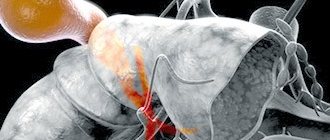
Cholecystitis is an inflammation of the gallbladder, accompanied by a violation of the outflow of bile. Gallstone disease, gallbladder dyskinesia, pathogenic bacteria and viruses, lamblia and roundworms can provoke such inflammation.
Treatment depends on the phase of the disease and is aimed at restoring normal functioning of the gallbladder and reducing inflammation. If treatment is not started on time, the inflammatory process will spread to adjacent organs.
Our expert will tell you in more detail about the most recommended and effective methods of treating cholecystitis: therapeutic nutrition, pharmacological agents, herbal medicine, physiotherapy, spa treatment and special physical education. These methods may help prevent the development of gallstones.
Diet therapy
This is the first and simplest method of correcting exacerbations of cholecystitis. The basic rules of nutrition for cholecystitis are as follows:
- split meals 5-6 times a day and unlimited fluid intake;
- mandatory breakfast and a light dinner 2-3 hours before bedtime.
This diet normalizes the flow of bile and leads to normal cholesterol metabolism.
The main diet is dietary table No. 5.
| Excluded: | Allowed: | Limited: |
| fried food | oatmeal and buckwheat porridge | legumes |
| butter | wheat and rye bread (yesterday's) | salt |
| smoked meats | lean meat | fresh fruits |
| fish and mushroom broths | steam cutlets | sweets |
| salo | boiled fish | cabbage |
| fat meat | cereal soups, milk soups | vegetable oil |
| sausages | broths are not strong | rich pastries |
| egg yolks | Vegetarian cabbage soup, borscht | |
| pickled products | cottage cheese, kefir, mild cheese | |
| alcoholic drinks | boiled and baked vegetables | |
| strong tea and coffee | cracker | |
| ice cream | vegetable juices | |
| chocolate | compotes, jelly, rosehip decoction | |
| confectionery | ||
| spices |
Dishes are steamed, boiled or baked. It is recommended to take food warm.
A therapeutic diet is not a panacea for cholecystitis, and only in combination with physiotherapeutic and drug treatment does it normalize the functioning of all digestive organs and the liver.
It is important
Three symptoms of chronic cholecystitis in adults
Medicines for cholecystitis
Only after an accurate diagnosis has been established, a gastroenterologist recommends comprehensive drug treatment. Taking medications relieves pain and eliminates symptoms of the disease.
Antispasmodics
Duspatalin. Photo: market.yandex.ru
This group of drugs helps to relax the spasmodic smooth muscles of the digestive organs.
To eliminate biliary dyskinesia and spastic pain, and reduce dyspeptic symptoms, the following are prescribed: Duspatalin, Neobutin, Sparex, Trimedat, Odeston.
Antispasmodics are taken 30-40 minutes before meals and drunk for 14-21 days.
show more
Antibiotics
Cefixime. Photo: market.yandex.ru
The basis of drug treatment of chronic cholecystitis is anti-inflammatory therapy. To achieve the best effect, antibiotics are combined with the use of pre- and probiotics.
Which antibiotic the doctor will prescribe depends on the cause of the disease and clinical manifestations.
Most often, gastroenterologists prescribe: Cefixime, Ceftriaxone, Amoxicillin, Clarithromycin.
The course of antibiotic therapy lasts from 10 to 14 days.
Diagnosis and treatment
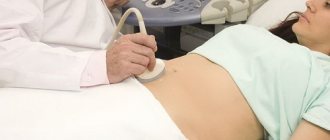
The symptoms of hepatic colic are similar to those of a number of other diseases. Therefore, an accurate diagnosis can be made only after the patient undergoes radiography and ultrasound examination of the liver and gallbladder.
Pain relief is achieved by taking antispasmodics and analgesics. Patients often combine it with the application of heat to the painful area of the body. And sometimes they try to get rid of pain with the help of choleretic drugs. If all this happens without the supervision of a doctor, the result is usually disastrous. Ordinary people do not have sufficient knowledge and experience to accurately diagnose the disease. And by self-medicating, they only put their body at risk.
