Pancreatitis
Pancreatitis is an inflammatory process in the pancreas. According to WHO, the number of cases of pancreatitis in the world is only growing every year. The victims include mainly people leading an unhealthy lifestyle: consuming large quantities of fatty foods, alcoholic beverages, and smokers. The habit of overeating also increases the risk of developing this disease.
The symptoms of the disease and the effectiveness of treatment for pancreatitis depend on how severely the pancreatic tissue is destroyed and the degree of inflammation that has already reached.
Causes of pancreatitis
As a rule, signs of pancreatitis in both women and men in most cases occur due to excessive consumption of alcohol-containing products. In 20% of cases, it is not possible to establish the cause of the disease at all.
At CELT you can get advice from a gastroenterologist.
- Initial consultation – 4,200
- Repeated consultation – 3,000
Make an appointment
Medical statistics are harsh: the risk of inflammation in the pancreas increases in patients suffering from:
- metabolic disorders – primarily lipid metabolism;
- diabetes mellitus;
- hormonal imbalance;
- diseases of the biliary system (in particular, cholelithiasis);
- vascular diseases;
- peptic ulcer;
- infectious diseases (mumps, viral hepatitis);
- autoimmune diseases (including primary biliary cirrhosis, inflammatory bowel disease, autoimmune thyroiditis and others).
Pancreatitis in children and adults can be triggered by injuries and wounds in the abdominal area, surgical interventions on the stomach and biliary tract, as well as taking a number of medications (including hormonal drugs). Some genetic disorders are associated with pancreatitis - familial hyperlipidemia, familial hyperparathyroidism.
Complications after taking medications
Medicines for pancreatitis, like any medicine, can lead to complications. Antibiotics - for digestive upset, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - for complications in the gastrointestinal tract and cardiovascular system. Enzyme preparations can cause allergies and lead to iron deficiency. Antisecretory drugs, although they are considered drugs with a minimum of side effects, can cause withdrawal syndrome: the appearance of heartburn and sometimes pain in the sternum after stopping their use. Even vitamins, if taken immoderately and without prior testing, can become not just a useless, but also a dangerous supplement.
Symptoms of pancreatitis in men and women
From a physiological point of view, the pancreas is a very important organ of our body, responsible for normal digestion, as well as the production of the hormone insulin. A lack of the latter can cause diabetes.
In acute pancreatitis, the symptoms are similar to severe poisoning. This happens because during inflammation, enzymes are retained inside the pancreas, causing its subsequent destruction. Dead cells enter the blood in large quantities, which is manifested by symptoms of intoxication.
The most common signs of acute pancreatitis are described as follows:
- Intense constant cutting or dull pain that does not go away for a long time (up to painful shock). Pain is felt under the ribs on both sides (together or separately), sometimes pain is felt throughout the entire area of the abdomen and radiates to the lumbar region.
- A sharp decrease or increase in blood pressure.
- Changes in complexion: with pancreatitis in children and adults, the skin turns pale, gradually approaching grayish shades.
- Increase in body temperature to high levels.
- Nausea, hiccups, belching, and a feeling of dry mouth. Vomiting with secretion of bile.
- Diarrhea (diarrhea) with pancreatitis is a common phenomenon. Moreover, the feces come out with foam, with a sharp unpleasant odor, and undigested pieces of food are noticeable in it. There may also be constipation.
- Abdominal muscle tension.
- The appearance of shortness of breath, a characteristic icteric coating on the tongue, as well as sticky sweat: all this is the result of a lack of electrolytes due to vomiting and diarrhea.
- Bloating.
Prevention
Primary prevention of pancreatitis is to avoid alcohol, eat a variety of foods that are low in fat, saturated fat and cholesterol, include grains, vegetables and fruits in the diet, and stop smoking.
Acute pancreatitis can develop not only in people who regularly abuse alcohol, but also as a result of a single intake of alcohol-containing drinks with a fatty, fried and spicy snack in large quantities. Small, proper nutrition for pancreatitis serves to prevent exacerbations of its chronic form.
Acute pancreatitis: treatment and first aid
When initial symptoms of the disease appear, you must call an ambulance. Treatment of acute pancreatitis takes place exclusively in a hospital setting under the constant supervision of specialists.
