The liver is responsible for many functions and takes part in almost all processes that occur in the body. Problems in its work immediately affect the patient’s well-being, causing a number of unpleasant symptoms: pain in the right hypochondrium, a yellow coating appears on the tongue, a sharp bitterness appears in the mouth, the skin acquires a yellowish tint.
When do you have doubts about your liver health?
Suspicion of the disease arises in people who have discovered characteristic symptoms in themselves, in people suffering from chronic diseases. If a person is sufficiently informed, then he knows that damage is possible with long-term treatment with potent drugs, poisoning, and food overload.
In a doctor’s practice, a check is necessary when examining pregnant women, during the preparation of the patient for surgery, and after general anesthesia. Few people know that the liver supplies components for the synthesis of sex hormones, so a liver test is carried out for all men with impaired potency and spouses in order to identify the causes of infertility.
Monitoring the functioning of the organ is necessary for patients who have suffered acute viral hepatitis with a chronic form of the disease. A liver examination is mandatory for patients with chronic anemia and neurological diseases.
For patients with renal failure when using hemodialysis, liver function is checked every course.
It is especially necessary to check the condition of the liver for people with alcohol and drug addiction. During the “bright” intervals, they understand that irreversible changes will inevitably occur, and they try to be treated.
In case of a disturbed psyche with severe irritability and depression, the main cause is intoxication of the brain with substances that the liver ceases to process. Diagnosis of liver diseases is a separate section dealt with by therapists, pediatricians, infectious disease specialists, and gastroenterologists (hepatologists have appeared in large specialized centers).
Reviews
08/02/2019 Welcome! Promptly! Qualitatively! I am sincerely grateful for the assistance provided in conducting an emergency ultrasound. I wish you prosperity and health! If necessary, only to you. I will recommend it to all my friends and acquaintances.
Tatiana
07/14/2017 Natalya Dmitrievna extended my ability to move and cured my back. I'm no longer helpless! Thank you! My best wishes to the RIORIT team!
Glebova
10/01/2017 I found out about the clinic by accident, but I didn’t regret that I trusted you! I am seeing a wonderful doctor - therapist Natalya Dmitrievna. A person who knows his business and approaches treatment with professionalism. Listens carefully and gives truly necessary and effective recommendations. Thank you very much for your treatment and results! See you again!
Patient
08/21/2019 I had an ultrasound examination and thank RIORIT MC for the good service. Polite, cultured staff, well received. I liked everything very much. Svyatenko
Svyatenko
Read all reviews
What symptoms indicate liver failure?
If the functioning of the liver cells is disrupted, then insufficient functions are manifested by typical symptoms. It is impossible to skip them, because an unhealthy appearance and general malaise do not give a person the opportunity to continue normal activities and life.
The most common symptoms that appear are: Yellowing first of the sclera, then of the skin, is associated with an increased level of the pigment bilirubin in the blood. Under normal conditions, it is released during the breakdown of old red blood cells and hemoglobin, destroyed in the liver, and excreted with bile into the intestines.
Jaundice indicates that the liver has stopped detoxifying this substance. Its accumulation in the future will lead to intoxication and brain damage. A yellowish coating may initially appear on the tongue.
Bright yellowness increases gradually, starting from the sclera
A feeling of heaviness in the right hypochondrium is initially disturbing after drinking alcohol, overeating fatty and fried foods, and spicy dishes. Then it becomes permanent. Pain appears only with congestion and swelling of the liver, when the size increases (tumor growth, cyst). The parenchyma presses on the capsule equipped with sensory nerve endings.
Liver problems always affect digestion in general. Failure in the production of bile acids leads to insufficient digestion in the intestines and interferes with the absorption of nutrients. Irritated bowels react with diarrhea or constipation. Feces become significantly lighter due to the lack of stercobilin (a derivative of bilirubin).
At the same time, the urine becomes dark as bilirubin from the blood passes through the kidneys and is converted into urobilin. Often, patients with impaired liver function lack appetite, experience nausea, and a feeling of bitterness in the mouth. People around you notice an unpleasant sweetish odor from your mouth.