It is necessary to combat hepatic colic and related diseases in a comprehensive manner. Medical gastroenterologists are ready to help you. Our specialists are leading practicing doctors in the Moscow region. They will quickly identify the disease and help neutralize it. For the convenience of patients, online registration is used. A flexible system of discounts is provided for regular clients of the clinic and patients from various social groups.
Spa treatment and balneotherapy
Sanatorium treatment is an important stage in the recovery of patients with diseases of the digestive system.
The effect of treatment outside the acute stage at a resort is higher than in a hospital. Natural healing factors (climate therapy, mineral waters, baths, mud therapy, therapeutic nutrition and physical exercise) have a beneficial effect on the functional state of the nervous system and bile secretion mechanisms, help restore immunity, normalize metabolism, and have an anti-inflammatory effect.
Balneotherapy - treatment with mineral waters - is a proven and effective method that corrects disorders of the digestive system.
When prescribing mineral waters, the state of the secretory function of the stomach must be taken into account. Bottled mineral waters are also successfully used - Essentuki, Slavyanovskaya, Smirnovskaya, Nagutskaya, Stelmas, Psyzh and others.
Essentuki. Photo: market.yandex.ru
Rinse the cup with hot water, then pour 1/3 glass of mineral water and slowly take it warm 25-40 minutes before meals.
On the recommendation of a gastroenterologist, tubage can be performed with mineral water with the addition of 20–25 g of xylitol or 1/2 teaspoon of Carlsbad salt. Mineral water is drunk in courses of 15-30 days.
show more
Psycho-emotional state of patients with gallbladder dyskinesia
Relevance: The classical works of I.P. Pavlov have proven strong mechanisms of connection between the two most important life-supporting systems of the body - the nervous and digestive. Diseases of the biliary system have not only medical, but also social significance: widespread among the young and working-age population, a pronounced impact on the quality of life, and large economic damage [4]. In recent decades, disturbances in psychoemotional status have been of great importance in the occurrence and development of diseases, especially pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract [5, 7]. Many studies have shown the involvement of the autonomic nervous system in individuals with gallbladder diseases. [3, 8]. Currently, one of the leading factors causing health problems is emotional stress with autonomic imbalance, which subsequently leads to the development of motor-tonic disorders of the biliary tract [1, 2,6]. Most patients with gastroenterological diseases have varying levels of reactive anxiety and need their correction. The level of anxiety acts as a central element in the formation of mental stress and is also one of the main psychological mechanisms of chronicity of somatic pathology. For successful treatment, it is necessary to take into account not only the somatic manifestations of the disease, but also the mental state of the patient, his attitude towards the disease. Many researchers consider gallbladder dyskinesia as a psychosomatic disease, in which the trigger is traumatic situations and deep-seated personal conflicts. The problem of psycho-emotional stress remains relevant for patients with diseases of the biliary system, and many treatment issues need clarification.
Purpose of the study : to study the state of psycho-emotional status in young people with gallbladder dyskinesia.
Materials and methods : A clinical and functional examination of 122 young patients with gallbladder dyskinesia was carried out, the average age was 25.1 ± 3.2 years, of which 43 were men, 79 women. The diagnosis of “Gall bladder dyskinesia” was verified in accordance with with the clinical classification of the Rome III consensus (2006).
Ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs was carried out using a LOGIQ P5 device with assessment of the shape, length and size of the walls of the gallbladder.
Gallbladder motility was assessed by the response to the choleretic stimulant, sorbitol. The dynamics of motor function are examined after 15, 30, 60 and 90 minutes; the volume of the gallbladder and the percentage of its emptying are determined.
The state of autonomic regulation in subjects with gallbladder dyskinesia was studied using the Valenta apparatus, according to the indicators of mode (Mo), mode amplitude (AMo), variation range (VR) and voltage index (TI).
The level of reactive anxiety was determined using the Spielberger-Khanin method: low level - up to 30 points, moderate - 31-44 points and high - more than 45 points.
Characteristics of the psycho-emotional state were carried out using the method of well-being, activity and mood according to the test - SAN (Doskin V. A., 1973).
