Splenomegaly is a clinical manifestation of a number of diseases, which is an abnormal enlargement of the spleen. In healthy people, the organ cannot be felt because it is closed on all sides by the ribs. When the spleen enlarges 2-3 times, it is determined by palpation
.
Splenomegaly is an indicator of serious pathological processes occurring in the human body. In young children, splenic hypertrophy is caused by imperfect functioning of the immune system. Pathology occurs in people of any age, gender and origin.
Despite the fact that the spleen is not a vital organ, it performs important functions:
provides immune protection, destroys old blood cells, and saturates the body with blood in emergency cases. This is a kind of “filter” that retains microbes and damaged formed elements, preventing their further spread. The spleen is the largest structure of the lymphatic system, which passes all the blood through itself and helps the body quickly respond to any negative external influence.
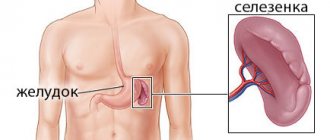
The spleen is located in the left hypochondrium.
Normally, it weighs 150 g. Its size in an adult is 11 cm. When the weight of the spleen reaches 400-500 g, splenomegaly is diagnosed.
With the help of modern diagnostic techniques, organ enlargement can be detected at earlier stages, especially if the patient has characteristic symptoms. In severe cases, the spleen can stretch up to 20 cm and weigh more than a kilogram.
Moderate splenomegaly occurs in infectious, autoimmune, and hematological diseases. A significant increase in the organ is observed in oncological processes - hemoblastosis.
The spleen becomes gigantic in size and fills most of the abdominal cavity. Splenomegaly of non-inflammatory origin is manifested by symptoms of the underlying disease. Clinical signs from the enlarged organ are blurred. Patients complain of discomfort and unpleasant sensations under the left ribs. An acute infectious-inflammatory process is accompanied by vivid symptoms with severe pain and intoxication syndrome - fever, weakness, chills, dyspepsia.
Diagnosis of splenomegaly is complex, including a general examination of the patient, palpation of the organ, and laboratory and hardware methods. Treatment of the syndrome is etiotropic, aimed at eliminating the causative disease. The spleen is removed when the disease does not respond to conservative therapy, the organ continues to enlarge, and irreversible changes occur in the tissues. Splenomegaly is a symptom that requires immediate medical attention. Ignoring the disease and self-medicating can lead to serious complications and even death.
What is splenomegaly
The spleen is the largest lymph node in the human body
, it is located on the left side of the peritoneum, in close contact with the colon, kidney (left), pancreas and diaphragm.
Splenomegaly
- a diagnosis made by doctors when the weight of the spleen exceeds 200g.
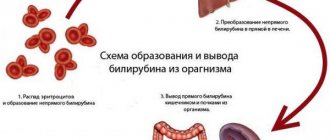
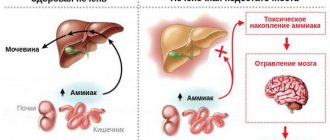
An enlarged organ is able to capture more blood cells, but its filtering function deteriorates. Removing large numbers of cells from the blood reduces the number of white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets
. Such rapid and active destruction of blood cells leads to anemia, private infectious diseases, and deterioration of blood clotting.
An enlarged spleen can be caused by diseases of various natures, from simple infections to cancer. If the spleen is not greatly enlarged, then there may be no pain, but sometimes the organ becomes so large that it begins to compress the nearby internal organs, causing discomfort and pain.
Organ sizes
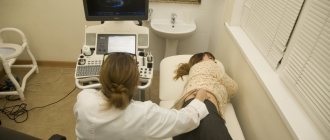
Ultrasound of the spleen allows you to determine not only the location and structure of the gland, but also its size, which is an important diagnostic point. In order to correctly carry out the ultrasound procedure of the spleen and obtain an accurate result, the subject must prepare for the manipulation being performed:
- refuse food 7-8 hours before diagnosis;
- 48 hours in advance, give up foods that stimulate flatulence (legumes, cabbage, sweets, flour products, carbonated drinks);
- if necessary, take the sorbent the evening before.
