Worms
(scientific name
helminths
) are worms that live inside humans. Worms are parasites, that is, organisms whose life activity is based on the exploitation of the host organism.
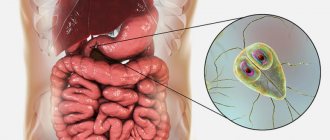
Helminths (worms) are the most common human parasites. According to research, every 4th person in the world is infected with worms. 70 species of worms have been registered in Russia. They all belong to three classes: roundworms, flatworms and flukes. The most common roundworms are roundworms, mainly pinworms, roundworms and whipworms.
There are also intestinal and extraintestinal helminths. Intestinal are those that live in the lumen of the human intestine, and extraintestinal (or tissue) are those living in muscle tissue or organs. Worms can affect the brain, lungs, liver, and lymphatic vessels.
Several types of helminths can parasitize one person at once, and this is a fairly common situation.
Infection of a person with worms is called helminthic infestation
.
helminthiasis
is also used .
Causes of helminthiasis
How does worm infection occur?
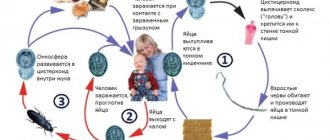
Adults inside humans lay a huge number of eggs (hundreds and thousands per day). Worm eggs are excreted from the human body along with feces. In order for a new host to become infected, it is necessary for the helminth eggs to enter his intestines. In most cases, this occurs along with food intake, for example, when eating with unwashed hands or when eating unwashed vegetables and fruits. Some types of helminthic infestations are geohelminthiases. In this case, the eggs of the parasite must first mature by being in the soil for some time (such as roundworms). Other types of worms are used for the maturation of intermediate “hosts” - animals. These are tapeworms - the most famous of the flat parasitic worms - bovine and pork. Their larvae mature in the muscles of animals and enter the human body along with meat that has not undergone proper heat treatment, and already inside a person they turn into an adult.
The opposite situation is also possible, when the human body is used by the helminth as an incubator for the larvae. The final host of such parasites is a predator. The predator is expected to catch the prey and eat the meat infected with the larvae. In this regard, a person is a dead end - a larva that gets into it will no longer turn into an adult, but the larvae
predator worms can cause us a lot of harm. In the human environment, two typical predatory animals are a dog and a cat. They can become a source of infection. The eggs of worms from these animals enter the human intestine, where they hatch into larvae, which can then migrate throughout the body. The liver is most often affected. To prevent infection from pets, you should not kiss them, and a dog that can become infected with helminths while running along the street must be subjected to regular treatment for worms.
Also, worm eggs can enter our body through inhalation of dust or with a sip of water when swimming in a pond. Flies carry worm eggs.
Popular questions
1. Does a person lose weight when he has worms?
Weight loss is a possible, but not obligatory, symptom of parasitic infestation. Weight loss due to parasitic diseases may be due to disturbances in microflora and nutrient absorption processes in the intestines.
2. How to remove worms without drugs?
Parasitic diseases (worms) are treated medically using antiparasitic drugs. Only a doctor can prescribe anti-worm medications. The choice of antiparasitic drugs depends on the type of worms.
3. Why do worms come out?
The movement of worms in the human body is determined by the characteristics of their life cycles. For most parasites, getting out is how they spread and transmit. When released, worms can be detected not only in feces, but also in sputum and exhaled air.
6
6
6
Article rating:
4.2 out of 5 based on 40 ratings
Author: Blazhko Valentina Sergeevna
Infectious disease physician. First category. Work experience more than 10 years.
Worms in children
Children become infected with worms more often than adults. Small children tend to put everything in their mouth. While walking, children play on the ground and in the sandbox. They can hug and kiss strangers and stray animals. They don't care about dirty hands.
Therefore, it is so important to try to instill hygiene skills in children as early as possible. Young children should be supervised during walks, always having water and disinfectants ready to wash their hands and wipe their faces in time. And at the first signs of helminthic infestation, you should consult a doctor.
In Moscow, the most frequently detected helminth infections are enterobiasis and ascariasis.
Competition “Bio/Mol/Text”-2020/2021
This work was published in the “School” category of the “Bio/Mol/Text” competition - 2020/2021.
The partners of the nomination are the Vita Medical and Biological School and the New School.