One of the important components of assessing quality of life in medical research is the patient’s subjective assessment of the severity of symptoms of the disease. For this purpose, we used the method of types of attitude towards illness (TOBOL), proposed by the Research Institute named after. Bekhterev (1987) as modified by Wasserman L.I. (2001). The questionnaire includes 12 tables - sets. Each set contains from 10 to 16 statements offered to the test subject. When working with the questionnaire, the patient is offered the freedom to choose one or more (no more than 3) answers.
The control group consisted of 25 practically healthy individuals matched by gender and age without negative behavioral risk factors.
Statistical data analysis was carried out using standard software packages (Statistica for Windows 6.1, Russian version) for personal computers. Comparison of two independent samples was carried out using Student's t test for quantitative data with a normal distribution of indicator values or U - Mann-Whitney test for ordinal and quantitative data with a non-normal distribution of indicator values.
Study results : Analysis of risk factors for the development of gallbladder dyskinesia in young people revealed malnutrition in 114 (93.5%), food allergies in 1 (0.8%), low physical activity in 72 (59.1%), smoking in 59 (47.2%), alcohol consumption in 24 (19.7%), psychoemotional disorders in 67 (54.9%) and autonomic disorders in 59 (48.4%) subjects, which contributes to the development of motor-tonic disorders of the biliary tract.
According to the results of ultrasound examination, anomalies in the shape of the gallbladder were revealed in the form of an inflection in 57 (47.1%), S-shaped gallbladder in 6 (4.9%) and oval in 59 (48.7%) patients. The length of the gallbladder in 91 (93.3%) was within 78.5 ± 0.2 mm, in 31 (7.4%) - over 100 mm; The dimensions of the gallbladder walls in 82 (67.7%) were 1.9±0.2 mm, over 4 mm in 40 (33%) subjects. In the control group, 24 (96%) people had an oval-shaped gallbladder, and 1 (4%) person had an S-shaped gallbladder. The length and dimensions of the gallbladder walls in the control group were within the recommended standards.
When studying the motor function of the gallbladder in patients with dyskinesia, it was revealed that after 15 minutes, 50% emptying of the gallbladder was in 46 (37.7%) patients, after 30 minutes - in 74 (60.7%), after 45 minutes - in 79 (64.8%), within an hour in 83 (68.1%) and within 90 minutes in 120 (98.4%). Analysis of data on the motor function of the gallbladder showed that the hypertonic - hyperkinetic type was in 74 (60.7%) and the hypotonic - hypokinetic type in 48 (39.3%) of the subjects. In the control group (n = 25), a normotonic type of gallbladder was identified.
Table 1
Assessment of autonomic tone in patients with gallbladder dyskinesia and the control group
| Indicators of autonomic regulation | Control group ( n=25) | Types of gallbladder dyskinesias | |
| Hypertensive-hyperkinetic ( n = 74) | Hypotonic-hypokinetic (n = 48) | ||
| Mo, s | 0,75±0,1 | 1,1±0,2 | 0,59±0,1 |
| AMo, % | 35 | 24 | 52 |
| VR, s | 0,18±0,2 | 0,32±0,1 | 0,13±0,1 |
| IN, arb. units | 129,6±0,2 | 34,1±0,3 | 339,8±0,2 |
Analysis of heart rate variability, used to assess the state of the autonomic nervous system and the general adaptive reaction of the body of patients with gallbladder dyskinesia, showed that in 48 (39.3%) patients with the hypotonic-hypokinetic type, sympathicotonia predominated, which was expressed in a decrease in Mo and BP by 21.3% and 27.8%, an increase in AMO by 48.6% and a tension index by 162.7% compared to the control group. In 74 (60.7%) subjects with the hypertonic-hyperkinetic type of dyskinesia, vagotonia occurred, which was expressed in an increase in Mo by 46.7% and BP by 77.8%, a decrease in AMo by 31.4% and a tension index by 73. 3% compared to the control group (Table 1).