The size of the spleen may vary among several healthy adults. This depends on the constitution of the subject’s body, his weight, the individual location of internal organs, and gender.
- splenic artery (diameter) – 2 mm±1 mm;
- splenic vein (diameter) – 6 mm±1 mm;
- echogenicity state – average;
- shape - crescent-shaped;
- maximum oblique cut area – 155-235 mm 2 ;
- weight – 200 g±50 g.
The volume of the spleen is calculated using a special formula: V = 7.5S (oblique section area) - 77.56. The ultrasound specialist must indicate the structure of the spleen, its location in relation to the pancreas, kidneys, adrenal gland, and stomach.
Etiology of the disease
The reasons for an enlarged spleen are as follows:
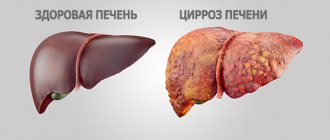
- liver diseases (the most common cause): cirrhosis, alcoholic hepatitis, hepatosis, hepatitis B, C;
- blood cancer;
- various infections: microbacteria, brucellosis, sepsis, etc.;
- blood flow disorders and thrombosis;
- viruses: rubella, mononucleosis, measles, AIDS, etc.;
- autoimmune diseases: rheumatoid arthritis, lupus erythematosus, periarteritis;
- entry into the body of arthropods and helminths;
Damage to the spleen (from a fall) can provoke the appearance of ulcers, tumors, heart attacks or splenic cysts, which also leads to malfunctions of the organ.
Liver pathologies
– the most common cause of spleen dysfunction. It is these two organs that interact most closely: blood filtered in the spleen from the digestive system enters the portal vein, and from there to the liver, where it is further cleansed of toxins. Thus, any disruption of the natural course of this process leads to splenomegaly. It is also true that improper functioning of the spleen necessarily leads to liver dysfunction.
Classification
Degrees of severity of spleen enlargement according to Siegenthaler W:
- Mild degree - moderate splenomegaly. Protrudes from under the edge of the rib by 2 cm. A moderate degree is noted with infection (acute or chronic), cirrhosis , acute leukemia , hemolytic anemia and portal hypertension .
- A significant degree. Increases to 1/3 of the distance to the navel. Such an increase, in addition to the diseases listed above, may occur with Hodgkin lymphoma .
- High degree. Increases to 1/2 the distance to the navel. It is found in Gaucher disease , splenic cysts , chronic myelogenous leukemia , and hemolytic anemia .
- Very high degree. Reaches the level of the navel. Characteristic of chronic myeloid leukemia , huge cysts and Gaucher disease .
Differential diagnostic value of the degree of enlargement of the spleen
Megasplenia in acute illness is regarded as a short-term macrophage reaction and a “physiological” response to inflammation. As a rule, such an increase does not cause further chronic pathology of the organ. With constant and prolonged increase, matrix proliferation occurs, which leads to disruption of the structure and function of the organ.
Symptoms of the disease
Many patients do not realize that the spleen is enlarged for a long time: the symptoms of the disease are ambiguous, and no signs may be observed. Depending on the form of splenomegaly, some signs of the disease can be identified:
- The inflammatory form
is characterized by pain in the left side of the peritoneum, high fever, a feeling of heaviness in the stomach (even with a small amount of food eaten), intoxication and nausea (rarely vomiting). The patient develops bruises under the eyes, decreases body weight, and the skin turns pale. - The non-inflammatory form
is manifested by rare pain in the left side, the temperature remains normal (the maximum rises to 38 degrees). Since the signs of the non-inflammatory form of splenomegaly are similar to the symptoms of a common cold, patients often do not seek qualified help, and the disease takes on more severe forms.
Clinical symptoms of an enlarged spleen are most often observed when the organ significantly exceeds the maximum permissible size. Other typical manifestations of splenomegaly in adults are:
- constipation;
- heartburn;
- pain in the left hypochondrium, which can radiate to the shoulder.