The skin becomes dry (collagen and elastin are lost), pale, flaky, spider veins are visible on the face, chest, and shoulders. The consequence of an increase in bilirubin levels is painful itching. Unhealed scratches can fester. Impaired blood clotting is indicated by a tendency to nosebleeds, oozing blood from the gums, and hematomas (bruises) on the body.
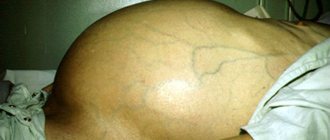
With severe liver damage, the pressure in the portal and inferior vena cava systems increases. This leads to bleeding from the dilated veins of the esophagus, expressed in the admixture of blood in the vomit and feces. The abdomen begins to enlarge (ascites) without an increase in body weight. Dilated saphenous veins protrude around the navel in the form of a ring.
Functional liver failure manifests itself in a toxic effect on brain cells, which causes fatigue, weakness, drowsiness, depression, insomnia, irritability, and changes in character. The appearance of these symptoms requires an immediate liver test.
The diagnostic scheme is based on objective manifestations and identification of impaired organ performance indicators. The patient's story and complaints must be taken into account.
Risks
The main enemies of the liver are alcohol, fatty foods, hepatitis virus and medications. You should be especially wary of certain products. This is primarily margarine and anything made with it, since it contains high amounts of trans fats (a form of fatty acids that are not fully saturated with double bonds). Margarine destroys liver cells and causes fatty liver. People with weak livers should be wary of fructose and fructose syrup. They stimulate the release of insulin, which in turn provokes the formation of fat in the liver, which leads to inflammation in this organ. Research shows that inflammation of the liver cells very often leads to cirrhosis and then to liver cancer. If you value your liver, you should try to exclude foods containing monosodium glutamate from your diet. For example, all Chinese instant food and soy sauce contain this chemical preservative. This component is completely foreign to the liver, which removes toxins from the human body. Monosodium glutamate, passing through the liver cells, causes oxidative stress, and the cell walls begin to break down. Destroyed tissue is replaced by scars, which prevent the regeneration of new, healthy cells. This process is called cirrhosis of the liver. The enemy of the liver is carbonated water with sweeteners. Sweetener is toxic to this organ and causes fatty deposits, in the layers of which cancer cells form.
What should a doctor identify during an appointment?
To determine liver disease, the doctor has the opportunity to question the patient, find out the most typical complaints and perform an examination. The result is a presumptive diagnosis. To confirm, the doctor decides which tests to order to check the liver. This is important, since not all high-quality studies can be carried out by the laboratory of the clinic; it is possible that some tests will have to be taken in private institutions on a paid basis.
During diagnosis, doctors use such an ancient method of determining the boundaries of the liver as Kurlov percussion. The method cannot be considered reliable in modern conditions, since it depends on the doctor’s practice and the ability to detect the slightest change in sound.
Percussion is carried out with short blows on the middle phalanx of the third finger of the pressed palm, the finger moves to the place where a change in sound is heard
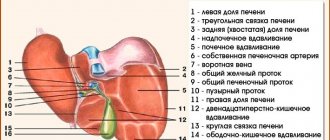
The liver percussion technique involves determining the boundaries of the lower and upper edges of the organ along the right midclavicular and parasternal (runs along the outer border of the sternum) lines. Then the distance between the extreme points is measured. Sometimes there is a need to percussion along the anterior axillary line on the right.
The position of the left lobe is clarified by percussion from the upper point of the midline of the sternum to the left at an angle of 45 degrees. The table shows the norm for children and adults.
| Line names | Size for children under 7 years old in cm | Size for children 7–10 years old in cm | Adult size in cm |
| Right midclavicular | 5,5–6,5 | 6,5–9,5 | no more than 10 |
| Right parasternal | 4,5 | 6,5 | 7–8 |
| Deviation at an angle | 5,5 | 7,5 | 7 |
Pediatricians believe that percussion is suitable for diagnosis in children after 7 years of age. Small deviations are possible with different body types (asthenics and hypersthenics). The given dimensions should not be confused with the size revealed by ultrasound. Most often, a displacement of the lower edge is detected, which is confirmed by further palpation (hepatitis).
