Although man is the crown of creation, he also serves as a food source for various parasites, microorganisms, bacteria and viruses. And you will have to come to terms with this fact. The main thing is to try to prevent infection with helminthic infestations or other pathogenic flora.
But sometimes the news just hits you, if not with a head, then with a whole butt. The child fell ill, underwent examinations, and the hair stood on end - intestinal lamblia was discovered! How could a baby catch this parasite and how to treat this disease?
Giardia, what a terrible beast?
Intestinal lamblia is a parasite
Giardia intestinalis is a simple organism that leads a parasitic lifestyle. Most often it settles in the small intestine of humans and mammals. But sometimes the liver can also be chosen. It is the causative agent of a disease such as giardiasis.
This is the only form of protozoa that lives in the human small intestine. Giardia intestinalis reproduces by division. Every 15–20 minutes the number of parasites doubles. Up to 1 million protozoan parasites can live on 1 cm2 of intestinal surface.
The life of Giardia is an alternation of active life and the cyst stage. In this state, protozoa survive unfavorable environmental conditions. A cyst is a very stable formation. In a reservoir in winter they remain viable for 2 months.
Maintain a temperature of 70 degrees for 10 minutes. It is not destroyed by gastric juice and travels well to the duodenum. This is the favorite habitat of Giardia. It enters an active form and begins to actively reproduce.
As it moves further through the body, the parasite enters the large intestine and again turns into a cyst. Together with the fecal matter, the protozoa will leave the body and wait for a new host and favorable living conditions. These protozoa die only when boiled.
As research results show: 1 cyst is enough - and in 30% of cases the diagnosis of giardiasis becomes a reality.
Prevention of Giardia in adults
Prevention of Giardia in adults comes down to the following measures:
- Timely detection of cases of invasion with subsequent high-quality treatment of patients with giardiasis.
- Following strict hygiene rules with regular hand washing.
- Use boiled or bottled water for drinking.
- Preventing fecal matter from entering the environment.
- Compliance with sanitary and hygienic measures in food and water supply institutions.
- Regular examination of people at risk for giardiasis.
- Conducting sanitary education work among the population by local authorities.
There is no vaccine for giardiasis, and the immunity that is developed after an illness is not very stable. Therefore, the risk of reinvasion remains high.
The main symptoms of giardiasis
Giardiasis comes in acute and chronic forms
Doctors distinguish between chronic and acute forms of giardiasis. The symptoms vary significantly. Acute giardiasis has the following symptoms:
- Chills and fever
- Increased body temperature
- Epigastric pain
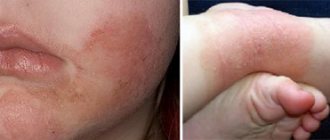
- Dermatological rashes. Giardiasis is often confused with measles or rubella, an allergic rash
- Vomiting, unstable stool
- High fatigue
- Weight loss to the point of anorexia
Without proper treatment, symptoms may subside and the disease may become chronic and asymptomatic. When the immune system is weakened - for example, after a cold - the disease becomes acute. Signs of chronic giardiasis:
- General long-term intoxication
- Apathy, depression
- Hypovitaminosis - this affects, first of all, the condition of nails, hair, skin
- Defecation disorder. Periods of diarrhea followed by periods of constipation
- Periodic vomiting
- Cramping pain in the epigastrium
- The skin is peeling. The nose is especially affected
- Cracks, jams on the lips. Dry skin
- Headaches, migraines
- Pain in the liver area
- Bitter taste in mouth
- Yellow coating on the tongue
- Asthmatic patients experience exacerbation of the disease
In children, several specific signs are added to the main symptoms:
- Dysbacteriosis
- Increased liver size
- Deterioration in attention and academic performance
- Dry cough
If you experience such symptoms, it is better to consult a doctor and get examined.
Classification
Signs of giardiasis may not be noticeable in a quarter of all cases.
This condition is called asymptomatic carriage. In this case, the person himself is not sick, but he becomes a source of infection for others. In half of all patients with giardiasis, the disease is subclinical. They also have no symptoms and do not consider themselves infected. Only diagnostics can help identify the disease.
And only in the remaining percentage of patients the disease has pronounced symptoms, which can be acute, subacute or chronic.
Diagnostic Basics
Intestinal lamblia is easily diagnosed
There are several methods to make the correct diagnosis:
- Stool analysis
- Endoscopic examination of the duodenal cavity
- PCR method
- Immunological tests
The simplest and most cost-effective way to identify the parasite is to have your stool tested. The laboratory technician will look at smears of fecal matter stained with Lugol's solution and give a conclusion whether there are parasites in the body or not.
Isolation of Giardia cysts occurs periodically. Therefore, you will have to take several samples in succession at intervals of 2–3 days. Sometimes you have to take up to 6 samples in a row, but in 90% of cases, 1 test is enough to make a correct diagnosis.
Endoscopic examination of intestinal contents is more informative. But if Giardia has chosen the middle or lower sections of the gastrointestinal tract, then the test result will be negative. Therefore, you will still have to take a stool test. The PCR method is highly accurate, but is used mainly in research laboratories.
When using immunological methods, antigens or antibodies to pathogens are determined. The material for research is feces.
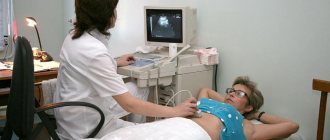
X-ray examination (MRI) of the abdominal cavity
To clarify the diagnosis, an MRI of the abdominal cavity was performed [8]. Official opinion of the radiologist: The causes of multiple formations in the liver are probably of an infectious nature, amoebiasis cannot be ruled out. Figures 1-3 show sequential images where multiple multilayered lesions are identified in both lobes of the liver with a highly hyperintense center surrounded by a capsule-like area and a zone of transition to normal tissue. This corresponds to a pathological formation with a fluid center and hyperemic, edematous edges. The presence of fluid in the right pleural cavity and the high position of the dome of the diaphragm were also noted, which also corresponds to an inflammatory process. A negative result was obtained for the tumor marker alpha-fetoprotein. The opinion of the attending physician, taking into account the data available to him, was still inclined in favor of the oncological process.
Trichopolum in the treatment of giardiasis
This is a good old drug that was used to treat our mothers and grandmothers. The main active ingredient is metronidazole. Effective dose in the treatment of giardiasis:
- Children under 12 years old - 375 mg 2 times a day - this is 1.5 tablets of 250 mg
- Adults – 0.5 g 2 times a day – 2 tablets of 250 mg
Contraindications to the drug:
- Blood diseases
- Organic damage to the central nervous system
- Individual intolerance
- Pregnancy - according to the doctor's decision
- Alcohol is prohibited during treatment
Side effects:
- Dyspeptic symptoms - nausea and vomiting, constipation or diarrhea
- Headaches, migraines
- Development of depression
- Convulsions
- Occasionally – red-brown urine
Routes of infection
Cysts live in the external environment for 1.5-2 months at temperatures from 0 to 50 degrees. Infection is carried out by the fecal-oral method in the following situations:
- Through contaminated water - drinking unboiled tap water or water from questionable sources.
- The nutritional route of infection is eating insufficiently heat-treated foods or poorly washed vegetables, berries, and fruits.
- Contact and household path. The main risk factor is failure to comply with personal hygiene rules. You can also become infected by sharing household items with an infected person.
Carriers can also be mice, cats, dogs and flies. People with weakened immune systems, gastrointestinal problems and children are most susceptible to infection.
Giardia infection in adults
Tinidazole in the treatment of giardiasis
Intestinal lamblia has a characteristic shape and flagella
The main active ingredient of the drug is tinidazole. Dosages are calculated according to the patient’s age:
- Children – from 50 to 75 mg per 1 kg of body weight 1 time per day
- Adults – 4 tablets per day
Contraindications to the drug:
- Systemic blood diseases
- Patient age up to 12 years
- Side effects of Tinidazole:
- Dry mouth
- Metallic taste
- Nausea
- Vomit
- Diarrhea
- Headache
- Migraine
- Loss of coordination
- Convulsions
- Peripheral neuropathy
- Allergic reactions
Ornidazole in the treatment of intestinal giardiasis
The main active ingredient is ornidazole. Available in tablet form. Recommended treatment regimens with ornidazole:
- Once at night - adults 3 tablets, children over 35 kg - also 3 tablets, children up to 35 kg according to weight from 30 to 40 mg per 1 kg.
- Adults – 1 tablet 3 days at night
Side effects of the drug are similar to similar drugs:
- Dyspeptic phenomena
- Dizziness
- Headache
- Possible liver dysfunction – ALT and AST values change
- Allergic manifestations
- Hematopoiesis disorder
- The drug is not prescribed to pregnant and lactating women.
Diet for giardiasis
Intestinal lamblia: diagnosis (staining)
There are foods that protozoan parasites respect. And food groups that suppress the development of Giardia. On this basis, the doctor will recommend the following diet:
- Removing carbohydrates and milk is a breeding ground for parasites.
- Protein and the more the better - it inhibits the reproduction of helminths.
- Acidic juices, berries, fermented milk products are good for the body, but protozoa do not like an acidic environment.
- Frequent meals up to 6 times a day. This promotes the production of bile, which is harmful to parasites.
- Dietary fiber must be present in the diet. It can be vegetables and fruits or oat bran.
Allowed products for giardiasis:
- Porridge
- Lean meat and fish
- Soups
- Bread with added bran,
- Kefir and other fermented milk products
- Vegetables fruits
- Lettuce and other greens
- Natural honey, marshmallow
- Eggs – no more than 1 pc. in a day