The general partner of the competition is the annual biotechnology conference BiotechClub, organized by the international innovative biotechnology company BIOCAD.
The sponsor of the competition is SkyGen: a leading distributor of life science products on the Russian market.
Competition sponsor: the largest supplier of equipment, reagents and consumables for biological research and production.
"Book" sponsor of the competition - "Alpina Non-Fiction"
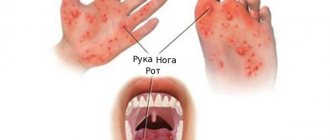
Enterobiasis – helminthiasis caused by pinworms
Pinworms are detected more often than other helminths (in 90% of cases of detection of worm infection).
Pinworms are grayish-white roundworms ranging from 2 to 12 mm in length. They parasitize the intestines. Females descend along the rectum, emerge from the anus and lay eggs in its circumference, after which they die. In this case, the patient feels severe itching in the anus. When scratching, pinworm eggs get on the skin of the hands and under the nails. Thus, if hygiene rules are not followed, constant self-infection is possible.
Pinworms have a short lifespan - 3-4 weeks. Theoretically, in order to be cured, hygiene procedures are enough - daily washing, keeping your hands clean, regularly changing your underwear and bed linen. And in a month the pinworms should disappear. However, since they primarily infect children, it is often impossible to ensure the necessary level of hygiene. Therefore, if you suspect enterobiasis, you should consult a doctor.
The main symptom of enterobiasis is itching in the anal area.
More about enterobiasis>>>
Consequences of untreated parasitic infestations
Helminthiasis poses a serious danger; without treatment, it can result in death or significant health problems. An infected child poses a danger to the entire family and environment, as it spreads the disease.
Complications of worms in children:
- inflammatory exacerbation of appendicitis;
- epileptic seizures;
- visual impairment of several types;
- allergic reactions with copious nasal discharge;
- developmental lag behind peers;
- sexually transmitted infections, the most common in girls is vulvovaginitis;
- various types of pulmonary manifestations, including bronchial asthma;
- in difficult cases - damage to the brain and heart.
Ascariasis - helminthiasis caused by roundworms
Ascariasis is diagnosed in 70% of cases of helminth infection.
Ascaris is a round worm, the length of which reaches 25 cm in males and 40 cm in females. Ascaris eggs must mature in the ground. Ripe eggs enter the human body when eaten with dirty hands or from unwashed vegetables and fruits. A larva hatches from an egg in the human intestine, but, unlike an adult, it requires air. Therefore, the larva, which at this moment has a microscopic size, penetrates the blood vessels and migrates throughout the body, reaching the lungs. In the lungs, the larvae grow and mature, moving through the alveoli into the bronchi, and from the bronchi into the trachea. The human body reacts to the helminth by coughing (this is a specific symptom of ascariasis). The larvae are expectorated along with sputum and are accidentally ingested by humans. This allows the already developed larva to enter the intestine again, where the adult continues to exist. The entire migration process takes about 2 weeks.
Roundworms can live in the human body for up to a year, in some cases longer. During this period, the waste products of the roundworm poison the body of the “host”, causing disturbances in the functioning of the digestive, nervous and reproductive systems.
Wide tapeworm
In severe cases of tapeworm infection, high fever and nausea occur.
Another dangerous flat parasite for humans, the broad tapeworm, causes a rather specific type of helminthiasis. We are talking about a disease called diphyllobothriasis.
This helminthiasis is distinguished by the long incubation period of its pathogen (it takes, on average, about two months for the worm to “take root” in the body). How is diphyllobothriasis diagnosed?
As a rule, the general condition of the patient with helminthiasis of this type is only slightly impaired. In some cases, the infected person may complain of slight dizziness or malaise, which appears only occasionally.
With a more severe form of infection that occurs with complications, the symptoms of diphyllobothriasis become more pronounced. The patient experiences an increase in body temperature (usually up to 37.5 degrees), nausea and diarrhea. Unpleasant, crusty rashes appear on the skin.
Most patients also complain of pain in the upper abdomen.
The easiest way to diagnose diphyllobothriasis is by assessing the condition of the patient’s oral cavity. Thus, when infected with a wide tapeworm, the mucous membrane of the host’s mouth becomes covered with bright red painful spots. A similar picture is observed in the tongue, where, in addition, atrophy of the taste buds can be noticed.
