Fatty hepatosis is an independent or secondary pathological syndrome accompanied by excessive accumulation of fat in the liver tissue due to medications, alcohol consumption, or metabolic disorders. To treat fatty hepatosis, an integrated approach is used, combining effective medications, diet and effective folk remedies.
Basic principles of treatment
Fatty hepatosis is a disease that is treated primarily with medications. Drug therapy is aimed at eliminating the cause or factor that provokes the accumulation of fat. An equally important role is given to rational nutrition and a healthy lifestyle.
Medicines prescribed for fatty liver are aimed at reducing the load on the organ, as well as reducing the aggressive effects of external factors. The main therapeutic measures for fatty liver:
- decreased tissue resistance to insulin;
- fight against lipidemia;
- use of hepatoprotectors;
- taking vitamin-antioxidant complexes;
- normalization of hormonal levels in the body.
In order to cure fatty liver hepatosis, it is necessary to normalize body weight, since in most cases the pathology develops against the background of obesity.
It should be taken into account that sudden weight loss leads to an exacerbation of the disease.
Therefore, gradual weight loss combining a low-calorie diet with regular physical activity is recommended. Weight loss is carried out only under the supervision of a doctor.
Prognosis and prevention
Preventive measures include maintaining a healthy lifestyle with the necessary physical activity, a balanced diet and avoiding alcohol.
It is extremely important to monitor your weight; your BMI should be between 18.5 and 25. For patients with diabetes, it is important to strictly follow doctor's instructions to control the disease, closely monitor sugar levels and take medications in a timely manner.
If treatment is started in a timely manner, the prognosis for life is favorable, work ability, as a rule, is not impaired; if a complication develops, there is a risk of death.
Groups of drugs for the treatment of fatty hepatosis
Medicines are selected after a full medical examination. Additionally, ultrasound examination, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging of the liver are prescribed. Therapy depends on what causes the fatty liver and what the symptoms of the pathology are.
Disorders of the liver and pancreas can be treated with the following medications:
- hepatoprotectors;
- bile acid preparations;
- folic acid preparations;
- hormonal agents;
- medications with detoxification effects;
- medications from the group of statins and biguanides;
- drugs to combat obesity.
Such medications help eliminate unpleasant signs of the disease, prevent necrotic processes in the liver tissues and fight inflammation. Drug therapy normalizes liver function, improves metabolism, and reduces fat deposits in all internal organs.
Choleretic agents
When treating fatty hepatosis, it is recommended to take tablets containing ursodeoxycholic acid. They inhibit cholesterol synthesis and normalize the production and excretion of bile.
Effective choleretic drugs:
- Ursosan
— contains active ingredients that disinfect toxic bile acid, strengthens the protective barrier of cell membranes, and lowers cholesterol levels. Ursosan fights stones and prevents their formation, as well as diffuse fibrotic changes in the parenchyma. - Ursoliv
- normalizes the composition, production and outflow of bile, strengthens the cellular structure of hepatocytes and reduces sugar levels in the bloodstream. - Ursofalk
- has an immunomodulatory and cholyrtic effect. It is one of the most effective medications prescribed for toxic organ damage.
Choludexan is also prescribed for fatty liver. This drug inhibits the development of sclerosis, fights cirrhosis and prevents its further development, and stops the death of hepatocytes.
Use of hepatoprotectors
Therapy for fatty hepatosis is carried out with the mandatory use of hepatoprotectors. Such medications contain essential phospholipids, which are structural components of liver cells. Main hepatoprotectors:
- Essentiale Forte
- a drug based on soybean extract, available in capsule form. For fatty liver, it is recommended to take 2 capsules three times a day. - Phosphogliv
— strengthens and regenerates the cellular structures of hepatocytes, normalizes lipid metabolism and has an antioxidant effect. - Essliver Forte
is used with extreme caution, as it contains B vitamins, long-term use of which can lead to hypervitaminosis.
