“Cholelithiasis is one of the most common chronic diseases in adults, ranking third after cardiovascular diseases and diabetes.” The reasons for its development are a number of factors, in particular heredity, women taking oral contraceptives, obesity, and eating high amounts of cholesterol .
Conservative therapy can be effective only at the pre-stone stage of the disease, which at this stage can only be diagnosed using ultrasound. At the next stages, surgical intervention is indicated. Surgery for gallstones can be reduced to complete removal of the gallbladder, removal of stones invasively or naturally (after crushing, dissolving).
Types of surgery, indications for performance
At the moment, there are several options for surgical intervention:
- Cholecystectomy – removal of the gallbladder.
- Cholecystolithotomy. This is a minimally invasive type of intervention that involves preserving the gallbladder and removing only deposits.
- Lithotripsy. This procedure involves crushing stones with ultrasound or laser and removing fragments.
- Contact litholysis is the dissolution of stones by direct injection of certain acids into the cavity of the gallbladder.
In most cases, cholecystectomy is performed - removal of the gallbladder. A sufficient indication is the detection of stones and characteristic symptoms of the disease. Mainly, this is severe pain and disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract.
Important! The operation is definitely performed for acute cholecystitis (purulent inflammation) or choledocholithiasis (presence of stones in the bile ducts).
In the asymptomatic form, surgery may not be performed unless polyps are found in the gallbladder, its walls are calcified, or stones exceed 3 cm in diameter.
When preserving the organ, there is a high risk of relapse - according to some data, up to 50% of patients experience recurrent stone formation. Therefore, cholecystolithotomy is prescribed only if organ removal is an unjustified risk to the patient’s life.
Cholecystolithotomy and cholecystectomy can be performed through an incision or laparoscopically. In the second case, there is no violation of the tightness of the body cavity. All manipulations are carried out through punctures. This technique is used more often than the usual open one.
Lithotripsy may be indicated for single small stones (up to 2 cm), the patient’s stable condition, and no history of complications. In this case, the doctor must make sure that the functions of the gallbladder, its contractility, and the patency of the outflow paths of liquid secretions are intact.
Contact litholysis is used as an alternative method when others are ineffective or impossible. It is developed and used mainly in the West; in Russia, only sporadic reports of a successful operation can be found. It allows you to dissolve only cholesterol stones. The big advantage is that it can be used in any size, quantity and location.
Preparing for surgery
If the patient’s condition allows, then it is better to extend the time before surgery to 1 – 1.5 months. During this period, the patient is prescribed:
- Special diet.
- Taking drugs with antisecretory activity and antispasmodics.
- A course of multienzyme drugs.
Before the operation, the patient must undergo general blood tests, urine tests, EEG, fluorography, and be tested for the presence of a number of infections. The conclusion of the medical specialists who are registered with the patient is mandatory.
Features of lithotripsy
The crushing procedure occurs during the period when the laser beam comes into contact with the surface of the stone. The doctor makes a puncture in the area where the gallbladder is located. Through the resulting puncture, a laser device with a camera is inserted, which broadcasts everything that happens on the monitor. Using a laser beam, the resulting stones are crushed to a sand-like state. Crushed stones are eliminated from the body on their own. The duration of laser surgery is 30 minutes. The procedure involves outpatient treatment.
Solid formations are crushed using an optical quantum generator. It creates coherent radiation with high power and density. Due to the fact that only a small incision needs to be made for the laser to work, doctors actively use this method in surgery.
The technique allows crushing gallstones in all patients, regardless of age.
Before prescribing the procedure, the doctor must conduct a comprehensive examination, which will allow him to assess the patient’s health condition and select the appropriate treatment.
Cavity (open) cholecystectomy
The operation is performed under general anesthesia. Its duration is 1-2 hours. A contrast agent is injected into the bile duct for better visualization. It is necessary to control the absence of stones in it. The incision is made either under the ribs or along the midline near the navel. First, the surgeon clamps with metal clips or sutures with self-absorbing threads all the vessels and ducts that are connected to the gallbladder.
