The color and consistency of stool can tell a lot about both the state of the child’s body in general and the digestive system in particular. Moreover, most often parents are faced with the phenomenon of very light-colored feces in their child. Many parents are confused and don’t know what caused this color change and whether it is dangerous.
Even doctors cannot give a definite answer as to what a child’s stool should be like normally. This is influenced by a fairly large number of different factors: the age of the child, the nature of his diet. In principle, the average variant of the norm is considered to be mushy, light brown stool, somewhat reminiscent of apricot puree. And even then, it will take at least a week to form. Until then, a newborn baby’s stool can be anything.
READ ALSO - Treatment of gastritis in children
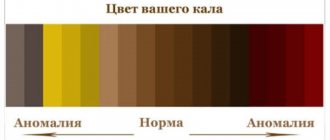
But if the baby’s stool is too light or, even more so, white, parents should be wary. Of course, you shouldn’t panic and assume the worst, but it’s still worth informing your pediatrician, since sometimes light-colored stool can be a symptom of various diseases. Feces acquire their standard brown color due to the presence of a special pigment in them - stercobilin. And if any malfunction occurs in the functioning of the internal organs, the production of this substance may not only be reduced, but also stop completely.
Causes of grayish-white stool
Errors in diet
The discharge of gray feces in adults is observed after excessive consumption of fatty foods.
Excessive amounts of neutral fats accumulate in the intestines; due to the increased load on the pancreas, lipids are not digested and are excreted in the feces. The consistency changes - the feces become soft, “greasy”, leaving marks on the walls of the toilet. Typically, stool frequency increases up to 3-4 times a day. Usually the symptoms disappear on their own, and the color of the stool normalizes the very next day. The reasons that provoke the passage of grayish-white stool in infants are improper introduction of complementary foods, the use of unbalanced milk formulas. Changes in the color of feces occur against the background of general weakness and lethargy of the child, constant crying and refusal to feed. These symptoms are an indication for consultation with a pediatrician.
Dysbacteriosis
Violation of the composition of the intestinal microflora causes digestive disorders and insufficient digestion of incoming food. The stool becomes liquid and grayish-white or dark gray in color. The frequency of stool with dysbacteriosis increases to 5-7 times a day, defecation is preceded by spasms and discomfort in the left abdomen. The stool has a foul odor and a light gray coating can be seen on the surface.
Hepatitis
Infectious causes cause destruction of liver cells and disturbances in bilirubin metabolism, which reduces the flow of stercobilin into the intestines, which colors stool brown. Gray feces appear at the height of hepatitis; the symptom is combined with a sharp darkening of the urine and yellowing of the skin. An increase in stool frequency and a change in its consistency are typical; before defecation, patients feel rumbling and “bubbling” in the abdomen.
The duration of the symptom depends on the type of liver inflammation. In mild forms of viral hepatitis A and E, grayish-white stool discharge persists for 2-3 weeks. With hepatitis B, the color of stool returns to normal after 1-2 months; in case of severe damage to the liver parenchyma, dark gray feces are excreted for up to six months. Alcoholic hepatitis, complicated by damage to the pancreas, often causes persistent lightening of the stool.
Cholelithiasis
The discharge of grayish-white feces indicates an exacerbation of cholelithiasis and blockage of the bile duct with a stone. In this case, bile does not enter the intestines, and symptoms of obstructive jaundice develop. The person notices that the stool becomes light, almost white, and the consistency of the stool often remains normal. Discoloration of the stool occurs simultaneously with severe pain in the right hypochondrium, nausea, and bitterness in the mouth.
Pancreatitis
A change in the color of stool to white in adults occurs with chronic pancreatitis, which is characterized by enzyme deficiency of the pancreas. The light color is due to the accumulation of undigested food in the feces. The stool is copious, grayish-white in color, with a strong fetid odor. There is an increase in stool frequency; during defecation, patients experience diffuse abdominal pain.
Disorders of pancreatic function are often irreversible, therefore, without prescribing replacement therapy, restoration of normal stool color is impossible. The patient's condition worsens under the influence of external causes - with the abuse of heavy food, drinking alcohol, the disease worsens. During this period, diarrhea with the release of a large amount of light-colored feces, accompanied by intense pain in the left hypochondrium and epigastrium, is a concern.
Other liver pathologies
Damage to liver cells of various etiologies is accompanied by parenchymal jaundice, which is typically characterized by the appearance of a grayish-white color of stool. Such changes persist for a long time, for several months. Abnormal bowel movements are associated with dull pain and heaviness in the right hypochondrium, nausea and vomiting with bile. Most often, stool discoloration is caused by the following reasons:
- Cirrhosis
: alcoholic, postnecrotic, biliary. - Space-occupying formations
: hepatocellular carcinoma, hydatid cyst, polycystic liver disease. - Functional disorders
: Gilbert's syndrome, Crigler-Najjar syndrome, cholestasis of pregnancy.
