general information
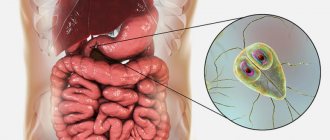
Giardia exists in two life phases - mobile (trophozoites) and immobile (cysts). The latter are attached by flagella to the intestinal wall of an infected living creature, damaging it, which causes swelling and irritation of the mucous membrane. Giardiasis can cause allergic manifestations, weakness, depression, and an increase in body temperature to 37.3-37.5 degrees C.
Cysts come out with feces and cause infection in people and animals. You can become infected through water; household contact is dangerous. Flies contribute to the spread of the disease.
Giardiasis requires timely detection and treatment. Children from three months to 7 years old suffer from it much more often than adults. The Unified Medical Center in St. Petersburg offers testing for giardiasis. Do not delay visiting the clinic if you or your children have symptoms of infection.
Giardia in children
“Perhaps the child has parasites?!” Parents may ask this question if their child suffers from allergies, indigestion, or poor appetite.
One of the common parasitic diseases in children is giardiasis.
How does infection with the causative agent of giardiasis, Giardia, occur? What tests should a child undergo for Giardia? How to get rid of these parasites?
These and other questions are answered by Elena Gennadievna Koroleva, a children's infectious disease specialist at Clinic Expert Tula.
— Elena Gennadievna, many parents have probably come across the term “giardia.” What is it and what does Giardia look like?
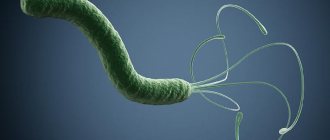
- These are small protozoan parasites invisible to the naked eye. They are the causative agents of giardiasis. They are an amoeba with a flagellum. Giardia lives in the small intestine of humans and other mammals, as well as birds. They are excreted with feces in the form of cysts.
— Where does Giardia come from in a child’s body?
— There are several ways that Giardia cysts can enter the body:
- Contact – when using common hygiene products, utensils
- Water – when swimming in polluted waters or drinking raw water from questionable sources
- Food – if the child eats unwashed vegetables, fruits, and also consumes foods without sufficient heat treatment (raw milk, meat, fish)
- Associated with animals. Giardia cysts can be carried by domestic animals that are kept or walked outside, as well as agricultural animals.
It is important that the Giardia cyst is very resistant to external influences. For this reason, it is not destroyed by gastric juice. Once in the duodenum, lamblia is released from the membrane and absorbs nutrients here with its entire surface.
— What are the symptoms of Giardia in children?
— In general, it is common for parasitic diseases in general, and Giardia in particular, to hide behind “masks” - signs of other diseases. Acute giardiasis, for example, is characterized by clinical signs of intestinal infection:
- nausea, vomiting,
- stomach ache,
- diarrhea (in the case of giardiasis - in the form of foamy stools).
It is quite difficult to suspect acute giardiasis.
Chronic forms of giardiasis manifest with symptoms similar to irritable bowel syndrome. Most often I hear complaints about periodic disorders of the digestive tract. May be noted:
- bowel dysfunction (constipation, diarrhea),
- pain around the navel,
- nausea, belching,
- loss of appetite,
- signs of biliary dyskinesia (in particular, a white coating on the tongue, sharp pain in the right side during physical activity, episodes of frequent loose stools, a burning sensation in the intestinal area after stress or eating sweets, weight loss),
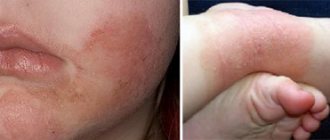
- allergic manifestations (dermatitis, urticaria, bronchial asthma).
Due to an imbalance in the function of the liver, biliary tract, and pancreas, characteristic oily stools and a specific skin tone on the abdomen with a brown halo around the navel are noted.
If the pathogen enters the body massively, the child’s body temperature may periodically rise to 37 - 37.5 degrees Celsius.
Sometimes giardiasis is asymptomatic, in some cases an extremely severe form of the course is observed (for example, in small children and in HIV-infected people).
— Elena Gennadievna, how to detect lamblia in children? What does the diagnosis of giardiasis consist of?
— Detection of Giardia cysts in stool is used (three times microscopic examination) and stool analysis by PCR (one time). The combination of these methods is the gold standard for diagnosing giardiasis.
Another diagnostic method is ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) of blood for Giardia. It allows you to detect not Giardia themselves, but antibodies to them. Based on the results of this research method alone, a diagnosis is not made. Usually ELISA is done in combination with PCR or stool microscopy, but sometimes when making a diagnosis we rely only on a blood test and on the clinical picture characteristic of giardiasis.
