Colitis is a group of diseases characterized by acute and chronic inflammation of the colon mucosa. There are acute and chronic forms of colitis. The pathological process can spread to the entire large intestine (pancolitis) or affect any one of its parts: the cecum, transverse colon, sigmoid colon or rectum (ileotiphlitis, transversitis, sigmoiditis, proctitis).
Chronic colitis is a chronic inflammatory lesion of the colon. It is often combined with inflammatory damage to the small intestine (enterocolitis) and stomach.
Etiology and pathogenesis
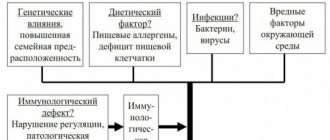
The cause of chronic colitis is quite often the causative agents of intestinal infections - Shigella, Salmonella, Campylobacter, Yersinia, Clostridia, etc. Chronic colitis can be caused by helminths, protozoa (amoebas, Giardia, Trichomonas, Balantidia), as well as opportunistic and saprophytic flora. When chronic colitis occurs, the pathogen may not be detected, but dysbacteriosis remains, changes not only in the motor and enzyme-secreting functions of the intestine, but also in the structure of the mucous membrane, intensify, which contributes to the chronicity of the process.
Colitis of nutritional origin is quite common. They are caused by a violation of the diet, a monotonous diet containing a large amount of carbohydrates or proteins, a diet devoid of vitamins, frequent consumption of indigestible and spicy foods, and alcohol abuse. There are also “drug-induced colitis”, which occur with prolonged and uncontrolled use of a number of medications (laxatives containing anthraglycosides, antibiotics, salicylates, digitalis preparations, etc.).
Colitis of an allergic nature is possible (with food and drug allergies), and the allergic component is also inherent in the so-called post-infectious colitis, in which there is increased sensitivity to certain representatives of the intestinal microflora, the products of their vital activity and decay.
Colitis can be caused by congenital enzyme deficiency, in particular disaccharidase deficiency, due to constant irritation of the colon mucosa by products of incomplete breakdown of food. A similar mechanism, along with viscero-visceral reflexes, underlies some “secondary” colitis, such as colitis accompanying atrophic gastritis, pancreatitis with impaired exocrine function of the pancreas, and chronic enteritis. Developing dysbiosis contributes to the occurrence of an inflammatory process in the colon, but can also be its consequence, as is secondary disaccharidase deficiency.
In the pathogenesis of the disease, damage to the mucous membrane of the colon as a result of prolonged exposure to mechanical, toxic, and allergic factors is essential. The nervous apparatus of the intestine is involved in the pathological process, which leads to disruption of the motor and secretory functions of the colon and aggravates trophic disorders in the intestinal wall. Dysbacteriosis is of great importance, characterized by a decrease in the number of microorganisms constantly present in the intestine (bifidobacteria, E. coli, lactobacteria), a violation of the ratio of bacteria in various parts of the intestine, increased proliferation of opportunistic flora and the appearance of pathogenic flora. Secondary fermentopathy occurs. All this leads to the development of intestinal dyspepsia, immune disorders with the appearance of autoantibodies to antigens of the colon mucosa. The likelihood of autoimmunization in the progression and chronicity of the process is quite high.
Types of inflammatory bowel diseases
Intestinal inflammation cannot go away on its own
Among all gastrointestinal diseases, intestinal inflammation ranks second in frequency of occurrence, it affects all age and social groups, and occurs with equal frequency in men and women. According to the location of inflammation, it is divided into the following diseases:
- Enteritis is an inflammatory process that affects the small intestine.
- Duodenitis - inflammation affects the duodenum.
- Colitis – inflammation occurs in the large intestine.
- Enterocolitis - inflammation spreads to almost the entire intestine.
These diseases can be acute or chronic, depending on this there should be a completely different approach and treatment method to them.
Clinic
The main symptoms of chronic colitis are unstable stools (diarrhea or constipation, change from constipation to diarrhea); bloating, rumbling, transfusions in the abdomen; pain, often spastic in nature, sometimes dull, aching, mainly in the lower half of the abdomen and in the flank area, sometimes in the left hypochondrium; Tenesmus and imperative urge to lower down are possible. Pain may decrease after the passage of gas, defecation, as well as after heat, antispasmodics and anticholinergics. Dyspeptic symptoms often occur: nausea, belching, bitterness in the mouth. Characteristic is asthenoneurotic syndrome, manifested by “sinking into illness,” weakness, fatigue, headache, decreased performance, and poor sleep.
Weight loss in chronic colitis is often associated with a decrease in the amount of food consumed due to fear of increased intestinal signs of the disease and long-term adherence to an excessively gentle diet.
Diagnostics
The examination allows you to determine the type of colitis and the degree of damage to the intestine so that the prescribed treatment is as effective as possible:
- laboratory tests: CBC, coprogram, fecal calprotectin test (done to exclude Crohn's disease);
- x-ray to determine the presence of tumors, stenosis and other lesions. It is carried out after the administration of contrast;
- colonoscopy and sigmoidoscopy for visual examination of the intestinal walls. Sometimes during the procedure, a section of tissue is removed for further examination;
- Ultrasound.
