Gallbladder deformity is a widespread disease in Russia and throughout the world. It may be congenital or acquired.
When the position of the neck or body of the gallbladder changes, its deformation occurs. It may look like a bend of the neck or a constriction. Other variants of this pathology are also possible.
Some forms of such deformation do not require treatment at all and go away on their own. But in general, this pathology is fraught with serious consequences, including death.
It can appear in different places of the gallbladder. It depends on where the partition is located. The consequences of gallbladder deformation are largely determined by how much its shape changes.
Under the influence of this process, stagnation of bile can occur. Stones, folds and bends may form in the gallbladder. It is important to diagnose this disease in time and receive the necessary treatment.
What it is?
In cases of deformity, different results can be observed after performing an ultrasound scan.
A disease such as gallbladder deformity can be present in a person from birth or acquired during life.
When the position of the neck or body of the gallbladder changes, its deformation occurs.
It may look like a bend of the neck or a constriction. Other variants of this pathology are also possible.
As a result, cholecystitis forms and adhesions form. The gallbladder may also become enlarged or blood flow to the liver may be impaired.
In this condition, the patient may experience very severe pain and dyspeptic disorders. For deformation associated with intense physical activity, no treatment is needed. She can go away on her own.
Often, patients exhibit deformation of the neck of the gallbladder itself. It often occurs when the patient has chronic cholecystitis. Due to the formation of adhesions on the walls of the gallbladder, this organ can also change its shape. In this case, the composition of bile changes and indigestion occurs.
Sometimes the gallbladder is completely twisted around its axis. This happens with prolonged physical activity. Also, the cause of torsion can be elongation of the neck of the gallbladder. If the cervix is twisted many times, blood flow is instantly disrupted. Deformation of the gallbladder of the contour type manifests itself in changes in the boundaries of this organ. With this form of the disease, the patient experiences pain after eating. They also appear if you constantly carry various weights.
In the case of an S-shaped deformation of the gallbladder, it is double bent. Most often it is associated with heredity. If such a deformity is acquired during life, it is caused by the rapid growth of the gallbladder compared to other organs. This form of deformation does not cause any problems for the patient and there are no symptoms either.
Sometimes bitterness appears in the mouth, stool changes and belching. When the outflow of bile is disrupted, flatulence and dyspepsia occur. There are also problems with the quality of digestion of fatty foods. Any type of gallbladder deformation requires a visit to the doctor.
You should also organize proper nutrition and lead a normal lifestyle.
Prevalence and significance
According to statistics, gallbladder kinks occur in half of the Russian population. The statistics are approximately the same for other countries of the world.
Deformation of the gallbladder can lead to a variety of diseases:
- various neoplasms;
- adhesive process;
- diseases of the digestive system;
- weak diaphragm;
- chronic inflammation in the biliary tract and others.
This disease often develops in patients with kidney stones. In older patients, the gallbladder and internal organs descend. The cause of this may be abdominal surgery or a hernia.
Some types of deformity do not require treatment, others can develop into serious health problems.
Risk factors
- lifting weights;
- heavy loads;
- alcohol abuse;
- high physical activity and overexertion;
- smoking.
What shape is normal for the gallbladder?
When examined with ultrasound equipment, many patients, having seen the images, wonder: a pear-shaped gallbladder, what does this mean? There is no need to worry, because normally this organ is pear-shaped. It is hollow inside and located near the right lobe of the liver. In its structure, the upper and lower surfaces adjacent to the liver are noted.
In adults, the gallbladder is from 7 to 10 cm long and 2.5 cm wide. Up to 35 ml of bile is placed in it, but if obstruction occurs and stagnation occurs, then the maximum volume is 300 ml.
Organ structure
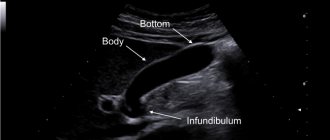
The structure of the organ has 4 departments, each of which is responsible for certain processes in the biliary system.
- the bottom of the organ represents the distal section and may slightly protrude beyond the contour of the liver from below;
- organ body - middle section adjacent to the duodenum and liver;
- A funnel is a segment with advanced options. It connects the neck of the organ to its body;
- The neck is located near the transition of the gallbladder to the common bile duct.
Reasons for appearance
Gallbladder deformities occur for several reasons:
- the innate nature of the problem. In this case, deformation of the gallbladder occurs due to disturbances during intrauterine development. The reasons are hereditary predisposition and poor lifestyle of the pregnant woman;
- gallbladder problems;
- its large size;
- adhesions.
