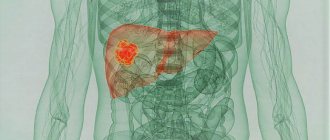
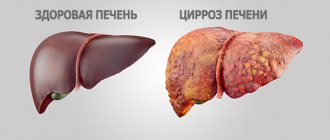
Liver cirrhosis is a chronic disease caused by pathological replacement of parenchymal tissue, which normally makes up the structure of the liver, with fibrous connective tissue or stroma. The result is a violation of blood circulation in the organ and a deterioration in its functioning, leading to malfunctions in the functioning of the entire organism.
Statistical data
Cirrhosis
– one of the common causes of death at the age of
30-60 years
. About 300 thousand people die from this disease in the world every year, which is 14-30 cases per 100 thousand deaths.
The frequency of deaths is growing rapidly every year; over the past decade, mortality has increased by 12%. The disease is asymptomatic in 12% of people with alcohol dependence. In approximately 20% of cases, it is possible to find out that a person suffered from this disease only after his death.
Cirrhosis occurs three times more often in men than in women, most cases after age 40 (although it can develop at any age).
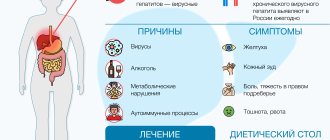
How cirrhosis manifests itself: the first signs
It is not always possible to detect signs of the disease in time, because cirrhosis often goes unnoticed. But early symptoms include:
- Temporary pain in the area of the right hypochondrium, aggravated by physical activity. Also, pain in this area of the body can occur after eating fried or fatty foods or alcoholic beverages.
- Often, especially in the morning, a bitter taste appears in the mouth.
- Increased gas formation, periodic diarrhea.
- Loss of body weight.
- Nosebleeds.
- Irritability and fatigue.
In most cases, cirrhosis is acute, so it is not always possible to diagnose it in the early stages.
Patient nutrition
The diet of patients must follow the following rules:
- cooking food without salt (individually, the doctor may allow the use of 0.5 to 2 g for adding salt to the plate);
- sufficient amount of protein (at least 70 g);
- frequent fractional feeding;
- lack of fried, smoked, salty foods and dishes;
- categorical prohibition of alcoholic beverages;
- limiting fluid to 750–1000 ml;
- providing calorie content from 1500 to 2000 kcal.
Prohibited items include:
- baked goods and sweets;
- canned food;
- fatty meat dishes;
- products with mushrooms;
- margarine and cooking fats;
- spicy seasonings, including mayonnaise;
- coffee and carbonated drinks.
Eating fruits daily will help compensate for the intake of vitamins
It is recommended to include in the daily menu:
- porridge (oatmeal, buckwheat, rice) and cereal casseroles;
- fresh vegetables and fruits;
- fermented milk products, cottage cheese;
- lean fish and meat;
- Rye bread;
- egg white;
- rosehip decoction.
Disease progression and new signs
With the gradual development of the disease, the following symptoms (main) may be added:
- Pain in the right hypochondrium increases and takes on the character of colic. They may be accompanied by a feeling of heaviness and increase (if hypokinetic dyskinesia is additionally observed).
- The patient experiences vomiting and nausea. Blood is sometimes visible in the vomit, which indicates bleeding from the esophagus or gastric veins.
- Skin itching is observed due to an excess of bile acids in the blood.
- Rapid weight loss can lead to exhaustion. There is a general decrease in muscle tone, they atrophy.
- Nervous system disorders: memory deteriorates, apathy and insomnia are observed.
- Tremor of the limbs, painful swelling of the joints.
- Enlarged spleen.
- Growth of mammary glands in men, impotence. Liver cirrhosis symptoms in women also include a decrease in secondary sexual characteristics: disruptions in the menstrual cycle or its complete absence. Men, like women, experience hair loss in the armpits and pubic area.
The severity of certain symptoms depends on the stage of the disease.
External characteristic signs of liver cirrhosis
As the disease progresses, the patient begins to experience noticeable changes in appearance:
- The skin acquires a yellow tint and begins to peel off. Severe jaundice indicates that the disease is in its final stage. Initially, the sclera of the eyes, the mucous membrane of the oral cavity, feet and palms acquire a yellow tint, and only after that the whole body.
- Xanthelasmas (also called “cholesterol plaques”) appear in the upper eyelid area.
- The fingers become thicker at the top, and the skin around the nails turns red.
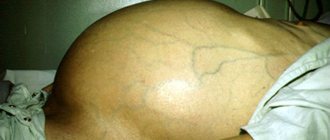
- The veins in the abdomen expand. Among the late complications of the disease, it is worth noting ascites - a pathological accumulation of a large amount of fluid in the peritoneum.
- Angiomas (vascular tumors) appear along the edges of the nose and in the corners of the eyes.
