What kind of disease is this
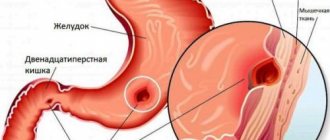
An esophageal diverticulum is an unpleasant defect caused by a limited protrusion of the mucous membrane. The defect looks like a pouch on the outer wall of the esophagus. Pathology can form in any area of the digestive organ, but mainly appears in the chest.
In most cases, a single location of the diverticulum is visible, but it happens that there are several defects on the wall at once. Diverticula are classified into types:
- Traction - characterized by an inflammatory process of surrounding tissues, pulling the walls of the esophagus towards the lesion.
- Pulsion - caused by the formation of a defect as a result of intra-food pressure that occurs during contraction of the esophagus.
Initially, the mechanism of diverticulum development is characterized by traction factors, then by pulsion factors. Sometimes the two types combine, and a traction-pulsion diverticulum appears. Esophageal diverticulum can be congenital or acquired. The birth defect is associated with weakness in the muscular wall of the esophagus. Formed inside the mother's womb. It may not bother the patient for many years. If a person is relatively healthy, then the diverticulum does not manifest itself in any way. If the patient experiences inflammatory processes in the digestive system, an exacerbation of the diverticulum may occur.
The acquired defect is associated with various pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract and other organs:
- chronic inflammation in the mediastinum;
- histoplasmosis (fungal infection of the lungs);
- pathologies of the lymph nodes;
- pulmonary tuberculosis;
- pathology of the duodenum;
- esophageal injuries;
- condition after surgery;
- chemical burn of the esophagus;
- motor dysfunction;
- other inflammations of the digestive system.
According to the type of structure, diverticula are classified as true and false. True ones consist of layers of the esophageal wall, and pseudodiverticula (false) do not have a muscular membrane. They appear at the moment of contraction of the esophageal wall, and at the moment of relaxation they disappear.
Sources
- Samanta J., Mandavdhare HS., Kumar N., Kumar-M P., Jafra A., Chauhan R., Gupta P., Kumar KH., Singh H., Dutta U., Kochhar R. Per Oral Endoscopic Myotomy for the Management of Large Esophageal Diverticula (D-POEM): Safe and Effective Modality for Complete Septotomy. // Dysphagia - 2022 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33533970
- Miutescu B.P., Khan S., Mony S., Khashab M.A. Role of Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy (POEM) in the Management of Esophageal Diverticula. // Clin Endosc - 2022 - Vol53 - N6 - p.646-651; PMID:33238358
- Gupta V., Darling G. Commentary: Measure Twice, Cut Once: Understanding the Anatomy and Physiology of Esophageal Epiphrenic Diverticula Guides Optimal Surgical Management. // Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg - 2022 - Vol33 - N1 - p.249-250; PMID:33171244
- Kamal F., Khan MA., Lee-Smith W., Sharma S., Marella HK., Iqbal U., McDonough S., Aslam A., Ismail MK., Tombazzi C., Adler DG. Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy Is a Safe and Feasible Option in the Management of Esophageal Diverticula: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. // Dig Dis Sci - 2022 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33123940
- Demeter M., Ďuriček M., Vorčák M., Hyrdel R., Kunda R., Bánovčin P. S-POEM in treatment of achalasia and esophageal epiphrenic diverticula - single center experience. // Scand J Gastroenterol - 2022 - Vol55 - N4 - p.509-514; PMID:32251609
- Basile P., Gonzalez JM., Le Mouel JP., Irarrazaval R., Caillo L., Barthet M. Per-oral endoscopic myotomy with septotomy for the treatment of distal esophageal diverticula (D-POEM). // Surg Endosc - 2022 - Vol34 - N5 - p.2321-2325; PMID:32144556
- Jacobs C., Draganov PV., Yang D. Two birds, one scope: peroral endoscopic myotomy as a treatment for achalasia and esophageal diverticula. // Endoscopy - 2022 - Vol52 - N2 - p.153; PMID:31991470
- Maydeo A., Patil GK., Dalal A. Operative technical tricks and 12-month outcomes of diverticular peroral endoscopic myotomy (D-POEM) in patients with symptomatic esophageal diverticula. // Endoscopy - 2022 - Vol51 - N12 - p.1136-1140; PMID:31614371
- Liu XY., Li QL., Jiao TW., Sun MJ., Zhou PH. Peroral endoscopic myotomy regains anatomical structure and improves emptying for achalasia with multiple esophageal diverticula. // Endoscopy - 2019 - Vol51 - N12 - p.E392-E393; PMID:31344726
- Sivanes S., Chang J. Gastrointestinal: A rare cause of upper gastrointestinal bleeding: Epiphrenic esophageal diverticula. // J Gastroenterol Hepatol - 2022 - Vol35 - N10 - p.1665; PMID:31273838
Symptoms
Symptoms of esophageal diverticulum manifest differently, depending on the location of the defect. If a diverticulum grows in the upper part of the esophagus, then it is characterized by the following symptoms:
- swallowing disorder (dysphagia);
- regurgitation of undigested food;
- dry cough;
- soreness or lump in the throat;
- nausea;
- voice change;
- increased salivation.