The organ itself is bluntly separated (to avoid cuts) from the liver, fatty and connective tissue. All ligated ducts and vessels are excised, and the gallbladder is removed from the body. A drainage tube is installed in the wound, from which blood and other body fluids will drain. This is necessary so that the doctor can monitor whether a purulent process has developed in the body cavity. If the outcome is favorable, it is removed within a day.
All fabrics are sutured in layers. The patient is transferred to the intensive care unit. Until the anesthesia wears off, strict monitoring of his pulse and blood pressure is needed. When he wakes up, there will be a probe in his stomach and an IV in his vein. Important! You need to relax, don’t try to move or get up.
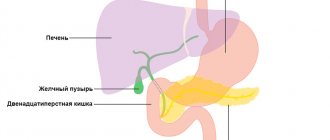
What Causes the Formation of Gallstones
You can learn about the disease only when stones form in the gallbladder ducts, which stimulate the development of cholecystitis. The stones have a heterogeneous structure. The formations can be calcareous or mixed, bilirubin (brown or black), cholesterol.
The disease doesn’t just manifest itself that way. Most often it is provoked by low physical activity. frequent pregnancies, congenital anomalies of the gallbladder and liver, increased breakdown of red blood cells, accumulation of salts.
Affects the appearance of the disease and the consumption of excessive amounts of fatty, spicy and salty foods, as well as a large amount of animal protein in the diet, cholecystitis, cirrhosis of the liver, chronic hepatitis, narrowed ducts, excessive body weight.
Content:
- What Causes the Formation of Gallstones
- When to use laser for treatment
- Signs of the disease
- Features of lithotripsy
- Undesirable consequences of the procedure
- Contraindications to laser surgery
The first symptoms of the presence of the disease will appear 5-10 years after the onset of gallstone disease.
But there are cases when the disease is asymptomatic, then the presence of stones in the gall bladder can be determined by ultrasound or x-ray.
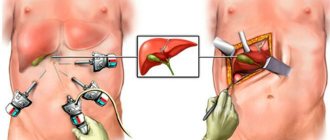
Laparoscopy
The cholecystectomy operation is also performed under general anesthesia; its time is slightly shorter than with an open one - 30-90 minutes. The patient is placed on his back. After the onset of anesthesia, the surgeon makes several punctures in the wall of the abdominal cavity and inserts trocars there. The holes are created in different sizes. The largest one is used for visualization using a camera attached to a laparoscope and removal of the organ.
Note. A trocar is a tool with which you can gain access to the body cavity and maintain the tightness of its walls. It is a tube (tube) with a stylet (pointed rod) inserted into it.
Carbon dioxide is injected into the patient's body cavity using a needle. This is necessary to create sufficient space for surgical procedures. At least twice during the operation, the doctor will tilt the table with the patient - first to move the organs in order to reduce the risk of damage to them, and then to move the intestines down.
The bubble is clamped with an automatic clamp. The duct and the organ itself are isolated using instruments inserted into one of the punctures. A catheter is inserted into the duct to prevent it from compressing or expelling its contents into the abdominal cavity.
The functions of the sphincter are examined. Inspect the duct to make sure there are no stones in it. Make a cut with microscissors. The same applies to blood vessels. The bubble is carefully isolated from its bed, while monitoring for damage. All of them are sealed with an electrocautery (an instrument with a loop or tip heated by electric current).
After complete removal of the gallbladder, aspiration is performed. All fluids accumulated there are sucked out of the cavity - gland secretions, blood, etc.
During cholecystolithotomy, the organ itself is opened and the stones are removed. The walls are sutured, and damaged vessels are coagulated. Accordingly, the ducts are not cut. Surgical removal of stones without removing the gallbladder is rarely practiced.
Lithotripsy
The full name of the procedure is extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL). It says that the operation is carried out externally, outside the body, and also that a certain type of wave is used, which destroys the stone. This occurs because ultrasound travels at different speeds in different environments. In soft tissues it spreads quickly without causing any damage, but when it passes into a solid formation (stone), deformations occur that lead to cracks and destruction of the stone.
This operation may be indicated in approximately 20% of cases of cholelithiasis. Important! It is not performed if the patient has any other formations along the path of the shock wave or if he must constantly take anticoagulants. They inhibit the formation of blood clots, which can complicate the healing of possible injuries and recovery after surgery.
