Scientists have long associated many diseases with the mental instability of patients, their low resistance to stress, and their tendency to depression.
The only debate is about how great the contribution of a labile psyche is to the development of a particular disease. Gastritis is a disease that is greatly influenced by the patient’s psycho-emotional state . Even the type of gastric juice secretion partly depends on the emotional factor.
Disputes about the psychosomatics of gastritis
Since ancient times, the influence of psychological state on the development of diseases and the speed of recovery of patients has been known. However, for a long time, scientists assigned emotions only the place of one of the risk factors, which can aggravate the course of the disease, but do not become the main cause of its occurrence.
Nowadays, medicine has accumulated enough data on the occurrence of certain pathological conditions under the influence of depression or stress.
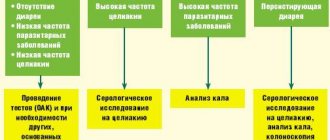
The main cause of chronic gastritis is the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. However, according to statistics, among 6 patients infected with it, only one develops the disease.
In addition, there are cases of spontaneous healing of ulcers and erosions, which occurred without adequate treatment against the background of high acidity levels.
These phenomena can be explained from the perspective of psychosomatics: in a patient with a stable psyche and a positive attitude, regeneration processes are more active and protective factors are stronger.
Experiences, anxiety, psycho-emotional overload, unresolved problems do not find an adequate way out and are realized in the form of a disease. Moreover, not only the gastrointestinal tract can be affected, but also the cardiovascular, endocrine, musculoskeletal, and respiratory systems. The part of the body through which negative energy will be released is determined by a combination of risk factors and heredity.
Historical reference . The first generally recognized psychosomatic diseases were called the “Chicago Seven”. The American doctor Franz Alexander classified bronchial asthma, peptic ulcer disease, ulcerative colitis, rheumatoid arthritis, hypertension, hyperthyroidism, and neurodermatitis into this category. Over time, the list was expanded to include diseases such as gastritis, diabetes, myocardial infarction and even cancer.
Ways to Heal
Whatever the nature of gastritis, healing should begin with simple and often difficult to follow rules:
- reduce the amount of alcohol consumed as much as possible;
- quit smoking and other similar addictions;
- make time for the pool, as it is very relaxing and relieves stress; in addition, you can choose dancing, yoga or any sport;
- establish a daily routine, and especially a rest routine;
- Walk more and get positive emotions.
Positive emotions are the best medicine
Moreover, the choice of how and where to get these most positive emotions depends only on you. Many psychologists advise getting a pet that can give non-judgmental love and acceptance. You can take up a hobby, expand your social circle, switch to new events, watch performances or visit exhibitions.
The main thing is to understand what you want and allow yourself to do it, rejoicing and having fun.
How does psychosomatic gastritis develop?
The influence of the patient’s state of mind on the functioning of the stomach is associated with several factors:
- In a stressful situation, adrenal hormones are actively produced , designed to mobilize all the body’s forces to fight. However, one of the effects of excessive concentration of these hormones in the bloodstream is the formation of ulcers and erosions of the gastric mucosa. Against the background of chronic stress, the risk of ulcer formation increases significantly, and formed erosions are difficult to treat.
- The digestive system has extensive innervation - 100 million nerve cells interconnected by numerous fibers. This is the metasympathetic (enteric) nervous system. In medical literature it is even called the “second brain.” It is believed that while the brain is responsible for thoughts, the abdominal brain is responsible for emotions. That is why he is so sensitive to changes in psychological background. For example, prolonged stress causes spasms of the smooth muscles of the stomach, which leads to a decrease in blood flow in the mucosa, and then to its atrophy.
- A pathological reaction to unfavorable conditions – the habit of “eating” stress – also contributes to disruption of the digestive tract. The stomach cannot cope with the increased load, as a result of which its motility and secretion suffer, and an inflammatory reaction develops.
Often problems with the gastrointestinal tract begin with a disorder of the nervous system
Here is a typical situation: two people eat the same thing, but one is completely healthy, and the other has a duodenal ulcer and Helicobacter pylori infection. Why is that? It turns out that diseases of the digestive system almost always begin with a nervous disorder.
The famous pathophysiologist Hans Selye created long-term stressful nervous tension in healthy rats in various ways and always received ulcers of the digestive tract . Roughly speaking, the nervous system simply “forgot” to control digestion during stress. This happened under stress of absolutely any nature (mental, temperature, traumatic stress, etc.).
