Nonspecific ulcerative colitis occurs quite often in residents of European countries. This is an inflammatory disease exclusively of the large intestine, which never spreads to the surface of the small intestine.
Ulcerative colitis is accompanied by an erosive process of the mucous membrane, which requires not only taking various medications, but also a constant diet. Ulcerative colitis is a chronic, relapsing disease, so eating healthy is extremely important. What should be the diet for nonspecific ulcerative colitis?
Causes and signs of ulcerative colitis
Ulcerative colitis is an inflammatory disease of the colon.
The causes of ulcerative colitis have not yet been precisely determined. It is difficult to say how much love for junk food, fast food and bad habits influence the development of this disease, but they are definitely provoking factors that increase the chances of developing ulcerative colitis.
Diet for nonspecific ulcerative colitis leads to relief of symptoms, but rarely allows you to get rid of the disease completely.
When a new provocateur of inflammation appears, the disease resumes. For this reason, a regular diet is very important and forms an integral part of the treatment.
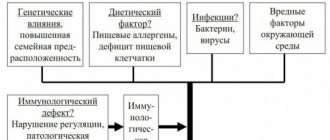
One of the provoking factors of ulcerative colitis is heredity. It has been proven that people who have close relatives with ulcerative colitis suffer from this disease many times more often.
Of course, external factors are also important. Poor nutrition, an abundance of fatty foods, alcohol, nicotine and a sedentary lifestyle negatively affect the entire condition of the intestines, creating favorable conditions for the development of infection and inflammation.
Various infections can also lead to ulcerative colitis. The influence of viruses and bacteria on the development of this disease is still being studied. However, the inflammatory process is almost always associated with disorders of the immune system. There are a number of symptoms of ulcerative colitis:
Treatment and nutritional advice for colitis
Antibiotics are used to treat ulcerative colitis.
Treatment of such a complex disease always includes a whole range of measures. It includes drug therapy, diet, and a total restructuring of lifestyle.
In case of severe disease, surgical intervention may be prescribed. Most often, general practitioners prescribe a number of medications and give advice on nutrition:
- Hormonal drugs. Taking hormones for ulcerative colitis helps reduce the inflammatory process, but they have their side effects. With long-term use of hormonal drugs, there may be a malfunction in the body, active growth of hair on the face and body, increased blood pressure, and the development of diabetes.
- Immunosuppressants. The drugs suppress the body's immune response, which also reduces inflammation, but these drugs should only be taken under medical supervision.
- Diet. Proper nutrition is necessary for ulcerative colitis. The effect of the drugs will not be enough if the intestines are constantly irritated by indigestible food. This is a chronic disease that requires a constant diet.
- Antibiotics. Antibacterial drugs are prescribed as additional therapy if ulcerative colitis is accompanied by signs of a bacterial infection: pus in the stool, elevated body temperature, fever.
- Painkillers. For severe abdominal pain, painkillers are prescribed, but it is not recommended to take them for a long time, since pain can be an alarming symptom of another acute disease, and the drugs blur the clinical picture.
- Antidiarrheal or mild laxatives. Bowel problems also require treatment. For diarrhea, fixative drugs and drugs that prevent dehydration are prescribed, and for chronic constipation, mild laxatives that do not cause intestinal irritation are prescribed.
A person with this disease must carefully monitor what they eat to avoid causing inflammation. As a rule, split meals are prescribed, in small portions 4-5 times a day, with the exclusion from the diet of any food that is difficult to digest.
With ulcerative colitis, it is important to adhere to nutritional rules that will help reduce intestinal motility, relieve spasms and reduce inflammation.
The need to follow a diet
Following a diet for colitis normalizes the functioning of the large intestine and the entire digestive tract as a whole. Also, a treatment table for illness will ensure the absorption of nutrients, vitamins and microelements, normalize appearance and weight, and stimulate the immune system.
Normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract has a beneficial effect on the mental state, eliminates emotional excitability, and has a positive effect on sleep.
In addition, if the patient follows a diet, all the unpleasant sensations associated with colitis are relieved, abdominal pain disappears, and stool normalizes.
Allowed and recommended products for ulcerative colitis
If you have ulcerative colitis, you can eat lean meat.
After making a diagnosis, the doctor himself will recommend a certain diet, make a list of permitted and undesirable, as well as prohibited foods that should be completely excluded.
The diet for ulcerative colitis is not as strict as it might seem at first glance. Giving up fast food and spices is difficult only for the first couple of weeks, then addiction begins, and the body no longer requires junk food.
The list of permitted products is controlled by a doctor. It can be expanded only after consulting your doctor. Allowed products for colitis:
- Lean meat. There is no need to give up such a nutritious product as meat, but it must be carefully selected and prepared (boiled or stewed, but not fried in oil). Suitable dietary products include fat-free veal, chicken (especially breast), turkey, and rabbit.
- Cereals. Any porridge (preferably with water, but also with milk) is allowed, except barley and millet. Porridges are considered dietary dishes, but you should not buy instant cereals in packs, they contain a lot of preservatives and flavorings.