Concomitant psycho-emotional stress in patients with gallbladder dyskinesia leads to an increase in the level of reactive anxiety. A high level of anxiety acts as a cause and consequence of stress, is a destructive personality trait and adversely affects a person’s life activity and performance. Objective criteria are the severity of psycho-emotional stress and the type of its autonomic regulation. In patients with gallbladder dyskinesia of the hypertensive-hyperkinetic type, the high level of personal anxiety was 48.6±1.3 points, the average was 40.3±0.6 points and the low level was 27.2±0.5 points. The level of reactive anxiety was 51.3±0.6 points, 43.6±0.4 points and 29.5±0.7 points, respectively. In the hypotonic-hypokinetic type, the high level of personal anxiety was 47.2±0.5 points, the average 34.3±0.4 points and the low 25.6±0.2 points. High level of reactive anxiety 49.6±0.2 points, average 32.5±0.3 points and 26.3±0.3 points, respectively (Table 2)
table 2
Levels of personal and reactive anxiety in patients with gallbladder dyskinesia
| Anxiety levels | Control (n=25) | Hypertensive-hyperkinetic type (n = 74) | Hypotonic-hypokinetic type ( n = 48) | ||||
| Abs | % | Abs | % | Abs | % | ||
| Personality anxiety | High | 6 | 24 | 27 | 36,4 | 11 | 22,9 |
| Average | 15 | 60 | 38 | 51,3 | 29 | 60,4 | |
| Short | 4 | 16 | 9 | 12,2 | 8 | 16,6 | |
| Reactive anxiety | High | 4 | 16 | 26 | 35,1 | 14 | 28,8 |
| Average | 19 | 76 | 37 | 50,1 | 26 | 54,4 | |
| Short | 2 | 8 | 11 | 14,7 | 8 | 16,7 | |
When studying the level of “Well-being”, “Activity” and “Mood”, in patients with gallbladder dyskinesia, it was revealed that the number of points was lower in terms of well-being by 26.1%, activity - by 35.7% and mood - by 42 .6% compared to the control group (Table 3).
Table 3
Assessment of well-being, activity and mood in patients with gallbladder dyskinesia
| Characteristics of psycho-emotional state | Control group ( n =25) | Patients with gallbladder dyskinesia ( n=122) |
| Well-being | 5,4±0,3 | 4,4±0,3 |
| Activity | 5,6±0,2 | 4,6±0,2 |
| Mood | 6,1±0,2 | 4,5±0,2 |
A study of the psychological reaction of patients with gallbladder dyskinesia showed that 77 (63.2%) patients were diagnosed with block I types of attitude towards the disease: harmonious - 34 (27.9%), anosognosic - 39 (31.9%), ergopathic - 4(3.3%), which are characterized by satisfactory psychosocial adaptation of the patient in connection with the disease. A significant number of patients - 33 (26.9%) were of a mixed type: consistent - 15 (12.3%) and inconsistent - 18 (14.8%), which indicates the influence of the disease on the specific response. Types of attitude towards illness with intrapsychic (apathetic) - 6 (4.9%) and interpsychic (sensitive) - 6 (4.9%) psychological reactions were found with equal frequency.
Thus, in young people with gallbladder dyskinesia, the hypertensive-hyperkinetic type with a predominance of vagotonia is more common. They had a high level of personal and reactive anxiety and a lower level of SAN compared to the control group. When studying the types of attitudes towards the disease, block I was noted. Our data confirm the need to include a psychological study of the condition of patients with gallbladder dyskinesia in the examination complex, as well as the development of methods for correcting mental status. It is necessary to take into account the presence and nature of psychosomatic characteristics and, depending on them, apply comprehensive approaches to treatment. Underestimation of mental disorders significantly reduces the effectiveness of treatment.
Literature:
1. Aleksandrova V. A., Rykova S. V. Functional disorders of the biliary system in children - Attending physician. - 2008 No. 7#8 p.60.
2. Diseases of the liver and biliary tract. Guide for doctors. Ed. V. T. Ivashkina. M.: Publishing house. House "M-Vesti", 2005.
3. Grigoryan E. G., Harutyunyan V. M., Manucharyan G. G., Kazaryan N. K., Sarkisyan R. A. Autonomic-vascular and psycho-emotional disorders in certain diseases of the digestive system and their correction by physical factors.// Clinical medicine.-2001.-No. 10, pp. 35–38.