Signs of a diverticulum located in the middle part:
- chest pain;
- night cough;
- dysphagia;
- nausea and belching.
- Moreover, small diverticula are asymptomatic, while large defects are manifested by the above symptoms.
- Signs of a diverticulum located in the lower part:
- cardiopalmus;
- reflex shortness of breath;
- bronchospasm;
- heart pain.
These symptoms are supplemented by signs of a middle location of the defect.
Features of the esophagus affecting the course of diverticulitis
The upper boundary of the thoracic section of the esophageal tube is the conventional line of the second thoracic vertebra from the posterior mediastinum (the space surrounding the heart). The lower one coincides with the esophageal opening of the diaphragm. The entire segment is 16–18 cm long in an adult. It is separated from the spine by a thin layer of fatty tissue.
It is in close contact with the inner layer of the pleura (mediastinal region). Passing from top to bottom, the esophagus is first located to the left of the trachea, then passes the area of the aorta and azygos vein, at the level of the fourth thoracic vertebra, located next to the left main bronchus and the bifurcation of the trachea.
Here, the left atrium of the heart and the pericardial wall, the aortic arch, and the subclavian artery are adjacent to the esophagus in front. Along its entire course, the esophagus is accompanied by the recurrent nerve and multiple groups of lymph nodes. The close proximity to important organs of the chest leads to their damage due to diverticula of the esophagus.
Which doctor should I contact?
If the described symptoms occur, you need to urgently make an appointment with a gastroenterologist. Our gastroenterologists are true professionals. They will listen to your complaints, conduct an examination, and prescribe therapy. At the Kuntsevskaya clinic you will receive truly qualified assistance.
IMPORTANT! Esophageal diverticulum is a dangerous disease that requires careful medical supervision and control. Often the diverticulum does not manifest itself for a long time.
However, if a person experiences symptoms of esophageal diverticulum, it is imperative to consult a gastroenterologist. Make an appointment with a gastroenterologist at the Kuntsevo Medical and Rehabilitation Center, who will conduct a full diagnosis and prescribe a complete detailed treatment plan for the person. This is followed by the rehabilitation phase, during which you will also be accompanied by our gastroenterologist.
Sign up
Diverticulum diagnosis – accuracy within 3 days
A comprehensive diagnosis of esophageal diverticulum in most Israeli clinics takes from 3 to 4 days. During this time, the patient undergoes all tests and receives an individual treatment program.
- Day 1
- Day 2
- Day 3
First day – arrival in the country
During the first day, the patient, accompanied by a curator, goes from the airport to the hotel, is accommodated in it and arrives at the hospital for the first consultation with a leading specialist. The doctor examines the medical history and prescribes a number of necessary tests.
Day two – diagnostics
During the second day, a diagnostic program is carried out. It usually includes the following studies:
- radiographic examination using barium contrast. This diagnostic method is the most common and accurate when examining patients with suspected diverticulum;
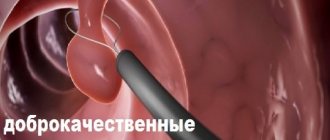
- endoscopic examination can also be effectively used in the diagnosis of medium and large diverticula. A flexible endoscope with a miniature camera at one end is inserted into the esophagus. Using this camera, the surgeon examines the condition of the mucous membrane and walls of the esophagus on a computer screen.
- Esophageal manometry is a study of the contractile activity of the esophagus, allowing one to measure the pressure in its lumen.
Third day – treatment program
On the third day, a medical council analyzes the diagnostic results and determines the final diagnosis. On the same day, an individual treatment program is developed - when drawing it up, doctors take into account the patient’s condition, his age, the presence of concomitant diseases, etc.
