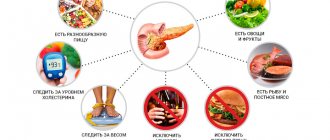
The liver and bile together form our metabolic center. Therefore, these organs should be supported and kept healthy, and the main helpers in this are healthy foods.
The liver is a kind of filter in our system through which all products pass without exception. It’s just that one food is quietly processed and moves on to the next stage, but harmful products disrupt its functioning, causing harm to the organ itself. Therefore, we suggest reconsidering your diet, focusing on foods that will be beneficial for our liver and bile duct.
General rules
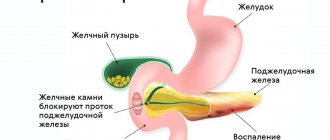
Diseases of the hepatobiliary system are represented by a wide range of diseases of the liver, gall bladder and biliary tract. The main ones include: acute/chronic hepatitis (viral, toxic), liver cirrhosis , alcoholic/non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, liver neoplasms (cancer, abscess, cyst), inflammation of the bile ducts, acute/chronic cholecystitis , cholangitis , cholelithiasis , dyskinesia of the gallbladder/biliary tract.
The hepatobiliary system is a complex multi-level mechanism that is actively involved in both the processes of digestion and metabolism (removal of metabolic products from the body). The result of a violation of its functions is a disruption of detoxification , metabolic processes, and immune response/antimicrobial protection.
Diet for diseases of the gallbladder and liver is an essential component of the treatment process. When prescribing a diet, the nature of liver damage (organic changes, inflammation), the stage of the disease and the patient’s condition are taken as a basis. The main goal of a diet for diseases of the organs of the hepatobiliary system is to spare them as much as possible, restore the structure/function of the liver and provide the patient’s body with a physiologically complete amount and ratio of food nutrients. For functional disorders of the biliary tract, treatment and diet are aimed at eliminating spasm of the sphincter of Oddi and normalizing the motor/evacuatory function of the biliary tract.
The basic diet for diseases of the liver and biliary tract is therapeutic nutrition within Table No. 5 / its varieties with dietary adjustments taking into account the type, form and specific course of the disease. In the acute period of diseases ( acute hepatitis , cholecystitis , exacerbation of chronic forms of these diseases), as a rule, Diet 5A , which ensures maximum sparing of the liver and normalization of function and bile ducts. Great importance is paid to diet.
It is advisable to eat food at the same time, 5-6 times in small portions. This is extremely important, since the body begins to secrete digestive juices at the usual time for eating, and irregular food intake at large intervals leads to a concentration of bile in the gallbladder, caused by the reabsorption of part of the water from the bile. Accordingly, when bile stagnates, a precipitate falls out of it, which serves as the basis for the formation of stones. In addition, regular food intake regulates the emptying of the gallbladder/ductal system.
Outside the acute period of illness, the best option for the gallbladder and liver is Diet No. 5 . In general, the diet is limited to fats, mainly animal fats, simple carbohydrates and salt (up to 10 g). The energy value of nutrition in patients with chronic hepatitis/chronic calculous cholecystitis is selected individually and can vary from 1800-2000 calories for elderly patients to 2800 kcal/day for middle-aged patients with an active lifestyle.
At the same time, it must be taken into account that an imbalance of basic food nutrients has an adverse effect on liver function. The diet should contain foods rich in protein at the rate of 1.2-1.5 g/1 kg of weight/day, while preference should be given to complete animal proteins that prevent the deposition of fat in the liver (lean veal, egg whites, cottage cheese, lean varieties of freshwater fish, cereals: buckwheat, oatmeal).
The total amount of fat should not exceed 1 g/1 kg of weight during the day. Preference should be given to vegetable fats containing polyunsaturated fatty acids, which activate lipolytic enzymes that help normalize fat metabolism/prevent fatty liver. It is not recommended to include foods rich in cholesterol in your diet: brains, internal organs of animals.
Fatty, smoked and fried foods, spicy seasonings, sauces, meat/fish broths, smoked foods, canned food, carbonated drinks, and alcohol should be excluded from the diet, as they contribute to spasm of the sphincter of Oddi.
The amount of carbohydrates in the diet is limited moderately, at the rate of 2-4 g/per 1 kg of weight/day. Excessive consumption of carbohydrates is converted into fat and deposited in the liver, thereby weakening its function. Easily digestible carbohydrates (sweets, jam, sugar) are excluded/sharply limited from the diet, as they contribute to bile stagnation. Preference should be given to foods containing complex carbohydrates.