- The tongue becomes brightly colored and swells.
- The upper part of the body may be covered with spider veins, the number of which increases during the acute form of the disease.
- The cheekbones stand out on the face and the salivary glands swell. Dilated capillaries give the face a red color.
Many of these signs appear only in the later and most severe stages of cirrhosis.
Why does cirrhosis occur: reasons
The occurrence of cirrhosis can be due to many reasons: other diseases of the liver and other organs, long-term use of certain medications or alcohol.
More than 80% of cases of cirrhosis are caused by viral hepatitis (mainly C and B) and alcoholism.
The causes of the disease are the following:
- Autoimmune hepatitis
. This is a kind of malfunction of the immune system when the body begins to produce substances that damage and destroy the liver. - "Metabolic" hepatitis
(congenital forms of cirrhosis). The disease occurs against the background of certain genetic pathologies (Wilson-Konovalov disease, hemochromatosis, galactosemia, tyrosinosis, etc.). - Prolonged cholestasis
, when the normal outflow of bile is disrupted due to poor patency of the bile ducts (blockage). - Parasitic liver diseases
. - Some diseases of other internal organs
: portal vein thrombosis, chronic heart failure, etc. - Excessive alcohol consumption
. The disease develops after 10 or more years of constant drinking.
Often (in about 20% of cases) it is not possible to establish the exact cause of the disease. Cirrhosis is then called cryptogenic.
The risk of developing the disease significantly increases the combined influence of several factors, for example, alcoholism in combination with the hepatitis virus.
Assessment of factors influencing life expectancy
The survival prognosis is assessed in each individual case based on the patient’s individual characteristics. Factors that determine the lifespan of cirrhotic liver disease include:
- the severity of the disease, according to the assigned medical stage and the duration of the pathology;
- the presence of complications, the degree of their progression;
- etiology of cirrhosis;
- gender and age of the patient;
- effectiveness of treatment;
- the patient’s eating behavior and lifestyle;
- the presence of other chronic pathologies.
The general psychological mood of a patient with such a diagnosis plays a special role. In the absence of a commitment to fighting the disease, it is unlikely that cirrhosis will gain additional time to live.
Diagnosis of the disease: basic methods
Diagnosis of this disease can be carried out by a gastroenterologist or hepatologist. After the consultation, the specialist can refer the patient to:
- conducting a biochemical blood test;
- blood test for viral hepatitis;
- coagulogram;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs, ultrasound of the liver;
- gastroscopy: to examine the veins of the esophagus and assess the risk of bleeding.
Among the additional diagnostic measures worth mentioning:
- liver biopsy;
- CT (computed tomography) to assess changes in the organ;
- scintigraphy of the organ to assess the work of its various departments.
An experienced specialist can suspect cirrhosis based on only one biochemical blood test: its indicators change according to a certain pattern. Thus, the amount of bilirubin in the blood is determined in excess, the levels of transaminases, alkaline phosphatase, globulins and specific liver enzymes increase. At the same time, cholesterol, prothrombin and urea levels fall.
What types of disease are there?
Liver cirrhosis can be of several types, which differ in course (symptoms) and prognosis.
- Alcoholic
. This type of cirrhosis occurs in people who consume alcohol-containing drinks in large quantities for a long time. In most cases, it accompanies existing alcoholic hepatitis. The peculiarity of this type of disease is effective treatment with complete cessation of alcohol consumption. - Primary biliary
. This type of disease is associated with poor bile flow and inflammation of the bile ducts. Such cirrhosis manifests itself as yellowness and itching of the skin, and elevated body temperature. - Autoimmune
. It develops as a result of a violation of the human immune system: the immune system perceives its own liver cells as foreign and fights against them. As a result, dead cells are replaced by connective tissue, which gives rise to the development of cirrhosis.
The autoimmune form is one of the most difficult to treat.
[media=
https://youtu.be/_hi926Vf3Kk
?t=16s]
Etiological classification
From an etiological point of view, the main causes of cirrhosis are viral infection and alcohol intoxication. It has been proven that the disease can be triggered by protein deficiency in the body, poor diet and lack of essential vitamins.
According to the etiological classification, there are:
- autoimmune cirrhosis;
- genetic;
- alcoholic;
- cryptogenic;
- toxic;
- biliary;
- viral;
- cardiac.
The most common are toxic and biliary cirrhosis. These varieties are considered less dangerous and less likely to lead to dangerous complications. According to the morphology of the disease, it is customary to distinguish macrono-micronodular and mixed cirrhosis.
Stages of the disease: severity
Each stage of the disease is characterized by distinctive symptoms. The stage will also be determined by the person’s general condition and the necessary therapy.
| Stage | First (compensated) | Second (subcompensated) | Third (terminal) | Fourth |
| Peculiarities | The initial stage is characterized by a practically asymptomatic course. If the disease can be identified during this period, then effective therapy is possible with the help of medications. A person may feel absolutely healthy (rare pain in the right side is acceptable), but changes are already visible in a biochemical blood test. | This stage is characterized by a pronounced decrease in the functioning of the organ. During this period, the first signs of the disease are observed: decreased performance and deterioration in general well-being, nausea and vomiting. With properly selected treatment, it is possible to transfer the patient from the second stage to the first. | This stage is characterized by a rapid increase in symptoms of the disease and further development of liver failure. There are chances of feeling better, but they are small. The sick person must be in a hospital: metabolic disorders are observed, ascites often develops. | The last stage of the disease has a very unfavorable prognosis: without a liver transplant, it is impossible to stop the progression of cirrhosis - everything ends in death. The pain is so severe that the person has to constantly take strong painkillers. |
The cause of death can be very serious complications of cirrhosis, including: liver cancer, peritonitis, pneumonia, hepatic coma.
How long do people live with abdominal dropsy?
The process of accumulation of exudate in the abdominal cavity affects life expectancy, but is still not a determining factor. Much depends on the timeliness and effectiveness of therapy, as well as compliance with the doctor’s recommendations. To make a correct prognosis, you need to take into account several important criteria - age, rate of progression of cirrhotic processes, development of side pathologies, diet.
Form of hepatic cirrhosis
Liver cirrhosis and ascites are two fundamental factors affecting the patient’s life expectancy. The prognosis is determined by the stage of cirrhosis and, accordingly, the effectiveness of treatment. With a compensated form of the disease, it is possible to minimize the negative consequences of abdominal dropsy and maintain the functional activity of the digestive gland. This means that if a salt-free diet is followed and the recommendations of the attending physician, a sick person can count on a good prognosis.
With subcompensated cirrhosis, the volume of exudate in the abdominal cavity can increase to 7 or more liters. Untimely pumping out of exudate leads to an increase in intra-abdominal pressure and, accordingly, the likelihood of internal bleeding. As a rule, it is hemorrhagic manifestations that cause death in patients.
Decompensated cirrhosis of the liver with ascites greatly reduces the patient's life expectancy. With this form of pathology, irreversible processes occur in the digestive gland, so approximately 80% of patients do not survive even 5 years without an organ transplant. Liver transplantation is the most effective method of getting rid of the consequences of abdominal hydrops. If the operation is successful, patients can live for decades.
At-risk groups
Many patients with liver cirrhosis are diagnosed with so-called refractory ascites. The disease is characterized by the absence of positive diuresis in patients. At the same time, the amount of urine formed in the body is not affected in any way by the use of diuretics and a salt-free diet. In such patients, mortality exceeds 65% within 2-3 years.
There are risk groups for which the consequences of edematous-ascitic syndrome are the least unfavorable:
- elderly people;
- persons suffering from arterial hypotension;
- patients who have been diagnosed with cancer;
- patients suffering from diabetes mellitus.
How long can a person live with ascites? Currently, hepatologists have learned to compensate for the condition of patients with well-chosen medications and diet. However, it should be borne in mind that there are forms of the disease (refractory, massive ascites) that are difficult to treat. In this case, it is almost impossible to extend life by at least a few years.
Parallel complications
With ascites, the greatest danger is not the exudate itself that accumulates in the abdominal cavity, but the consequences of the pathology. Intercellular fluid provides a suitable environment for the proliferation of pathogenic agents. If you do not get rid of ascitic fluid in time, this will lead to the development of bacterial peritonitis.
Bacterial peritonitis is a serious disease with a mortality rate of 62-77%.
It is important to understand that the accumulation of fluids in the peritoneum is accompanied by an increase in intra-abdominal pressure. In this regard, the risk of crushing the intestines and, as a result, internal bleeding increases. Failure to provide medical care in a timely manner often results in death.
Are there any chances to cure the disease: therapy for cirrhosis
It is currently impossible to completely get rid of cirrhosis without a donor organ transplant. However, if the disease was identified at an early stage of its occurrence, then it is possible to stop its progression with correctly selected drug therapy. If the disease is in advanced stages, then attempts can be made to delay or prevent the development of serious complications.
Therapy is selected strictly individually, taking into account the clinical manifestations of the disease and its stage.
Treatment is based on:
- Eliminating the cause that contributed to the development of the pathology. In cases where the disease is in a compensated stage.
- Getting rid of alcohol addiction.
- A strict diet, with complete abstinence from alcohol and harmful foods, optimal content of proteins and carbohydrates in the diet.
- Limiting physical activity.
- Individually selected drug therapy.
Heat treatment is not recommended for cirrhosis. Also, you should not use traditional medicine without consulting a doctor.