For fatty hepatosis, you can also take other hepatoprotectors - Hepatomax, Phosphogliv Forte, Antraliv, Phosphonciale, Gepagard, Essentiale N. When diagnosing fatty liver, these medications prevent damage to the cell membranes of hepatocytes and accelerate their natural recovery.
Amino acid preparations
Medicines containing amino acids are used in the complex treatment of fatty liver hepatosis. They stimulate the synthesis of phospholipids, restore the structure of hepatocytes and have a choleretic effect. Most often, such medications contain taurine, an amino acid that stimulates the removal of toxic compounds from the body.
Common amino acid preparations:
- Methionine
— increases the level of amino acids and lowers cholesterol; - Heptral
- strengthens hepatocytes and protects from further destruction; - Espa-Lipon
- normalizes fat and carbohydrate metabolism, fights free radicals; - Dibikor
- saturates the body with taurine, has an antioxidant and regenerating effect.
Amino acid preparations accelerate the cleansing of liver cells, normalize the functional state of hepatocytes, reduce cholesterol and activate the outflow of bile. Such drugs can additionally have an analgesic effect, relieving colic in the liver area.
Medications for detoxification
Medications with a detoxification effect effectively cleanse liver cells of toxic compounds, strengthening their structure and improving functioning. Most often, the following drugs are prescribed for fatty hepatosis:
- Polysorb
is an effective enterosorbent that fights toxic decay products, allergens, and toxic substances; - Antral
- used for the treatment and prevention of inflammatory liver lesions; - Kholosas
is a shiro made from rose hips, containing an increased concentration of ascorbic acid and cleansing hepatocytes of toxins.
Also common enterosorbents include Enterosgel - acts against metabolic products and toxic substances, Ovesol - cleanses the liver and fights bile stagnation, improving its outflow.
In the treatment of fatty liver, other enterosorbent drugs can be used - Atoxil, Polyphepan, sodium thiosulfate, activated carbon.
In order to accelerate the elimination of toxic substances and prevent the development of dysbiosis, detoxification solutions are prescribed for cleansing enemas. The most commonly used are Normaze or Duphalac.
Classification and stages of development
In Russian clinical practice, the working classification according to the Brunt system is used, dividing hepatosis depending on the degree, activity of inflammation, and degree of fibrosis.
According to the degree of steatosis:
- 0 degree:
the pathological process has begun, microscopic fatty compounds are present in the parenchyma, but it is impossible to diagnose the disease, since there are no symptoms, the ultrasound picture does not change the structure, the biochemical blood test is within the physiological norm; - 1st degree:
characterized by small sizes of fatty lesions, steatosis up to 33%, accumulations of degenerated hepatocytes are determined visually on ultrasound, there are no clinical symptoms; - Grade 2:
33–66% of hepatocytes are subject to fatty degeneration, infiltration foci are numerous and vary in size, and lipid inclusions inside normal hepatocytes are also detected. Ultrasound visualizes heterogeneous parenchyma, its size is increased; - Grade 3:
the vast majority of cells are replaced by lipids. The liver is enlarged, there is pronounced dysfunction, the infiltrates are voluminous and numerous, and are cystic in nature. Clinical manifestations are pronounced.
According to the degree of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis:
- I degree:
characteristic steatosis of 1–2 degrees, there is lobular inflammation in the stage of dispersion or minimal infiltration, slight balloon degeneration, portal inflammation is absent or insignificant; - II degree:
steatosis of any severity, moderate portal and lobular inflammation, slight persinusoidal fibrosis; - III degree:
pancreatic steatosis, active balloon degeneration, active lobular and portal inflammation.
According to the course of fibrosis:
- Grade 1:
focal or widespread fibrosis; - 2nd degree:
periportal; - 3rd degree:
bridge-like; - 4th degree:
liver cirrhosis.
There are also acute and chronic processes of hepatosis. Acute develops rapidly. The leading symptom is intoxication caused by a sharp decrease in the functional abilities of the organ. Liver cells quickly die, causing skin icterus, hyperthermia and vomiting. Treatment of the acute form is inpatient.
Anti-obesity drugs
Weight loss is considered an important part of the treatment of fatty hepatosis in men and women. For this purpose, drugs are used that stimulate metabolism, accelerate lipid metabolism, and reduce hunger. Anti-obesity drugs inhibit the absorption of calories and their conversion into fat cells. To normalize weight, use:
- Meridia
- provides a long-lasting feeling of fullness even after small portions of food and can be used for type 2 diabetes; - Metformin
- used for obesity against the background of type 2 diabetes mellitus (contraindicated for insulin dependence); - Acomplia
— affects directly the points of the brain “responsible” for hunger and reduces the need for food; - Orlistat
- inhibits the enzyme lipase, inhibiting the absorption of fats; - Sibutramine
- reduces the feeling of hunger and delays the absorption of calories.
Weight loss medications are not always prescribed - only if dieting and exercise have not brought noticeable results. It is better not to take such medications on your own, as they can cause negative side reactions.
Anti-obesity drugs should not be taken without consulting a doctor, as they have many contraindications - glaucoma, arterial hypertension, prostate disease, neurological disorders and disorders of the thyroid gland.
Lipid-lowering drugs
Lipid-lowering drugs are prescribed to normalize blood cholesterol levels, as well as fatty acid compounds. Thanks to a complex of vitamins, such medications have an antioxidant effect, protecting liver cells from free radicals and toxic substances.
- Chophytol
is a herbal preparation based on artichoke extract that has a choleretic effect; - Acarbose
— eliminates disruptions in lipid metabolism, including diabetes; - Karsil
is an effective hepatoprotector based on milk thistle extract, accelerating the removal of toxic elements from liver cells; - Pantethine
- stimulates the oxidation of fatty acids; - Lecithin
- fights fatty deposits in the liver and prevents their reappearance.
The use of lipid-lowering drugs is aimed at correcting liver function, eliminating unpleasant symptoms of hepatosis and factors leading to the accumulation of fat in hepatocytes. Most often, they contain natural, organic components that have a complex effect - anti-inflammatory, regenerating, choleretic and antidepressant.
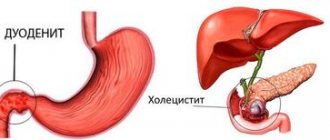
Fatty liver. Clinic. Diagnostics. Prevention
In the human body, one of the largest vital unpaired internal organs is the liver. Its weight is usually 1200-1500 g. The liver is located under the diaphragm in the right hypochondrium of the abdominal cavity and consists of two lobes: the large right and small left, separated above by the falciform ligament and below by the transverse groove.
The main function of the liver is to process everything that enters the body through the gastrointestinal tract (detoxification of the body), in addition, it is responsible for replenishing glycogen reserves (the main source of glucose), a complex of blood plasma proteins and bile, necessary for the metabolism and absorption of fats. Under its strict control, the accumulation of vital vitamins (A, D, E, K), the breakdown of hemoglobin and the metabolism of iron occur. It is also involved in the body's defense reactions against microbes and foreign substances from outside.
All these processes are very important for the proper maintenance of a healthy state of the human body. But what happens to the liver when one of its vital processes is disrupted?
Physician of the highest category Urazbayeva Gulzhanat Serikovna spoke about fatty hepatosis at a lesson at the health school “Active Longevity”.
What is fatty liver?
Fatty liver (fatty hepatosis, liver steatosis) is excessive deposition of fat in hepatocytes (liver cells). Literally from the English term “fatty liver” - fatty liver, which is used all over the world.
Fatty hepatosis is usually divided according to the cause of its occurrence: alcoholic steatohepatitis and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis or steatohepatosis, although the manifestations of these forms of the disease are largely similar.