If these symptoms are detected, you should contact a gastroenterologist, oncologist or hematologist.
In most cases, an enlarged spleen is a secondary sign of a disease (as a symptom of the underlying disease).
How to treat the disease?
Therapy for splenitis requires an integrated approach and the creation of special conditions favorable for healing. They include mandatory bed rest until complete recovery, plenty of fluids and strict adherence to a special nutrition program with the complete exclusion of fatty foods.
In addition, patients should be ensured that they are not exposed to stress. It is recommended to combine the use of medications with folk remedies such as herbal teas, infusions, etc. Only an integrated approach will help to quickly get rid of the inflammatory process.
Medicines
In almost all cases of splenitis, antibiotic drugs are prescribed to eliminate the inflammatory process.
To eliminate pain, taking painkillers and NSAIDs is indicated.
Since inflammation of the spleen often causes upset of the digestive processes, their normalization also requires taking certain medications.
To eliminate hyperthermic reactions, antipyretic drugs are taken, and patients are also prescribed drugs that restore blood circulation.
If the patient is diagnosed with purulent accumulations in the spleen, then the purulent masses are removed through drainage.
Drug therapy is prescribed when the inflammatory process is minor and there are no purulent foci or they are very small and amenable to drug therapy.
For splenitis, remedies of homeopathic origin such as Aconite 3 or Mercuris 3, Nux vomica 3, Arsenica 3 or Hina 3 are often used.
If drug therapy is not effective, the patient is sent for surgery.
Breathing exercises for diseases of the spleen
For almost all diseases of the spleen, patients are recommended to rest, therefore, unfortunately, a treatment method such as exercise therapy is not used. But there are several breathing exercises that alleviate the condition and promote faster recovery.
Exercise 1. Starting position - lying on your back, legs bent at the knees, hands under your head. Breathe so that the abdominal wall moves (this breathing is called diaphragmatic breathing), gradually accelerating the rhythm of inhalation and exhalation. Make 10–20 breathing movements until you feel dizzy.
Exercise 2. Starting position – the same. Inhale deeply, and then exhale the air in small portions, pronouncing the syllable “cha” and trying to make the abdominal wall move sharply with each exhalation. For each inhalation there should be 3-4 exhalations. Repeat the exercise 3–8 times.
Exercise 3. Starting position – the same. Inhale, drawing in your stomach, exhale freely. Then inhale, sticking out your stomach, exhale freely. Take 6-12 breaths, alternately drawing in and protruding your stomach.
Exercise 4. The starting position is the same, but the exercise can also be performed standing, placing your hands with your palms on your stomach. Inhale quickly through your nose and mouth at the same time, protruding your stomach. Take a few breaths and then one calm exhale. Start the exercise with 6-10 breaths, gradually increasing their number to 40.
Exercise 5. Starting position – the same. Inhale while making a yawning movement without opening your mouth. After inhaling, hold your breath for 3 seconds, then exhale freely. Repeat the exercise 10–15 times.
Exercise 6. The starting position is the same, only the hands rest on the hips. Take a deep breath, sticking out your stomach, then bring your hand to your mouth and slowly exhale into your palm, pursing your lips into a tube. Take the next breath, drawing in your stomach, and exhale in the same way, changing your hand. Repeat the exercise 6-10 times.
Folk remedies
To increase the effectiveness of drug therapy, it is recommended to use traditional medicine, but only on the recommendation of a doctor. Self-medication is fraught with the development of complications, so it is not worth the risk.
The following recipes are used in the treatment of pathology:
- Sow thistle with carrot juice and radish. The greens of the plant (20 g) are crushed and brewed with boiling water (1 l), left for 15 minutes, filtered and mixed with 100 ml of carrot juice and the same amount of rare juice. The resulting product should be taken for two weeks, 5 times a day. The daily dose of the medicine is prepared according to the indicated proportions.
