Signs of fibrosis and fatty infiltration of the liver
Diffuse changes in the liver are usually detected by ultrasound.
Ultrasound diagnostics. shows that the liver has heterogeneous areas with increased echogenicity. Such heterogeneities are regarded by the ultrasound diagnostic doctor as an inflammatory process in the liver, requiring clarification of the diagnosis by a hepatologist. The inflammatory process in the liver is called hepatitis. It requires treatment, as it is a signal that pathological processes are occurring in the liver, which can result in the formation of cirrhosis and liver cancer.
Diffuse changes in the liver can be expressed to varying degrees and may be accompanied by an increase in the size of the liver (hepatomegaly), painful sensations in the form of heaviness and dull pain. However, most often, diffuse changes in the liver do not cause any unpleasant sensations and are often detected for the first time in an already advanced form of liver damage.
Causes
The accumulation of fatty molecules in liver cells is due to either their excessive intake or impaired excretion. Risk factors for this process may include:
- Overweight;
- Impaired glucose tolerance or diabetes mellitus;
- Hereditary predisposition;
- Taking medications (corticosteroids, oral hormonal contraceptives, NSAIDs, antibiotics, cytostatics);
- Dyslipidemia and atherosclerosis;
- Disorders of the thyroid gland;
- Adrenal gland disorders;
- Hypertension, coronary heart disease;
- An unbalanced diet with an excess of fats, fried foods, simple carbohydrates;
- Lack of physical activity.
Separately, fatty hepatosis is distinguished as part of the general mechanism of development of alcoholic liver disease. In this case, ethanol consumption is a key factor in the disruption of the structure of hepatocytes and the development of dystrophic changes.
Features of diagnosis and treatment
Typically, an ultrasound diagnostic doctor, describing the ultrasound results, notes the severity of hepatitis with a subjective assessment as a moderately expressed process, mildly expressed, moderately expressed. However, such an assessment cannot give an idea of the true condition of the liver .
To clarify the degree of liver damage, it is necessary to conduct an examination using the Fibroscan device. It allows you to determine the density of the liver tissue, which increases if there are any factors in the liver that destroy it.
Causes of diffuse changes
The most common causes of liver damage are hepatitis B and C viruses, as well as fatty liver disease (steatosis). In the case of viral hepatitis, the destruction of liver tissue occurs with its replacement by connective tissue and fibrosis is formed with subsequent progression of the process to cirrhosis. With fatty hepatosis, liver tissue is replaced by fatty tissue, which does not function like a healthy liver and can also lead to cirrhosis.
Diagnostics using the Fibroscan device (elastometry)
Unlike ultrasound diagnostics, which gives only a qualitative assessment of liver damage, the results obtained with the Fibroscan device describe the exact degree of fibrosis from 0 to 4 (4 - cirrhosis), and the exact degree of steatosis from 0 to 3 (3 - requires treatment, since it is threat of cirrhosis formation).
Liver elastometry - examination prices:
- Degree of fibrosis
3,500 rubles
- Degree of fatty hepatosis
2,500 rubles
- Consultation on results
for free!
on PROMOTION! (Moscow, Park Kultury metro station)
You can get tested:
- from 9:00 to 17:30 on weekdays
- from 9:00 to 15:00 on Saturday
Sign up by phone
+7
Seven days a week from 9:00 to 21:00
Request a call back
Moderate food consumption is the mother of health.
M.V. Lomonosov
Let's talk about another conclusion often found in ultrasound practice: “Diffuse changes in the pancreatic parenchyma.” Moreover, I am sure that most patients do not understand what it is. "Pancreas!" - they tell their relatives as they leave the ultrasound room.
But what kind of organ is this? Why is it needed? Why does everyone suffer from him?
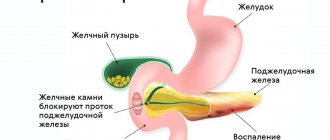
The pancreas is located, you guessed it, under the stomach. Its larger part (tail) is on the left, the smaller part is in the middle (body) and on the right (head). The gland is adjacent to different organs (liver, duodenum and other parts of the intestine, stomach, spleen, kidneys, blood vessels, excretory bile ducts), so if you are worried about pain in the upper abdomen, don’t blame everything on the poor pancreas! It’s better to get checked, because in addition to the organs listed, pain can be projected here even from the heart.