The upper border of the liver is in contact with the right lung. An increase is possible with a large cyst, tumor, or abscess. Fixation of reduced sizes is possible. This symptom accompanies primary biliary cirrhosis and other types of fibrosis of the liver tissue.
Preparing for the test
Some medications may interfere with the test, so your doctor may ask you not to take them until after the test. It is also recommended to do the test on an empty stomach, but drink some water first.
Liver tests are just like any other blood test—blood is drawn with a syringe from your forearm into a vial and then sent to a laboratory for testing. To avoid a hematoma after the needle is inserted, apply pressure to the wound with a piece of gauze or cotton until the bleeding stops. If you are afraid of blood, tell the nurse performing the procedure.
What tests do you need to take to check your liver?
Be sure to check:
- general blood test - often an increase in ESR, hemoglobin is detected, eosinophilia is found in autoallergic processes;
- a positive test for urobilin in urine is significant;
- Gregersen's reaction - in case of a positive result, indicates hidden bleeding.
It will not be possible to check the liver only with general tests, because changes often accompany various diseases and are not specific. Among the methods of laboratory diagnostics, the main importance is attached to biochemical tests.
The following must be checked in blood serum:
- protein and its fractions - against the background of a decrease in the overall level in liver diseases, globulins predominate over albumins;
- bilirubin - identified by type (direct or indirect), the increase in indirect (unconjugated) bilirubin indicates a failure in its processing in the liver cells, accumulation leads to jaundice;
- thymol test - important for diagnosing inflammation in hepatitis;
- coagulation disorders - can be confirmed by poor tests for fibrinogen and prothrombin index.
Changes in fat metabolism and the onset of fatty hepatosis are judged by the concentration of cholesterol, triglycerides, lipoproteins
The importance of enzyme tests
A blood test can reveal abnormal levels of enzymes, which are found mainly in hepatocytes. Therefore, their growth indicates the degree of destruction of liver cells (hepatitis, cirrhosis, cancer). Transaminases - aspartic and alanine - proportionally reflect the degree of damage. Alkaline phosphatase - increases more often during a tumor process.
In addition, lactate dehydrogenase, gammaglutamyltransferase, sorbitol dehydrogenase, gammaglutamine transpeptidase, fructose-1-phosphate aldolase (F-1-FA) are determined. To exclude pancreatic diseases, blood aldolase and urine diastase are checked.
A comprehensive laboratory examination of the liver, allowing to assess its main functions and indicators of protein, carbohydrate, fat and pigment metabolism.
The examination results are issued with a doctor’s interpretation.
Synonyms Russian
- Tests to evaluate liver function
- Liver disease screening
English synonyms
- Laboratory liver panel
- Liver function tests
- Liver check-up
Research method
- Coagulogram No. 1 (prothrombin (according to Quick), INR) – method of detecting side light scattering, determining the percentage by end point
- Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) – UV kinetic test
- Serum Albumin – BCG Method (Bromocresol Green)
- Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) - UV kinetic test
- Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (gamma-GT) – kinetic colorimetric method
- Total bilirubin – colorimetric photometric method
- Direct bilirubin – colorimetric photometric method
- Total alkaline phosphatase – colorimetric photometric method
- Total cholesterol - colorimetric photometric method
- Indirect bilirubin – colorimetric photometric method
- Bilirubin and its fractions (total, direct and indirect) - colorimetric photometric method
Units
- Coagulogram No. 1 (prothrombin (according to Quick), INR) – % (percent), sec. (seconds)
- Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) – U/L (unit per liter)
- Serum albumin – g/l (grams per liter)
- Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) – U/L (unit per liter)
- Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (gamma-GT) – U/L (unit per liter)
- Total bilirubin – µmol/l (micromoles per liter)
- Direct bilirubin – µmol/l (micromol per liter)
- Total alkaline phosphatase – U/l (unit per liter)
- Total cholesterol – mmol/l (millimoles per liter)
- Indirect bilirubin – µmol/l (micromol per liter)
- Bilirubin and its fractions (total, direct and indirect) – µmol/l (micromoles per liter)
What biomaterial can be used for research?