Diagnostics
During the examination, the doctor will ask the patient about the signs of the disease - when the symptoms began and how they manifest themselves. The patient then undergoes blood and urine tests. Of the instrumental methods, the most effective is gastroscopy. But in this case, it is important to undergo a study under the guidance of an experienced doctor, since you need to do the procedure carefully so as not to hurt the diverticulum.
The Kuntsevo Medical Center uses Japanese endoscopes of the latest generation, with an ultra-thin tube. In addition, the gastroenterologist who will perform the procedure is an experienced doctor who has performed the procedure more than once. The doctor irrigates the patient's mouth with an anesthetic solution and inserts a cable into the esophagus. The entire process is displayed on the monitor screen. The location of the diverticulum, its size and other subtleties are visible.
If the patient turns out to be hypersensitive, then anesthesia is used and gastroscopy is performed “in sleep”. So the patient will not feel anything.
In addition, magnetic resonance imaging of the esophagus is used. The diverticulum is examined in all projections.
Treatment
Esophageal diverticulum should be treated based on the causes of the disease and the characteristics of the patient. First, we eliminate the factors that led to the development of the disease. Then we look at how much the defect interferes with everyday life. If the diverticulum is small and does not manifest itself in any way, then we do not touch it. You just need to stick to a diet so as not to provoke a “bag”, and constantly be monitored by a specialist.
If the diverticulum is large and causes discomfort, it is removed and the walls of the esophagus are sutured. There is a possibility that the defect will form again if the root cause is not eliminated. Therefore, it is necessary to visit your doctor.
The diet should be based on the exclusion of fried, salty, heavy foods. After a meal, be sure to drink a glass of warm water and spray your mouth with a weak antiseptic solution. Maintain temperature conditions - food and drink should be warm. Drug therapy is used in case of inflammation of the digestive system. Painkillers, anti-inflammatory, and antibacterial drugs are prescribed. It all depends on the concomitant disease.
Diverticula of the lower third of the esophagus
Drug treatment of such patients should be aimed at slowing the growth rate of the diverticulum and preventing its complications. In this regard, it is necessary, if possible, to eliminate or at least level out concomitant diseases of the esophagus that can cause degenerative changes in its wall and increase intraesophageal pressure (idiopathic dyskinesias, achalasia cardia, reflux esophagitis).
It is possible to prevent the development of some complications by prescribing an appropriate diet (esophageal diet) and periodic sanitation of the diverticulum cavity.
- Surgery
The choice of treatment method for esophageal diverticula depends on their location, size, clinical features, and the presence of various complications.
For small sizes of the pharyngoesophageal diverticulum (stage I), drug treatment is indicated. In the II and especially III stages of the disease, in the presence of severe dysphagia, stagnation of food masses in the cavity of the diverticulum, accompanied by symptoms of diverticulitis, surgical treatment is indicated, which gives a complete cure in the vast majority of patients.
The operation is performed from the cervical approach. The incision is made at the site of the projection of the anterior edge of the left sternocleidomastoid muscle. The left lobe of the thyroid gland is mobilized, retracting it medially, and the neurovascular bundle - laterally. The diverticulum is carefully isolated from the surrounding tissues up to the neck. The most radical operation is diverticulectomy. In this case, the neck of the diverticulum is sutured with a catgut suture on an atraumatic needle or using stitching devices (USL-25, UKL-40), and the diverticulum is removed. After this, the defect in the muscular lining of the esophagus is sutured with separate non-absorbable sutures.
Less radical interventions are diverticulopexy and invagination of the diverticulum into the lumen of the esophagus, followed by strengthening its muscular membrane with separate sutures. Such operations are used more often when the diverticulum is small and there is a high risk of surgical intervention.
In recent years, reports have appeared in foreign literature about the important role of achalasia of the cricopharyngeal part of the inferior pharyngeal constrictor and spasm of the upper esophagus in the occurrence of esophagopharyngeal diverticula. Based on this, it was proposed to transect this part of the muscle with simultaneous diverticulectomy. In addition, some surgeons use longitudinal subdiverticular myotomy over 3-4 cm to eliminate spasm. Apparently, in a number of cases such tactics are quite justified.
Due to the fact that epibronchial diverticula are tractional in nature, are easily emptied of food that has entered their lumen and rarely reach large sizes, conservative treatment is most appropriate for this disease. In case of severe clinical symptoms (primarily dysphagia), failure of drug treatment, development of complications (esophageal-bronchial, esophageal-pleural, esophageal-pericardial fistulas, bleeding, abscess formation in the diverticulum cavity, malignancy), surgical treatment is indicated.