Another method for identifying Giardia is gastroscopy with examination of the contents of the duodenum. Since this procedure is difficult to perform on a child, they are usually limited to the above methods.
Read materials on the topic:
Diagnosis of infections using PCR: what is it? ELISA blood test: when is it used?
— Please tell us how to test for Giardia. Do I need to prepare for it somehow?
— Blood for ELISA must be donated on an empty stomach. For microscopic examination of stool, it is necessary to collect several portions of it; in some laboratories, stool is examined only in warm form.
— How to remove Giardia from a child? What does modern medicine offer?
— Treatment of Giardia in children is a long-term three-stage therapy, which takes 1.5-2 months. The treatment regimen, dose and frequency of drug intake are selected by the doctor individually for each child. At the first – preparatory – stage, the intestinal microflora is restored, sorbents and enzymes are used. Next comes antiprotozoal therapy, and then the recovery stage using immunomodulators.
I would like to emphasize that the identification of parasites, including Giardia, in one of the family members is a direct indication for appropriate therapy for the whole family.
— What preventive measures will help prevent giardiasis in children?
— First of all, it is necessary to teach hygiene skills to children from an early age, in particular, to wash their hands regularly (before eating, after using the toilet, walking, interacting with pets). Do not allow drinking raw water (unfiltered, from the citywide water supply system), or swimming in polluted water bodies. It is important to regularly treat pets against parasites.
Addressing parents, I would also like to say that in case of any suspicious symptoms or sluggish chronic processes in a child, it is imperative to consult a doctor. Timely identification of parasites will help to avoid many related health problems.
Interviewed by Sevilya Ibraimova
You can make an appointment with a pediatrician here
You can sign up for tests here. ATTENTION: services are not available in all cities
The editors recommend: Attention, echinococcosis! Often – how much? A child who is often ill at a pediatrician's appointment
For reference:
Koroleva Elena Gennadievna
Graduate of the pediatric faculty of the Kyrgyz State Medical Institute in 1992. In 1993, she graduated from an internship specializing in “Children’s infections.” She currently holds the position of pediatric infectious disease specialist, pediatric anesthesiologist and resuscitator at Clinic Expert Tula. Receives at the address: st. Boldina, 74.
Signs of giardiasis
Giardia lamblia is a protozoan flagellated parasite that lives in the intestines of living things. It interferes with digestion and disrupts metabolism. Giardia covers the intestinal mucosa, which causes:
- weak production of intestinal juice;
- insufficient digestion, poor absorption of food;
- intoxication with waste products of parasites.
It is better to do a Giardia test for all ailments of the digestive tract. Infection with parasites may be indicated by:
- debilitating diarrhea several times a day;
- frequent attacks of nausea, repeated vomiting;
- rumbling in the stomach, intestinal soreness;
- constant alternation between constipation and diarrhea;
- increased gas formation;
- weakness, headache, and with a long period of infection - poor sleep, skin rash, increased fatigue and moodiness.
Giardiasis is considered a rather insidious disease. Clinically, its symptoms appear only after 1-3 weeks. They are easily confused with a mild intestinal disorder, general malaise due to a cold or acute respiratory viral infection (low-grade body temperature), fatigue. If an adult body is sometimes able to cope with an invasion on its own, then children need to be treated.
Which study is most informative for helminthiasis?
To diagnose giardiasis and other types of helminthiases, a stool examination is first prescribed. If adult helminths, their eggs or cysts are found in the samples, this can already become the basis for making a final diagnosis. If the result is negative, and all signs indicate helminthic infestation, an additional comprehensive examination is prescribed in the form of a repeat stool analysis and a serological ELISA test. In addition, PCR may be prescribed to clarify the type of causative agent of the disease.
Even after recovery, the risk of contracting giardiasis remains, so it is important to follow hygiene rules
Diagnosis of helminth infections is the first step to recovery. Further actions take place in several stages:
- cleansing the intestines with a diet, eliminating symptoms of intoxication and restoring digestive processes;
- taking specific anthelmintic drugs;
- restoration of the body with probiotics and a gentle diet;
- re-testing.
In order to ensure the absence of Giardia, stool and blood tests must be taken three times with an interval of several days. This method completely eliminates possible errors and false negative results. If at least one cyst was found in the material after three-stage treatment, it must be repeated again. With drug therapy, you can wait until the liver and digestive tract organs have recovered from the previous medication. However, during this period the patient becomes infectious and poses a danger to household members and the team.
Blood tests are an informative and reliable method for diagnosing giardiasis and other helminthiases. Despite the high accuracy of ELISA results, stool microscopy is still performed first. This is due to the low invasiveness of the method, in contrast to ELISA and PCR, which require venous blood. However, in case of a questionable result, additional tests can be performed.
Types (methods) of analyzes
Giardia is detected using different methods:
- Microscopic, that is, visual analysis of feces for the content of Giardia cysts. Reliability up to 50% and a large number of false negative results.
- Giardia lamblia antigen test (up to 70% accuracy).
- Blood test for IgM and IgG antibodies produced by the body to the Giardia antigen. It should be carried out after 14 days from the moment of infection. A laboratory blood test determines the presence of antibody complexes, their class and quantity. However, with weak immunity, antibodies may not appear, which gives a false negative result.
What other parasitic diseases can be detected in a blood test?
It is necessary to donate blood for helminths as prescribed by a doctor. This procedure is not preventive, but can detect a number of parasitic diseases in the early stages. ELISA is a universal diagnostic method that can be used to identify not only protozoan parasites. Multicellular worms can also be detected through blood tests. Such diseases include:
- ascariasis and alveococcosis;
- opisthorchiasis;
- echinococcosis and toxocariasis;
- trichinosis and others.
Changes in blood tests occur at any location of helminths. The immune system fights the pathogen, which is reflected in the concentration of antibodies. However, some varieties of worms live in the human bloodstream and can be detected by simple microscopy. These helminths include heartworms - dangerous worms that migrate with the bloodstream and can cause blockage of blood vessels and cause myocardial infarction.
Analysis transcript
- Microscopic analysis of stool for Giardia can give a negative result (giardia cysts are not found, the patient is not infected) and a positive result (cysts are found, the patient is a carrier of G. Lamblia with acute or chronic giardiasis). In doubtful cases, a repeat test or blood test for antibodies is recommended.
- A test for G. Lamblia antigen in the absence of antigen is interpreted as negative (the patient is not infected with Giardia). If an antigen is detected, the test is considered positive (carrier, acute/chronic giardiasis).
- A blood test for Giardia antibodies determines the proportion between antibodies and antigens in the patient's blood plasma. There are three possible results:
- 0.85 OPD (negative) - the patient does not have lamblia;
- 0.85-1.0 OPD (doubtful) - you need to take the test again;
- more than 1.0 OPD (positive) - giardiasis or carriage.
An unfavorable prognosis is when microscopic analysis confirms the presence of cysts, but no antibodies are detected in the blood. This indicates weak resistance of the immune system.
Carrying out the procedure and deciphering the results
The algorithm for donating blood to determine helminths is simple. The patient must appear at the appointed time, taking into account the doctor’s recommendations regarding preparation for the procedure. The study is carried out using the standard in vitro method (from Latin in vitro - in glass or in a test tube), that is, outside a living organism. Blood is drawn from a vein and then sent in a tube for further analysis.
Blood test using ELISA method
Blood testing ELISA, or enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, is the determination of certain types of immunoglobulins. They are specific proteins (antibodies) that are produced by the human immune system in response to the appearance of an irritant and the accumulation of its waste products. This analysis is suitable for diagnosing helminthiasis, viral, bacterial and fungal diseases. With each of them, certain classes of immunoglobulins are activated. For the diagnosis of giardiasis, Ig G, A, M are important.
The basic principle of ELISA is the biological reaction of binding an antigen (foreign protein) with an antibody of the human immune system. Its peculiarity is that only a certain type of immunoglobulin is suitable for each pathogen. They are not activated in response to other stimuli, so a positive course of the reaction can be the basis for making an accurate diagnosis.
The attending physician interprets the tests. The amount of immunoglobulins is expressed in OPD units (diagnostic optical density). If it is less than 0.85, the result is defined as negative. A value above 1 indicates an increase in the class of antibodies being studied, and a range from 0.85 to 1 is considered doubtful.
The results of a blood test for giardiasis using ELISA in a child or adult can be:
- an increase in IgM levels indicates an acute period of helminthiasis;
- simultaneous increase in all classes of antibodies - indicates an exacerbation of giardiasis after its long chronic course;
- a negative IgM result with an increase in other types is a sign of chronic giardiasis;
- positive response from IgG – there is a history of the disease, but it has already passed with the formation of immunity against the pathogen;
- the absence of a positive reaction of all types of antibodies is the norm for a healthy person.
To test for giardiasis, venous blood obtained on an empty stomach is required.
Blood test for AT (antibodies) is more often prescribed in case of a negative stool test, if the symptoms of helminthiasis continue to bother the patient. This procedure is longer and more expensive; it requires preliminary preparation and compliance with the storage conditions of the material. It is used to clarify the diagnosis if the clinical signs fit the description of several types of helminthiases. Worms that live in the human digestive tract can appear in the stool periodically, and the immune system constantly produces antibodies.
PCR analysis for giardiasis
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a complex chain of biological reactions that can detect DNA fragments of parasites. It takes place in 3 stages using venous blood serum. Sections of genetic material are identified, so after PCR it is possible to say exactly what type of pathogen it is. The complexity of the reaction lies in the need for special, expensive equipment. It is not available in small laboratories. The equipment must be operated by qualified personnel, who must first undergo special training and periodically attend advanced training courses.
REFERENCE! PCR is considered the most reliable method for diagnosing a viral infection, since it can recognize even the smallest concentrations of the pathogen. However, it is used infrequently for helminthiasis, since there is a possibility of obtaining a false negative result and the high cost of the procedure.
Preparation, how to take the test correctly
The test for giardiasis involves collecting venous blood. You should avoid fatty, fried foods 12 hours before your visit to the laboratory, and do not smoke for 30 minutes before donating blood. Usually the test is prescribed in the morning and is done on an empty stomach. You can drink still water.
Stool analysis is a little more complicated:
- defecation in clean, washed dishes without traces of detergents;
- do not use laxatives or enemas;
- a week before stool collection, stop taking medications;
- About 2 teaspoons of feces should be taken from different areas, especially more liquid ones;
- The stool is delivered to the laboratory while still warm, the interval should not exceed 20 minutes.
We are waiting for you in the laboratory of the Unified Medical Center. Sign up by phone and on the website.
Recommendations for preparing for testing
Before donating blood for Giardia in children and adults, the doctor conducts a detailed consultation. It is important for the patient to prepare properly so that the results are as reliable as possible. The study is most often carried out in the first half of the day, on an empty stomach. On the eve of donating blood, you must follow the instructions:
- do not eat fatty and fried foods;
- exclude alcohol and carbonated drinks - it is better to drink only still mineral water;
- stop smoking (at least a few hours before the test);
- do not eat food 8–10 hours before donating blood;
- If you are taking any medications, please provide this information to your doctor.
IMPORTANT! Recommendations regarding nutrition and drinking regimen have little effect on the results of blood tests. Antibodies to helminths or DNA will be detected even if the test is performed on a full stomach. However, these nuances may distort the results if other indicators need to be further checked.
Causes
Giardia is the simplest microscopic unicellular parasite from the class of flagellates.
In the human intestine it can be in two forms - vegetative and spore. Giardia reproduces by division and doubles in number every 10-12 hours. The habitat of vegetative forms is the upper section of the small intestine. Cysts are immobile, oval in shape and protected by a capsule. In this form, Giardia exists in the colon, as well as in the external environment. This way they can remain viable for a long time. The main causes of giardiasis are the entry of cysts into the human body. This happens when eating unwashed vegetables and fruits, violating hygiene rules, and using unboiled water. This route of transmission is called fecal-oral, since the source of the spread of giardiasis pathogens is an infected person who excretes cysts along with feces. Pets can also be carriers of giardiasis, and flies and cockroaches act as carriers.
Provoking factors can be overcrowding, living in a polluted environment, poor condition of water supply and sewerage systems, and non-compliance with sanitary and hygienic rules. A predisposition to the disease has been identified in children under the age of 10 years, in people with malnutrition or dystrophy, congenital defects of the biliary tract, diseases of the stomach and intestines with a reduced level of acidity, as well as in those adhering to diets with too low a protein content.
Treatment
Giardiasis requires complex treatment.
Therapy for uncomplicated forms is carried out on an outpatient basis. When the diagnosis is confirmed, one of the antigiardiasis drugs is prescribed, which must be combined with the use of choleretic drugs, as well as drugs that improve intestinal microflora. The chronic course requires long-term complex treatment, which will include not only medication, but also a diet for giardiasis, which limits the intake of carbohydrates into the body. Etiotropic drugs help to cope with protozoa, and immunotherapy helps to increase a person’s natural defenses. Choleretic agents and probiotics must be prescribed to restore intestinal microflora.
Modern medicine in the treatment of giardiasis offers some clinical recommendations. At the first stage, diet therapy and fasting days are prescribed, as well as taking choleretic and, if necessary, antihistamines.
At the second stage, the patient takes special antiprotozoal drugs prescribed by the doctor. To get rid of Giardia, not one, but two courses are often prescribed.
At the third stage, multivitamins, enterosorbents, enzyme preparations, immunostimulants, and herbal medicine are used.