Principles of treatment
Is it possible to cure cirrhosis with ascites? Unfortunately, at present, no drugs have been invented that could help restore the functional activity of the liver. With the development of cirrhotic processes, liver cells (hepatocytes) die and are replaced by connective tissue, which does not perform the necessary functions. That is why irreversible processes occur in the body, which entail the development of side pathologies - portal hypertension, hepatic encephalopathy, abdominal dropsy, etc.
Treatment of liver cirrhosis with ascites involves the use of medications, as well as diet and drinking regimen. When a large amount of exudate accumulates in the peritoneum, laparocentesis is performed - a puncture of the abdominal wall with subsequent pumping of fluid from the body. Timely surgical intervention helps prevent internal bleeding, intestinal crushing and the development of bacterial peritonitis.
Pharmacotherapy
Before treating the patient, the specialist conducts a functional diagnosis of the liver. After determining the stage and type of the disease, an appropriate treatment regimen is prescribed. Cirrhosis of the liver and abdominal dropsy can be treated with the following drugs:
- hepatoprotectors (“Allahol”, “Karsil”) - choleretic drugs that normalize intestinal motility and restore the digestion process;
- essential phospholipids (“Phosphogliv”, “Essentiale”) - stimulate the growth of new hepatocytes, eliminate symptoms of intoxication and restore protein metabolism in the liver;
- diuretics (“Diacarb”, “Aldactone”) - accelerate the process of excretion of salts along with urine, prevent the development of abdominal dropsy;
- amino acid preparations (“Methionine”, “Ornithine”) - soften the manifestation of cirrhosis, restore carbohydrate and lipid metabolism in the digestive gland.
Albumin-based drugs are the most effective medications for liver cirrhosis with ascites. They contain protein fractions that increase oncotic pressure in the blood. Increasing the density of the intercellular fluid makes it possible to reduce the severity of edematous-ascitic syndrome and, as a consequence, the likelihood of complications.
Therapeutic diet
The diet for liver cirrhosis with ascites comes down to limiting salt and fluid intake. When drawing up a dietary program, a strict ban is imposed on the consumption of canned food, fatty meat and fish, sweets, mayonnaise, brewed coffee, fried potatoes, etc. A balanced diet for liver cirrhosis can significantly reduce the load on the digestive gland and prevent the accumulation of fluid in the tissues and internal cavities.
The standard menu for liver cirrhosis looks something like this:
first breakfast - egg white omelet, 1 piece of black bread and 100 ml of herbal decoction;- second breakfast - 150 g of uneaten crackers and 100 ml of weak black tea;
- lunch - rice soup with pieces of chicken fillet, cabbage and fresh cucumber salad and 100 ml of jelly;
- snack - rye bread crackers with honey, 100 ml of tea;
- dinner - buckwheat soup with turkey and 100 ml cherry jelly.
If you eat right and promptly replenish the lack of magnesium and potassium in the body, you can live with abdominal dropsy for more than 10-12 years.
Treatment with folk remedies involves the use of herbal decoctions that have diuretics. Decoctions of hernia and bearberry, rose hips and juniper berries, coltsfoot and green beans help reduce the severity of abdominal dropsy.
Consequences of cirrhosis and prognosis
How long do people live with a diagnosis of liver cirrhosis? The answer is that the disease can have a different prognosis. So, if a person reconsiders his lifestyle and adheres to the established treatment regimen, then in the first stages (when the functionality of hepacides is preserved) survival rate of more than 7 years is over 50%.
At the subcompensated stage of the disease, the average life expectancy is 5 years; at later stages, no more than 40% of people live 3 years. In most cases, a person dies from developing complications that are incompatible with life.
In some cases, proper therapy can compensate for the disease for a fairly long period (up to 20 years or more) and maintain the functioning of the affected organ.
Liver cirrhosis, symptoms in men - how long people with this diagnosis live depends on timely detection of the disease and selection of the correct therapy. Even with developed ascites, you can live for about 2 years with drug therapy, but if you refuse treatment, only 25-50% of people with cirrhosis survive six months.
Literature:
- Gastroenterology: National Guide / Ed. V.T. Ivashkina, T.L. Lapina. - M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2008. - 704 p.
- Mukhin N.A., Lopatkina T.N., Abdurakhmanov D.T. Etiotropic therapy of liver cirrhosis. Clinical pharmacology, therapy. 2006, no. 1.
- Alcohol disease. Damage to internal organs / Ed. V.S. Moiseeva. — 2nd ed. reworked and additional - M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2014. - 480 pp.: ill.
- Grigoriev P.Ya., Yakovenko A.V. Clinical gastroenterology: Textbook for medical students. — 3rd ed. reworked and additional - M.: Medical Information Agency, 2004. - 768 p.