The surgical approach is a right thoracotomy in the fifth-sixth intercostal space. The optimal volume of intervention is diverticulectomy with suturing of the defect in the muscular lining of the esophagus. When the diverticulum is small, invagination into the lumen of the esophagus is used. When internal fistulas form, diverticulectomy is performed in combination with various operations on neighboring organs.
Indications for surgery for epiphrenal diverticula (which by their nature are often pulsational) are the same as for pharyngoesophageal diverticula. It should be noted that in a number of patients epiphrenic diverticula are combined with achalasia of the esophagus, hiatal hernia, and chronic reflux esophagitis. In this regard, taking into account the characteristics of the clinical picture of the disease and the data of preoperative instrumental examination, diverticulectomy is performed in combination with surgery for concomitant disease of the esophagus.
The most appropriate access in these conditions is a left-sided thoracotomy, which allows for synchronous surgical interventions. The optimal volume of intervention is diverticulectomy. Invagination of the diverticulum into the lumen of the esophagus and diverticulopexy, which prevents food masses from entering the diverticulum cavity, are used much less frequently. Surgical interventions for concomitant hiatal hernias, reflux esophagitis, and esophageal achalasia are performed according to generally accepted principles.
The prognosis for surgical treatment of esophageal diverticula is favorable. Mortality, according to domestic and foreign statistics, averages 1-3%. If the neck of the diverticulum is insufficiently excised, a number of patients experience relapses of the disease. In case of excessive excision of the mucous membrane of the esophagus in the area of its neck during diverticulectomy, tissue swelling with symptoms of dysphagia often occurs. If during the main stage of the operation no corrective intervention is performed for the above-mentioned concomitant diseases of the esophagus, most patients will continue to have the complaints that existed before the operation, which can be regarded as the ineffectiveness of the surgical procedure. In this regard, a thorough analysis of the patient’s complaints, as well as instrumental examination data before surgery, and determination of the optimal volume of the planned surgical intervention is necessary.
Treatment results and lifestyle after recovery
The effectiveness of treatment will depend on how well the patient follows the points of the therapeutic program. An esophageal diverticulum is like a time bomb; anything can happen. Therefore, after treatment, strictly follow the recommendations of the gastroenterologist. Visit a specialist from time to time.
Learn a few rules for yourself:
- walk more in the fresh air;
- follow a diet;
- establish a work and rest schedule;
- get rid of bad habits;
- play sports.
We are talking about light exercises. Kuntsevo has its own exercise therapy room. Under the guidance of experienced instructors, do gentle exercises.
What complications does diverticulitis cause?
Inflammation of the diverticulum over a long period of time can lead to:
Hiatus hernia
- to attacks of suffocation;
- phlegmon of the neck;
- chronic bronchitis;
- aspiration pneumonia, lung abscess;
- bleeding;
- abscess formation of a diverticulum;
- mucosal erosion;
- perforation into surrounding tissues;
- mediastinitis with esophageal-mediastinal fistula;
- esophageal polyps;
- cancerous degeneration.
Bifurcation diverticulitis has the rarest tendency to complications.
Why is it better to seek treatment from us?
Early detection of esophageal diverticulum and a complete assessment of the risk of the disease for a particular patient allows doctors at the Kuntsevo Treatment and Rehabilitation Center to fully assess the person’s condition and choose the most effective treatment tactics in each individual case. In addition, modern diagnostic methods available at the Kuntsevo Treatment and Rehabilitation Center (gastroscopy, MRI of the esophagus, MRI of the esophagus “in sleep”) allow the doctor to monitor the patient’s dynamics, evaluate the effectiveness of therapy and make changes to speed up the person’s recovery process.
IMPORTANT! You should not self-medicate if you discover this symptom. Cold hands can be a manifestation of both the physiological norm of your body and a pathological process that develops in the body.
The Kuntsevo Multidisciplinary Center has doctors of the highest category and doctors of medical sciences. Using modern equipment and high-tech devices, diagnosing esophageal diverticulum has become easier and more effective. You will be pleasantly surprised by the best prices and friendly staff. Don't delay treatment - make an appointment!
The contents of this article have been checked and confirmed for compliance with medical standards by gastroenterologist-nutritionist Tatyana Vladimirovna Lucheninova