While waiting for doctors, to alleviate the patient’s condition, you can put cold on his stomach. As for medications, you can take any antispasmodics - papaverine, no-shpu, smazmalgon, etc. From the moment the first symptoms appear, you should stop any food intake (including juices) and go to bed. Doctors say that no medicine treats pancreatitis better than cold, hunger and rest.
Treatment in a hospital is carried out taking into account the clinic. Antispasmodics, prokinetics, anti-inflammatory drugs, antisecretory, antibacterial drugs are used (for the prevention or treatment of bacterial complications). Treatment is carried out by infusion (through a dropper). Diet therapy (when the patient is allowed to resume eating) is of great importance. Enzyme preparations are used during meals.
When should you make an appointment with a doctor?
If nausea does not go away for a long time, it is accompanied by vomiting, diarrhea, or an increase in body temperature, you need to consult a doctor. Often these symptoms are confused with food poisoning and mild stomach upsets. This may be an exacerbation of pancreatitis. A gastroenterologist treats pancreatitis; he will diagnose, prescribe treatment, and monitor the healing process. The examination is carried out using new equipment, doctors use modern treatment methods. JSC "Medicine" (clinic of academician Roitberg) is located in the center of Moscow, at 2nd Tverskoy-Yamskaya lane 10, not far from the metro stations Chekhovskaya, Mayakovskaya, Belorusskaya, Novoslobodskaya, Tverskaya.
Symptoms of chronic pancreatitis in adults and children
Chronic pancreatitis develops against the background of prolonged inflammation of the pancreas, which causes pain and decreased function of the gland.
Doctors distinguish two periods: at the initial stage, symptoms appear and disappear, and at the final stage they bother the person on an ongoing basis. The initial stage can last years and decades, causing pain in the upper abdomen, in the heart and left side of the chest. As a rule, such sensations appear after heavy feasts, abuse of junk food, carbonated and alcohol-containing drinks. The pain is often accompanied by vomiting and diarrhea, nausea, bloating and general weight loss.
Long-term chronic pancreatitis results in serious dysfunction of the pancreas. Gradually, the pain disappears, but dyspepsia increases, and jaundice of the skin may appear. Exocrine and endocrine pancreatic insufficiency develops.
What is the pancreas?
The pancreas is an important organ of the digestive system, which has a mixed function: external (exocrine) and internal (endocrine). The function of external secretion is to secrete pancreatic juice, which contains digestive enzymes necessary for the complete digestion of food. The endocrine function is to produce the appropriate hormones and regulate metabolic processes: carbohydrate, fat and protein.
What does the pancreas do?
Exocrine function
Every day, the pancreas produces 500-1000 ml of pancreatic juice, consisting of enzymes, salts and water. Enzymes produced by the pancreas are called “proenzymes” and are produced by the pancreas in an inactive form. When a bolus of food enters the duodenum, hormones are released, which trigger a chain of chemical reactions that activate pancreatic juice enzymes. The most powerful stimulator of pancreatic secretion is hydrochloric acid of gastric juice, which, when it enters the small intestine, activates the secretion of secretin and pancreozymin by the intestinal mucosa, which, in turn, affects the production of pancreatic enzymes.
These enzymes include:
- Amylase, which breaks down carbohydrates;
- Trypsin and chymotrypsin, involved in the process of protein digestion, which begins in the stomach;
- Lipase, responsible for the breakdown of fats that have already been exposed to bile coming from the gallbladder.
Additionally, pancreatic juice contains microelements in the form of acidic salts, which ensure its alkaline reaction. This is necessary to neutralize the acidic component of food coming from the stomach and create suitable conditions for the absorption of carbohydrates.
The secretion of pancreatic juice is regulated by nervous mechanisms and is associated with food intake, i.e., food of varying composition stimulates the production of juice of different volumes and enzyme content. It accumulates in the interlobular ducts, which join the main excretory duct, which flows into the duodenum.
Endocrine function
The internal secretory function of the gland is to release the hormones insulin and glucagon into the blood. They are produced by groups of cells interspersed between the lobules and without excretory ducts - the so-called islets of Langerhans, located in significant numbers in the tail of the gland. The islets of Langerhans consist mainly of alpha cells and beta cells. Their number in healthy people reaches 1-2 million.
- Insulin is produced by beta cells and is responsible for the regulation of carbohydrate and lipid (fat) metabolism. Under its influence, glucose moves from the blood into the tissues and cells of the body, thereby lowering the blood sugar level. Beta cells make up 60-80% of the islets of Langerhans.
- Glucagon is produced by alpha cells and is an insulin antagonist, i.e. it increases blood glucose levels. Alpha cells also take part in the production of the substance lipocaine, which prevents fatty degeneration of the liver. Their share in the islets of Langerhans is about 20%.
The islets of Langerhans also contain other cells in small quantities, for example, delta cells (1%), secreting the hormone ghrelin, which is responsible for appetite and stimulates food consumption. PP cells (5%) produce pancreatic polypeptide, formed by 36 amino acids and suppressing pancreatic secretion.
The destruction of beta cells leads to inhibition of insulin production, which can trigger the development of diabetes. Symptoms of this are constant thirst, itchy skin, and increased urine output.
The pancreas is in close relationship with other organs of the digestive tract. Any damage or disruption of its activity negatively affects the entire digestive process.
Diagnosis and treatment of chronic pancreatitis
Abdominal CT scan
- Cost: 6,000 rub.
More details
The diagnosis of pancreatitis should be suspected based on the clinical picture (patient complaints, medical history and examination).
To clarify the diagnosis, laboratory diagnostic methods are used (blood tests - clinical, biochemical, including the study of amylase in the blood and urine, stool tests), ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs, computed tomography and MRI.
A gastroenterologist treats chronic pancreatitis. An important part of therapy is strict adherence to a diet with limited fatty, high-calorie foods, exclusion of alcohol, smoking, and adherence to a diet. Depending on the clinical manifestations, enzyme preparations, antispasmodics, prokinetics, antisecretory agents, multivitamin preparations, pre- and probiotics are prescribed.
The patient needs to be monitored by a gastroenterologist, under whose supervision the therapy is adjusted and the prognosis is assessed.
The multidisciplinary CELT clinic sees highly qualified gastroenterologists who have extensive experience in managing patients suffering from pancreatitis. At the clinic, you can conduct a full examination and, if necessary, obtain a consultation with a surgeon.
Our services
The administration of CELT JSC regularly updates the price list posted on the clinic’s website. However, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we ask you to clarify the cost of services by phone: +7
| Service name | Price in rubles |
| Ultrasound of the abdominal organs (liver, gall bladder, pancreas, spleen) | 3 800 |
| Pancreatocholangiography | 4 500 |
| MSCT of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space of the abdomen | 6 000 |
All services
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
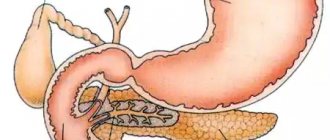
Where is the pancreas located in humans?
The pancreas is located in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach, closely adjacent to it and the duodenum, at the level of the upper (first-second) lumbar vertebrae. In the projection onto the abdominal wall, it is located 5-10 cm above the navel. The pancreas has an alveolar-tubular structure and consists of three sections: head, body and tail.
The head of the pancreas is located in the flexure of the duodenum so that the intestine encloses it in the shape of a horseshoe. It is separated from the body of the gland by a groove through which the portal vein passes. The blood supply to the pancreas is carried out through the pancreatic-duodenal arteries, and the outflow of blood occurs through the portal vein.
The body of the pancreas is divided into anterior, posterior and inferior surfaces. It also has upper, anterior and lower edges. The anterior surface is adjacent to the posterior wall of the stomach, slightly below. The posterior surface is adjacent to the spine and abdominal aorta. The vessels of the spleen pass through it. The lower surface is located below the root of the transverse colon. The tail of the gland is cone-shaped, directed upward and to the left and reaches the gate of the spleen.
The pancreas consists of 2 types of tissue that perform different functions (endocrine and exocrine). Its main tissue consists of small lobules - acini, which are separated from each other by layers of connective tissue. Each lobule has its own excretory duct. Small excretory ducts connect with each other and merge into a common excretory duct, which runs through the thickness of the gland along its entire length, from tail to head. At the right edge of the head, the duct opens into the duodenum, connecting with the common bile duct. Thus, the pancreatic secretion enters the duodenum.
Between the lobules there are groups of cells (islets of Langerhans) that do not have excretory ducts, but are equipped with a network of blood vessels and secrete insulin and glucagon directly into the blood. The diameter of each island is 100-300 µm.