When compiling a diet, you should take into account the effect of certain products on the motor function of the gallbladder/bile tract. Thus, for hypotension of the gallbladder, it is recommended to consume weak meat/fish broths, soft-boiled eggs, sour cream, cream, vegetable oils (2-3 times a day, a teaspoon 30 minutes before meals).
In the hypokinetic form, it is recommended to drink mineral waters of medium mineralization 30 minutes before meals (200 ml 3 times a day). With the hyperkinetic type of dysfunction, you should sharply limit in your diet foods that stimulate gallbladder contraction (vegetable oils, rich meat/fish/mushroom broths, animal fats). For the hyperkinetic form, still/lightly carbonated waters of low mineralization (2-5 g/l) are indicated, 3-4 times a day, 100-150 ml 1 hour before meals, warm.
Since a number of diseases (chronic hepatitis/ cholecystitis ) are accompanied by frequent constipation, the diet for the gallbladder and liver in such cases involves the introduction of foods containing a lot of fiber into the diet - vegetables, especially beets, fruits (prunes, dried apricots), cereals, seed products, oatmeal bran. If it is necessary to enhance the process of bile secretion, vinaigrette/salads seasoned with vegetable oils (unrefined) should be introduced into the diet.
Therapeutic nutrition for a number of liver diseases (fatty hepatosis) in obese /overweight individuals should be aimed at normalizing weight. To do this, subject to the general principles of dietary nutrition in Medical Table No. 5 , the energy value of the diet is adjusted depending on body weight exceeding the norm, age, gender, and level of physical activity.
In general, for effective and safe weight loss, the calorie content of the diet should be reduced by 500-600 kcal/day from the physiological norm. A higher rate of weight loss is associated with a high risk of developing “acute” steatohepatitis with subsequent formation of fibrosis . Such patients benefit from weekly fasting days: milk with crackers, kefir-curd, apple, fruit and berry (according to the season). Complete fasting with a diseased liver is strictly contraindicated, as it increases metabolic disorders.
Treatment of liver diseases in most cases requires the inclusion in the diet of additional foods that have a hepaprotective effect - artichoke (leaves), pumpkin seeds/oil, licorice, milk thistle oil, St. John's wort. If it is not possible to take them in their natural form, it is recommended to take medications based on them - Artichoke extract , Tykveol , Karsil , Silimar , Gepabene , Legalon , Hofitol , Peponen , Cynarix , as well as hepaprotectors of animal origin - Progepar , Erbisol , Hepatosan , which are quite effective for alcoholic hepatosis , hepatitis , cirrhosis .
In most cases, phospholipids ( Essliver Forte , Phosphogliv ), which, being integrated into the structure of liver cells, reduce energy costs of the liver/restore the cell wall, as well as fatty acids ( Ursofalk , Ursosan , Ursodez , Ursoliv ) are also prescribed. Amino acid derivatives ( Heptor , Heptral ), dietary supplements ( LIV52 ), liver preparations, immunomodulators ( Velferon , recombinant interferons ) also have similar restorative/detoxifying properties.
If it is necessary to increase the secretion of bile/reduce its viscosity, herbal preparations such as corn silk , convaflavin , flakumin , berberine ; the effect is due to the properties of the essential oils, flavones, phytoncides, and resins they contain. In general, hepaprotectors form the basis of basic therapy during exacerbations and have a supporting effect during remission.
What foods are good for the liver, cleanse, restore it and remove toxins?
These liver products must be in your diet to improve and improve its functioning. And not only for the period of illness, but also for preventive purposes.
Useful foods for the liver:
- Apple – The pectin in apples helps the liver remove toxins and heavy metals from the digestive system. In addition, its soluble fiber lowers cholesterol levels, protecting the liver from overload and promoting liver function. It is recommended to consume a raw apple or a fresh glass of apple juice daily - preferably in the morning.
- Avocado provides a lot of glutathione. This substance is produced in almost all cells of our body, but especially in liver cells. Glutathione is essential to protect our body from free radicals. With its help, the liver can also be indirectly protected from damage by toxins. And two avocados once a week for one month can restore damaged liver. In addition, the pear-shaped fruits contain a lot of monounsaturated fatty acids. This reduces the level of bad cholesterol, which in turn clears the liver. For example, avocado goes well with salads or smoothies.