Let's continue. Why is it called a gland? A gland is an organ that can produce some important substances for the body. So, the pancreas, weighing about 60–80 g per day in an adult, produces about 1.5–2 liters of pancreatic juice! Most of the cells of which it consists produce this particular juice, which flows through the duct into the intestines and there helps to digest proteins, fats and carbohydrates. In older people, the mass of the organ decreases due to age-related changes, as well as after all the problems suffered during life, therefore less juice is produced. This means that as you age, nutrition should be in small amounts, easily digestible, and low in calories. “I’ve never been so bloated before!” - you hear from patients, and 10-20 years ago the pancreas produced more juice, food was digested faster and easier.
Only about 2% of pancreatic cells produce insulin , which regulates blood sugar levels, i.e. About 1.2–1.6 g of cells are given to us throughout our entire lives, just think about it! Now think about how many carbohydrates (sweets) you consume in your life? How many “sweets” do you buy for your children? eats 24–28 kg of sugar per year (in Russia - up to 40 kg!). Add to this about 50 tons of food, which the average person eats with a life expectancy of 70 years. Well, let’s not forget about alcohol and medications (which can be freely purchased at the pharmacy!!!). And our little pancreas must digest it all!
I would also like to talk about the effect of sleep on the pancreas. Lack of sleep leads to misfolded proteins and can potentially lead to cell death, especially in old age. A study by scientists from the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine (USA) is about just that. As well as research by Joseph Baur and his colleagues. The body must either correct or dispose of incorrect proteins. The scientist found that in older animals the reaction to such stress is weakened, that is, with age, lack of sleep can have an increasingly stronger effect.
Therefore, think twice before drinking tea at night while watching (and especially something stronger) or watching your favorite movie until one in the morning.
So, with modern abundance in nutrition and variety in lifestyle, one should not be surprised if problems with digestion begin (bloating, a feeling of heaviness, bowel movements, etc.). Many in the study admit: “So I don’t eat anything like that anymore, but Does not help!" The key word here is “already” , i.e. For many decades, we eat everything in a row, and “go on a diet” only when the body begins to give us digestive problems or elevated sugar levels in tests. Unfortunately, it is sometimes difficult to help here.
What does the doctor see on an ultrasound?
Usually, at the first problems with the gland, there may be no changes on ultrasound, and this is wonderful! Although many would like to see them, patients remain disappointed.
Remember! Single inflammations in the gland can pass without a trace and without changes according to ultrasound.
But if the doctor does find a pathology, then it is most likely irreversible or will leave its mark on the functioning of the organ.
In most cases, the doctor describes approximately the following picture: the contours of the gland are uneven, unclear, the echogenicity is increased or high, the size can be normal, increased or decreased. Rarely there is an enlargement of the gland duct and even stones in it. In such a situation, the doctor writes in the conclusion the notorious “Diffuse changes”, i.e. The gland has experienced stress many times throughout its life and some of its cells have died or been replaced by fat and scar tissue, and it can no longer work as before.
What to do with this conclusion? An additional examination is definitely necessary (first a gastroenterologist, a therapist) to determine the degree of digestive disorders and the condition of the body as a whole, because if the pancreas suffers, then there are problems in the whole body (impaired carbohydrate and fat metabolism, usually accompanied by atherosclerosis, there may be skin manifestations etc.).
But the situation as a whole, of course, depends on you. The doctor will prescribe treatment and help temporarily normalize the symptoms that bother you. But control over nutrition is completely in your hands. If your ultrasound has already revealed diffuse changes, do not load the pancreas, give it the opportunity to provide you with a comfortable life longer!
Nutrition for fatty hepatosis and pancreatitis
Diseases of the liver and pancreas are well treated with dietary nutrition:
- Meals must be taken at least 5 times a day, and portions should be of a modest size.
- The menu must exclude dishes that complicate digestion and contribute to weight gain - sweets, fatty and smoked foods, spices.