Venous blood.
How to properly prepare for research?
- Do not eat for 12 hours before the test.
- Avoid physical and emotional stress for 30 minutes before the test.
- Do not smoke for 30 minutes before the test.
General information about the study
The liver is the largest gland in the human body. This organ performs about 5,000 different functions. Basic liver functions can be assessed using a comprehensive laboratory test.
1. Synthetic liver function
- Albumin is the main blood protein that performs a transport function and ensures the maintenance of oncotic pressure. When the synthetic function of the liver is impaired, the concentration of this protein usually decreases. It should be noted that this decrease is observed in severe liver diseases, such as fulminant hepatitis and severe liver failure. On the contrary, with torpid or latent liver diseases (hepatitis C, alcoholic hepatitis), the level of total protein may remain within normal limits. In addition, changes in albumin concentration can be observed in many other diseases and conditions, such as starvation, malabsorption, nephrotic syndrome, infectious diseases, etc.
- Prothrombin according to Quick (another name is prothrombin time) and international normalized ratio (INR) are the main indicators used to assess the extrinsic pathway of blood clotting (fibrinogen, prothrombin, factor V, VII and X). The liver is the main source of synthesis of these factors, and diseases of this organ can be accompanied by a violation of the coagulation mechanism and lead to increased bleeding. It should be noted, however, that clinically significant blood coagulation disorders are observed in the later stages of liver disease.
- Cholesterol can be synthesized in almost any cell of the body, but most of it (up to 25%) is synthesized in the liver, from where this compound enters the systemic circulation as part of very low-density lipoproteins (VLDL) or into the gastrointestinal tract as part of bile acids. Hypercholesterolemia is a characteristic feature of hepatic cholestasis observed in cholelithiasis, primary sclerosing cholangitis, viral hepatitis, primary biliary cirrhosis and some other diseases. Hypocholesterolemia is of less clinical significance. Different fractions of cholesterol are associated with different effects on human health. Thus, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) is a well-known risk factor for heart disease, while HDL-C is considered one of the protective factors.
2. Metabolic function of the liver
- ALT and AST are enzymes necessary for the metabolism of amino acids. Although these enzymes can also be found in many other tissues and organs (heart, skeletal muscle, kidneys, brain, red blood cells), changes in their concentration in the blood are more often associated with liver disease, hence their name - hepatic transaminases. ALT is a more specific marker of liver disease than AST. With viral hepatitis and toxic liver damage, as a rule, there is an equal increase in the levels of ALT and AST. In alcoholic hepatitis, liver metastases and cirrhosis, a more pronounced increase in AST is observed than in ALT.
- Alkaline phosphatase, ALP, is another key liver enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of phosphate groups between different molecules. The level of alkaline phosphatase is determined if cholestasis is suspected: the concentration of total alkaline phosphatase is increased in almost 100% of cases of extrahepatic obstruction of the biliary tract. In addition to hepatocytes, alkaline phosphatase is present in bone tissue and intestinal cells, and an increase in total alkaline phosphatase can be observed not only with liver damage, but also with other diseases (bone diseases, myocardial infarction, sarcoidosis).
- Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase, gamma-GT, is a liver enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of the gamma-glutamyl group of glutathione to other molecules. Currently, gamma HT is the most sensitive marker of liver disease. An increase in the concentration of gamma-GT can be observed in all liver diseases, but the greatest significance of this marker is in the diagnosis of biliary tract obstruction. With obstruction of the biliary tract, the concentration of gamma-GT increases 5-30 times. A study of the gamma-GT level makes it possible to verify that the increase in total alkaline phosphatase is caused by liver disease and not by other reasons, primarily by diseases of the skeletal system. As a rule, with obstruction of the biliary tract, a parallel increase in the level of gamma-GT and total alkaline phosphatase is observed. High levels of gamma-GT are characteristic of metastatic lesions and alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver. With viral hepatitis, there is a moderate increase in the level of gamma-GT (2-5 times).