Product overview
- In broccoli you will find, among many other valuable nutrients, numerous mustard oil glycosides. These phytochemicals are very stimulating to the liver and bile function. In addition, they can even destroy gallstones that are in the initial stage - the so-called gallstones. Mustard oil glycosides also improve the overall environment in the digestive tract, promoting a healthy composition of intestinal flora. Broccoli can be steamed like a vegetable. Broccoli sprouts are especially rich, which you can easily grow from organic seeds yourself at home.
- Grapefruit contains various antioxidants, such as glutathione, which helps the body neutralize free radicals and remove heavy metals from the liver. In addition, naringenin, a flavonoid found in grapefruit, helps break down fat and thus facilitates liver function. The fruit also contains a lot of pectin and vitamin C, helping to naturally cleanse the liver. It is recommended to eat grapefruit daily or drink a glass of fresh juice in the morning.
- Green tea contains phytochemicals called catechins. They have an antioxidant effect and thus remove unhealthy fat accumulations or prevent too much fat from being deposited in the liver. In turn, the organ advances in its detoxification function. In general, 2-3 cups of green tea per day should be enough to strengthen the cleansing organ.
Drink beet juice and eat boiled beet salad!
- Oats contain choline and beta-glucan. They have a detoxifying and defatting effect, and also support the regulation of lipid metabolism. They lower cholesterol, bind bile acids and prevent harmful accumulation in the blood. Thanks to these effects, the liver can regenerate better. And since oats are high in fiber, they additionally support liver function. The healthiest oats are in the form of freshly prepared oatmeal.
- Garlic contains many sulfur-containing substances. They can stimulate enzymes in the liver, which in turn are responsible for releasing toxic substances from the body. In addition, garlic contains the trace element selenium, which further accelerates the liver detoxification process and protects the organ from poisons. You can use it in salads and also after cooking in numerous dishes such as sauces, soups or vegetable dishes. But if you have liver disease, you should be careful! Also, you should not indulge in such a fragrant plant more than 3 cloves per day.
- Sauerkraut has beneficial effects on liver function as a probiotic food. Healthy microorganisms strengthen the intestinal flora and prevent inflammatory processes. Since healthy intestinal flora also influences the healthy production and elimination of bile acids, less fat accumulates in the liver. Probiotics may promote and accelerate the regression of fatty liver. Of course, all this affects the liver, simultaneously facilitating and strengthening it. Try sauerkraut raw as a salad.
Don't forget about persimmons
- Walnuts provide three very beneficial substances for the liver: omega-3 fatty acids, the amino acid L-arginine and glutathione. They help the liver in its natural cleansing and especially in detoxifying harmful ammonia. In addition, the polyphenols contained in walnuts protect the liver from damage. But do not eat roasted nuts, but use them raw.
- Lemon strengthens liver function. Also worth mentioning is D-limonene, an antioxidant secondary phytochemical found in lemons. It activates various liver enzymes and thus helps detoxify the body. In addition, lemons ensure better absorption of minerals in the liver, which leads to a balanced pH in the body. Citrus fruits are also often mentioned in the fight against fatty liver. It is recommended to drink lemon juice with warm water in the morning on an empty stomach. Lemons are prohibited for cleansing the liver for gastrointestinal diseases!
- Milk Thistle – One common use of milk thistle is to treat liver problems. The active ingredient in milk thistle, silymarin, acts as an antioxidant, reducing the production of free radicals. It has a detoxifying effect, so silymarin may be useful in treating various liver diseases. Milk thistle oil is most often recommended.
Replace sweets with dried fruits!
Indications
- 5A - for acute hepatitis / cholecystitis , exacerbation of hepatitis / cholecystitis , liver cirrhosis in the compensation stage.
- 5B - exacerbation of chronic hepatitis / cholecystitis , with cirrhosis of the liver with moderate insufficiency, combined peptic ulcer / gastritis with hepatitis or cholecystitis .
- Diet No. 5 - for chronic liver/gallbladder diseases (beyond the acute stage).
- 5P - when cholecystitis with pancreatitis .
- 5F / 5 L/F - after cholecystectomy / hypotension of the gallbladder with bile stagnation.