In both diseases, fat is deposited in the liver cells, but since the causes are different, they are separated. One thing happens in people who abuse alcohol, the other happens in people who consume a lot of food and exercise little. And today we can talk about a real epidemic of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in developed countries. It has already taken first place among liver diseases, displacing both the alcoholic variant of the disease and chronic hepatitis. The liver strives to get rid of excess fat and releases it into the bloodstream. As a result, atherosclerotic plaques form in the vessels, they narrow, and all this leads to atherosclerosis, heart attacks and strokes.
Causes Leading to Fatty Liver
Alcohol, obesity, diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia, hereditary diseases, metabolic syndrome, as well as some medications, operations on the gastrointestinal tract. The above factors can be combined.
What happens in the liver during fatty hepatosis?
Normally, the fat content in the liver is 5%; with fatty hepatosis, this figure can reach up to 50%.
The liver bears the main burden of oxidizing fatty acids, as a result of which the body replenishes energy reserves. Alcohol damages the membrane of liver cells and disrupts the function of enzymes involved in the transport and oxidation of fatty acids. This leads to disruption of their normal metabolism and accumulation of fat in the cell. In type 2 diabetes mellitus (typical of middle-aged and elderly people), obesity and hyperlipidemia, the relationship between the amount of fat penetrating the liver cell and the cell’s ability to utilize it is also disrupted. The main danger of this condition is that excess fat, under the influence of various factors, is oxidized to form highly active compounds that further damage the cell. And this is the next stage of the disease – hepatitis, that is, inflammation of the liver. The progression of inflammation leads to the death of liver cells (hepatocytes), their replacement with skeletal connective tissue, and ultimately to impaired blood circulation in the liver and the development of liver failure, then cirrhosis.
A fatty liver can lead to hepatitis, cirrhosis and even cancer.
How does the disease manifest itself?
Clinically, fatty liver or hepatosis does not manifest itself in any way. Typically, patients consult a doctor with a feeling of heaviness or dull pain in the right hypochondrium, nausea, and an unpleasant taste in the mouth. According to their own feelings, patients believe that their liver hurts. But there is nothing to hurt in the liver, because there are no nerve endings there, they are only present in the capsule and bile ducts. Typically, painful sensations are associated with impaired motor activity (dyskinesia) of the biliary tract. In most people, signs of fatty liver are detected by chance during an examination for some other reason. For example, a patient undergoes an ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the abdominal organs or he consults a doctor about some other disease (coronary heart disease, diabetes mellitus, etc.), and during the examination the doctor reveals abnormalities in the structure and function of the liver.
Diagnosis of “fatty liver”
Ultrasound, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging, biochemical blood test. But the most accurate diagnostic method is a liver biopsy. Under anesthesia, the doctor may remove a tiny piece of liver tissue and then examine it under a microscope.
Treatment of "fatty liver"
First of all, it is necessary to eliminate or reduce the effect of the factor that led to the deposition of fat in the liver. Patients with diabetes mellitus and hyperlipidemia should be monitored jointly by an endocrinologist and a cardiologist, respectively. In treatment, hepatoprotectors are almost always prescribed - drugs that protect and support liver cells, as well as choleretic herbs, antioxidants, vitamins and other medications.
All patients require a low-fat diet as well as adequate daily physical activity.
Only an experienced doctor can determine what causes liver changes in a particular patient and how severe they are. If you have any suspicions, consult a gastroenterologist or hepatologist.
In most cases, fatty liver disease is completely reversible if the causes leading to its formation are eliminated.
Prevention of “fatty liver”
In order for the liver to function fully and perform its functions, it should be properly taken care of and a number of preventive measures should be carried out:
1. First of all, it is necessary to eliminate or reduce the factors that contributed to the disease and begin to lead a healthy lifestyle.
2. Healthy eating
. Given that the liver converts all the food we consume into energy, you should include in your diet as much as possible fresh fruits and vegetables, which are rich in nutrients and low in calories. Fiber is the most beneficial for the liver: cereal dishes, whole grain bread, fresh plant products. As a preventive measure to relieve stress on the organ, nutritionists recommend table No. 5, which excludes salty, spicy, sour, smoked and fried foods.