- St. John's wort decoction. You need to brew a large spoonful of the herb with a glass of just boiled water and leave it in the bathhouse for about half an hour. The broth is cooled and filtered, then more boiling water (250 ml) is added to it. Take 1/3 cup of the decoction half an hour before meals.
- Chamomile. You need to brew the flowers of the plant and take a glass of tea 3 times a day 2 hours before meals.
- Mix celery juice (15 g) with dill juice (25 g) and take a dessert spoon 4 times a day.
- Apply a cold or hot compress to the spleen area.
- Treatment with wormwood. To do this you need: pour 100 g of wormwood into 1 liter of water; boil and cook for another fifteen minutes; strain and take a tablespoon three times a day before meals for two weeks.
- Treatment with sage: mix sage and nettle in equal quantities; grind and take a small pinch of this powder three times a day.
- Their herbal remedy: mix calendula and yarrow in equal quantities; pour boiling water (0.5 liters of water per 20 g of herbs); leave for an hour and take half a glass twice a day.
In combination with treatment, doctors advise using traditional recipes. Self-medication aggravates the course of the pathological syndrome; before use, you should consult a doctor.
Treatment with millet
In folk medicine, millet is used to treat various diseases, but products based on it are often recommended for removing toxins from the body. Harmful substances often accumulate in the spleen, so cleansing with millet helps cope with enlargement and relieve pain. Preparation: Rinse 250 gr. millet. Pour water (2 liters) over the millet and cook, avoiding boiling. The cereal should be completely boiled. Drain the broth and use for treatment. Drink the prepared product throughout the day. Dosage for one time – 100 ml. Duration of treatment is a week. If necessary, repeat the course after a break of 7-10 days.
Treatment with wormwood
A decoction based on wormwood will help quickly cure the spleen. Homemade medicine can cause allergies, so during the course of treatment, monitor your general health - if irritation appears on the skin, stop taking it and consult a doctor. Preparation: Place 20 grams in a small container. wormwood. Bring water (220 ml) to a boil and brew the plant material.
Infuse under the lid; to obtain a rich decoction, wrap the container with a towel. Filter, use gauze cloth folded in 3 layers. Add 25 gr. honey, mix. Take the product three times a day, it is recommended to take it half an hour before meals. Dosage for one time – 100 ml. The duration of the course of treatment is two weeks.
Treatment with propolis
It is recommended to treat the spleen with propolis infusion. You can buy the product at the pharmacy or prepare it yourself. Before use, please note that it contains alcohol. Preparation: Place propolis (60 g) in a dark glass container. Pour the bee product with alcohol, high-quality vodka, and homemade pervach (200 ml). Leave in a cool, dark place for a week.
Propolis infusion should not be taken in its pure form; before use, dilute with boiled cool water (30 drops of product per 60 ml of water). Reception is carried out according to the scheme. For a week and a half, take the composition daily every three hours. Take a short break (5 days), continue taking it, but use the product only three times a day.
Diet
The patient's diet also requires special attention. It is necessary to adjust it and eat according to a certain regimen. Diet therapy is an integral part of the treatment process for splenitis.
You should definitely drink as much plain water as possible. Drinking plenty of fluids thins the blood flow, which makes it easier for the spleen to filter blood.
It is necessary to exclude from the diet unhealthy foods such as pickles, smoked foods, spicy dishes, etc. It is necessary to take as the basis of the diet foods rich in fiber and unrefined substances, cabbage and pomegranates, herbal decoctions such as sage, wormwood, chicory, rosehip infusion, fruit drinks, jams or compotes .
Operation
If the spleen is damaged and bleeding occurs, which can threaten the patient’s life, then the doctor raises the question of removing the organ.
Although the spleen is not a vital organ, experts are not particularly keen to remove it completely. Usually doctors try to preserve at least part of the organ so that it can partially perform its functions.
If the pathology picture is complex, the patient has an abscess, the organ’s vessels are damaged or it is greatly enlarged, there are injuries or ruptures, then complete removal of the organ or splenectomy is performed.
The operation can be performed open or laparoscopically.