Products for a diseased liver: diet rules for fatty liver, cirrhosis, hepatic encephalopathy
Of course, in case of diseases, products for the liver should be selected not only taking into account the name of the disease, but also taking into account the medical history. But we propose to briefly consider the most popular options.
Products for a diseased liver:
- For fatty liver
In general, the goal of treating fatty liver is to eliminate the causes or risk factors. For fatty liver caused by alcohol consumption, alcohol consumption should be avoided in general. You should use a diet with reduced energy consumption, that is, you need to consume the optimal amount of calories, but with the lion's share of protein for rapid cell regeneration.
In addition, you should consume more than 30 grams of fiber per day and increase the proportion of monounsaturated fats (canola oil, olive oil, etc.). Don’t forget to drink enough water - at least 1.5 liters, and including first courses - about 2 liters. Carbohydrates should be in your menu, but keep simple elements like sugar and sweets to a minimum. Be sure to include proper amounts of riboflavin, vitamin B 12, and niacin.
Choosing products
- Diet for cirrhosis
Basically, the diet is based on the rules of a light diet. In addition, it is necessary to ensure an adequate supply of energy and nutrients, since the metabolic function of the liver may be impaired. If there are complications in addition to the underlying disease, further nutrition in the form of additional vitamins should be considered. It is helpful to eat soft foods and avoid other irritants such as too hot drinks and food. In addition, you should take small meals frequently. The basis of your menu is soups, low-fat foods, boiled vegetables, meat and fish. Taboo - all fried and fatty foods, with an abundance of hot or aggressive spices!
We recommend reading “The Pevzner Diet - 15 Tables” with a sample menu for liver disease.
- Hepatic encephalopathy
Excessive intake of heavy foods burdens the affected liver and can flare up neuronal symptoms. A vegetarian diet with milk, dairy products and eggs is recommended. Research shows that this diet can reduce symptoms faster than meat and fish.
Important: For all liver diseases, alcohol consumption should be strictly avoided.
Do's and don'ts for a diseased liver
Authorized Products
Therapeutic nutrition for diseases of the gallbladder and liver includes in the diet:
- Soups based on vegetable broths with the addition of pureed vegetables, cereals, small vermicelli without dressing.
- Dried wheat bread. If well tolerated - rye bread, dry biscuit in small quantities.
- Lean varieties of red meat (beef/veal), poultry (chicken, turkey), rabbit meat, boiled, lean types of white river fish, boiled/baked with vegetables.
- Chicken/quail eggs soft-boiled/steam omelet.
- Cereals (oatmeal, buckwheat), white rice in the form of well-cooked porridges and casseroles.
- Low-fat fermented milk products (cottage cheese, kefir, acidophilus, bifidum-kefir). Milk/sour cream may be used as an additive to ready-made first courses.
- Vegetables, including garden greens, baked/stewed (mashed potatoes, caviar), raw - in the form of salads with the addition of vegetable oil.
- Vegetable-based sauces and sour cream and milk mixtures. Butter/vegetable oil without heat treatment, added only to ready-made dishes.
- Sweet berries/fruits in fresh and cooked form (compotes, jelly, mousses).
- Desserts include caramel, marmalade, jams, honey, marshmallows, and toffee.
- Rosehip infusion, wheat bran decoction, table still/lightly carbonated water, vegetable juices, weak tea/coffee with milk.