- Low-fat cottage cheese and sour cream. Dairy products are good for the intestines, but it is advisable to avoid milk with a high percentage of fat content. Low-fat or low-fat cottage cheese is recommended.
- Flour products. It is advisable to consume flour products without baking, creams and not fresh. You can eat biscuits, day-old bread, crackers, and toast made from wheat bread. Occasionally, you can allow yourself to bake with poor dough. Pasta is also allowed.
- Vegetables and fruits. Fresh fruits and vegetables are healthier because of the fiber, but they can irritate the intestines and cause bloating. You can drink jelly or eat pureed vegetables and fruits. Sweet fruits can be eaten fresh in limited quantities.
- Eggs. It is advisable to eat soft-boiled eggs or in the form of steam omelettes. Hard-boiled and fried eggs are not advisable.
- Greenery. Fresh or dried herbs (dill, parsley) can be added to dishes.
- Fish. It is advisable to eat low-fat steamed or boiled or stewed fish, but avoid canned fish and semi-finished products.
- Beverages. You can drink weak black or green tea, fresh coffee in limited quantities, natural fruit drinks and compotes.
Recipes
First meal
Meat broth with egg flakes
Weak beef broth, egg, butter.
Add salt to the broth, bring to a boil, add butter. Through a colander, add a well-beaten egg into the broth and stir quickly.
Poultry puree soup with rice
Chicken meat, rice, water, butter, crackers.
Boil the rice well and puree. Also puree the pulp of boiled chicken or beat it in a blender. Combine the rice water with the pureed meat, add salt and oil, and boil everything together.
Second courses
Meat meatballs with rice
Beef, rice, salt.
Add boiled and grated rice to the prepared minced beef, add salt and beat. Cut the mixture into balls and cook in a double boiler.
Boiled cod with Polish sauce
Cod, for sauce - fish broth, flour, salt, egg.
Cut the fish into portions and boil in salted water. Dry the flour in a frying pan without oil, add fish broth, add salt and boil for 3-5 minutes. Add chopped or grated boiled egg. When serving, pour the sauce over a portion of cod.
Beverages
Blueberry jelly
Blueberries, sugar, potato starch, water.
Sort the blueberries, puree and squeeze out the juice. Pour water over the pulp and boil for 10 minutes. Strain the finished broth and add sugar, boil and gradually pour in some of the juice with starch. Stirring, bring to a boil and add the rest of the juice at the end.
Prohibited Products
Fast food should absolutely not be consumed if you have ulcerative colitis.
There is also a list of products that it is advisable to completely avoid or significantly limit their quantity.
The doctor will advise what to replace them with if the craving for junk food is very strong, but, as a rule, diet is a matter of habit. During the remission stage, the diet is usually expanded, but this should be discussed with your doctor. Forbidden:
- Delicious baked goods. Baking is undoubtedly a tasty treat, but its harm to the intestines is obvious. Butter baked goods cause severe constipation and intestinal spasms, which is extremely undesirable for ulcerative colitis. This does not mean that it should be excluded completely, but you can eat baked goods rarely, in small quantities and not at night, to give it time to digest.
- Alcohol. Alcoholic drinks are harmful to the entire body. They reduce the body's protective functions, disrupt the digestion process and increase the acidity of gastric juice, accelerating degenerative processes. Light carbonated alcoholic drinks are especially harmful to the intestines: sparkling wines, beer, cocktails with various additives. Quitting alcohol will bring many benefits to the body and help alleviate the condition.
- Fast food. It’s not for nothing that fast food is called “junk food.” Rarely eating a small amount of fast food will not harm a healthy body, but if you have chronic ulcerative colitis, it is better to avoid hamburgers, French fries, soda, pizza, chips, etc. These products, as a rule, are fried in oil; they contain a large amount of carcinogens, spices, preservatives, and flavor enhancers, which are irritating to the mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines.
- Sweets, chocolate. It is advisable to reduce sweet, creamy, chocolate foods. These products disrupt the body's metabolism, promote weight gain, and negatively affect digestion.
- Fried and fatty meat. Fried fatty foods are difficult to digest and disrupt the functioning of the stomach, liver, pancreas and intestines. The load on the digestive organs increases several times.
- Hot spices, onions, garlic. Fresh onions and garlic, hot spices irritate the intestinal mucosa, which increases spasms and provokes an exacerbation of ulcerative colitis.
- Pickles and canned food, marinades. Salinities and marinades increase the acidity of gastric juice, cause heartburn, and impair digestion.
Conclusion
A person suffering from ulcerative colitis should always contact their doctor and dietitian before making any dietary changes.
Foods that may cause symptoms of ulcerative colitis vary from person to person. Therefore, you should keep a food diary and note any symptoms that a particular food causes.
However, certain snacks may potentially help relieve symptoms, including melon salads, roasted chickpeas, white bread and oatmeal.