The operation is performed under epidural anesthesia (injection of painkiller into the spine) or intravenous. Before performing an ultrasound, the doctor selects the optimal position of the patient and brings the emitter device to the selected location. The patient may feel slight tremors or even pain. It is important to remain calm and not move. Often, several approaches or sessions of lithotripsy may be needed.
The operation is considered successful if no stones or their parts larger than 5 mm remain. This happens in 90-95% of cases. After lithotripsy, the patient is prescribed a course of bile acids, which help dissolve the remaining fragments. This procedure is called oral litholysis (from the word per os - through the mouth). Its duration can be up to 12-18 months. Removal of sand and small stones from the gallbladder is carried out through the ducts.
It is possible to dissolve stones using a laser. However, this new technique is still under development and there is still little information about its consequences and effectiveness. The laser, as a shock wave, is directed to the stone through a puncture and focused directly on it. Sand is evacuated naturally.
Process description
The crushing process lasts 20-30 minutes
Before the operation, the doctor makes a small puncture at the location of the organ. A special device displays an image of the crushing process on the monitor.
After this, a catheter with a laser is installed. Under ultrasound visualization control, the device is brought directly to the stone itself.
Using a high-energy laser beam, gallstones are crushed and turned into sand or small fragments. After crushing, they enter the intestines and leave the body on their own.
The advantage of this method is that the crushed fragments do not remain in the biliary tract and do not cause the development of jaundice. The entire procedure for crushing stones takes only 20 minutes or half an hour.
In this case, laser treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis, so the patient does not need to stay in the hospital all the time. After the operation is completed, the patient is usually discharged. But at the same time, he is recommended to visit a doctor for advice and monitoring of possible complications.
An optical quantum generator produces coherent radiation with high density and power. This allows you to crush stones of large sizes and any degree of hardness. Age does not matter when prescribing laser surgery. Before removing any hard formations, the patient should only thoroughly examine his health. No other special preparation is needed for laser crushing.
The disadvantage of the method is the possibility of severe burns to the bladder wall with the slightest deflection of the laser beam. The same can happen to neighboring organs, resulting in ulcers and perforations. Laser crushing is prohibited for patients weighing more than 120 kilograms , in severe general condition of the patient and in old age.
Laser treatment is a popular way to get rid of stones. But a medical institution must have special expensive equipment for this.
Possible results and consequences
Removal of stones using a laser occurs without direct intervention in the gallbladder. This allows it to fully retain its functions of normal digestion of food. This procedure does not involve open surgery, so the patient recovers his health much faster.
An undesirable consequence of this procedure is the likelihood of new formation of stones after a certain time. Sometimes, if the laser beam is directed incorrectly, a burn to the wall of the organ occurs. This not only causes discomfort for the patient, but also leads to the appearance of large ulcers.
Despite the high effectiveness of this method, such treatment can be dangerous to the patient's health. In addition to the burn of the mucous membrane, one can also note the possibility of injury to the walls of the gallbladder by the sharp edges of the stones after their laser crushing. Therefore, each patient must independently decide whether to undergo this procedure.
To use the device, the institution must have the appropriate license
Contact litholysis
This is an operation to remove stones with complete preservation of the organ. When the underlying disease is cured, it has a very good prognosis. In Russia, the technique is under development, most of the operations are carried out abroad.
It includes several stages:
- Application of a microcholecystotomy. This is a drainage tube through which the contents of the gallbladder are removed.
- Assessment by injection of a contrast agent of the number and size of stones, which allows you to calculate the exact amount of litholytic (solvent) and avoid its entry into the intestine.
- Introduction of methyl tert-butyl ether into the cavity of the gallbladder. This substance effectively dissolves all deposits, but can be dangerous for the mucous membranes of neighboring organs.
- Evacuation through a bile drainage tube with litholytic.
- Introduction of anti-inflammatory drugs into the cavity of the gallbladder to restore the mucous membrane of its walls.