Complications of pharmacotherapy
A short-term change in the color of stool to grayish-white is a natural reaction after taking barium sulfate orally for X-rays of the digestive tract. Light-colored stool passes 10-12 hours after the examination; the atypical color of stool persists for 2-3 days. Normally, these changes are not accompanied by dyspeptic disorders or abdominal pain.
Gray feces are also provoked by other reasons: taking antacids, iron. Microelements, which are contained in large quantities in these medications, accumulate in the feces and cause the appearance of a characteristic grayish-white color. When using iron supplements, the color becomes darker, even black. Discoloration of stool is possible with prolonged use of antibiotics and anti-tuberculosis drugs.
Rare causes
- Inflammatory bowel diseases
: Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, chronic enteritis. - Celiac disease
. - Malignant tumors
: cancer of the head of the pancreas, cancer of the duodenum. - Bile duct atresia
.
Baby food
If, apart from the change in the color of the child’s stool, nothing else bothers the baby, parents should also check the color of the child’s urine. If the color of the child’s urine has not changed and it has not become more saturated, stop panicking and just carefully watch the baby. Pay attention to your child's sleep, appetite, and behavior while awake. If something is bothering the baby, attentive parents will notice it very quickly.
READ ALSO - The clinic offers a range of services
When you first notice light-colored stool in your child, try to remember what your child ate the day before. Of course, if we are talking about a baby who feeds exclusively on mother’s milk, it is the mother who needs to reconsider her diet. If your baby is fed artificial milk formula, remember if you changed it the day before.
And even more so, it is necessary to pay special attention to what exactly the child ate if he is already old enough to eat the same thing that adult family members eat. For example, foods high in calcium can cause a child’s stool to become white, with a very thick and viscous consistency, like clay.
Think about whether your child ate cottage cheese with sour cream the day before, or maybe you overdid it with vitamins? In addition, this can happen due to the fact that the baby ate a lot of food rich in carbohydrates the day before. Therefore, carefully monitor what exactly and in what quantities your child eats.
Diagnostics
A gastroenterologist is involved in identifying the cause of gray stool. The specialist collects anamnesis and complaints to determine why dyspeptic disorders appeared. Diagnostics includes instrumental visualization methods, which, if indicated, are supplemented with invasive techniques. To clarify the diagnosis, laboratory tests are prescribed. The most informative methods:
- Coprogram
. Microscopic analysis of grayish-white stool reveals remains of undigested food, muscle fibers, and starch grains. The absence of stercobilin is pathognomonic. To confirm the diagnosis of pancreatitis, a fecal elastase level test is performed. Bacteriological analysis is necessary to identify dysbiosis and bacterial overgrowth syndrome. - Blood chemistry
. With obstructive jaundice, cholestasis syndrome is determined - an increase in the amount of cholesterol and the enzyme alkaline phosphatase. An increase in ALT and AST levels indicates cytolysis and parenchymal jaundice. To test the exocrine function of the pancreas, the concentration of pancreatic lipase and amylase is measured. - Ultrasonography
. In order to detect the organic cause of a grayish-white stool, a survey ultrasound of the abdominal cavity is performed with targeted scanning of the organs of the hepatobiliary zone. The study allows you to visualize signs of the inflammatory process of the gallbladder, heterogeneous echogenicity of the liver parenchyma, and rounded volumetric neoplasms. - Duodenal sounding
. To assess the flow of bile into the intestine, several portions of bile are taken sequentially after stimulation with secretory drugs. Typically there is a slow release of bile or its complete absence in case of blockage of the common bile duct. The collected material is sent to the laboratory for bacteriological analysis. - Cholangiopancreatography
. White feces usually appear when the biliary tract is damaged, so RCCP is required. The method involves examining the papilla of Vater and bile ducts using endoscopic technologies. The study reveals stones in the bile ducts, signs of inflammatory and tumor pathologies.
Reproduction
You can get new calla lilies in three ways:
- tubers;
- shoots;
- seeds.
Tubers
Use this method exclusively for colored plants. Separate the small daughter tubers from the adult tuber. They are so small that they will have to be grown. Deepen the seed into the soil mixture to a depth of 4 cm. In April, you can plant them in separate pots. While the nodules are developing, maintain the room temperature at +20°C. Maybe a little more, but not less.
By shoots
In this case, a shoot is taken from the main stem and placed in a nutrient substrate. As soon as the roots appear, you need to transplant it into a separate pot with a drainage layer and fertile soil.
Seeds
It is advisable not to use this method for novice gardeners, as it will be incredibly difficult to get new bushes. Even experienced flower lovers do not always produce shoots. But if you want, you can try.
Pre-soak the seeds in a growth stimulator for about 6 hours. After removing, set aside for a week in a warm place. When you notice that the seeds have sprouted shoots, plant them in a container. The planting depth should not exceed 1 cm. It is best to water the planting through the drainage hole in the bottom.
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
Grayish-white stool caused by dietary errors does not need to be treated. The patient is advised to eat easily digestible foods (stewed vegetables, soups, lean meat) for several days and reduce the size of portions. You can't drink alcohol. If during this time the stool has not returned to normal, you should consult a doctor to determine the cause of the disorder.
To avoid diarrhea and stool discoloration when taking antibiotics and other toxic drugs, it is advisable to drink natural kefir and yogurt, which are rich in beneficial bifidobacteria and lactobacilli. Self-administration of enzyme preparations to improve digestion is not recommended, as this can cause disruption of the pancreas.
Conservative therapy
Treatment of dyspeptic disorders, including grayish-white feces, is mainly aimed at eliminating the cause of the symptoms, after which the color and consistency of the stool normalizes. Medications must be supplemented with a special therapeutic diet, which is selected depending on the disease. In clinical practice, the following drugs are used:
- Enzyme preparations
. Medicines containing pancreatic extract improve the processes of parietal and cavity digestion in the small intestine. Gray feces disappear a few days after starting medication, and the severity of other dyspeptic disorders decreases. - Probiotics
. They are a mixture of beneficial bacteria that populate the large intestine and prevent the proliferation of pathogenic microflora. In adults, they are prescribed for long-term antibiotic therapy and combined with prebiotics, which stimulate the growth of bifidobacteria. - Choleretic agents
. They increase the contractility of the gallbladder and dilate the ducts, improve the colloidal properties of bile, due to which it is released into the intestines in the required quantities. Additionally, hepatoprotectors are recommended, which protect cells from the toxic effects of bile acids. - Antiviral drugs
. For chronic hepatitis of viral etiology, special treatment regimens with interferons and RNA polymerase inhibitors are used. Medicines reduce the viral load in the blood and inhibit viral replication in liver cells. They are combined with detoxification agents.
Bloom
Usually the serpentine blooms in the second year. The tall peduncle is topped with small flowers, wrapped in a bright leaf-spread. At this time, the plant needs frequent watering and regular feeding.
At the end of flowering, remove the tuber from the pot, shake off the soil mixture, and rinse under running water. Let it dry. After a few days, carefully separate the leaves. Leave it for 2 weeks, then remove the roots and rotten parts, wrap it in paper and leave it alone. Keep in a room with a temperature of +16-18°C and do not wet it under any circumstances. After 3-6 months, you can plant the tuber in a new flowerpot.
Diseases
Due to the relatively humid environment, calla lilies can be susceptible to various diseases:
- rhizome rot (brown spots at the base of the stem, rhizome and root);
- wet rot of the base of the stem (rotting of the rhizome and roots, white coating);
- spotting (spots and stripes on leaves).
Pathogens develop at high temperatures and high humidity. As a precaution, it is recommended to sterilize the substrate before planting the tubers and ensure proper air circulation around the plant. The development of diseases is facilitated by excessive overwatering of plants and low soil permeability.
Another disease of callas is a fungus of leaves and inflorescences caused by fungi of the genera Coniothecium, Alternaria and Phyllosticta. The disease occurs when the leaf is over-sprayed at a relatively high ambient temperature.
Callas are also susceptible to leaf mosaicism caused by Dachenne mosaic virus and calla mosaic virus (Zatemchia Mic Mosais – ZaMMV). Viruses cause leaf discoloration, necrosis and plant death.
Heavily infested plants should be removed and burned to prevent the pathogens from spreading.
Kinds
We are used to seeing white callas. They look noble, and a snow-white blanket envelops the inside of the flower, which can be yellow, pink, greenish or orange. They usually bloom in May and are pleasing to the eye until the end of summer. They have rhizomes.
Mixed callas surprise with perianths of various colors and shades. The breeders tried to ensure that there were a great many of them. They belong to tuberous crops.
At home, they most often contain the following types:
- Elliott is a profusely blooming species with a contrasting color: greenish on the outside and yellow on the inside, with white spots scattered on the leaves;
- Ethiopian - the leaves grow up to 45 cm in height, and the stem and flower on it stretch up to a meter;
- remanna - grows up to half a meter, possessing bright pink and red flowers;
- amethyst – has a pleasant aroma and violet flowers.
Be sure to try growing these beautiful elegant flowers at home. You can use them to form bouquets and present them to your loved ones or brides. Just a little attention to the plant, and it will repay with beautiful and lush flowering.
Dietary recommendations
The diet is followed against the background of drug therapy. It involves giving up everything smoked, spicy and fatty, as well as including fiber in the diet.
In case of lactose deficiency, the patient is advised to stop consuming dairy products.
Allowed to use:
- pasta;
- cereals (except pearl barley);
- lean fish;
- boiled vegetables;
- vegetable and fruit juices;
- lean meat;
- jelly;
- berries (any).
What should a chair be like?
The main criteria for normal stool look like this:
- consistency – dense;
- stool color is brown. This shade is due to the presence of stercobilin. If a person eats dairy products, then the color of the stool becomes less intense and yellow tints are present. When eating meat products, stool takes on a dark brown tint.
The optimal number of bowel movements is 1-2/24 hours.
It would be a good idea to find out: Is it possible to become infected with fungus in the pool?