This way you can show the organ system, including the gallbladder
How are anomalies detected?
Inna Lavrenko
auto RU
With any anomalies, it is impossible to determine its type by symptoms. A number of analyzes are necessary, in particular:
- An ultrasound examination is most often prescribed to determine the size and shape of an organ and its pathologies. Not all cases of anomalous structure are detected by ultrasound;
- MRI or CT clarifies the most complex cases of developmental anomalies;
- Oral cholecystography involves the patient taking a contrast agent, after which an x-ray is taken;
- Retrograde cholecystopancreatography performed endoscopically. From the intestinal tract, contrast is introduced using an endoscope and an X-ray examination is performed.
Read also: What type of bandage is needed after gallbladder removal?
Rarely, an anomaly is discovered by surgeons during an operation to treat cholelithiasis or cholecystitis.
Symptoms of the disease
The patient's pain depends on the form of the deformity. Problems with bile secretion can lead to problems with the digestive tract. Twisting of the gallbladder is accompanied by pain in the right side. Inflammation and poor circulation in this organ lead to a deterioration in overall health.
One of the symptoms is a change in complexion, bitterness in the mouth, and increased sweating. When the neck of the gallbladder is twisted, bile immediately enters the abdominal cavity. As a result, acute pain may occur in the left side and throughout the abdomen. Sometimes, when the gallbladder is deformed, the temperature rises and weakness appears.
Also a sign of the disease is bloating after eating food. During the examination, the pain may become stronger and take on the character of an attack. This requires immediate contact with a specialist. With the sudden development of the disease, the patient feels pain in the liver and gall bladder. Another symptom is yellow skin and nausea.
An aversion to any food may also appear. A yellow coating may be found on the tongue. With the gradual development of the disease, the functioning of the biliary tract occurs. As a result, faeces become discolored, loss of appetite occurs, and the patient begins to lose weight.
Also characteristic signs of gradual deformation are dyspepsia, pain in the intestines and right hypochondrium. Necrosis of the gallbladder neck as a result of prolonged deformation is accompanied by the penetration of bile into the abdominal cavity.
As a result, peritonitis develops and the patient may die without medical attention.
How should you prepare for an ultrasound?
In order for the echography of the gallbladder to be accurate and informative, patients need to go on a diet. The main goal of the diet is to reduce the process of gas formation in the intestines. Gas bubbles interfere with the passage of ultrasound waves, which affects the quality of the ultrasound image.
A few days before the ultrasound scan you should avoid:
- carbonated and alcoholic drinks,
- dairy products,
- fatty and spicy foods,
- fresh vegetables,
- sweet fruits,
- legumes,
- black bread and yeast baked goods.
If patients are prone to flatulence, they are recommended to take adsorbents (activated carbon) and enzyme preparations (pancreatin). If you need to take any medications, you should tell your doctor about them. Taking medications may affect the accuracy of the results. The procedure is carried out on an empty stomach. The last meal is allowed 8-10 hours before the ultrasound. During this period of time, the gallbladder has time to fill with bile again, so it will be easier to examine it.
Dietary restrictions also apply to children. Remove sweets and fruits from your child's diet a few days before the ultrasound. Children, like adults, undergo the procedure on an empty stomach. Children under one year old should not be fed 3 hours before an ultrasound scan, children under 4 years old should not be fed 4 hours before, and children under 8 years old should not be fed 6 hours before. Preparation for an ultrasound examination for children over 8 years of age is the same as for adults.
If you have previously undergone an ultrasound examination of the gallbladder, then take with you copies of the protocols; by comparison, you can evaluate the dynamics of recovery or worsening of the organ’s condition. Bring a small amount of food to the clinic before your ultrasound function test. This could be boiled chicken egg yolks, cottage cheese or sour cream. You will be told exactly what to take and in what quantities when you schedule an ultrasound.
Diagnostic methods
The most informative method for examining the abdominal organs is ultrasound. It allows you to quickly detect the disease and prescribe treatment. This method can be used to monitor the condition of organs in pregnant women and children due to its safety.
An ultrasound can show deformation of the walls of the gallbladder and their thickening. It manifests itself as calcium deposits, depressions and protrusions. Using ultrasound, you can see the deformation of the gallbladder from different angles.
How is the procedure done?
