Home » Diagnostics » Colonoscopy » Checking the intestines
Every person has problems with their intestines from time to time. The functionality of internal organs depends on the way of life, on nutrition and daily routine, and the presence of bad habits. Intestinal pathologies are extremely dangerous, as the disease rapidly moves from the initial stage to the advanced stage, from benign to malignant.
It is important to pay attention to your health, pay attention to any symptoms that appear and consult a doctor. It is recommended to have a bowel check every six months. Today, medicine uses all kinds of methods for diagnosing the gastrointestinal tract. Updated equipment allows you to assess the condition of the intestines and make a diagnosis even at an early stage of the pathology.
Most often, patients are embarrassed to talk about a problem such as bowel dysfunction. Patients consider this topic shameful and consult a doctor in advanced cases. It is extremely important not to progress the disease and begin treatment as early as possible. Self-medication has a negative impact on a person’s health, so you should contact a qualified worker.
Capsule endoscopy
When using this technique, the study is carried out in a special capsule equipped with cameras and other sensors, which the patient must swallow. It scans the digestive tube as it naturally progresses and transmits data via wireless communication systems. This technique is one of the options for examining the intestines for diseases without the use of colonoscopy.
Main advantages:
- Simplicity and painlessness.
- Extensive data on the state of the digestive tract.
- High quality images and a lot of additional data.
Capsule endoscopy also has disadvantages, the main one being the inability to take a biopsy and perform other manipulations. The movement of the capsule cannot be controlled, so the suspicious area cannot be examined in more detail.
The essence of the method and principle of operation
This method is used for visual examination (video is transmitted to the monitor) of the rectum by introducing into it a medical device ( anoscope) resembling a tube or a small gynecological speculum, the length of which is 10 cm.
The method serves as a supplement to a digital examination to obtain a more accurate clinical picture of the disease and identify hidden diseases of the rectum.
It is the predecessor to all endoscopic research methods (video-rectoromanoscopy, colonoscopy).
For medicinal purposes, this device is an indispensable assistant. Used for:
- for infrared coagulation and sclerosing therapy of hemorrhoids;
- for ligation of hemorrhoids with latex rings;
- for the administration of drugs, for electrocoagulation of polyps.
Irrigoscopy
The procedure consists of injecting a contrast agent into the large intestine (barium enema) and taking x-rays in several projections.
This allows you to accurately localize pathological areas of the intestine, detect peristalsis disorders, diverticulosis and other diseases. Irrigoscopy is safe, painless and does not take much time.
The main disadvantage of irrigoscopy is its low information content. There is also a fairly high probability of receiving false data when part of the intestinal contents is mistaken for a tumor or other pathology. As a result, a colonoscopy will still be required to clarify the diagnosis.
Methods for diagnosing intestinal diseases
Today, the all-Russian medical examination program includes the analysis of stool for occult blood for people over forty years of age. Laboratory testing reveals signs of the presence of malignant tumors in the body. After receiving the test results, the attending physician decides to conduct further diagnostic studies. Abdominal ultrasound and computed tomography are often performed.
The following types of research are used in diagnostic centers, private and public clinics:
- laboratory methods;
- instrumental methods;
The diagnostic method used depends on the patient’s condition, the presence of concomitant diseases, and complications.
Laboratory methods
After the initial consultation, the patient is required to undergo laboratory tests. These include a general analysis of blood, urine and feces. The results are analyzed by the attending physician, after which the presence of problems and abnormalities in the body is determined. Thus, the following are diagnosed:
- infectious and inflammatory processes in the body;
- parasitic diseases;
- gastrointestinal bleeding;
- malabsorption syndromes;
- presence of neoplasms.
Tests are carried out on an empty stomach in the morning, since it is at this time that the test results will be most accurate. Blood is taken from a vein or finger. If there is a suspicion of intestinal pathology, ESR levels increase, anemia or anemia develops. A biochemical blood test will detect malabsorption of nutrients in the intestine.
A general urine test conducts detailed studies that are associated with impaired absorption of substances and dehydration. We are talking about constant diarrhea and vomiting. To do this, the patient uses a sterile container to collect biological material. Urine collection is carried out in the morning. After this, the materials should be delivered to the diagnostic center as soon as possible. A signal of impaired functioning of the body is called saturated color of urine, turbidity, and increased density.
The coprogram allows you to examine feces and detect the presence of an infectious and inflammatory process.
Magnetic resonance and computed tomography
Whether an MRI can be done instead of a colonoscopy depends on the intended diagnosis and other individual characteristics of the patient. This procedure has a number of advantages:
- Simple and fast procedure.
- There is no radiation exposure to the body and no discomfort.
- Quite high accuracy.