Table of permitted products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| zucchini | 0,6 | 0,3 | 4,6 | 24 |
| broccoli | 3,0 | 0,4 | 5,2 | 28 |
| cauliflower | 2,5 | 0,3 | 5,4 | 30 |
| potato | 2,0 | 0,4 | 18,1 | 80 |
| carrot | 1,3 | 0,1 | 6,9 | 32 |
| pumpkin | 1,3 | 0,3 | 7,7 | 28 |
Fruits | ||||
| apricots | 0,9 | 0,1 | 10,8 | 41 |
| quince | 0,6 | 0,5 | 9,8 | 40 |
| watermelon | 0,6 | 0,1 | 5,8 | 25 |
| bananas | 1,5 | 0,2 | 21,8 | 95 |
| pears | 0,4 | 0,3 | 10,9 | 42 |
| melon | 0,6 | 0,3 | 7,4 | 33 |
| kiwi | 1,0 | 0,6 | 10,3 | 48 |
| peaches | 0,9 | 0,1 | 11,3 | 46 |
| plums | 0,8 | 0,3 | 9,6 | 42 |
| persimmon | 0,5 | 0,3 | 15,3 | 66 |
| apples | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 47 |
Berries | ||||
| strawberry | 0,8 | 0,4 | 7,5 | 41 |
| blueberry | 1,1 | 0,4 | 7,6 | 44 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| raisin | 2,9 | 0,6 | 66,0 | 264 |
| dried figs | 3,1 | 0,8 | 57,9 | 257 |
| dried apricots | 5,2 | 0,3 | 51,0 | 215 |
| dried apricots | 5,0 | 0,4 | 50,6 | 213 |
| prunes | 2,3 | 0,7 | 57,5 | 231 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| buckwheat (kernel) | 12,6 | 3,3 | 62,1 | 313 |
| semolina | 10,3 | 1,0 | 73,3 | 328 |
| oat groats | 12,3 | 6,1 | 59,5 | 342 |
| pearl barley | 9,3 | 1,1 | 73,7 | 320 |
| rice | 6,7 | 0,7 | 78,9 | 344 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| pasta | 10,4 | 1,1 | 69,7 | 337 |
| buckwheat noodles | 14,7 | 0,9 | 70,5 | 348 |
Bakery products | ||||
| wheat bread | 8,1 | 1,0 | 48,8 | 242 |
Confectionery | ||||
| jam | 0,3 | 0,2 | 63,0 | 263 |
| jelly | 2,7 | 0,0 | 17,9 | 79 |
| marshmallows | 0,8 | 0,0 | 78,5 | 304 |
| fruit and berry marmalade | 0,4 | 0,0 | 76,6 | 293 |
| paste | 0,5 | 0,0 | 80,8 | 310 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| honey | 0,8 | 0,0 | 81,5 | 329 |
| sugar | 0,0 | 0,0 | 99,7 | 398 |
Dairy | ||||
| kefir 1.5% | 3,3 | 1,5 | 3,6 | 41 |
| curdled milk 1% | 3,0 | 1,0 | 4,1 | 40 |
| acidophilus 1% | 3,0 | 1,0 | 4,0 | 40 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cottage cheese 1% | 16,3 | 1,0 | 1,3 | 79 |
| cottage cheese 1.8% (low-fat) | 18,0 | 1,8 | 3,3 | 101 |
Meat products | ||||
| beef | 18,9 | 19,4 | 0,0 | 187 |
| rabbit | 21,0 | 8,0 | 0,0 | 156 |
Bird | ||||
| boiled chicken breast | 29,8 | 1,8 | 0,5 | 137 |
| boiled chicken drumstick | 27,0 | 5,6 | 0,0 | 158 |
| boiled turkey fillet | 25,0 | 1,0 | — | 130 |
Eggs | ||||
| chicken eggs | 12,7 | 10,9 | 0,7 | 157 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| flounder | 16,5 | 1,8 | 0,0 | 83 |
| pollock | 15,9 | 0,9 | 0,0 | 72 |
| cod | 17,7 | 0,7 | — | 78 |
| hake | 16,6 | 2,2 | 0,0 | 86 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| butter | 0,5 | 82,5 | 0,8 | 748 |
| sunflower oil | 0,0 | 99,9 | 0,0 | 899 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| mineral water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| apricot juice | 0,9 | 0,1 | 9,0 | 38 |
| carrot juice | 1,1 | 0,1 | 6,4 | 28 |
| peach juice | 0,9 | 0,1 | 9,5 | 40 |
| pumpkin juice | 0,0 | 0,0 | 9,0 | 38 |
| rose hip juice | 0,1 | 0,0 | 17,6 | 70 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Fully or partially limited products
The diet for diseases of the gallbladder and liver excludes the following products:
- All types of fresh bread, dough (butter, puff pastry), pastries, pies, buns, fried pies.
- Fatty meats/fish, sausages, canned food, fast food, semi-finished products, smoked meats, caviar, salted/dried fish. By-products containing a lot of cholesterol (cod liver, brains, liver, kidneys).
- Cooking and animal fats, waterfowl meat (goose and duck), chicken/quail eggs, hard-boiled and fried.
- Highly extractive dishes (broths), foods high in oxalic acid (sorrel/spinach), essential oils (garlic, onion, radish).
- Vegetables with coarse fiber - radishes, turnips, radishes, as well as all types of legumes (beans, peas, chickpeas, lentils), if poorly tolerated, cabbage - white cabbage.