As a rule, ultrasound is performed in the first half of the day, always on an empty stomach. Under no circumstances should you drink or eat before the procedure. Even a small amount of water or food provokes the release of bile from the bladder. The organ decreases in size, which makes it difficult to diagnose. You should also refrain from chewing gum before visiting the clinic; it also provokes the secretion of gastric juice and bile. If you are scheduled for an ultrasound examination in the afternoon, then a light breakfast is allowed 6-8 hours before the ultrasound.
The duration of the procedure is 10-15 minutes. The patient is asked to remove his outer clothing and lie on his back on the couch. Before the ultrasound, the sonologist applies a small amount of gel to the patient's skin in the area being examined. The gel ensures continuous contact between the ultrasound transducer and the skin and improves the transmission of ultrasound waves.
During the scan, the doctor moves the sensor over the patient's skin at the location of the organ. To view the gallbladder from a different angle, the patient is asked to change position (sit down or roll over on his left side). The monitor displays the organ and surrounding tissues. The data obtained is included in the study protocol, which is given to the patient. Your attending physician will decipher it and make a preliminary diagnosis.
Carrying out an ultrasound with a choleretic breakfast differs from the standard procedure. During the study, the patient needs to eat several chicken eggs, a glass of full-fat sour cream or cream. Instead of food, a sorbitol solution can be used. First, the organ is scanned at rest. Then the patient must eat a choleretic breakfast, after which 4 ultrasounds are performed at intervals of 15 minutes. On each of them, the ultrasound specialist notes how much the gallbladder has shrunk. Ultrasound with determination of function allows you to determine which type of biliary dyskinesia the patient has (hypomotor or hypermotor disorder).
What are normal indicators for the gallbladder?
During an ultrasound, first of all, the shape, contours and size of the organ are determined. The gallbladder has the shape of a hollow pear, with smooth and clear edges. Its length ranges from 7-14 cm, and its width from 3 to 5 cm. The thickness of the bubble walls is 2-3 mm. The volume of the bile is 40-70 ml. These parameters are considered normal ultrasound for an adult. Normal sizes for the gallbladder of children depend on the height and weight of the child; they are determined using specially compiled tables.
In addition to determining the size of the organ, during the scanning process its ductal system (common bile and lobar bile ducts) is studied. Their diameter, permeability and the presence of concretions (stones) in them are determined. The diameter of the lobar ducts is 2-3 mm, and the common bile duct is 6-8 mm. The common bile duct unites with the Wirsung (pancreatic) duct and flows into the duodenum. Bile enters the gastrointestinal tract along this route.
In normal condition, the organ and its ducts do not have stones or other formations. If any deviations from normal values are detected, the patient is prescribed additional diagnostics.
The norm for ultrasound to determine function is considered to be a reduction of 70% from the initial level, which suggests the absence of dyskinesia.
Treatment
Conservative therapy is used for almost any deformation of the gallbladder. A congenital change in the shape of the gallbladder does not cause problems for the patient and does not require treatment. But acquired organ deformation with painful symptoms requires treatment. It allows you to eliminate pain and inflammation, as well as restore bile excretion.
Treatment of gallbladder deformation involves mandatory bed rest in the acute period. It is also important to drink plenty of fluids other than mineral water. The immune system is strengthened with the help of various vitamins, for example, ascorbic acid, B vitamins, tocopherol and others.
Physiotherapy procedures, for example, electrophoresis with novocaine, are of great importance. Abdominal massage and exercise therapy help remove bile and prevent the formation of stones. To prevent the bladder from twisting along the longitudinal axis, it is important not to carry heavy objects and avoid heavy physical exertion.
Possible different options for deformation of the gallbladder
Drugs
To normalize the functioning of the gallbladder, various medications are used. Antibiotics and painkillers are often used to reduce pain. These include analgesics and antispasmodics: Baralgin and No-shpa in the form of injections. In severe cases, Tramadol is used.
The doctor may also prescribe antibacterial drugs of the antimicrobial spectrum, for example, Ampicillin. Choleretic drugs are used after antibiotic therapy and completion of the acute period. These include Cyqualon, Famin, Gepabene and others. But before using them, you need to be sure that there are no stones in the gall bladder.
Surgery
If a bend in the gallbladder blocks the outflow of bile, a rupture of its wall may occur. In this case, the gallbladder is surgically removed.
Folk remedies
In the absence of complications, you can use traditional methods of treating gallbladder deformity. But treatment with herbal infusions should be long-term, at least 3 months. The following herbs are most often used individually or in combinations: buckthorn, marshmallow, mint, tansy, sage, immortelle, St. John's wort, celandine, lemon balm and chamomile.