With open access, an incision is made above the spleen, the skin layer and muscles are pulled apart, then the vessels are cut off and the spleen is removed from the peritoneum. The wound is then sutured and covered with a surgical dressing.
The laparoscopic splenectomy method involves removing the organ through a small incision using a laparoscope and other necessary instruments. After removal, the incisions are sutured and covered with gauze. The operation lasts about 40-60 minutes.
The patient remains in the hospital for a few more days, and after the stitches are removed he is sent home, sometimes even earlier. The length of postoperative hospital stay depends on the method of surgery, the patient's condition and the presence of complications.
Surgery is needed if treatment of the spleen with medications does not produce results. For cysts, oncologies, and abscesses, tablets are almost never used—surgical intervention is immediately prescribed. If suppuration occurs, it is drained: a needle is inserted, through which the pathological masses are removed and the medicine is administered. The procedure is safe, but it is used for abscesses up to 5 cm in size. Other types of operations: Removal of a tumor - often performed laparoscopically (through a puncture of the abdominal wall).
This is how cysts and operable tumors are treated. The operation is low-traumatic, has a short rehabilitation period, but is expensive: 70,000-120,000 rubles. Resection of the spleen - part of the organ is removed in case of benign tumors, injuries, cysts. The laparoscopic method of removing the spleen is less painful than the traditional method. Its use will reduce the incidence of postoperative complications, shorten the postoperative period and improve the quality of life of patients.
Splenectomy - removal of the spleen is carried out in case of its rupture, multiple suppurations, or cancerous tumors. Such an operation can save a patient with inflammation of the peritoneum, but is dangerous due to decreased immunity and changes in blood composition.
Diagnosis of splenomegaly: research methods
To diagnose an enlarged spleen, the doctor first conducts a questioning. Purpose of the conversation
– identification of infectious diseases in the past that could cause hardening of the spleen (malaria, typhus), chronic infections (syphilis, chronic malaria). The doctor also takes into account the presence of diseases of the hematopoietic system (leukemia), liver diseases, diseases of the cardiovascular system (portal vein thrombosis, endocarditis).
Inspection and palpation: these methods are informative when the organ is significantly enlarged. During palpation, the doctor examines its mobility, surface (smooth, lumpy), consistency (soft or dense), edges and volume.
Other methods for diagnosing the disease:
- Blood tests: complete blood count, biochemical blood test. Blood tests allow you to assess the number of leukocytes, erythrocytes, confirm/exclude anemia, leukocytosis, assess the level of necessary microelements in the blood;
- stool analysis for worm eggs;
- X-ray;
- spleen puncture;
- Ultrasound of internal organs.
How does splenomegaly manifest?
Symptoms of the disease become more intense as the organ grows. Sometimes it is possible to notice pathology only when the spleen is very enlarged. Doctors distinguish 4 stages of splenomegaly:
- Stage 1
– the organ can be palpated, which is impossible given its normal size; - Stage 2
– the spleen occupies the area from the navel to the hypochondrium; - Stage 3
– the organ reaches the midline of the abdomen; - Stage 4
- the spleen protrudes into the pelvic region and the right side of the peritoneum.
Treatment of splenomegaly
For patients with an enlarged spleen, the cause and treatment of the disease may be completely different. Therapy is always aimed at eliminating the disease
, resulting in pathological growth of the organ, the last resort of treatment is its removal. Removal of the spleen (splenectomy) can be performed using the classical method or through small holes in the abdomen (laparoscopy). This radical method of treatment is resorted to in cases where there is no improvement from the therapy, bleeding of the spleen is observed or it is too damaged. Surgery is also performed when the spleen begins to rapidly destroy red blood cells, causing anemia.
In other cases, conservative treatment is recommended:
- Depending on the cause of the pathology, antibacterial, hormonal, and antitumor drugs are prescribed.
- If the organ has been removed, a course of antibiotics and antiviral drugs is prescribed.
- In some cases, radiation therapy is performed.
- Patients are recommended to have a special diet: the diet should contain large quantities of fruits and cereals. All food should be easily digestible. The patient must avoid alcohol, fatty and spicy foods.