- Full-fat dairy products (milk/cream), mayonnaise, hot seasonings, spices and sauces.
- Sweet carbonated drinks, alcohol, chocolate, cocoa, black coffee.
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| canned vegetables | 1,5 | 0,2 | 5,5 | 30 |
| eggplant | 1,2 | 0,1 | 4,5 | 24 |
| swede | 1,2 | 0,1 | 7,7 | 37 |
| peas | 6,0 | 0,0 | 9,0 | 60 |
| bulb onions | 1,4 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 41 |
| chickpeas | 19,0 | 6,0 | 61,0 | 364 |
| cucumbers | 0,8 | 0,1 | 2,8 | 15 |
| salad pepper | 1,3 | 0,0 | 5,3 | 27 |
| parsley | 3,7 | 0,4 | 7,6 | 47 |
| radish | 1,2 | 0,1 | 3,4 | 19 |
| white radish | 1,4 | 0,0 | 4,1 | 21 |
| iceberg lettuce | 0,9 | 0,1 | 1,8 | 14 |
| tomatoes | 0,6 | 0,2 | 4,2 | 20 |
| dill | 2,5 | 0,5 | 6,3 | 38 |
| beans | 7,8 | 0,5 | 21,5 | 123 |
| horseradish | 3,2 | 0,4 | 10,5 | 56 |
| spinach | 2,9 | 0,3 | 2,0 | 22 |
| sorrel | 1,5 | 0,3 | 2,9 | 19 |
Berries | ||||
| grape | 0,6 | 0,2 | 16,8 | 65 |
Mushrooms | ||||
| mushrooms | 3,5 | 2,0 | 2,5 | 30 |
| marinated mushrooms | 2,2 | 0,4 | 0,0 | 20 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| nuts | 15,0 | 40,0 | 20,0 | 500 |
| peanut | 26,3 | 45,2 | 9,9 | 551 |
| seeds | 22,6 | 49,4 | 4,1 | 567 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| millet cereal | 11,5 | 3,3 | 69,3 | 348 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| pasta | 10,4 | 1,1 | 69,7 | 337 |
| dumplings | 11,9 | 12,4 | 29,0 | 275 |
Bakery products | ||||
| buns | 7,9 | 9,4 | 55,5 | 339 |
| Rye bread | 6,6 | 1,2 | 34,2 | 165 |
Confectionery | ||||
| pastry cream | 0,2 | 26,0 | 16,5 | 300 |
| shortbread dough | 6,5 | 21,6 | 49,9 | 403 |
Ice cream | ||||
| ice cream | 3,7 | 6,9 | 22,1 | 189 |
Chocolate | ||||
| chocolate | 5,4 | 35,3 | 56,5 | 544 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| mustard | 5,7 | 6,4 | 22,0 | 162 |
| mayonnaise | 2,4 | 67,0 | 3,9 | 627 |
Dairy | ||||
| milk 4.5% | 3,1 | 4,5 | 4,7 | 72 |
| cream 35% (fat) | 2,5 | 35,0 | 3,0 | 337 |
| whipped cream | 3,2 | 22,2 | 12,5 | 257 |
| sour cream 30% | 2,4 | 30,0 | 3,1 | 294 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| parmesan cheese | 33,0 | 28,0 | 0,0 | 392 |
Meat products | ||||
| fatty pork | 11,4 | 49,3 | 0,0 | 489 |
| salo | 2,4 | 89,0 | 0,0 | 797 |
| bacon | 23,0 | 45,0 | 0,0 | 500 |
Sausages | ||||
| smoked sausage | 9,9 | 63,2 | 0,3 | 608 |
Bird | ||||
| smoked chicken | 27,5 | 8,2 | 0,0 | 184 |
| duck | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
| smoked duck | 19,0 | 28,4 | 0,0 | 337 |
| goose | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| smoked fish | 26,8 | 9,9 | 0,0 | 196 |
| black caviar | 28,0 | 9,7 | 0,0 | 203 |
| salmon caviar granular | 32,0 | 15,0 | 0,0 | 263 |
| salmon | 19,8 | 6,3 | 0,0 | 142 |
| canned fish | 17,5 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 88 |
| salmon | 21,6 | 6,0 | — | 140 |
| trout | 19,2 | 2,1 | — | 97 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| animal fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| cooking fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
Alcoholic drinks | ||||
| dry red wine | 0,2 | 0,0 | 0,3 | 68 |
| vodka | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,1 | 235 |
| beer | 0,3 | 0,0 | 4,6 | 42 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| soda water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| cola | 0,0 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 42 |
| instant coffee dry | 15,0 | 3,5 | 0,0 | 94 |
| sprite | 0,1 | 0,0 | 7,0 | 29 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Harmful and difficult foods for the liver or foods that the human liver does not like
The list of foods that negatively affect the liver is quite large. The main prohibited foods for the liver are: alcohol, salt, sugar, starchy foods, fatty foods and some animal products. And we will now take a look at why they should be avoided not only by people with a diseased liver, but even by healthy people.
Harmful and difficult foods for the liver:
- Animal products. The liver is unable to properly metabolize proteins and break down amino acids produced by the body when eating animal products. Avoid red and fatty meats such as pork, lamb, and all types of lard . Protein plays an important role in overall nutrition, so choose lean poultry and non-meat protein sources like beans and nuts. You can also include soy milk in your diet.
We exclude all smoked meats!
- Foods with a high sodium capacity. Salt contains sodium, which is not fully processed, especially by a damaged liver. Canned food and all possible chemical spices, in addition to harmful E-fillers, also contain a lot of salt and sugar, which causes swelling of the abdominal cavity and fluid retention. Eating a low-sodium diet is optimal for preventing further liver damage as well as unnecessary inflammation. Use garlic, pepper or natural spices to flavor foods instead of salt.
- Sweet and junk food. Avoid sugary foods such as candy, ice cream and cakes, and salty foods such as potato chips, snacks, nuts and other beer snacks, which are simple carbohydrates high in sugar and sodium, respectively. Eat foods with natural sugars and fibrous carbohydrates, such as strawberries, oranges, or apples, to avoid unhealthy levels of sugar and sodium in your liver.
We exclude
- Alcohol at any level. Depending on the severity of the damage to your liver, there may be a chance of regeneration if you abstain from all alcoholic beverages. Chronic alcoholism causes liver damage because it interferes with the proper absorption of nutrients, causing the liver to become toxic. Reduce or minimize your consumption of beer, wine or champagne, and any liquor. Strong drinks are not included in the discussion at all. Please note that some medications also contain alcohol, such as cough syrup.
- Limit your fat intake. Too much fat increases the risk of obesity and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. According to dietary guidelines, you should consume no more than 20-35% of your total daily calories from fat. In particular, reduce your intake of saturated fat to less than 7 percent of total calories and eliminate your intake of trans fat. Foods such as margarine, cookies and fatty meats contain unhealthy fats! Train yourself to eat food steamed rather than fried in oil!
Harmfulness rating
Advantages and disadvantages
| pros | Minuses |
|
|
Reviews and results
Therapeutic nutrition for diseases of the gallbladder and liver is the main component of therapy, allowing you to maintain the organs of the hepabilliary tract in a satisfactory condition, slow down the progression of the process and normalize the functions of the liver/gallbladder.
- “... After suffering from hepatitis, a year later I was diagnosed with fatty liver hepatosis. They said that it was necessary to switch to dietary nutrition and prescribed hepatoprotective drugs. I was on a strict diet for 3 months, and then began to gradually expand my diet. During this period, my general health improved significantly, my tests came back almost to normal. During the period of following the diet, I lost 4 kg, in principle, the diet does not bother me, I think that I will periodically switch to it”;
- “... I suffered from cholelithiasis for almost 10 years. But then the colic became more frequent, became unbearable, and an ultrasound revealed gallstones measuring 1.5 cm in size. Laparoscopic surgery was suggested. The operation was successful and a diet was prescribed. After 5 months, the condition more or less returned to normal, and I began to gradually expand my diet. At the same time, I noticed that with serious violations in nutrition (I drink a little, overeat, eat fatty foods, complications begin). This means that you cannot stray far from the principles of dietary nutrition and the set of recommended products”;
- “...I had viral hepatitis. I followed the diet strictly, especially in the first month, and then, as my general condition improved, I began to make mistakes in eating and this immediately made itself felt - heaviness appeared under the rib. I had to go back to diet food again, and decided to complete the treatment and stay on a diet, as the doctor recommended, for at least 6 months.”