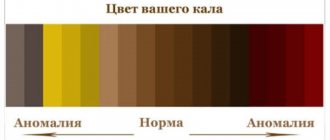
The frequency of stool, as well as urination, is one of the signs of the normal functioning of the body of both a child and an adult. And if adults sometimes do not pay attention to themselves, then the parents vigilantly monitor the baby’s stool and its quality. Any violation of defecation causes anxiety in the mother. And the delay in the process is sometimes even more disturbing than diarrhea.
Constipation occurs due to the low rate of transport of feces in the intestines. How to deal with constipation in babies? When can a situation be resolved using home methods? And when is seeing a doctor a prerequisite for maintaining a child’s health?
A little about the frequency of bowel movements in children of different ages
Young children may have bowel movements very often.
The quantity and quality of feces depends on the age of the baby. And sometimes what seems like adult constipation or diarrhea may turn out to be a personal physiological norm for a toddler. Normal frequency of bowel movements in babies of different ages:
- The first six months of life before the introduction of complementary foods - 1-2 times a day. The stool is unformed, soft, mushy.
- After 6 months to a year, subject to the introduction of complementary foods - 1-2 times a day. The feces are shaped, dense, but soft. Already resembles adult feces.
- From 1 to 3 years – frequency of bowel movements at least 6 times a week. The stool is soft and shaped. The process itself takes place without significant discomfort.
- From 3 years and older - at least 3 trips to the toilet per week.
If, with such a frequency of bowel movements, the baby develops normally and enjoys life, then there is no need to worry about his bowel movements.
Diagnosis of constipation in children
Today, in accordance with international recommendations, in order to verify constipation in a small child, the doctor only needs to correctly collect anamnesis, i.e. interview parents about the duration of complaints, features of defecation, compare with the clinical picture and take into account diagnostic criteria. All! There is no need to test coprogram and feces for dysbacteriosis! If necessary, the attending physician may prescribe additional instrumental diagnostic methods (ultrasound of the abdominal organs, X-ray contrast studies, etc.).
Symptoms of anxiety
If you suspect constipation in a young child, pay attention to the so-called “red flags”, i.e. symptoms, the presence of which indicates the need to consult a doctor!
- early onset of constipation (less than 1 month of life);
- passage of meconium after more than 48 hours in a full-term newborn;
- family history of Hirschsprung's disease;
- ribbon stool;
- blood in the stool in the absence of anal fissures;
- fever combined with stool retention;
- vomiting bile;
- severe bloating.
When rare bowel movements are a pathology
If you suspect that constipation is a consequence of pathological processes, you should monitor the general condition of the baby. Signs of pathology:
- stomach ache;
- incomprehensible anxiety and tearfulness of children;
- the process of defecation occurs with difficulty, with straining and pain;
- The consistency of feces is too thick and dry.
If these symptoms continue for more than 3 months, then we can talk about the chronic course of the disease. In addition, a vicious circle often forms - the child begins to fear the process of defecation and restrains the urge to have a bowel movement. Thereby provoking overstretching of the rectum and new constipation.
Psychological aspects
In children under one year of age, defecation occurs uncontrollably.
After a year of life, babies begin to control the process of defecation. For some this happens earlier, for others later, but gradually the functions of control over the anal sphincter become conscious.
When unfavorable factors come together, the baby begins to restrain his urges. This could be a new environment, potty training, solving problems of defecation retention with an enema, a period of adaptation in kindergarten, or any psychological attitudes introduced by adults.
Regular suppression of urges leads to stool becoming denser and harder. And even sitting on his favorite potty at home, the baby begins to feel pain when trying to go big. As a result, the child begins to be afraid to defecate even in familiar comfortable conditions.
Pediatric gastroenterologist: where to turn for help?
To get rid of this problem, you need to visit a pediatric gastroenterologist. First you need to find out why constipation occurs, adjust your diet, and then, depending on the cause, competent therapy is prescribed.
Contact the First Children's Medical Center: we have pediatric gastroenterologists who have experience working with children of all ages. We monitor the constant improvement of staff qualifications and offer the services of only highly qualified doctors.
You can make an appointment for a consultation from 8.00 to 20.00 by calling (8452) 244-000. Reception is by appointment only.
Functional constipation
Failure to drink properly can cause functional constipation.
This type of constipation is organic in nature. Its causes may depend on the behavior of the child and his environment, but can also be a sign of serious pathological processes in the baby’s body. Why functional constipation develops:
- Poor nutrition over a long period. This could be vegetarianism, an excess of meat products in the diet with a lack of plant fiber.
- Non-compliance with drinking regime.
- Sedentary lifestyle.
- Kids need to move. Pediatricians recommend walking for several hours in any weather. Older children should attend sports clubs and dances. Sitting at the computer or in front of the TV with cartoons has a bad effect on intestinal motility and constipation develops.
- Dysbacteriosis caused by illness or taking aggressive medications, an unbalanced diet.
- A form of allergic reaction of the body to some product. In this case, damage to the intestinal villi occurs and the processes of food absorption are disrupted.
- Insufficient production of enzymes due to pathology or immaturity of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Helminthic infestations.
- Rickets is a pathology accompanied by a decrease in the activity of the intestinal muscles. The result is constipation.
- Thyroid dysfunction.
- Disruption of cause-and-effect relationships in the brain due to the influence of various psychological factors - psychological constipation.
- The effect of certain medications taken on an ongoing basis.
- Drug abuse.
- Irrational use of laxatives and enemas. This leads to an imbalance of cause-and-effect relationships in the brain.
According to medical statistics, parents are most often to blame for a baby’s constipation.
When to contact a medical facility urgently:
- sharp pain in the abdomen;
- discharge of blood from the rectum;
- the appearance of liquid, uncontrollable feces with persistent constipation.
What to do if your baby is constipated?
Before 6 months of life, true constipation is rare. The main food for a child of this age is breast milk or adapted milk formula, which have a liquid consistency. In children of the first year of life, constipation most often occurs when complementary foods are introduced into the diet. This is not something to be afraid of, since changes in stool consistency due to the appearance of new foods in a child’s life are quite logical.
However, there are a number of conditions that can cause constipation and deserve special attention.
- Intestinal obstruction or intussusception: the child experiences paroxysmal restlessness, severe crying, and refusal to eat. The body temperature is normal, the abdomen is soft. After 5-6 hours, stool retention and bloody discharge from the rectum appear. This condition requires emergency care in a pediatric surgical hospital!
- Hirschsprung's disease: a disease in which the innervation of the colon is impaired. Constipation has been observed since birth.
- Congenital hypothyroidism: the movement of stool through the intestines slows down.
- Pathology of the central nervous system: often in diseases of the central system, which are associated with changes in muscle tone, a weakening of perilstatics is observed.
- Spina Bifida: a malformation of the spinal cord in which constipation is quite common.
So, if constipation in a child is still associated with changes in the usual diet, what should be done:
- Perform a tummy massage for the baby - use careful, soft finger movements to press on the anterior abdominal wall, paying attention to the baby’s reaction;
- you can take a warm bath - this will help relieve spasm from the intestinal muscles;
- postpone the introduction of a new product until the stool normalizes;
- in case of stool retention for more than three days - a cleansing enema/microenema or laxative suppositories (from three months);
- If constipation occurs regularly, contact your pediatrician!
Of course, such a delicate problem raises many questions, and when a small child has constipation, it also gives rise to a lot of fears. However, timely consultation with a doctor and proper treatment will help solve this non-children’s problem.
Treatment tactics
Bacterial starters are useful for constipation.
You should not hope that the problem will be solved on its own. Chronic constipation in a baby leads to developmental delays due to lack of nutrients, intoxication with decay products, and the development of gastrointestinal pathologies.
Where to start treatment? Initially, you should review the child's diet. Introduce foods rich in fiber - raw vegetables and fruits, limit fatty meat products. Copes well with drainage constipation in any form - raw, compotes, prunes. Maintain drinking regime.
Fermented milk products – yoghurts, kefir, fermented baked milk – must be present in the diet. It is advisable to make homemade drinks using bacterial starter cultures. Physical activity is indicated. Walk more with your child.
To overcome your child’s psychological discomfort when traveling or on vacation, take your favorite, familiar potty from home. This will make the child feel calm.
Do not make false educational claims that going to the toilet is generally indecent and you should restrain yourself. Teach your child to the idea that defecation is a natural mechanism and should not be embarrassed about it. Just like solving your problems on an unfamiliar toilet.
If constipation is a one-time short-term phenomenon, then you can use laxatives. Glycerin suppositories and preparations containing lactulose are safe for children of any age. In emergency cases, an enema. But these are emergency drugs and you shouldn’t get carried away with them.
Psychological assistance during treatment
- To restore normal bowel movements, you need to teach your child not to be afraid to poop, even if this process is currently causing inconvenience.
- Explain that the doctor will help, but you need to follow his instructions.
- Don't be afraid to poop, even if it hurts. Don't hold back the urge.
- The best position for defecation is squatting.
- Do not scold the baby, but empathize and rejoice at the results of his efforts.
- The best way to deal with constipation is to prevent it. And if you already have problems with bowel movements, then don’t delay solving them.