Compliance with the diet is recommended throughout the entire period of treatment and rehabilitation period, especially if the organ has been removed.
Forecast
The prognosis is determined by the timeliness of diagnosis and treatment of the underlying disease, as well as its severity. With correct diagnosis, acute infectious diseases are cured and at the same time megasplenia disappears. In chronic myeloid leukemia , in which the organ reaches enormous size, the prognosis depends on age, the number of blast elements and the response to treatment. In general, medications ( Imatinib ) can increase the life expectancy of patients by many years while significantly improving its quality. Five-year survival in chronic myeloid leukemia with the use of imatinib is observed in more than 90% of patients.
With thrombocytopenic purpura, with modern treatment, the prognosis for life in most cases is favorable. Outcomes can be: recovery, remission or chronic relapsing course. In rare cases, death can occur if there is bleeding in the brain.
In classic Hodgkin's lymphoma, no signs of the disease are considered cured for five years after the end of treatment. When chemotherapy with or without radiation therapy, Relapse after 5 years is rare. Risk factors for relapse include: male gender, advanced stage, age over 45 years, as well as low albumin , anemia and leukocytosis . Patients who do not achieve remission after treatment or have a relapse in the first year have a poor prognosis.
Causes of enlarged spleen in children
A child has an enlarged spleen; the causes and treatment have their own characteristics. The main causes of splenomegaly in children are blood diseases and infections. In infants, the disease often develops due to low filling of the organ with blood, as well as against the background of flabbiness of the abdominal muscles and rickets.
Other common diseases that provoke pathology in children include:
- typhoid fever;
- Congenital heart defect;
- tuberculosis;
- measles, rubella, diphtheria;
- leukemia;
- toxoplasmosis.
The development of pathology in children can be facilitated by helminthiasis, in particular schistosomiasis and echinococcosis (rare for CIS countries).
General information
The spleen is an unpaired organ located in the abdominal cavity.
Its size increases with age. In adults, the weight of the spleen is 150-170 g. Normally, the spleen is hidden by the lower ribs and is not palpable. It can be detected by palpation with a magnification of 1.5-3 times. It is a well-supplied lymphoid organ that performs various functions. Functions of the spleen in the body:
- Participation in the formation of an immune response to foreign antigens. This organ is involved in the production of antibodies (synthesis of IgG , properdin and tuftsin ).
- Filtration of blood and elimination (removal) of microorganisms and blood elements loaded with antibodies. This organ is a large accumulation of reticuloendothelial tissue, the main function of which is phagocytosis performed by macrophage cells. Normal and abnormal blood cells are also eliminated.
- Participation in lymphopoiesis. The white pulp of the spleen, as a lymphatic organ, produces lymphocytes .
- Depositing blood. This function is performed by the red pulp of the spleen. Normally, one third of all platelets and a large number of neutrophils, which are produced during bleeding or infection, are deposited in it.
- Participation in hematopoiesis in certain diseases (in adults, the organ of hematopoiesis is the bone marrow).
- Regulation of portal blood flow due to the common vascular network with the liver.
- Participation in metabolic processes.
In many conditions and diseases, changes in the spleen in the form of splenomegaly are observed. Splenomegaly, what is it? This term is used to refer to the enlargement of a given organ to one degree or another. A synonym is the term megasplenia. Changes in size and structure occur in response to infectious, immune and hemodynamic factors. Changes in the spleen always indicate an acute or chronic process in the body - this is an indicator of pathological conditions.
Splenomegaly is an early and sometimes leading symptom of a number of diseases, without being an independent nosological entity. You need to know that an increase in this organ is always the body’s reaction to hematological, non-hematological diseases or a consequence of portal hemodynamic disorders. Therefore, the classification always takes into account the underlying disease against which this symptom developed. The splenomegaly code according to ICD-10 R16.1 is established if the enlargement of this organ is not classified in other categories.