- Food is prepared in gentle ways - boiled, baked, stewed.
- Vegetables and meat are consumed pureed.
- It is prohibited to consume cold food and drinks.
- Limit the consumption of purine-containing foods (tomatoes, meat broth, offal) and salt.
- All dishes are prepared in accordance with dietary table No. 5.
- The duration of the diet is from two weeks to several years.
Prohibited foods for fatty hepatosis
Fatty hepatosis can be cured with proper nutrition.
To allow the liver and pancreas to recover, the following products are excluded from the menu:
- Fish and meat (fatty types).
- Sauces and all marinades.
- Confectionery group of products.
- Legumes.
- Chicory.
- Alcohol.
- Hibiscus.
- Conservation.
- Stevia extract.
- Carbonated drinks.
- Puff pastry.
- Juices.
- Sushi.
- Sausages.
- Spices.
- Pancakes.
- Broths, except vegetable ones.
- Corn.
- Caviar.
- Milk and fermented milk products with a fat content of more than 1%.
- Mushrooms.
- Tomatoes.
- Eggplant.
- Offal.
- Sorrel.
- Waffles.
- Donuts.
- Sour berries and fruits without heat treatment.
- Barley grits.
- Green onions.
- Nuts and seeds.
- Coffee, green tea, cocoa.
- Ginger.
- Radish.
- Green pea.
- Raw cabbage.
Symptoms
With diffuse fatty liver hepatosis, the patient experiences the following symptoms:
- nausea and vomiting;
- liver enlargement;
- pain in the right hypochondrium;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- fatigue;
- feeling of heaviness;
- headache;
- irritability;
- lack of appetite.
In some cases, the disease occurs without pronounced symptoms. They can appear with overeating, alcohol abuse and increased physical activity.
Description of the disease
With diffuse changes such as fatty hepatosis, hepatocytes accumulate large amounts of fat. Therefore, normal cells of the organ gradually die off and its tissues become heterogeneous.
Such changes in the liver are a consequence of pathological processes in the tissues of the organ. They can appear at any age. Diffuse fatty infiltration is known in 3 types:
- local - damage to one lobe of the liver;
- total - means damage to the entire organ;
- focal - a separate area of the liver is involved.
This pathology is one of the most common diseases today. It often occurs in childhood. But this disease mainly occurs in adulthood and old age.
Risk factors
The following factors negatively affect the condition of the entire liver and provoke diffuse changes in its tissues:
- smoking;
- alcohol;
- poor nutrition;
- hereditary pathology;
- viruses;
- medications.
Fatty hepatosis of the pancreas - treatment
Treatment of pancreatic hepatosis must begin with changing your usual diet. Not only the composition of the diet is subject to correction, but also the meal schedule and portion size. Note that diet is the main part of therapy.
The second part of treatment is taking medications. As a rule, treatment is symptomatic. Antispasmodics (No-shpa and Papaverine) are prescribed for pain and spasms, and enzyme preparations (Mezim, Pancreatitn) are prescribed to improve food digestion. To maintain liver function, hepatoprotectors are additionally prescribed - Heptpral, Essentiale, Karsil. If the disease is caused by pancreatic insufficiency, the endocrinologist may prescribe prescription insulin drugs.
In rare cases, when the pancreas is firmly enclosed in a fatty “cocoon”, surgery may be required. This operation is complex and can be life-threatening for the patient.
Considering the complexity of the disease and the high cost of treatment, it is better to practice prevention. Proper nutrition, maintaining a normal weight, a positive emotional background and exercise prevent fatty infiltration of the pancreas.
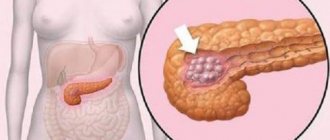
Fatty hepatosis and pancreatic lipomatosis
Pancreatic lipomatosis is a sluggish, progressive and in most cases asymptomatic disease. The pathology consists of a pathological accumulation of fat around the organ. Over time, fat cells penetrate inside and lead to complete fatty infiltration of the pancreas. This pathology has a similar development mechanism to liver hepatosis, since it is caused by the same reasons - obesity, consumption of fatty foods in large quantities, endocrine diseases.