This type of diagnosis makes it possible to detect pathological changes in the intestinal wall that are 1 cm or more in size. The main disadvantage of the method is the inability to take material for biopsy and low resolution. Typically, MRI is used to clarify data obtained by other methods, for example, to accurately localize metastases in cancer.
CT scans also provide fairly detailed images. To increase the resolution of the procedure, complete bowel emptying and the introduction of a radiocontrast agent are required. Regular air is often used for this purpose.
The main disadvantage of computed tomography is its high radiation exposure. If the patient is not properly prepared, false results can be obtained. Therefore, CT is used relatively rarely in the diagnosis of colon diseases.
Features of examination of the small and large intestines
Health care providers specialize in examining two segments of the intestine, namely the small intestine and large intestine. Diagnosis of these departments has different specifics. The small intestine digests food, absorbs nutrients, and is responsible for metabolism. The large intestine, in turn, is responsible for the formation and elimination of feces.
To diagnose both segments, a scatological examination is performed. This laboratory analysis allows the doctor to establish an accurate diagnosis and analyze the nature of the disease. At the same time, the consistency of stool, the presence of bloody, mucous and purulent discharge, and the color of stool are analyzed.
One of the most informative diagnostic methods is examination of the intestine using an endoscope. Diagnostics is carried out using specially equipped equipment. Examining the small intestine with an endoscope is more difficult, since the location of the organ is considered difficult to access.
Stool tests
How to check in another way is a question that is relevant for most people over 40 years old. Regularly performing this endoscopic procedure is associated with quite a lot of inconvenience for the patient and requires careful preparation and diet. An alternative may be DNA testing of stool. They are aimed at identifying specific DNA molecules belonging to tumor cells.
Stool can also be analyzed for the presence of occult blood and a fecal immunochemical test can be performed. All these laboratory techniques make it possible to accurately detect cancer, even at the earliest stages of development.
Important
Please note that any intestinal examination cannot serve as a complete replacement for colonoscopy. In most cases, they are used as screening, that is, to detect signs of pathology in the early stages of development.
Symptoms to watch out for
In what cases should you consult a doctor and undergo a comprehensive examination of the intestines? According to medical statistics, patients notice nonspecific symptoms, including:
- flatulence;
- pain in the abdomen and anus;
- gastrointestinal disorders, constipation and diarrhea;
- prolonged nausea and vomiting;
- lack of appetite;
- belching after eating;
- bloating;
- blood impurities in stool;
It is recommended to undergo an intestinal examination if there is constant malaise, weakness and drowsiness, weight loss or rapid obesity with adequate nutrition. Diagnosis is mandatory if the patient has undergone surgery to remove a tumor in the intestine. Annual preventive diagnostics are carried out for people over forty years of age. At this age, age-related changes occur in the body and intestinal pathologies develop.
Patients who suffer from colorectal cancer of the colon and rectum attend bowel screening on a regular basis. This disease causes death in most cases if there is no timely treatment and medical supervision.
In 95% of cases, when pathology occurs, it is possible to stop the development of the disease and be cured completely. To do this, you should begin treatment, remove intestinal polyps, thereby stopping the growth of tumors. As a rule, polyps develop into malignant tumors in a short period of time. It is recommended to visit a proctologist and gastroenterologist not only for older people, but also for young people. In recent years, the statistics of inflammatory processes in adolescents and young people of working age has increased.
If there are no specific symptoms, the patient has no idea about the development of the disease and, accordingly, does not seek help from a qualified specialist doctor. The early stage quickly turns into an advanced stage. Determining the presence of the disease is only possible through laboratory tests and diagnostic tests. That is why preventive studies must be carried out without fail even in the absence of symptoms.
How to do endoscopy of the rectum with a proctoscope
Usually the study is performed in the knee-elbow position on the couch. A special device in the form of a metal tube with a diameter of about 1.2 cm with an optical system is inserted through the anus. Rectoscopy, in the absence of inflammation of the anal canal, is painless. During the examination, some discomfort may occur when air is forced inside. Rectoscopy differs from colonoscopy in that only the rectum is examined, and the rest of the colon remains unexamined, and therefore we recommend that you always sign up for a total colonoscopy. In the absence of contraindications and the patient’s personal desire, the use of anesthesia is allowed. The duration of the study ranges from 5 minutes to 30 minutes
.
Anesthesia
A special type of intravenous sedation used during colonoscopy is anesthesia with the drug “propofol”, the most gentle way of temporarily switching off consciousness, after which the patient wakes up alert and rested at the end of the procedure. This anesthesia is used in the most advanced clinics in the world.
Our Clinic performs about 2,000 diagnostic and therapeutic colonoscopies annually. An objective indicator of the quality of diagnosis is the highest rate of finding “polyps” during colonoscopy in Russia. Repeated visits by patients to the same specialists for follow-up studies also indicate a high level of trust and quality of medical services provided!
Consultation
The proctologist begins the examination of the patient with a conversation.
Each proctologist begins his examination of the patient with a conversation. With the help of such a conversation, he has the opportunity to find out the person’s true complaints, obtain information about previous illnesses, and clarify the presence of parallel pathologies.
It should be noted that the patient must be extremely attentive and honest in such a conversation.
How quickly you will be given the correct diagnosis and prescribed the most effective treatment will depend on how frank and complete your presentation is. In order to be prepared for a conversation with a proctologist, think about your answers to the following questions in advance:
- Do you often have the urge to go to the toilet when you need to?
- Does it happen that there are foreign inclusions in your stool? (blood, pus or mucus).
- Do you experience pain during bowel movements? (sensation of pain, burning, stinging).
- What is your diet? (an approximate set of foods you consumed last week).
- How would you assess the general condition of your body during the period of illness? (weakness, dizziness, signs of exhaustion, increased body temperature).
Think about comprehensive answers to these questions in advance and pay utmost attention to even the smallest details. Only under these conditions will a conversation with a proctologist be fruitful and will certainly speed up the establishment of a correct diagnosis.
Endoscopic examination
Endoscopic examination is used to detect tumors and polyps.
This diagnostic method is used to determine the patient’s hidden pathologies, such as polyps and tumors. The process is safe for the patient and also painless.
Thanks to endoscopy, the condition of the intestinal mucosa can be accurately assessed. The doctor examines the lining of the esophagus, stomach, duodenum, large intestine and small intestine.
The process is carried out on an empty stomach. The patient must first stimulate cleansing with laxative medications. The next stage is the introduction of an ultrasound sensor into the rectum.
Then, when the device reaches the required area of the intestine, the doctor assesses the condition of the formation or other pathology and, based on what he sees, takes further actions and treatment methods.
Contraindications. Endoscopy is not recommended for people with heart or lung disease due to exposure to special medications. But in any case, this issue is resolved individually with each patient, based on the conditions of the particular case.
When to see a doctor
Even the slightest discomfort in the gastrointestinal tract cannot be ignored. Usually people who have been suffering from stomach problems for a long time try to treat themselves. But this can be dangerous, because indigestion affects the condition of the entire body. Often, intestinal problems are a consequence of gastritis, liver or gallbladder pathologies. In this case, the patient is usually already being treated by a therapist or gastroentrologist. But it is very important to know when you need to see a doctor urgently.
Typically, intestinal problems are indicated by the following signs:
Symptoms and treatment of intestinal diseases
- pain during defecation;
- prolonged constipation;
- frequent diarrhea;
- blood, mucus, or undigested pieces of food in the stool;
- pain in the navel or lower abdomen;
- decreased appetite;
- nausea, vomiting;
- flatulence, bloating, increased gas formation;
- belching, heartburn;
- weight loss, metabolic disorders;
- decreased immunity;
- general weakness, decreased performance.
Important: if at least a few of these symptoms appear, it is necessary to undergo examination. After all, the problems will gradually progress, disrupting the functioning of the entire body.
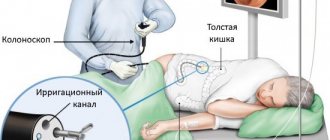
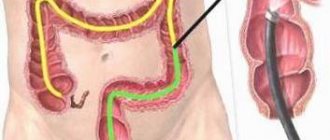
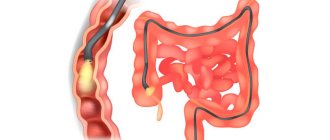
Colonoscopy
Colonoscopy is a method of studying and assessing the condition of the walls of the gastrointestinal tract.
This is a diagnostic method that many patients do not like. You can’t call it painful, rather it’s unpleasant, but its effectiveness is very high.
Colonoscopy is performed using a fiber colonoscope, which is inserted into the patient’s body after cleansing the intestines with a special laxative. The procedure lasts about 30 minutes, during which the patient may feel bloating.
A fiber colonoscope is a medical tourniquet that has a flexible texture and is equipped with an optical system. Thanks to this device the following manipulations are possible:
Preparing to see a specialist
Before a medical consultation, the patient should keep a food diary. With its help, the doctor will study the patient’s diet and try to find out the reasons for the development of pathology.
If plaque forms on the patient’s tongue during illness, do not clean it off before examination. The color, thickness and consistency of this plaque will help the doctor make a diagnosis.
3 days before the examination, you must give up gas-forming foods (raw and pickled vegetables, canned meat and fish, fatty meats, chocolate, milk, carbonated drinks).
You should come to your appointment after 8-12 hours of fasting. You should cleanse the intestines in advance using a regular water enema or medical microclyster (for example, Normacol, Microlax, Proctum).