Splenomegaly is often, but not always, accompanied by hypersplenism . Hypersplenism is a pathological condition that is characterized by a decrease in the number of formed elements (erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets) in the circulating blood due to increased spleen function. pancytopenia develops , which is life-threatening.
Hypersplenism is associated with increased blood-destructive function of the spleen. This may be due to a number of reasons: difficulty in the outflow of blood from this organ, increased contact of formed elements with spleen macrophages, or increased activity of macrophages. Changes appear only in the peripheral blood, and the bone marrow remains normal. In many cases, the spleen is enlarged without symptoms of hypersplenism , and the latter can also occur with normal spleen sizes. In most patients, hypersplenism requires removal of the spleen, after which the blood picture and the patient’s condition return to normal.
Symptoms of splenomegaly in children
| Inflammatory form | Non-inflammatory form |
| Diarrhea | Mild pain in the left hypochondrium |
| Acute pain in the left hypochondrium | A slight increase in temperature to 37.5 degrees (the temperature may remain normal) |
| High temperature (reaching 40-42 degrees) | Palpation does not cause pain |
| Nausea and moderate vomiting |
The baby’s spleen can be damaged by inept palpation, so only a doctor should feel the baby’s abdomen!
Prevention of splenomegaly
It should be understood that an enlarged spleen itself rarely leads to serious consequences. The root cause of splenomegaly is much more dangerous. It is important to take preventive measures to prevent the development of the disease:
- rejection of bad habits;
- timely vaccination;
- treatment of all diseases in history;
- preventive examinations by specialists.
It is important to get vaccinated before traveling to exotic countries.
Prevention of splenomegaly involves taking measures against possible organ rupture. This means always wearing seat belts, not jumping from heights, and avoiding strong impacts to the abdominal area.
List of sources
- V.V. Voitsekhovsky, N.D. Goborov. Splenomegaly in clinical practice / Amur Medical Journal. — No. 2 (26) 2022, p. 62-77.
- Russian clinical guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of lymphoproliferative diseases / ed. ed. I.V. Poddubnoy, V.G. Savchenko. M. 2016. 419 p. Fainshtein F.E., Kozinets G.I.,
- Vorobiev A.I. Guide to Hematology. 3rd ed., revised, additional. M.: Newdiamed, 2005. T.3. 409 p.
- L.M. Pasieshvili, L.N. Beaver. Splenomegaly syndrome in the practice of a family doctor / Ukrainian Therapeutic Journal. - No. 2, 2007, pp. 112-119.
- S.P. Krivopustov. Splenomegaly in pediatric practice / Children's doctor. — No. 5 (26), 2013. pp. 5-8.
Prognosis after treatment
Sometimes (for example, with infectious mononucleosis) the spleen returns to its previous size and continues to function normally when the underlying disease is eliminated. The prognosis with timely diagnosis of the pathology and properly selected treatment is quite favorable: the symptoms of splenomegaly become less pronounced, the patient’s quality of life does not deteriorate.
If you have had a splenectomy ( removal of an organ
), a person becomes more vulnerable to infections. People who have had a splenectomy are recommended to be vaccinated against the infections of pneumonia, influenza and meningitis.
Forecasting and warning
Splenomegaly is a sign of serious diseases that requires careful diagnosis and adequate therapy. The prognosis of the syndrome depends on the causative pathology. Due to the multifactor nature of this condition, it is difficult to draw any conclusions regarding future prospects.
Specific prevention that can protect a person from splenomegaly has not currently been developed. General preventive measures are aimed at preventing the development of diseases that can lead to sudden enlargement of the organ. To do this, it is necessary to undergo an annual medical examination, promptly identify and treat infectious diseases and other pathological processes, sanitize inflammatory foci, strengthen the immune system, lead a healthy and active lifestyle without nicotine and alcohol, and get vaccinated in accordance with the National Calendar.
Splenomegaly is a serious process, but not as dangerous as its underlying disease. Modern medicine knows of cases where the size of the spleen returned to normal after adequate complex therapy for the causative pathology.