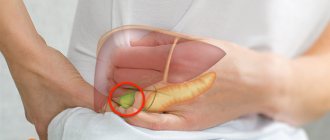
- inflammatory (hepatitis)
- sclerotic and degenerative (cirrhosis, fatty hepatosis)
- tumors (primary and metastases)
Stomach diseases:
- gastritis
- peptic ulcer (more often when ulcerative defects are located in the pylorus)
Diseases of the duodenum
- duodenitis
- peptic ulcer
- tumors and blockages of the Vater nipple - the exit point of the common bile duct, which removes bile and pancreatic secretions.
Referring pain in the right hypochondrium may reflect pain from distant organs:
- appendix (inflammation)
- right fallopian tube and ovary in women (inflammation, ectopic pregnancy, tumors)
- large intestine (tumors, ulcerative colitis).
Pain in the left hypochondrium
Usually associated with the following pathologies.
Pancreatic diseases:
- inflammation
- tumors
Spleen diseases:
- blood pathology
- splenic injury
- some infectious diseases
“Referred” pain in the left hypochondrium may be associated with diseases:
- heart (infarction, pericarditis)
- kidneys (usually with kidney stones)
- large intestine (tumors, ulcerative colitis)
- lungs (pleurisy or inflammation).
The localization of pain in the hypochondrium does not always coincide with the location of the diseased organ - the source of pain. Painful sensations in most diseases can spread both to the opposite side and to the entire upper abdomen.
Side back pain
Back pain is a pronounced symptom of problems in the body. Shooting, aching, sharp or dull sensations may affect a specific part of the back, the right or left side. There are many diseases that can cause back pain; you should not ignore this symptom or self-medicate. Patients often come to our clinic with complaints of unilateral back pain, so in this article we have collected symptoms to preliminary determine the cause. Only a qualified doctor can identify the exact cause and prescribe effective treatment.
Causes of pain on different sides of the back
Often pain on the left or right side of the back indicates some kind of pathology. However, the causes are often incorrect posture, excessive muscle tension, and hypothermia. Therefore, it is impossible to independently determine why negative feelings arose.
Symptom on the right side
If there is pain in the right side of the lower back, this may indicate a malfunction in the digestive tract, genitourinary system, or the functioning of various organs. The location and nature of the sensations are important.
Pain in the right side from the back may indicate impaired kidney function. In this case, the concentration of pain is noted closer to the center and radiates to the side. If negative sensations appear under the shoulder blade, most often it is neurology (pinched nerve). With this symptom, it is necessary to examine the lungs to exclude the presence of pleurisy, cancer, or pneumonia.
Pain in the right side of the back under the rib has many causes, including diseases of the liver, gall bladder, and pancreas. The sensations may be accompanied by additional symptoms such as nausea, fever and may not subside for several days. As a rule, these are signs of cholecystitis. At the same time, it hurts in the right side and radiates to the back. Another cause of negative feelings are diseases of the urinary system, spine, and hernia.
Symptom on the left side
If pain is noted in the left side of the back, its location is important. When pain is in the lumbar region, this may indicate mechanical damage, pathologies of the skeletal system, joints, infections, metabolic disorders and other diseases.
The cause may be neurogenic or psychogenic factors. Unpleasant sensations on the left side of the back occur during heavy physical exertion, when a person leads a sedentary lifestyle and remains in the same position for a long time. Usually such negative manifestations go away on their own within a few hours.
What does back pain indicate?
Nagging pain on the left side of the back can appear with spondylolisthesis (displacement of the vertebrae), sharp pain with a hernia, lumbago, rheumatism, stabbing pain with urolithiasis. Sometimes the cause is inflammation of the sciatic nerve, piriformis syndrome, or dysfunction of the left kidney.
Sharp pain in the right side of the back may indicate the presence of acute cholecystitis. Sometimes they radiate into the sternum, under the corresponding shoulder blade. Additionally, a number of other symptoms appear - nausea, fever, etc. Very often, pain on the right side manifests itself in a number of respiratory pathologies. For example, with inflammation of the lungs, bronchi, “dry” pleurisy, accumulation of air in the pleural cavity and other ailments.