4. Ilchenko A. A. Pharmacotherapy for diseases of the gallbladder and biliary tract / A. A. Ilchenko M.: Med. Information agency, 2009.- 152 p.
5. Maev I.V. [et al.] Psychosomatic aspects of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract // Clinical medicine. - 2002. - Volume 80, N11. — P. 8–13. — ISSN 0023–2449.
6. Poborsky A. N., Yurina M. A., Lopatskaya Zh. N., Deryagina E. Yu./The level of anxiety and the state of autonomic regulation depending on the predicted examination grade in students living in unfavorable environmental conditions.// Physiology person - 2009. -Vol. 35, No. 4, pp. 28-33.
7. Rutgaiser Ya. M. Possibilities of using clinical and psychological methods in gastroenterology // Russian Journal of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, Coloproctology 1997.-No. 7 (6).-P. 38–45
8. Al-Homaindhi HS/Biliary diskinesia in children // Pediatr. Surg. Int.2002. Vol.18. No. 5–6. –P 357–360.
Phytotherapy
Herbal medicine for chronic acalculous cholecystitis can enhance the therapeutic effect of medications.
Medicinal plants are used in the form of infusions and decoctions, which gently, safely, and naturally improve bile secretion and have a beneficial effect in inflammatory diseases of the liver and gall bladder.
The following have a valuable effect on cholecystitis:
- sandy immortelle flowers,
- corn silk,
- peppermint herb,
- tansy flowers,
- elecampane root
- centaury grass,
- dandelion root,
- common yarrow herb,
- wild chicory root,
- dog-rose fruit,
- caraway seed,
- fragrant dill seed,
- lemon balm herb.
Herbal infusions and decoctions will help enhance the effect of medications. Photo: Pixabay
Freshly prepared infusions and decoctions are used ½ cup 30-40 minutes before meals. It is advisable to repeat herbal medicine courses 3 times a year, the duration of one course is from 30 days.
For the best effect, during herbal medicine for gallbladder diseases, it is recommended to give up coffee and strong tea.
show more
Functions of the liver and gallbladder
You may not think about your organ health until you experience pain or digestive problems. The gallbladder is very small by the standards of the rest of the body: it is pear-shaped and located in the upper right corner of the abdomen, under the liver. In fact, it is a storage facility for digestive fluid - bile. When you eat fatty foods, the liver produces bile, a thick, viscous yellow-green fluid that helps the body break down fats, absorb fat-soluble vitamins and some minerals, and synthesize and eliminate cholesterol .
It is synthesized in liver cells, flows down the ducts and accumulates in the gallbladder, and then is released into the small intestine through the common bile duct - common bile duct. Bile saponifies fats, breaking them into tiny droplets, which are absorbed by the intestinal wall and used by the body for various purposes. Without it, dietary fat is absorbed extremely poorly, remains in the intestinal lumen and forms “fatty” stool.
The gallbladder in our body has a strictly defined function - to store and store bile between meals, but we can live without it if it is damaged and needs to be removed. After its removal, natural discomfort occurs and a diet is required.
External lithotripsy
Using external shock wave lithotripsy, soft and small (up to 2.0 cm) stones can be crushed. The procedure is virtually painless, does not require anesthesia, you do not have to walk around with drains and worry about the healing of endoscopic or standard incisions.
Good to know
6 methods for treating gallstone disease in adults
For patients undergoing this procedure, surgical care must remain available for several months, since fragments of broken stone may take a long time to come out. For large stones or pathological changes in the gallbladder itself, the doctor recommends removing the gallbladder.
Risk group for cholecystitis
Not everyone develops cholecystitis and, even if a person’s nutrition is far from ideal, he can live with a healthy gallbladder all his life. There are risk factors that increase the chances of developing the disease.
- Genes. If your relatives suffered from cholecystitis, you are also at risk.
- Weight jumps. Both weight gain and weight loss are stressful for the body. Often this process is associated with changes in diet - strict diets or overeating, fasting or eating more fatty foods.