Stages of the disease from the perspective of psychosomatics
Gastritis against the background of mental disorders does not occur overnight; it takes time to fully manifest. Pathological changes in the body go through three stages:
- Conversion disorder is the presence of symptoms that are not supported by any abnormalities in the physiology or anatomy of the organ. For example, a patient is bothered by nausea and vomiting, but examination does not reveal any changes in the gastric mucosa, and even his motility does not suffer.
- Functional syndromes are characterized by dysfunction of an organ in the absence of changes in its structure. For example, according to gastroscopy, there is no pathology in the gastric wall, but the evacuation of food into the duodenum is impaired.
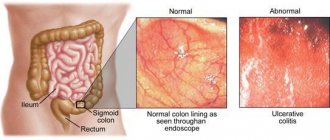
- Actually, psychosomatic illness is associated with a violation of both the anatomy and physiology of the organ. In this case, FGDS in the stomach can reveal a variety of changes - from mucosal atrophy to multiple erosions.
The pathological process can be stopped at any stage, but this requires adequate treatment. And a patient who usually does not advertise his psychological problems does not receive competent help.
In the video, a hypnotherapist will tell you what psychological causes most often cause gastritis.
Types of food pathology
Bulimia nervosa has different forms of manifestation, but has a common pattern of eating behavior: periods of uncontrolled food intake alternate with periods of active weight loss. Overeating (hyperphagia) can be:
- paroxysmal;
- permanent nature;
- at night.
A bulimic is unable to independently control outbreaks of irresistible hunger. When starting to eat, a person is unable to stop on his own until he clearly feels pain in the stomach and nausea.
People suffering from bulimia are more concerned about their figure than others. After another attack, they usually feel depressed due to guilt and remorse after what happened. Therefore, patients try in any way to avoid weight gain. For this reason, bulimia is divided into two types:
- classic nervous (cleansing ). She is characterized by a constant preoccupation with food and a desire to consume it in repeated episodes. Getting rid of hyperphagia involves taking drugs that have diuretic and laxative properties, forced gastric emptying (vomiting), and enema;
- compulsive _ Its peculiarity is that uncontrolled preoccupation with food is accompanied by careful monitoring of body weight. This type is characterized by other drastic measures for weight loss - exhausting mono-diets, additional physical activity, conscious fasting. At the same time, bulimics do not rid themselves of what they eat artificially. At a certain point, a person breaks down and begins to absorb food in even greater quantities.
Experts have identified so-called atypical kinorexia . This subtype has much in common with the classic form of eating disorder. However, an incomplete picture of the clinical manifestations required for a given mental pathology does not provide grounds for a doctor to determine a final diagnosis. The reason for this is an insufficient number of key symptoms of the disease. For example, after overeating and subsequent forced rejection of food, there is a complete absence of concern about being overweight and the desire to have ideal shapes.
Psychosomatics for different types of gastritis
It is believed that different negative emotions have different effects on the functioning of the stomach.
Hyperacid gastritis usually develops in people with a hypertrophied sense of responsibility, who tend to blame themselves for all failures. This applies, in particular, to workers who are responsible for the life and health of people: pilots, machinists, air traffic controllers, rescuers, doctors. They are characterized by increased anxiety and internal tension, even if it does not manifest itself externally.
Hypoacid gastritis affects dependent, driven patients who do not want to be responsible for their lives and their actions, but prefer to simply go with the flow, relying on circumstances and the people around them. Against the background of infantility and lack of initiative, the functional activity of the digestive tract also decreases.
Gastritis with a normal level of acidity is typical for active, versatile people who have a lot of hobbies and interests. Despite the fact that such individuals usually achieve success in all endeavors, sometimes this burden turns out to be too heavy for them and the disease develops even against the background of positive emotions.
Peculiarities. This type of gastritis is typical for teenagers who are looking for themselves in life, quickly change hobbies, communicate in different companies and receive a huge amount of new information every day. That is why parents need to pay attention to the activities of their son or daughter and make sure that they do not overload themselves. For the same reason, it is not recommended to enroll children in five clubs and English language courses at once - everything is good in moderation.
Causes
The basis of the disease is a complex of causes that are biopsychosocial in nature. The consciousness of modern man is influenced by many factors: social, biological, cultural. By promoting certain ideals of beauty, the media programs the population to conform to them. The general situation is aggravated by public opinion and advertising campaigns.
This eating disorder, like any other mental disorder, has both biological and psychological background.
Biological factors in the occurrence of the disease include disruption of the normal functioning of the brain. These include organic damage in the area of the brain center responsible for human nutritional activity, as well as disruption of metabolic processes occurring in the body. Bulimia can also be triggered by traumatic brain injury, brain tumors, or hormonal imbalance that results in disruption of the normal functioning of the pituitary gland or hypothalamus.
The causes of psychological illness are more varied, but they are more difficult to detect. These include:
- emotional stress over a long period of time;
- neuroses of various types;
- low self-esteem;
- depressive states;
- increased anxiety or obsessive mental disorders;
- tendency to heredity.
Bulimia nervosa can develop against the background of excessive enthusiasm for all kinds of diets. Limiting oneself for a long time in favorite foods, after finishing such a “poor” diet, a person literally pounces on food.
Children and adolescents from wealthy families are most susceptible to kinorexia. The high demands that parents place on them lead to the child’s loss of personal self-esteem and its underestimation. Gradually, the still unformed personality begins to “eat up” the lack of warmth and affection from loved ones. At the same time, as already mentioned, an important role is played by the media, which promote standard beauty.
The child, realizing that he eats too much and can no longer refuse it, feverishly begins to look for ways to consume an incommensurate amount of food, but at the same time not lose weight.
It is characteristic that in those countries where excessive “boning” is not considered a standard of beauty, bulimia, as a mental pathology, is very rare.
Louise Hay's theory
Psychotherapist from the USA Louise Hay believes that all diseases are psychosomatic in nature. They need to be treated, first of all, by influencing the spiritual component. Certain negative emotions lead to a specific disease or symptom. According to Louise Hay, uncertainty and doom lead to the development of gastritis.
The American has developed a system of affirmations that are aimed at treating a specific disease. You need to say them every day, in the morning, to set the right mood for the whole day. An affirmation for correcting gastritis sounds like this: “I love and approve of myself. I'm safe".
For convenience, Louise systematized the data and compiled a table in which the first column contains the name of the disease or symptom, the second - the negative emotions that cause it, the third - healing affirmations.
Clinical manifestations
When the mucous membrane becomes inflamed, the fundic glands, in which hydrochloric acid is synthesized, are affected. As a result, the acidity of the stomach either increases or decreases significantly.
Symptoms of hyperacid gastritis:
- pain in the upper abdomen (often on an empty stomach);
- heartburn;
- belching with a sour taste.
Symptoms of hypoacid gastritis:
- bloating (due to increased gas production);
- rumbling in the stomach;
- decreased appetite;
- belching of air (often with an unpleasant odor);
- pain syndrome (usually localized in the epigastric region);
- intestinal disorders (diarrhea).
Features of treatment
If there is a suspicion that gastritis is caused by mental discomfort, the patient is referred for consultation to a psychotherapist or psychiatrist. The specialist makes a conclusion about the presence and type of mental disorders.
With the proven psychosomatic nature of gastritis, psychotherapeutic assistance comes to the fore. It is based on the following areas:
- general calming effect on the patient;
- normalization of his mood;
- formation in the mind of the correct picture of the disease;
- the patient's mood for a positive result of therapy.
However, if, against the background of the psychosomatic component, other factors are identified that provoke the development of inflammation - increased acidity, the presence of reflux, H. pylori, then their treatment cannot be neglected.
Eradication therapy is carried out in full, medications are prescribed that reduce the secretion of hydrochloric acid and normalize the motility of the digestive tract.
Standard therapy, on the recommendation of a psychiatrist, is supplemented with sedatives, anti-anxiety drugs, and antidepressants.
Socrates once said: “It is wrong to treat eyes without a head, a head without a body, just as a body without a soul.” The spiritual and physical principles in every person are inseparable. It is impossible to eliminate individual symptoms of a disease without looking into its essence.
That is why, in cases where gastritis is difficult to treat or its occurrence cannot be explained by standard reasons, this is a reason to suspect the psychosomatic nature of the inflammation. Indeed, in the modern rhythm of life, maintaining emotional balance can be very difficult.