3. Excretory function of the liver
- Bilirubin is a pigment formed during the breakdown of hemoglobin and some other heme-containing proteins in the liver, spleen and bone marrow. It exhibits toxicity to the nervous system and must be eliminated from the body through bile or urine. Bilirubin excretion is a multistep process in which the liver plays a major role. There are two main fractions of bilirubin: direct and indirect bilirubin. When bilirubin binds to glucuronic acid, conjugated bilirubin is formed in the liver. Since this type of bilirubin can be determined directly by a direct laboratory test, it is also called direct bilirubin. Bilirubin that has not undergone conjugation with glucuronic acid is called unconjugated. In laboratory conditions, it is not possible to determine the level of unbound bilirubin: its concentration is calculated based on the concentrations of total and bound bilirubin. For this reason, this type of bilirubin is also called indirect. Total bilirubin consists of both fractions. An increase in bilirubin levels can be observed in many liver diseases, but the greatest value of this marker lies in the differential diagnosis of jaundice. Hemolytic (prehepatic) jaundice is characterized by an increase in total and indirect bilirubin. For hepatic jaundice, an increase in both fractions (direct and indirect bilirubin) and total bilirubin is typical. Obstructive (subhepatic) jaundice is characterized by an increase in total and direct bilirubin.
This comprehensive study includes indicators to assess the basic functions of the liver. In some situations, however, additional tests may be required. It is recommended to perform repeated tests using the same test systems, that is, in the same laboratory.
What is the research used for?
- To assess liver function and early diagnosis of diseases affecting it.
When is the study scheduled?
- During a preventive examination;
- in the presence of symptoms of disease of the liver, gallbladder and bile ducts: pain or discomfort in the right hypochondrium, nausea, abnormal stool, darkening of the color of urine, the appearance of jaundice, edema, increased bleeding, fatigue;
- when monitoring a patient receiving hepatotoxic drugs for any disease (methotrexate, tetracyclines, amiodarone, valproic acid, salicylates).
What do the results mean?
Reference values
Coagulogram No. 1 (prothrombin (according to Quick), INR)
- Prothrombin according to Quick: 70 - 120%.
- INR
| Age | Reference values |
| Less than 3 days | 1,15 — 1,35 |
| 3 days – 1 month | 1,05 — 1,35 |
| 1 month – 1 year | 0,86 — 1,22 |
| 16 years | 0,92 — 1,14 |
| 6 – 11 years | 0,87 — 1,20 |
| 11 – 16 years | 0,97 — 1,30 |
| More than 16 years | 0,8 — 1,2 |
| Week of pregnancy | Reference values |
| 1-13th | 0,8 — 1,2 |
| 13-21st | 0,56 — 1,1 |
| 21st-29th | 0,5 — 1,13 |
| 29-35th | 0,58 — 1,17 |
| 35-42nd | 0,15 — 1,14 |
- Prothrombin time
| Age | Reference values |
| Less than 3 days | 14.4 - 16.4 sec. |
| 3 days – 1 month | 13.5 - 16.4 sec. |
| 1 month – 1 year | 11.5 - 15.3 sec. |
| 1-6 years | 12.1 - 14.5 sec. |
| 6-11 years | 11.7 - 15.1 sec. |
| 11-16 years old | 12.7 - 16.1 sec. |
| More than 16 years | 11.5 - 14.5 sec. |
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT)
| Age, gender | Reference values | |
| 0 - 1 year | ||
| 1 – 4 years | ||
| 4 – 7 years | ||
| 7 – 13 years | ||
| 13 - 18 years old | ||
| > 18 years old | men | |
| women | ||
Serum albumin
| Age | Reference values |
| 28 - 44 g/l | |
| 4 days - 14 years | 38 - 54 g/l |
| 14 – 18 years old | 32 - 45 g/l |
| > 18 years old | 35 - 52 g/l |
Aspartate aminotransferase (AST)
| Age, gender | Reference values | |
| 0 - 1 year | ||
| 1 – 4 years | ||
| 4 – 7 years | ||
| 7 – 13 years | ||
| 13 - 18 years old | ||
| > 18 years old | men | |
| women | ||
Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (gamma-GT)
| Age, gender | Reference values | |
| 0 - 1 year | ||
| 1 – 4 years | ||
| 4 – 7 years | ||
| 7 – 13 years | ||
| 13 - 18 years old | ||
| > 18 years old | men | |
| women | ||
Total bilirubin
| Age | Reference values |
| Less than 1 day | 24 - 149 µmol/l |
| 1-3 days | 58 – 197 µmol/l |
| 3-6 days | 26 - 205 µmol/l |
| More than 6 days | 0 - 21 µmol/l |
Direct bilirubin: 0 - 5 µmol/l.
Total alkaline phosphatase
| Age, gender | Reference values | |
| 2 – 5 days | ||
| 5 days - 6 months. | ||
| 6 - 12 months | ||
| 1 – 4 years | ||
| 4 – 7 years | ||
| 7 – 13 years | ||
| 13 - 18 years old | male | |
| female | ||
| > 18 years old | male | 40 – 130 U/l |
| female | 35 - 105 U/l | |
Total cholesterol:
Indirect bilirubin: calculated indicator.
Reasons for increase/decrease depending on the indicator being determined:
- Coagulogram No. 1 (prothrombin (according to Quick), INR)
- Alanine aminotransferase (ALT)
- Serum albumin
- Aspartate aminotransferase (AST)
- Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (gamma-GT)
- Total bilirubin
- Direct bilirubin
- Total alkaline phosphatase
- Total cholesterol
- Bilirubin indirect
- Bilirubin and its fractions (total, direct and indirect)
What can influence the result?
Reasons depending on the indicator being determined:
- Coagulogram No. 1 (prothrombin (according to Quick), INR)
- Alanine aminotransferase (ALT)
- Serum albumin
- Aspartate aminotransferase (AST)
- Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (gamma-GT)
- Total bilirubin
- Direct bilirubin
- Total alkaline phosphatase
- Total cholesterol
- Bilirubin indirect
- Bilirubin and its fractions (total, direct and indirect)
What is needed to test for viral hepatitis?
How long does it take to test for hepatitis?
If viral hepatitis is suspected, confirmation with marker tests is necessary. This requires immunological reactions:
- for total antibodies;
- viral load.
In a specialized laboratory, immunological methods for studying the liver are used:
- linked immunosorbent assay;
- immunoblotting;
- radioisotope diagnostics.
Using the polymerase chain reaction method, it is possible to identify the type of virus in hepatitis using a minimal amount of genetic information.
Liver biopsy
For a biopsy, a piece of tissue is taken from the liver, and then a laboratory examination of the cells is performed. This method is used if other diagnostic methods do not provide complete information about organ damage (type and severity) and the presence of complications. A gastroenterologist may prescribe a biopsy for jaundice of unknown origin and suspected tumor2. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia and ultrasound guidance.
They try not to prescribe a biopsy without serious reasons, since it may cause complications: damage to neighboring organs, wound infection, internal bleeding and less severe consequences such as general weakness, dyspepsia and increased body temperature.
Liver examination using medical equipment
In modern medicine, to check liver pathology, objective indicators are used from devices created on the basis of the penetrating and reflective ability of ultrasonic vibrations, the resonating capabilities of magnetic radiation, and the accumulation of isotopes in “related” tissue.
Ultrasound diagnostics of the liver is carried out routinely and urgently in any hospital. The procedure is safe for small children and pregnant women. Allows you to identify the exact size of the organ, the density of the parenchyma structure, the node and localization of the neoplasm, cysts, and the degree of damage.
Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are even more informative. They give results in a multidimensional image, allowing you to see the degree of replacement of the parenchyma with scar tissue. Better display of intrahepatic ducts and vessels. Scanning is carried out using intravenous injection of isotopes, which are delivered by blood to the liver. Here they are distributed throughout all functioning cells.
When scanning, it is possible to identify areas of scar changes in non-functioning tissue, establish tumor growth (the isotope does not pass into malignant cells), and the extent of the remaining healthy parenchyma. Biopsy is prescribed only if the results of other types of studies are insufficient, for differential diagnosis with tumors.
During a biopsy, a needle is inserted into the liver, with which material is removed and subsequently processed in the laboratory.
Should you test yourself with beets?
Popular recommendations for checking the liver after eating boiled beets, although there are sufficiently accessible methods in medical institutions, do not have proven effectiveness. The beetroot “test” requires eating medium-sized boiled beets in the evening. Next comes the “decoding”
If the liver is working well, then the urine should become colored after 16 hours; with earlier coloring (for example, after 3 hours), a conclusion is drawn about poor function. It seems to us that this test will work better to convince people suffering from alcoholism to stop drinking at least for a while. In other cases we do not recommend using it.
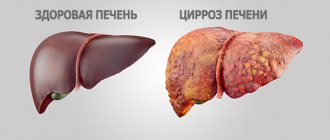
What is done to detect cirrhosis?
To identify cirrhosis, the patient undergoes all the described diagnostics. Fibrogastroduodenoscopy is also necessary. In conclusion, the doctor notes the blood-filled and dilated veins of the stomach and esophagus, signs of concomitant gastritis, duodenitis. To determine the type of cirrhosis, all immunological and biochemical tests are necessary.
In addition to the alcoholic cause, the disease can be a consequence of chronic viral hepatitis C. It is important to consider that for a long time the pathology is asymptomatic. Much more than for other pathologies, a liver biopsy is indicated.
In some cases, it is necessary to resort to laparoscopy under general anesthesia (insertion of an optical tube into the abdominal cavity). Anyone can have their liver checked if they feel something is wrong with their health or find typical symptoms. The main thing is not to delay and get an answer to solve your problem.
Cost of all comprehensive examinations
| Service | Price according to Price | Discount |
| Annual cancer screening for women (ultrasound OMT, breast ultrasound, tumor markers) | 6300 rub. | 4999 rub. |
| Annual cancer screening for men (ultrasound of the prostate, tumor markers) | 3550 rub. | 2999 rub. |
| Men's health passport (comprehensive ultrasound, tests) | 12350 rub. | 9999 rub. |
| Woman's health passport (comprehensive ultrasound, tests) | 10840 rub. | 8999 rub. |
| Full check-up for male athletes (comprehensive ultrasound, tests) | 18500 rub. | 14999 rub. |
| Full check-up for female athletes (comprehensive ultrasound, tests) | 18900 rub. | 14999 rub. |
| Check your kidneys - comprehensive kidney examination (kidney ultrasound, tests) | 3530 rub. | 2999 rub. |
| Check your liver - comprehensive liver examination (liver ultrasound, tests) | 4670 rub. | 3999 rub. |
| Check your thyroid gland - a comprehensive examination of the thyroid gland (ultrasound of the thyroid gland, hormone tests) | 3800 rub. | 2999 rub. |
| Comprehensive ultrasound (ultrasound of the abdominal cavity + ultrasound of the kidney + ultrasound of the thyroid gland) | 3200 rub. | 2599 rub. |
| Comprehensive ultrasound for women (ultrasound of the abdominal cavity + ultrasound of the kidneys + ultrasound of the thyroid gland + ultrasound of the pelvis with an abdominal probe + ultrasound of the mammary glands) | 5800 rub. | 4599 rub. |
| Comprehensive ultrasound for men (ultrasound of the abdominal cavity + ultrasound of the kidney + ultrasound of the thyroid gland + ultrasound of the prostate gland with an abdominal probe) | 4700 rub. | 3699 rub. |
| “Healthy Legs” program (duplex scanning of the veins of the lower extremities with assessment of valves and perforating veins and duplex scanning of the arteries of the lower extremities) | 4500 rub. | 3999 rub. |
| Comprehensive diagnosis of headache or dizziness (MRI of the brain, MRI of the cervical spine, ultrasound of the brachiocephalic vessels, consultation with a neurologist) | 10900 rub. | 7500 rub. |
| Author's body cleansing program - Reboot (tests, IVs, autohemotherapy) | 23660 rub. | 18999 rub. |