- Alcohol abuse.
- Diabetes types 1 and 2.
- Metabolic disorders.
- Taking COCs, especially between the ages of 30 and 45 years.
- Pregnancy and other hormonal changes.
- Other gastrointestinal diseases are Crohn's disease, cirrhosis and fatty liver hepatosis, congenital pathologies of the gallbladder.
- Helminthic infestations.
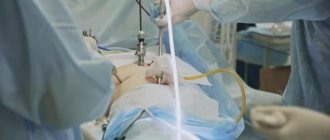
Surgery for cholecystitis
The only indication for emergency surgery within the next few hours from the moment the patient is admitted to the hospital is diffuse biliary peritonitis.
The majority of patients are operated on as planned after acute inflammatory phenomena have subsided. Because each subsequent attack can cause the development of acute cholecystitis with severe complications from the liver and pancreas.
Currently, most operations are performed endoscopically and are much easier for patients to tolerate. This minimally invasive technique has significantly reduced mortality and the number of postoperative complications.
Popular questions and answers
Our expert Elena Nilova , drawing on more than thirty years of experience in medicine, answered the most common questions.
Why does cholecystitis occur?
The occurrence of the disease is promoted by: ● disruption of the outflow of bile with damage to the mucous membrane of the bladder, ● volvulus of the gallbladder and bending of its neck, ● reflux of pancreatic enzymes, ● pinching of a stone in the neck of the bladder.
Acute inflammation of the gallbladder occurs when an infection enters the gallbladder (Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, staphylococcus, enterococcus, etc.).
How to stop an attack of cholecystitis before the ambulance arrives?
If you feel a paroxysmal dull aching pain in the right side of the abdomen right under the ribs, then you need to lie down in a comfortable position, after drinking sodium chloride mineral water without gas, and apply a cold compress to this area.
Is it possible to treat cholecystitis with folk remedies?
It can be treated, but it cannot be cured. Long-term treatment with herbs alone can lead to an exacerbation of the chronic inflammatory process and the activation of infection in the gallbladder. Traditional recipes can be used as an auxiliary therapy and only on the advice and under the supervision of a doctor.
Is it possible to cure cholecystitis forever?
Considering the variety of factors and complex mechanisms of development of biliary tract pathology, we can say for sure that if you undergo patient, long-term and consistent treatment, it is only possible to exclude exacerbations of cholecystitis. And if there is a genetic predisposition, then you will have to be constantly attentive to the state of the gastrointestinal tract.
How to avoid gallbladder inflammation?
Primary prevention of cholecystitis includes maintaining a healthy lifestyle, limiting alcohol intake and eliminating bad habits such as smoking and overeating.
It is imperative to lead an active lifestyle, undergo regular medical examinations, and avoid stressful situations. These rules seem easy to follow. But worldwide there is a steady increase in the number of gastrointestinal diseases. And every year the number of gall bladder operations and the number of postoperative complications are growing. Correct assessment of clinical symptoms, the use of modern diagnostics and the prescription of complex treatment can prevent the development of pathological processes in the digestive organs.
Symptoms of cholecystitis
There are two main forms of cholecystitis - acute and chronic.
Spicy
. If stones get into the bile ducts, a blockage occurs, the organ tissues are damaged by bile and inflammation develops. Everything happens quickly. Often, a person with biliary colic is taken straight to the emergency room to have the gallbladder removed.
Symptoms: severe sharp pain in the area where the organ is located (on the right, in the liver area), nausea and vomiting, constipation, increased body temperature, fever, yellowness of the eyes.
Chronic cholecystitis
. It develops slowly and often unnoticed by the patient. The pain may be unobtrusive and only intensify if you eat a large amount of heavy food or are in a serious stressful situation.
Symptoms: dull pain in the organ area, heaviness and poor digestion, bitter taste in the mouth, nausea, bloating, constipation, low-grade body temperature (37*C).
If you notice the symptoms listed above, hurry up and see a doctor before it becomes a severe attack.
!Never use the tubage method (warming the liver with lemon juice and oil) to treat or prevent disease. This may result in the removal of the gallbladder.