Drug dissolution of stones
Only cholesterol stones with a diameter of up to 2 cm can be dissolved (this method does not work on limestone and pigment stones). For this purpose, analogues of bile acids Ursosan, Henofalk, Urofalk, Henochol, etc. are used.
At the same time, stimulation of the contractile function of the gallbladder and bile production can be carried out with the help of Allochol, Holosas, Zixorin, Liobil.
Contraindications:
- Various concomitant diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (ulcer, gastritis) and kidneys;
- Taking oral contraceptives containing estrogens;
- Obesity;
- Pregnancy.
Flaws:
- High frequency of relapses (10-70%), since after stopping the medications, the level of cholesterol in the bile rises again;
- Long duration of treatment (from 6 months to 3 years);
- Side effects such as diarrhea (10% of cases), changes in liver tests (ALT and AST);
- High cost of drugs.
On this topic:
Preparations for dissolving gallstones
Complications
Many surgeons believe that cholecystectomy eliminates not only the consequences of the disease, but also its cause. Doctor Karl Langenbuch, who performed this operation for the first time in the 19th century, said: “It is necessary [to remove the gallbladder] not because there are stones in it, but because it is he who forms them.” However, some modern experts are confident that if the etiology is unclear, surgical intervention will not solve the problem, and the consequences of the disease will bother patients for many years.
Statistics confirm this to a large extent:
- Almost 100% of patients experience problems in the gastrointestinal tract after surgery.
- A quarter of patients note that their condition has not improved, and almost 30% say it has worsened.
- Disability after surgery is assigned to 2% to 12% of patients.
- A third of patients develop what is called postcholecystectomy syndrome. This term refers to dysfunction of the sphincter of Oddi after surgery - a ring-shaped muscle that compresses the duct going into the stomach from the liver, pancreas and gallbladder. The complication manifests itself in severe, prolonged pain.
- In some patients, the mucous membrane of the duodenum is damaged due to the constant release of bile without its accumulation in the bladder, which leads to the development of reflux, duodenitis, etc.
The following factors increase the risk of complications:
- The patient's excess weight, his refusal to follow the doctor's instructions and diet.
- Errors during the operation, damage to neighboring organs.
- The patient is elderly and has a history of other gastrointestinal diseases.
The main danger of operations that do not involve removal of the gallbladder is a recurrence of the disease, and, accordingly, all its unpleasant symptoms.
Ultrasound crushing of stones
This method is based on crushing stones under high pressure and vibration of a regenerated shock wave. Ultrasound destroys stones and crushes them into smaller particles with sizes not exceeding 3 mm, which are subsequently discharged through the bile ducts into the duodenum. Ultrasound lithotripsy is suitable for patients who have a small number (up to 4 pieces) of fairly large cholesterol stones (up to 3 cm in diameter), without calcareous impurities in their composition.
Contraindications:
- Bleeding disorders;
- Chronic inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (cholecystitis, pancreatitis, ulcers);
- Pregnancy.
Flaws:
- Possible blockage of the bile ducts as a result of vibration;
- Damage to the walls of the gallbladder by sharp edges of stone fragments.
Recovery period after surgery
For several months, patients will have to follow certain recommendations, and the doctor’s instructions regarding nutrition will have to be followed for the rest of their lives:
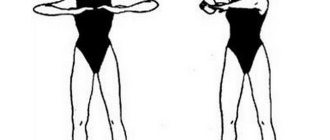
- In the first months after surgery (even minimally invasive), you need to limit physical activity. Exercises such as “bicycle” and arm swings from a lying position are useful. Your doctor can recommend precise exercises.
- For the first weeks, you should wash only in the shower, avoiding getting the wound wet. After hygiene procedures, it must be treated with an antiseptic - iodine or a weak solution of potassium permanganate.
- For 2-3 weeks, the patient must adhere to diet No. 5 (excluding fried, salty, fatty, sweet, spicy) and take choleretic drugs. After this period, such products are allowed to be taken only in very limited quantities.
- It is advisable to get used to eating small meals, 5-6 times a day with breaks in the first month after surgery of 1.5-2 hours, subsequently - 3-3.5 hours.
- Annual visits to sanatoriums are recommended, especially preferably 6-7 months after surgery.