A dull pain in the right side of the back appears with flatulence and pancreatitis. Accompanied by additional unpleasant sensations. Pain on the right sometimes occurs with diseases of the urinary system. For example, if there is a violation of the outflow of urine, kidney stones, renal colic.
Severe pain in the right side of the back may indicate damage to the spinal cord or disorders of the nervous system. The most common cause is spinal curvature due to poor posture. Pain in the right side of the back in women often occurs during pregnancy. They also appear with inflammation of the pelvic organs, cysts and ovarian tumors. Aching pain in the right side of the back appears with intervertebral hernia, spondylosis, hydronephrosis.
Diagnostics
So, unilateral back pain can occur due to various diseases. Therefore, only a thorough diagnosis will help identify the true cause. Back pain is a reason to contact two specialists at once. An osteopathic doctor will conduct a general examination to exclude injuries, obvious signs of infectious diseases, hernia, and stenosis. If a neurological cause of pain is suspected, a neurologist is involved in the examination.
Biochemical and general urine and blood tests are also often taken to identify the inflammatory process. If necessary, a biopsy is performed.
Who should I contact?
If the pain is prolonged and intense, then the best solution is to consult a doctor. Initially, it is necessary to undergo an examination by a therapist, who, after the examination, refers to the necessary doctors. Based on a detailed diagnosis, the doctor prescribes a specific treatment program.
Self-medication is unacceptable, since only in a clinical setting can an accurate diagnosis be made. To quickly relieve pain, you can take a painkiller, but this will not solve the problem, but will only suppress the symptom. Remember that any self-medication can lead to serious complications.
Diagnostic stages
1. Consultation with a gastroenterologist, who prescribes an examination plan and consultations with other specialists.
2. Examination of organs located in the upper half of the abdomen and adjacent areas.
- Laboratory tests, including blood tests, examination of secretions (stomach juice, feces, bile, etc.), tests for Helicobacter, etc.
- Endoscopic examination of the stomach, duodenum and other parts of the intestine.
- Echoscopic examinations (ultrasound), including those combined with endoscopic examinations (endo-ultrasound).
- X-ray examination, CT (including virtual colonoscopy) and MRI.
- Special studies aimed at searching for tumor formations, for example, MR diffusion (MRI tumor search).
Treatment
Getting rid of pain in the hypochondrium is certainly associated with effective treatment of the disease that caused it. The Clinical Hospital on Yauza has all the necessary conditions for quick and accurate differential diagnosis on a single basis of the diagnostic and treatment center, including all the necessary specialists.
Based on an exhaustive diagnosis, our hospital specialists formulate a diagnosis and, taking into account the individual characteristics of each patient, select the optimal treatment path. Both conservative and surgical methods can be used, including minimally invasive organ-preserving techniques that are most suitable for a specific clinical case.
If you experience pain in the hypochondrium, contact the Clinical Hospital on Yauza, where you will be quickly and expertly diagnosed and treated.
You can see prices for services
Acute renal failure
Acute renal failure (ARF) is a condition in which all intrarenal functions are suddenly and dramatically disrupted: blood circulation and hydrodynamics, glomerular filtration, tubular secretion and reabsorption (reabsorption of fluid). The following changes occur in the patient's body:
- Increased nitrogen levels in the blood;
- Deep disturbances of water-electrolyte metabolism, acid-base status;
- Increased blood pressure;
- Anemia.
- The reasons why acute renal failure develops are divided into 3 main groups:
- Prerenal – decreased renal blood flow;
- Renal – direct damage to the renal parenchyma;
- Postrenal – closure of the lumen of the urinary tract.
By changing the resistance of the afferent and efferent glomerular arterioles, the intensity of renal blood flow and glomerular filtration rate remain at the same level even during large fluctuations in mean arterial pressure. If blood pressure is below 70 mm Hg, self-regulation is impaired, and the glomerular filtration rate decreases in proportion to its decrease. Renal autoregulation depends on a combination of dilation of the afferent arterioles, caused by nitric oxide and prostaglandins, and constriction of the efferent arterioles, caused by angiotensin-2.
Drugs that interact with these mediators (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or selective COX-2 inhibitors, ACE inhibitors or ARBs) can cause prerenal acute renal failure in certain clinical situations. The risk group includes elderly people with atherosclerotic cardiosclerosis, patients suffering from chronic kidney disease and with reduced renal perfusion, which is caused by dehydration, narrowing of the renal artery or hypotension.
Early signs of acute kidney failure are often minimal and short-lived:
- Circulatory collapse, an episode of acute heart failure in prerenal acute renal failure;
- Renal colic in postrenal acute renal failure;
- Acute gastroenteritis due to poisoning with salts of heavy metals;
- Local and infectious manifestations in multiple trauma.
- Many symptoms of the initial stage of acute renal failure (lack of appetite, weakness, drowsiness, nausea) are nonspecific. Therefore, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital use laboratory methods for early diagnosis of acute renal failure: determining the level of creatinine, potassium and urea in the blood.
- Signs of clinically developed acute renal failure include symptoms of loss of homeostatic renal function:
- Acute disturbances of the acid-base state and water-electrolyte metabolism;
- Increasing azotemia (increased nitrogen levels in the blood);
- Damage to the lungs, digestive organs, central nervous system (uremic intoxication);
- Acute fungal and bacterial infections.
Oliguria with urine output less than 500 ml is found in most patients with acute renal failure. In 3-10% of patients, anuric acute renal failure develops, in which diuresis is less than 50 ml per day. Oliguria and especially anuria can quickly be accompanied by symptoms of extracellular (cavitary and peripheral edema), then intracellular hyperhydration (edema of the brain, lungs, acute left ventricular failure).
The cardinal sign of acute renal failure is azotemia - an increase in the concentration of nitrogen in the blood. Its severity reflects the severity of acute renal failure. In acute renal failure, azotemia increases rapidly. In the non-catabolic form of acute renal failure, the daily increase in blood urea levels is 10-20 mg%, and creatinine increases by 0.5-1 mg%.
To treat postrenal acute renal failure, urologists eliminate the obstruction and restore normal urine passage. After this, postrenal acute renal failure is eliminated in most cases. If, despite restoration of ureteral patency, anuria persists, dialysis methods of therapy are used.
When prerenal acute renal failure is diagnosed, doctors direct efforts to eliminate the factors that caused acute vascular failure or hypovolemia, and discontinue medications that induce prerenal acute renal failure. To recover from shock and replenish the volume of circulating blood, large doses of corticosteroids, large-molecular dextrans (polyglucin, rheopolyglucin), plasma, and albumin solution are administered intravenously. In case of blood loss, red blood cells are transfused.
If the cause of acute renal failure is hyponatremia and dehydration, saline solutions are administered intravenously. All types of transfusion therapy are carried out by doctors in the intensive care unit under the control of diuresis and the level of central venous pressure. After stabilizing blood pressure and replenishing the intravascular bed, they switch to intravenous, long-term administration of furosemide with dopamine.
Nephrologists at the Yusupov Hospital treat renal acute renal failure in stages. With the development of oliguria in patients with urate crisis, multiple myeloma, hemolysis (decomposition of red blood cells), rhabdomyolysis, continuous long-term infusion alkalizing therapy is carried out. It includes the administration of mannitol with isotonic sodium chloride solution, glucose with furosemide and sodium bicarbonate. This therapy prevents intratubular deposition of cylinders and ensures the removal of free myoglobin, hemoglobin, and uric acid.
At the early stage of renal acute renal failure, during the first two to three days of the development of acute glomerular insufficiency, in the absence of complete anuria and hypercatabolism, treatment is carried out with furosemide, mannitol, and fluid infusion. Evidence of the effectiveness of conservative therapy is an increase in diuresis with a daily decrease in body weight by 0.25-0.5 kg. A patient’s weight loss of more than 0.8 kg/day, combined with an increase in the level of potassium in the blood, is an alarming sign of overhydration, which requires tightening the water regime.
For patients with some variants of renal acute renal failure, basic conservative therapy is supplemented with antibiotics, immunosuppressants, and plasmapheresis. If acute renal failure is caused by sepsis or toxic substances, hemosorption is used, which ensures the removal of toxins from the blood. Conservative therapy if there is no effect within 2-3 days is futile and dangerous due to the increased risk of complications from the use of large doses of furosemide (hearing impairment) and mannitol (hyperosmolarity, acute heart failure, hyperkalemia). In this case, dialysis treatment is used. In order to undergo treatment and examination of acute renal failure, call the contact center.