3. Compliance with sanitary and hygienic rules
: wash your hands thoroughly after using the toilet and before eating, and also rinse fruits, vegetables, etc. with running water. This also helps protect the body from parasites.
4. Taking medications correctly
. Drug therapy should be carried out strictly as prescribed by the doctor. Abuse of tablets and medications in any form (suppositories, capsules, tinctures, etc.) in combination can put a lot of stress on the liver, as a result of which excess fat accumulates in its cells. When choosing drugs, you should focus on those that indicate that the drug is completely eliminated from the body. You should not combine medications and alcohol.
4. Taking hepatoprotectors
. For the preventive protection of liver tissue, drugs are used - hepatoprotectors that can have a positive effect on hepatocytes. Such protective drugs are used during times of increased stress on the liver, for example, such as taking antibiotics, a diet aimed at rapid weight loss, prolonged alcohol consumption, etc.
5. Maintaining a Healthy Body Weight
. Move more and eat less. The cause of the accumulation of fat in the liver and, as a consequence, the occurrence of non-alcoholic fatty disease of the organ can be excess weight as a result of a sedentary lifestyle and the abuse of junk food. Recently, scientists have proven that eating fast food for just four weeks leads to illness. This was proven in an experiment on healthy student volunteers. Moreover, the first signs of liver damage and an increase in fat content in it began to appear after the first week of eating fast food.
6. Regular physical activity
. Daily physical activity and regular exercise are necessary to relieve the liver (walking, swimming), and will also help control your own weight within normal limits. It is necessary to reduce weight gradually (no more than 400-500 g per week).
6. Careful handling of toxic substances
. Direct contact with toxins contained in insecticides and household chemicals should be limited. When using cleaning products and household sprays, it is necessary to ensure good ventilation of the room, use protective rubber gloves and a face covering.
7. Limiting alcohol and nicotine consumption
. Excessive alcohol consumption can cause liver inflammation, leading to cirrhosis. Nicotine is also broken down and eliminated by the liver. The more poisons an organ has to neutralize, the faster it is destroyed.
Liver diseases are much easier to prevent than to cure!
Center for the formation of a healthy lifestyle BMC UDP RK
Application of enzymes and vitamins
Enzymes are used to eliminate excess fat in the liver, restore health and ensure proper functioning of the organ. These include Panzinorm Forte, Digestal and Festal.
They contain bile enzymes and pancreatin - these components normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, disturbed by hepatic obesity.
An auxiliary method of treating fatty hepatosis is taking multivitamin complexes. They should be taken no more than once every 6 months.
Vitamins are selected only by a doctor, taking into account the individual characteristics of the body - this can be Vitrum, Biomax, Complivit. It is advisable to select complexes that, in addition to vitamins, contain vital micro- and macroelements and amino acids. In addition to vitamins for fatty hepatosis, biotin and selenium preparations, as well as dietary supplements of plant origin, can be prescribed. The most common ones include capsules or powders of artichoke, oats or milk thistle.
What are the risks of organ obesity?
When a diagnosis is made, it is necessary to immediately begin treatment for fatty hepatosis and adhere to the above rules. If you do not treat the disease, abuse bad habits, do not lead a healthy lifestyle and overeat, then the pathology will transform into fibrosis, and then into cirrhosis. Hardening of the liver with scarring of normal cells, the formation of liver failure, and oncology can occur. The consequences in 30% of obese patients are the formation of hepatitis. Liver disease leads to decreased immunity, hormonal imbalance, and poisoning of the body.
If a specialist has diagnosed fatty hepatosis, everything possible must be done to eliminate it. Take a comprehensive approach to treatment, use prescribed medications, follow a diet, and exercise. To fully restore the liver, several months of intensive therapy will be required.
Herbal products
Treatment of fatty hepatosis can be carried out with effective and safe herbal preparations, as well as folk remedies - various decoctions, infusions and tinctures.
Among drugs with an organic composition, Gepabene, Tykveol, Karsil, Galstena are most often used.
It must be remembered that despite the naturalness of the components, herbal hepatoprotectors have a number of contraindications. Therefore, they should not be taken without consulting a doctor.
Popular folk recipes for fatty hepatosis:
- Rose hips - 100 g of berries should be poured with 4 cups of boiling water, covered and left to steep for 8-10 hours. Take the finished infusion one glass three times a day.
- Rose hips and corn silk - 2 tablespoons of crushed raw materials should be poured into 1 liter of hot water and left to infuse for 8-10 hours. Take 200 ml 3-4 times a day.
- Pine nuts - for fatty hepatosis, it is useful to eat a teaspoon of nuts every morning, on an empty stomach.
Herbal medicine also recommends eating ½ cup of any dried fruit every day, drinking freshly squeezed carrot juice and green tea with the addition of peppermint leaves.
For what symptoms should drug treatment be started?
Fatty hepatosis in the early stages can be practically asymptomatic. Organ dysfunction progresses as excess fat accumulates, inflammation and fibrosis develop. You should consult a doctor if the following symptoms appear:
- nagging pain and discomfort in the right hypochondrium;
- nausea;
- bitterness in the mouth;
- belching and heartburn;
- general weakness.
Only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis and, if necessary, select medications for fatty hepatosis after a comprehensive diagnosis.
Diet for fatty liver hepatosis
Diet is an essential element in the complex treatment of fatty liver hepatosis. The diet is based on low-calorie foods with a minimal glycemic index.
| Authorized Products | Prohibited Products |
| Dietary varieties of fish and meat | Fatty pork, lamb |
| Turkey, chicken | Goose, duck |
| Yesterday's bread and pastries made from rye flour | Fresh baked goods made from wheat flour |
| Fermented milk products | Fermented milk products with high fat content |
| Vegetables, fruits and berries except those prohibited | Onions, garlic, tomatoes, radishes, radishes and sorrel |
| Cereals | Pasta |
| Marmalade, pastille, honey | Chocolate, candy, cakes, pastries |
An approximate menu can be taken from diet No. 5 according to Pevzner. It includes cereal and vegetable soups, porridges, meat and poultry without skin and fat. Several times a week you can eat herring (soaked), black caviar, and chicken eggs.
A few words about fatty hepatosis
Fatty hepatosis is one of the most common liver diseases that disrupts its proper functioning. In the absence of timely treatment, the disease leads to the development of fibrosis and then cirrhosis.
For hepatosis, an integrated approach is used, combining the use of medications of several categories, vitamin complexes and dietary supplements. Following a special diet and using natural traditional medicine will help increase the effectiveness of drug therapy.
Treatment tactics for patients with NAFLD and metabolic syndrome due to hepatitis C
If concomitant liver damage is detected in patients with HCV as a result of metabolic syndrome (non-alcoholic fatty liver disease - steatosis), it is necessary to conduct additional examination for indicators of metabolic and hormonal disorders characteristic of this disease.
To assess the degree of liver damage, it is recommended to use a blood test - Fibromax, which makes it possible to separately assess the degree of liver damage by the virus and separately by metabolic syndrome.
Treatment tactics depend on the degree of liver damage as a whole, and separately for each damaging factor. Treatment with antiviral drugs can be started immediately, and further treatment of metabolic syndrome after receiving SVR.
If the degree of liver damage from the virus is significantly less than from metabolic syndrome, it is possible to begin antiviral therapy after treatment of metabolic syndrome.
In cases of concomitant liver diseases, it is necessary to set the goal of treatment not only to obtain SVR, but also to preserve and restore the liver damaged by other pathological factors.
The most important component of successful treatment of NAFLD and fatty liver disease is proper nutrition.
up