Undesirable consequences of the procedure
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
Not in every case, laser crushing of gallstones allows you to get rid of the disease completely. There is a possibility that stones will form again. It is important after surgery to follow a special diet that will prevent relapses.
The procedure requires maximum concentration and precise movements of the doctor, since the slightest deviation can provoke the occurrence of severe burns, which gradually degenerate into ulcers.
In other words, despite the effectiveness of the procedure, every patient should know all its risks. Among the disadvantages of manipulation: injury to the walls of the gallbladder with a laser or sharp fragments of crushed stones; burns of the mucous membranes of the organ. The patient can refuse this type of surgery and choose more classic abdominal or ultrasound surgery, or other methods suggested by the doctor. Choose clinics with experienced staff and expensive, high-quality and ultra-precise equipment.
Patient reviews
The main question on forums dedicated to cholelithiasis is whether or not it is worth having surgery. Unfortunately, organ-preserving intervention methods have not yet been perfected, and you have to compare risks and make difficult decisions. Different doctors may have their own opinion about the need for surgery and the time frame for it to be carried out.
Laparoscopy has earned many positive reviews. Patients are satisfied with the absence of stitches and the quick recovery time. Those who have experienced colic and severe pain associated with a stone entering the duct are pleased to note a feeling of lightness and comfort.
Surgery today, unfortunately, is the only effective way to get rid of cholelithiasis. Despite the development of minimally invasive and organ-preserving surgical interventions, in most cases it is necessary to resort to removal of the bladder. The operation has a number of complications, some symptoms can haunt patients for the rest of their lives, but they cannot be compared with the pain caused by stones.
Questions most often asked by patients with gallstone disease
Is it necessary to somehow prepare for surgery for laparoscopic treatment of cholelithiasis?
If you are planning surgical treatment of cholelithiasis, I ask you to carefully study the preoperative preparation section.
What anesthesia do you use for laparoscopic treatment of cholelithiasis?
Puchkov K.V. in the TV show “Health with Elena Malysheva”
If you would like to learn in more detail about the methods of pain relief used in the surgical treatment of cholelithiasis, please carefully read the relevant sections of the site.
What innovative surgical technologies do you use?
Among the minimally invasive surgery technologies I use are electrosurgery using the LigaSure device (USA) and the PerClot hemostatic system (Italy), which allows for reliable hemostasis in the area of the gallbladder bed in difficult cases where the venous sinuses are close to the surface of the liver, and reduces the amount of blood loss during surgery, ultrasonic scissors, synthetic absorbable suture material, anti-adhesive barriers and liquid media for the prevention of adhesive disease after surgery, compression hosiery for the prevention of thrombosis and thromboembolism and a number of other techniques that can significantly improve the speed, quality and efficiency of the operations I perform.
Is it possible to simultaneously perform laparoscopic surgery for cholelithiasis and, for example, fibroids?
The minimally invasive surgery techniques I use make it possible to perform two and sometimes three operations simultaneously by a team of several surgeons. The issue of simultaneous operations, including for cholelithiasis (chronic calculous cholecystitis), is discussed in more detail in a special section of the site. The simultaneous performance of several surgical interventions allows you to reduce the load on the body, reduce hospitalization time, and speed up the recovery of the body compared to performing several operations with an interval of 5-6 weeks.
Where can I have surgery with you?
I conduct the initial consultation with all patients in Moscow at the Swiss University Clinic. On the website you can get acquainted in more detail with my main clinical sites in Moscow and Switzerland.
Contraindications to laser surgery
Before laser surgery is performed, the patient is referred to undergo an additional examination, which will determine the presence or absence of contraindications. Among them it is worth noting: the patient is overweight (over 120 kilograms); limestone type stones; presence of a pacemaker in the body; the presence of ulcers or chronic cholecystitis in the body; low level of blood clotting; the number of gallstones is more than 4. It is worth noting that the procedure is not performed on patients aged 60+, or in clinically serious condition. If the disease is severely advanced, lithotripsy is pointless.
More fresh and relevant information about health on our Telegram channel. Subscribe: https://t.me/foodandhealthru
We will be grateful if you use the buttons: