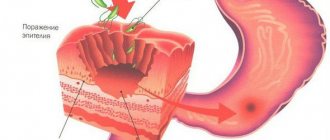
Superficial bulbitis is a disease of the duodenum with minor inflammation. The pathology has characteristic symptoms of gastritis and should be treated with adequate therapy. Superficial type bulbitis is easy to treat, so timely diagnosis allows you to completely restore the functioning of the digestive system and prevent the development of serious consequences.
Root Causes
This form of the disease is both chronic and acute in nature. Often, bulbitis occurs due to ulcerative pathologies. The acute form of the pathology occurs as a result of improper and unregulated nutrition, food poisoning, and regular exposure to alcohol. Also, one of the predisposing factors is damage to the duodenal mucosa by a foreign body.
The chronic form develops as primary and secondary forms of the disease. The precursors of a chronic primary disease are regular stress that the body experiences, problems with eating habits, and abuse of spicy foods.
Secondary bulbitis of a chronic nature can occur as a result of a pre-existing disease - chronic gastritis, ulcers or infection. Almost 70% of this pathology occurs when Helicobacter is activated. Infection most often occurs when the patient has antral gastritis. This is explained by the fact that the patient’s body begins to intensively produce pepsin, a violation of the integrity of the mucous bulb occurs, followed by the penetration of bacteria from the intestines.
An equally important cause remains short bowel syndrome. Occurs as a postoperative consequence during intestinal resection. The lack of sufficient amounts of essential substances that can regulate gastrin leads to increased inflammation.
Experts pay attention to the speed of movement of the food bolus through the intestines, since this is also an important factor in the development of primary bulbitis.
Characteristics of diseases
Superficial gastritis is an initial stage disease that can subsequently develop into an ulcer. During illness, the glandular epithelium of the stomach becomes inflamed and changes. Basically, the disease occurs against the background of other disorders, often called concomitant.
Bulbit affects and inflames the most important organ of digestion (duodenum, directly the bulb). It is considered a type of duodenitis.
Disease bulbitis
How to identify a superficial, just beginning bulbitis?
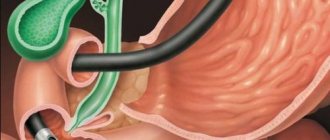
The pathology at the initial stages has mild clinical symptoms. The presence of the above complaints may correspond to several diseases of the digestive system. In order to verify the diagnosis, the patient is comprehensively examined. The doctor prescribes blood and urine tests and an ECG. The main method of examination is fibrogastroduodenoscopy (FGDS).
The condition of the mucous membrane of the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum is visually assessed, after which the doctor writes a conclusion based on the endoscopic picture. Radiation diagnostic methods (ultrasound and fluoroscopy) do not provide the necessary information about morphological changes in the duodenum at the initial stages of inflammation. They are used to study the motor function of the gastroduodenal zone.
What is superficial bulbitis from an endoscopy point of view? Examination of the mucous membrane of the duodenum on FGDS in the superficial form of the disease reveals a heterogeneous state of the tissues. Inflammation appears as swollen areas and alternates with intact intestinal lining. Foci of plethora (hyperemia) up to 0.2-0.3 cm in size appear above the altered areas of the mucosa. Physiological folds at the level of inflammation are slightly increased in volume. To clarify the nature of the pathology, the endoscopist takes the material for analysis. Detection of H. pylori confirms the bacterial etiology of inflammation of the duodenum and helps determine treatment tactics.
Symptoms
Superficial gastritis has three stages, with more severely aggravated symptoms.
- The first, moderate stage is considered to be a minimal number of inflamed cells. The symptoms are mild, discomfort is felt in the stomach area.
- The second stage involves the active division of painful bacteria. The symptoms are much more pronounced and appear when the first stage is ignored. Inflammation penetrates into the middle sections of the stomach.
- The third stage provokes constant heartburn, pain in the stomach area, and poor appetite. It is considered a dangerous stage when inflammation affects the muscle tissue of the stomach.
Bulbit, like superficial gastritis, can express symptoms vividly or less expressively. Inflammation is accompanied by nausea and vomiting, periodically with bile.
General symptoms
Rotten breath and stomach pain combine both diseases. In the initial stages, the symptoms are mild and not too pronounced. If you experience frequent nausea or even vomiting, you should definitely consult a doctor; either bulbitis or gastritis may develop.
Diagnostics
Patients diagnosed with primary bulbitis must necessarily go to a gastroenterologist. After a consultation examination, a decision is made on hospitalization and planned therapy. If the patient’s pain syndrome is not pronounced, then you can limit yourself to home treatment. However, if the patient is diagnosed with hypoproteinemia in a blood test, then hospitalization remains a prerequisite.
How is subsequent diagnostics carried out?
| Research method | Image | Short description |
| Esophagogastroduodenoscopy | A special method of endoscopic examination that helps to identify pathologies of the stomach and duodenum. When a patient has superficial bulbitis, the clinical picture is as follows: a focus of uneven swelling is clearly visible, the inflamed areas are characterized by hemorrhages of microscopic size. When examining the lumen, an accumulation of mucus is noted. Bleeding of the inflamed mucosa as a result of endoscope manipulation cannot be ruled out. | |
| Endoscopic biopsy | When examining epithelial cells, their degeneration is revealed, as well as infiltration of the mucous membrane with lymphocytes | |
| Radiography | First of all, radiography can confirm the speed of passage of the food bolus, retrograde perestation |
It is recommended to undergo additional research methods - antroduodenal manometry, impedance measurement. Thus, it is possible to accurately confirm the clinical picture and differentiate bulbitis from cholecystitis, pancreatitis, hernia and ulcer.
Treatment and preventive measures
- If we talk about the secondary form of pathology, then first of all they begin to treat the main ailment that caused the bulbitis. If a parasitic lesion or the presence of bacteria is detected, individual specific therapy is prescribed.
- Superficial bulbitis in acute form first of all requires nutritional adjustments, so diet No. 1 is used. It is based on the use of anticholinergics (Atropine), antispasmodics (Novocaine, Drotaverine).
- In case of exacerbation of chronic superficial bulbitis, the patient is sent to hospitalization. The complex of therapeutic actions includes the use of diet No. 1, taking antispasmodics (No-Shpa, Papaverine, Novocaine, Drotaverine), astringents (oak decoction, Tannin), antacids, anticholinergics (Atropine), drugs for gastric motility (Mukofalk, Lactitol), enveloping substances (De-nol, Almagel). Additionally, vitamin therapy (mineral-vitamin complex as prescribed by a doctor) may be prescribed. If hypoproteinemia is detected, protein hydrolysates are administered perinatally.
Causes of inflammation of the duodenal bulb
Bulbit is often associated with gastritis. Therefore, the causes of this disease in many cases are similar:
- Helicobacter pylori infection (especially for catarrhal bulbitis);
- unhealthy diet (overeating, dry food, spicy, smoked, fried foods);
- alcohol consumption;
- too hot food;
- taking certain medications, especially anti-inflammatory drugs, and chemicals (for example, acetic acid or alkalis).
Accidental or intentional ingestion of any objects can lead to focal bulbitis - what does this mean: a foreign body lingers in the bulb and compresses its wall, a local inflammatory reaction develops under and around it. Giardia and helminths can also cause inflammation of the bulb, especially in children.
Rarely, duodenal bulbitis becomes a manifestation of Crohn's disease. This pathology can affect any part of the digestive tract, from the oral cavity to the anus. In particular, Crohn's disease can begin to develop precisely in the duodenal bulb.
Compliance with a therapeutic diet
The therapeutic diet for superficial bulbitis is based on limiting the daily diet and is the main criterion for successful recovery.
The following products should be excluded:
- Fatty and salty foods;
- Hot spices;
- Products containing coarse fiber;
- Strong tea, coffee;
- Canned products;
- Sorrel, cabbage, as they provoke excessive production of gastric juice, which adversely affects the recovery process;
- Medicines that can cause additional irritation of damaged mucous membranes;
- Following other diets to adjust personal weight;
- Biologically active additives.
During a therapeutic diet, you can eat the following foods:
- Steamed boiled foods without adding oil;
- Vegetable soups with lean meat;
- Low-fat fish varieties;
- Fruits vegetables;
- Sweet juices and compotes.
It is best to organize split meals up to 5-6 times a day every 2-3 hours, since rare snacks can aggravate the overall course of the disease. All cooked food should be crushed as much as possible for easier digestion.
To prepare dishes, you need to use safe cooking methods (steaming, stewing, baking). After 3–6 months, if your general condition improves, you can add additional foods to your diet:
- Dairy products (cottage cheese, sour cream);
- Vegetable puree;
- Wheat bread, biscuit;
- Kissel;
- Dried fruits compote;
- Freshly squeezed juices without sourness;
- Clean, still water;
- Weak tea.
Before eating directly, you can drink 1-2 tbsp on an empty stomach. Spoons of vegetable oil.