Symptoms of helminthiases
The body tries to resist the penetration of worms. The first consequences of helminth infestation are precisely related to the body’s immune response to the ingress of helminth eggs and larvae. This acute stage lasts (depending on the type of parasite) from several weeks to several months. An allergic reaction can be expressed in the form of a rash, swelling, swollen lymph nodes, cough, etc.
If all the body’s protective barriers are broken, then helminthiasis enters the chronic stage.
The larva develops into an adult. In the case of single parasites, a person may not notice their presence, but if there are many helminths, then the consequences of their presence inside the body significantly affect health.
Worms damage tissues by attaching to them using their fixation organs (hooks, spines, etc.), as a result of which inflammation can develop in this place.
Worms create a comfortable environment for themselves. In particular, they cause suppression of the immune system so that the body's defense system no longer reacts to their presence. Reduced immunity causes a person to become susceptible to various infectious diseases.
The presence of worms in the human intestines disrupts metabolism, as the worms absorb nutrients (proteins, minerals, vitamins, carbohydrates). Some varieties of worms secrete substances that neutralize the digestive enzymes of the host. The waste products of worms cause changes in the intestinal microflora, promoting the development of pathogenic microorganisms.
Many types of worms are hemophages, that is, they feed on the host’s blood, contributing to the development of anemia and vitamin deficiency (worms absorb the much-needed vitamin B12).
If the parasite lives not in the intestines, but in the tissues of some organ, then its growth causes compression and deformation of the tissues, which can lead to disruption of the functions of this organ (brain, liver, eyeball).
Suspicion of helminthiasis, first of all, causes disruption of the digestive system and neurological disorders.
Gastrointestinal manifestations of helminthic infestation
The consequences of the presence of worms in the body are not specific and can be mistaken for symptoms of various diseases. A person may complain of occasional pain in the abdominal area of unclear localization, flatulence, or a feeling of fullness in the abdomen. Appetite may increase or be completely absent. Bowel disturbances (constipation or diarrhea) may occur.
Neurological manifestations of helminthic infestation
Helminthic infestation is often the cause of neuropsychiatric disorders - this is the result of the presence in the blood of toxins produced by helminths. The patient may feel general weakness, emotional instability, fatigue, and loss of concentration may be observed.
Trichinella
Trichinella disrupts heart rhythm.
Trichinosis, or infection of the body with roundworms - Trichinella, usually occurs in three phases:
- an asymptomatic incubation period, which usually lasts no more than one and a half months;
- phase of disease development, accompanied by characteristic clinical symptoms (fever, chills, general weakness, muscle pain and swelling);
- peak of the disease, characterized by persistent fever, myalgia of the muscles of the neck, calves and lower back, puffiness of the face and allergic skin rashes (the latter appear as a result of an allergic reaction to helminths, accompanied by an increase in the level of eosinophils in the blood).
If trichinosis reaches its peak stage, the active development of accompanying respiratory tract diseases, such as bronchitis, pleurisy or even pneumonia, begins. The cardiovascular system suffers no less.
Thus, for carriers of Trichinella, heart rhythm disturbances, tachycardia and arterial hypertension are very typical. As is the case with damage to the body by other helminths, prolonged presence of parasites in the body of the carrier can ultimately lead to appendicitis and peritonitis, anaphylactic shock, internal bleeding, the initiation of oncological processes, or even brain damage.
Methods for diagnosing helminthiasis
Since the symptoms of helminthiasis coincide with the signs of many other diseases, before prescribing treatment, it is necessary to make sure that worms are actually present in the body. For this purpose, various laboratory diagnostic methods are used.
Analysis of stool for worm eggs
If a helminthic infestation is suspected, the first step is to perform a stool test for worm eggs. To be more confident in the absence of worms, it is recommended to do such an analysis several times (a negative result in the case of a single analysis does not guarantee that there are no worms). However, enterobiasis cannot be detected using stool analysis.
More information about the diagnostic method
Scraping for enterobiasis
Scraping for enterobiasis allows you to identify pinworm infection.
Serological blood test
In difficult situations, additional tests are possible, in particular, a serological blood test for the presence of antigens and antibodies to a particular type of parasite.
More information about the diagnostic method
Sign up for diagnostics To accurately diagnose the disease, make an appointment with specialists from the Family Doctor network.