Treatment of chronic colitis
Treatment should be aimed at eliminating the etiological factor, normalizing the functional state of the intestine and the reactivity of the body, correcting disturbances in the water-electrolyte balance (with diarrhea) and the microbial spectrum of the intestine, reducing the inflammatory process in the intestine.
In case of exacerbation, a mechanically and chemically gentle diet is prescribed (No. 6 for frequent loose stools - No. 4 for several days), frequent split meals (5-6 times a day). The diet should be complete and contain 100-120 g of protein, 100 g of fats, except refractory ones, 300-450 g of carbohydrates, 8-10 g of table salt. Whole milk and “store-bought” lactic acid products are excluded if they are poorly tolerated, coarse plant fiber (white cabbage, radishes, etc.), gas-forming products (rye bread, legumes, etc.), and cold dishes. The diet includes foods and dishes that reduce intestinal peristalsis: mucous soups, pureed porridges, jelly, blueberries, bird cherry, pears, quince, strong tea. Vegetables and fruits are given boiled, pureed or homogenized.
As for medications during an exacerbation, short courses of antibacterial drugs are prescribed (sulgin, phthalazole, chloramphenicol or other broad-spectrum antibiotics, intetrix, nevigramon when Proteus is detected, etc.) followed by the prescription of colibacterin, bifidumbacterin, bificol, lactobacterin 5-10 doses per day to normalize intestinal microflora. A good and more lasting effect is observed with gradual withdrawal of these drugs. For diarrhea, astringent, enveloping and absorbent agents are recommended. For flatulence, carbolene, a decoction of chamomile flowers, peppermint leaves, and dill are indicated.
Make an appointment
How to deal with constipation due to colitis
First of all, it is important to consult a doctor. Laxatives can be part of the complex treatment of colitis, and the specialist will take into account the type of pathology, severity of symptoms, and general health. The main goal of the course of treatment is to get rid of the cause of constipation - colitis itself. Antibacterial drugs, anti-inflammatory therapy, including glucocorticoids, and agents to improve recovery processes and mucosal regeneration may be prescribed.
Chronic forms of colitis require the use of intestinal motility regulators, antispasmodics (with caution for prolonged constipation) and other agents.
For emergency assistance, medications can be used that help soften stool and promote bowel movements. Laxatives for colitis with constipation should be selected with caution. One of the approved drugs is the British drug “Fitomucil Norm”. It contains the pulp of plum fruit and the shell of plantain seeds, which are plant fibers. The fibers absorb water and turn into a soft mucous gel, helping to soften and remove stool. The product does not cause increased gas formation, cramps or pain, acts predictably and can be used for a long time. The drug is not addictive.
It should be remembered that if at the time you started taking Fitomucil Norm you had not had a bowel movement for 3 days or more, it is recommended to first cleanse the intestines using a cleansing enema or a suppository with glycerin.
It is worth noting that colitis is accompanied by a change in the balance of intestinal microflora. Thus, when performing bacteriological studies in patients with colitis, the growth of opportunistic flora is detected. And in people over 40 years of age, suffering from alternating constipation and diarrhea, there is a decrease in bifidobacteria and an increase in defective strains of E. coli. Shaposhnikov and Storozhuk studied and found that “in persons over 60 years of age suffering from persistent constipation, there is a sharp decrease in obligate microflora (bifidum and lactobacilli) in the stool with a simultaneous increase in the level of opportunistic microflora” (Shaposhnikov, Storozhuk, 2013, p. 130). Therefore, it may be advisable to prescribe a course of medications to normalize the balance of intestinal microflora: probiotics and prebiotics.
Get rid of intestinal problems
The natural British drug is not addictive and works immediately
Find Phytomucil with benefits
Diet features
Treatment of constipation due to intestinal colitis is necessarily accompanied by nutritional recommendations. Following a diet helps not only prevent constipation, but also improve the condition of the underlying disease. The doctor will give individual recommendations taking into account the form of colitis and individual characteristics.
An important goal of a special diet is to reduce the load on the digestive system. At the same time, it is necessary to provide the body with the necessary vitamins and minerals.
There are several principles of diet for colitis:
- frequent meals in small portions - this will help reduce the functional load on the intestines;
- eating foods at a comfortable temperature;
- chopping food or eating pureed dishes - to reduce mechanical irritation of the mucous membranes;
- inclusion of steamed or boiled dishes;
- refusal of fried foods, smoked meats, spices, marinades;
- eating foods with fiber;
- reducing the amount of fat and carbohydrates consumed.
You need to stick to the diet for a long time, even after symptoms have eased and you have recovered.
Causes
At the moment, there is no exact data on what can cause spastic colitis, that is, it is unclear what triggers cause this disease. This is due to the fact that in most patients the causes of colitis are often different.
The etiology of spastic colitis identifies neurogenic factors as the main causes of spasms in the intestines. These can be prolonged stress and fears, regularly occurring conflict situations, hormonal imbalances, and overwork. Apparently, this is why spastic colitis is more common in women, since fluctuations in hormonal balance associated with the menstrual cycle have a significant impact on the emotional state.
About 30% of patients who sought help acquired spastic colitis after acute intestinal infections. Among them, the main ones were salmonellosis and dysentery. The disease is often preceded by dysbiosis, which develops as a result of prolonged antibacterial therapy.