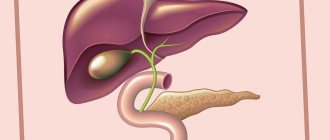
Biliary dyskinesia is a pathology that has developed as a result of a functional disorder of the motor activity of the gallbladder and its ducts. As a result, there is an acceleration or slowdown in the outflow of bile into the duodenum. The disease is quite widespread.
Dyskinesia itself is not dangerous, but the disease can be a trigger factor in the development of other, more serious diseases and lead to complications. For example, to the formation of stones in the gall bladder, which, in turn, can cause its perforation (perforation) and the occurrence of peritonitis (inflammation of the peritoneum). Therefore, you should contact a gastroenterologist on time, even when the first signs of the disease appear, and follow all the specialist’s recommendations.
At CELT you can get advice from a gastroenterologist.
- Initial consultation – 4,200
- Repeated consultation – 3,000
Make an appointment
Etiology
Based on the causes of occurrence, dyskinesia is divided into secondary and primary. The latter is less common and is caused by various congenital anomalies of the biliary system, among which are:
- abnormal shape of the gallbladder;
- double the number of ducts;
- incorrectly located or additional bubble.
Secondary dyskinesia develops in connection with existing pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract: diseases of the liver (for example, hepatitis), gall bladder, stomach (gastritis, ulcer), duodenum (duodenitis), etc. In such cases, dyskinesia accompanies and complements clinical manifestations of these diseases.
An interesting fact is that the secondary form of the disease often occurs against the background of diseases of the female genital area, helminthic infestations (for example, giardiasis), endocrine disorders (hormonal disorders of the thyroid gland, diabetes, obesity) and even chronic infections (caries, tonsillitis, etc. ).
Factors influencing the development of dyskinesia are:
- psychogenic disorders - psychotraumatic situations, against the background of which the motility of the biliary tract is disrupted;
- nutritional factors – irregular and unhealthy diet, abuse of alcohol, fried and fatty foods;
- physical inactivity;
- avitaminosis.
Why is JVP dangerous?
The disease does not pose a direct threat to life, but can significantly worsen health. Due to digestive disorders, the body experiences a lack of nutrients and vitamins. A patient with dyskinesia has an increased risk of developing urolithiasis, cholelithiasis, and polyarthritis. Stagnation of bile is harmful to the gallbladder. Against the background of gallstones, cholecystitis develops, stones can form, and the functioning of the pancreas, which is connected to the gallbladder by the duct, is disrupted.
Pain and a feeling of heaviness cause a lot of trouble and interfere with normal performance and rest.
Classification
Dyskinesia is classified according to the etiological mechanism into primary and secondary forms, the causative factors of which were mentioned above.
Based on the type of tone disturbance and motor reflexes, hyperkinetic and hypokinetic dyskinesia are distinguished. The first, which is also called spastic, occurs when the influence of the parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system prevails. In this case, bile enters the intestines too quickly and in insufficient concentration, which negatively affects the digestive processes. This type of dyskinesia is more often characteristic of young people.
The hypokinetic or atonic form of the disease indicates the predominance of sympathetic innervation and is characterized by the slow movement of bile through the ducts. This leads to the fact that bile stagnates and a high concentration of it is released into the intestine, which subsequently is fraught with the development of an inflammatory process (duodenitis) and cholelithiasis. The atonic form of dyskinesia is more common among middle-aged and elderly people, as well as among people with unstable mental health.
Whatever form of the disease develops, the lack of optimal rate of bile secretion leads to disruption of digestive functions. The difference is observed only in clinical manifestations.
Possible complications
JVP is not a normal condition for the body. Treatment must be carried out in full. Otherwise, the following complications may develop:
- cholecystitis - an inflammatory process involving the gallbladder;
- the appearance of stones in the gallbladder;
- acute and chronic pancreatitis;
- duodenitis is an inflammatory process in the duodenum.
Clinic
One of the main symptoms of the hyperkinetic form of dyskinesia is severe paroxysmal pain in the projection of the gallbladder, which can spread to the muscles of the right shoulder girdle. The development of an attack is preceded by various triggering factors - acute stress, eating disorders or severe physical activity. The pain syndrome can stop on its own or be eliminated by taking antispasmodics. During the interictal period, the patient feels relatively well, but may be bothered by unexpressed pain in the right hypochondrium, in the navel or epigastric region.
At the time of the attack, nausea, vomiting, excessive urination, and bowel dysfunction in the form of constipation or diarrhea are often noted. In addition, pain syndrome is often accompanied by cardiovascular symptoms (rapid heartbeat, heart pain, decreased blood pressure) and neurovegetative disorders (increased sweating, increased irritability, etc.). Objectively, a positive Ker's symptom is noted - pain at the point of projection of the gallbladder.
The hypokinetic form of the disease is accompanied by constant pain of moderate intensity. Painful sensations are often accompanied by bitter belching, nausea, bloating, loss of appetite, and bowel dysfunction. Neurological manifestations are also present: depression, general fatigue, etc. An objective examination reveals a positive Ortner (Grekov) symptom - pain when tapping on the right costal arch.
If symptoms appear that are suspicious of biliary dyskinesia, you must consult a gastroenterologist for timely diagnosis and treatment.