Diet
Diet plays a big role in the treatment of this disease. It is important not to eat spicy, salty, sour, fried, smoked or fatty foods. It is allowed to eat boiled, steamed, baked and raw food. It is not recommended to eat cold or very hot food.
Also, avoid drinking carbonated drinks. Food should be light: soups, purees or porridge. Diet is important and we eat small portions. The patient needs to drink about 2 liters of water per day.
Forecast
The consequences of gallbladder deformation are largely determined by how much its shape changes. Under the influence of this process, stagnation of bile can occur. Stones, folds and bends may form in the gallbladder. Long-term circulatory disorder in the biliary organs occurs when the bladder twists and is completely bent.
As a result of this deformation, necrosis of the bladder tissue and perforation of its walls may begin. In this case, the bile secretion enters the abdominal cavity. This leads to the development of bile peritonitis. Intoxication of the whole body begins, and dysfunction of all organs is observed.
Lack of timely assistance for peritonitis can lead to death. But some forms of gallbladder deformity may disappear on their own without any treatment. This applies to labile and congenital deformities. But medical supervision is required in any case to prevent complications.
Possible anomalies in the structure of the gallbladder
In the vast majority, the gallbladder has a normal, pear-shaped shape. Anomalies in the outline of an organ occur in only 2% of the population, and they relate to position, shape, size or quantity.
Incorrect position
- Vagal type gallbladder. If there is a long mesentery, it is possible to move the organ, the so-called. wandering. It can even be found in the pelvis or in the left side of the peritoneum;
- an inflection occurs when there is a large stone at the bottom with a long mesentery. As a rule, excesses are often found in the female half of the population. The bend is close to the neck;
- ectopia of the organ is accompanied by its location in different places. If it is inside the liver, then the gallbladder is surrounded on all sides by hepatic parenchyma. In some cases, it is localized above the liver, behind it, above the diaphragm, or retroperitoneally. With cirrhosis, the right lobe of the liver is missing or its small size, the gallbladder and distal large intestine are located between the diaphragm and the liver. There have also been cases of location in the falciform ligament, the anterior part of the peritoneum, or in the transverse colon.
Read also: Is it possible to live without a gallbladder?
Abnormal size
It is important to know!
78% of people with gallbladder disease suffer from liver problems! Doctors strongly recommend that patients with gallbladder diseases undergo liver cleansing at least once every six months... Read more...
| № | Helpful information |
| 1 | Increased organ size is called cholecystomegaly and occurs in pregnant women, patients with diabetes or sickle-type hemoglobinopathy, obesity, or after vagotomy |
| 2 | reduced size is observed in the case of cystic fibrosis. In this case, the gallbladder contains a lot of thick bile and cholesterol stones. Cystic fibrosis is characterized by the presence of viscous bile with thick sediment at the bottom |
Form anomalies
- The Phrygian cap form is the most common, occurring in 6% of all patients. The name is associated with the appearance of the organ, reminiscent of the Phrygian caps - high headdresses with a small end tilted forward. With this shape, the bottom bends in the organ like the inclined end of a cap. This form is an anomaly, but does not cause harm to health;
- multiple septa in an organ - a large number of transverse septa are found inside, and the surface is lumpy. The shape of the organ is normal, the size does not differ from the norm, all internal chambers communicate with each other. Partitions are a congenital provoking factor for stagnation of bile and intense stone formation in the biliary system;
- Diverticula in the organ are represented by bulging walls. Such pouch-like growths do not cause symptoms and can be in any part of the bladder. As a rule, there is one protrusion, the size of which varies depending on the specific case. Such formations contain all the layers of the organ walls, this is the difference from pseudodiverticula, which do not contain a muscle layer. Diverticula can be of the acquired type, developing due to adhesions or pathologies of the duodenum.
Quantitative anomalies
- Agenesis is characterized by the congenital absence of the gallbladder, which occurs during the formation of the fetus in the womb. Most children with this anomaly have other abnormalities in the heart, anus, bones, fistulas between the rectum and vagina;
- organ duplication occurs in one case out of 4000. It is caused by a longitudinal septum that is constantly present in the organ. This often results in doubling of the cystic ducts. The anomaly provokes kinks, carcinoma, papilloma, mechanical jaundice, and secondary biliary cirrhosis. If a cholecystectomy is necessary, surgeons remove both organs. In clinical practice, cases of three and four gallbladders in one body are known.
Read also: Causes of acne due to stagnation of bile