Ways of helminths entering the body
There are several of them, but the most common ways are four:
- From person or animal to person. This is how, for example, pinworm infection occurs. If a person infected with this type of worms touches various objects without washing their hands, then this will become a risk factor for others (it is not without reason that enterobiasis - and this is what pinworm infection is called - is an occupational disease of teachers, because pinworms are a real scourge of primary schoolchildren) .
- Through the soil. Worm eggs enter it along with human and animal feces, after which they are carried by water, insects, pets or wind (with dust particles) and end up on food or directly into the digestive tract or respiratory tract.
- When eating food that has not been subjected to heat treatment. Raw or half-raw meat or fish infected with worms are very dangerous. Therefore, you should very carefully choose restaurants that serve sushi.
- For insect bites. This happens quite rarely, but the risk of contracting helminthiasis through a bite increases when traveling to exotic countries.
Methods for treating helminthiases
Despite the fact that helminthiasis is a common occurrence, it cannot be treated as something normal.
Worm infestation is a serious problem for the body, in some cases it can even lead to death. Worms cannot be tolerated. Infection with worms must be prevented, and if it occurs, the worms must be removed. To treat helminthiases, courses of special medications are prescribed.
If you suspect a worm infection, you should consult a therapist, and if you are talking about a child, a pediatrician or family doctor. In some cases, the doctor may recommend that the whole family take anthelmintic medications.
Pediatricians, family doctors and therapists at Family Doctor have extensive experience in identifying and treating various helminthiases. It is worth remembering that getting rid of parasites is a serious increase in our health!
Deworming
The procedure for removing worms from the body is called deworming
.
Along with anthelmintic drugs, the course of treatment usually includes drugs that help remove and bind toxic substances produced by worms, as well as antiallergic drugs.
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Rate how useful the material was
thank you for rating
Clinical cases
Patient K., 35 years old, complained of frequent painful urination that appeared after the summer holidays. At the end of urination, blood was sometimes released. The duration of the disease is 1.5 months. She was treated with antibiotics and other drugs with a diagnosis of cystitis. The treatment brought temporary relief, and then the complaints intensified again. According to ART diagnostics, schistosoma haematobium (schistosoma) was identified. After a course of BRT therapy and homeopathic medicine for two weeks, my health improved significantly. At a follow-up examination after 1 month, schistosoma is not tested.
A 6-year-old child was referred due to a herpes rash on the face. ART testing revealed ascariasis. After homeopathic treatment, BRT therapy, herbal medicine, ascariasis is not tested. Herpes did not recur.
Patient B., 45 years old, applied due to an existing polyvalent allergy to foods, medications, and household allergens, which manifested itself in urticaria and angioedema. Due to illness, she left her job. An examination using the ART method revealed: toxoplasmosis, ascariasis, fascioliasis. After a course of treatment for a year, my health improved significantly, I learned a new specialty, and got a job.
Make an appointment
The clinic offers the services of an experienced gastroenterologist, candidate or doctor of medical sciences, who will make a preliminary diagnosis, prescribe only the necessary studies according to the results of the examination, and write out a treatment plan. Having our own laboratory allows us to quickly obtain tests, and the absence of queues and appointments by appointment allows us to prescribe treatment as soon as possible. To make an appointment, select the doctor you like and fill out the form on the website, use the general appointment form, the function to order a call back, or simply call our contact center.
Prevention
To ensure that treatment of worms in children is not required at all, it is necessary to actively engage in prevention, which consists of both daily precautions and hygiene procedures, as well as taking medications.
How to protect your baby from parasitic infection:
- Maintain hygiene – regularly wash your child’s hands and bathe him;
- regularly care for toys - washing and cleaning (after diagnosis, all toys must be disinfected);
- cut your nails as often as possible, clean them every day;
- iron clothes after washing;
- get rid of bad habits - sucking fingers, pens, biting nails;
- give only boiled water to drink and explain the reasons;
- avoid swimming in natural bodies of water;
- use repellents (insects often carry worm eggs), destroy all insects that enter the house;
- regularly check pets for parasites;
- Wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly, conduct sufficient heat treatment of meat and fish.
Some types of helminthiases are difficult to cure, so we recommend preventive measures to avoid infection. When contacting the clinic, parents will receive full advice on how to properly carry out prevention to avoid problems in the future.