Prognosis and prevention
The disease will occur chronically throughout life, but by following a diet and a healthy lifestyle, the development of painful attacks can be avoided.
Among the complications of self-medication or non-compliance with doctor’s recommendations, calculous cholecystitis and cholangitis may develop.
Preventive measures include adherence to the principles of a healthy diet, normalization of sleep, avoidance of stress and mandatory treatment of diseases that can lead to the development of secondary VSD.
Diagnostics
When conducting diagnostics, it is important to differentiate primary dyskinesia from the secondary form caused by organic pathologies. You should also understand the type of dyskinesia: what motor impairment occurs in a particular case.
Standard examination methods include the following list:
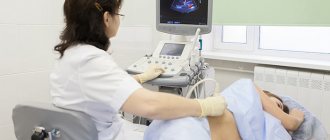
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs, which allows you to evaluate the anatomical structure of the biliary system. Functional activity can also be analyzed using this method. To do this, it is enough to compare the ability of the gallbladder walls to contract before and after eating.
- X-ray examination allows us to assess the rate of evacuation of the contents of the stomach and duodenum.
- Scintigraphy.
- Sphincter of Oddi manometry is used to measure the pressure in this muscle valve.
- Magnetic resonance imaging of the abdominal organs with MR cholangiography.
Of the laboratory diagnostic methods, it is worth noting stool analysis (for coprogram and dysbiosis), blood tests (clinical, biochemical).
How does JVP manifest itself?
You can suspect dyskinesia based on the following signs:
- after eating a meal with a predominance of fatty and spicy foods, pain appears on the right side, which can radiate to the shoulder blade and chest.
- the patient may experience periodic discomfort in the area of the liver and gallbladder: heaviness, aching or acute pain.
- after eating, signs of flatulence appear and stool is disrupted.
- Nonspecific signs include a feeling of bitterness in the mouth, the appearance of plaque on the tongue, and bad breath.
You should know that such symptoms are typical for many gastrointestinal diseases, so only a gastroenterologist can make a final diagnosis after diagnosis.
Treatment
Effective treatment of dyskinesia requires an integrated approach. First of all, the diet is adjusted: fatty and cold foods, flour products, as well as foods that provoke flatulence are excluded from the diet. You should take care to change not only your culinary preferences. It is important to follow a diet and give up bad habits.
Therapy is aimed at eliminating the cause that led to the development of dyskinesia, be it a source of chronic infection, helminthic infestation, food allergy, intestinal dysbiosis or vitamin deficiency. Accordingly, antibacterial, desensitizing, antiparasitic or anthelmintic therapy is prescribed. It is quite possible that treatment will be limited to the administration of probiotics and vitamin complexes.
The need to correctly determine treatment tactics once again emphasizes the importance of differential diagnosis, because the treatment approach largely depends on the type of dyskinesia motor disorder. Thus, the hyperkinetic form of the disease dictates the need to prescribe sedatives (herbal sedatives), choleretics (choleretics), and antispasmodics. It would be a good idea to drink well-heated, slightly carbonated mineral water. Non-drug methods also give good results: psychotherapy, reflexology, physiotherapy, treatment with medicinal leeches, massage.
For the hypokinetic form of dyskinesia, the therapeutic approach is different. Experts recommend tonic medications, cholekinetics (drugs that increase bile secretion), herbal medicine, and highly mineralized waters. Treatment without medications is also encouraged: “blind” probing, physiotherapy, physical therapy and massage are used.
Patients suffering from biliary dyskinesia should be observed by a gastroenterologist and neurologist. It is necessary to annually undergo a course of balneological (sanatorium-resort) treatment and take a responsible approach to the implementation of all treatment and preventive recommendations of specialists.
At the CELT multidisciplinary clinic, highly qualified professional doctors with a huge amount of knowledge and practical experience are waiting for you. We create an individual treatment plan for each patient, taking into account personal characteristics.
Folk remedies
At home, treatment of dyskinesia is best done in combination with traditional methods. But before preparing and taking them, you should consult your doctor.
Infusions, decoctions, extracts and syrups of herbs are used that can activate the formation of bile and improve the motor function of the sphincters and bile ducts.
- For the hypertonic and hyperkinetic type, mint, chamomile flowers, motherwort herb, licorice root, dill fruits, and valerian root are used.
- In the hypotonic and hypokinetic form, rose hips, immortelle flowers, St. John's wort, corn silk, oregano, nettle leaves, and chamomile are used for herbal medicine.
Milk thistle, immortelle, tansy, dandelion leaves and root, corn silk, chicory, rose hips, fumaria, parsley, turmeric root, cumin, yarrow have a choleretic effect.
Herbal decoctions are used 20-30 minutes before meals.
Our services
The administration of CELT JSC regularly updates the price list posted on the clinic’s website. However, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we ask you to clarify the cost of services by phone: +7
| Service name | Price in rubles |
| Gastroscopy (videoesophagogastroduodenoscopy) | 6 000 |
| Colonoscopy (video colonoscopy) | 7 000 |
| Ultrasound of the abdominal organs (liver, gall bladder, pancreas, spleen) | 3 800 |
| Fluoroscopy and radiography of the stomach | 4 800 |
All services
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions