transport, going on a visit, a date) is triggered by the “head” and not the “stomach”. Often, when the patient gets out of an exciting situation, the urge and discomfort stop.
Classification of drugs for the intestines
Drugs for the treatment of intestinal disorders can be classified according to the clinical manifestations for which they are appropriate to use.
In case of predominance of flatulence and abdominal pain, antispasmodics are used. This choice is due to the fact that pain is often based on spasm. Antispasmodics relax the intestinal muscles, which improves intestinal motility. Enzyme preparations are also used for abdominal pain and indigestion.
Figure 2. Antispasmodics relax the intestinal muscles. Picture: makyzz / freepik.com
If the leading clinical symptom is constipation, preference is given to laxatives. They are divided into 2 types:
- Irritating intestinal receptors. This group includes plant preparations containing anthraglycosides.
- Increasing the volume of intestinal contents (saline laxatives).
- Stool softeners (oils, glycerin).
For diarrhea, preference is given to enveloping, adsorbent and anti-inflammatory drugs. In some cases, probiotics or intestinal antiseptics may also be recommended. Diarrhea leads to large fluid loss or even dehydration, so it is necessary to take rehydrating medications that will restore water balance.