Women experience chest pain quite often, according to experts - an order of magnitude more often than men. Some of them are signs of chronic diseases, others signal the development of acute pathologies. Knowing the causes of pain of this nature is important - this is necessary for finding treatment methods.
What can hurt your chest?
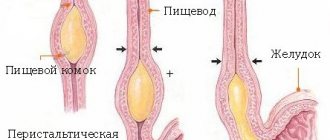
To understand why the chest hurts when you inhale, you will have to remember the anatomical structure and location of the organs in this part of the body. In the thoracic region are located:
- the heart located in the cardiac sac; pericardium;
- thoracic spinal column;
- trachea, branching in the lower part into bronchi;
- aorta; the largest artery of the human body;
- lungs covered with pleura - a protective film that softens their friction against the costal arches.
In the lungs themselves there are bronchi and bronchioles, which are supplied with nerve cells, as well as the pleura and all the organs listed above. Any pathologies in the thoracic organs; pleura, trachea, heart or pericardium, accompanied by inflammation or irritation of pain receptors, can cause chest pain on inspiration. In addition, colic from an inflamed gallbladder or from the stomach or duodenum, covered by an ulcerative process, can radiate (spread) into it.
As you can see, there is a lot of pain in the chest and each case should be dealt with separately.
Finally, for various reasons, the intercostal muscles may hurt from excessive stress (for example, pain during intense training or due to prolonged coughing) or the ribs themselves, if they have been injured.
Why else can you feel chest pain?
Chest pain can be related to the respiratory, digestive and muscle organs.
Respiratory problems
- Pneumonia. Pneumonia is a complication after suffering from influenza or other colds. The patient experiences shortness of breath and severe pain when trying to take a breath.
- Lung collapse. Pneumothorax, or collapsed lung, occurs when air gets trapped between the lungs and the ribs. The patient experiences shortness of breath and severe pain.
- Pleurisy. A disease characterized by inflammation of the pleura. Pain in the chest of a patient with pleurisy occurs during every attempt to take a breath.
- Lungs' cancer. Pain can occur even at rest. This is often accompanied by a wet cough with blood in the sputum.
Digestive problems
Pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract also cause chest pain:
- Heartburn. This condition occurs when gastric juice enters the esophagus. Often with heartburn, a burning sensation appears behind the sternum.
- Diseases of the pancreas and gall bladder. Gallstones or inflammation of the gallbladder can cause pain in the right side of the chest.
- Dysphagia. Pathology characterized by problems with swallowing. In some cases, it can cause severe chest pain.
Muscle and bone problems
Muscle and bone problems causing chest pain:
- Rib injuries. Pain occurs with fractures or bruises of the ribs and soft tissues.
- Fibromyalgia. The disease is characterized by dull pain in the muscles, the nature of which is still unknown. The pain caused by fibromyalgia can last for several months.
- Costochondritis. A disease in which the cartilage connecting the chest and ribs becomes inflamed. Signs of costochondritis resemble a heart attack.
Heart pathologies are a dangerous cause of chest pain
In women after menopause, heart and vascular diseases
occur with the same frequency as in the stronger sex. Before menopause, the female body is protected from them by the hormones estrogen. Heart disease usually causes pain on the left side of the body, but it is also very common in the mid-chest area.
Pain due to angina pectoris is the most common. They appear during movement, after walking, or physical activity: the more the coronary vessels are affected, the less stress can provoke discomfort. If pain occurs at rest, this reflects an advanced stage of the disease. During an attack of angina, pain can radiate to the back and shoulder blades, arm, shoulder, neck and even jaw. Symptoms of angina pectoris include:
- feeling of squeezing, pressure on the chest;
- feeling that it is difficult to breathe, shortness of breath on exertion;
- weakness, dizziness.
A much more dangerous condition is myocardial infarction.
. Pain during a heart attack is very pronounced and cannot be relieved by taking pills. The pain can spread to any area of the chest, stomach and back, accompanied by a burning sensation, pressure on the chest, fear of death, and fainting. During such an attack, the important task is to call an ambulance in time and begin treatment. Also in women, chest pain occurs due to heart defects, thrombosis, pericarditis, but such causes are less common.
When pain is deadly
The most dangerous pain sensations are those associated with heart and lung diseases. This condition can be recognized by the following signs:
- The painful sensation lasts more than 5 minutes.
- A sharp burning pain behind the sternum, which gradually spreads to the neck, shoulders and back.
- There is a feeling of pressure and tightness in the chest.
- The heart rate increases greatly, the patient finds it difficult to breathe, and shortness of breath appears.
- The person breaks into a cold sweat, dizziness begins, weakness and nausea with vomiting appear.
If any of the listed symptoms occur, you should immediately call an ambulance.
Gastrointestinal diseases and chest pain
If the chest hurts in the middle, the causes in women may also relate to pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract. Most often, pain in the center of the chest is caused by chronic gastritis and reflux esophagitis in the acute stage. The causes are inflammation of the stomach walls and reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus. Such conditions can be triggered by stress, alcohol consumption, smoking, consumption of spicy and hot foods, and treatment with certain medications. The symptoms are as follows:
- aching chest pain in the middle and left;
- pain below the chest - in the upper abdomen;
- heartburn, fever in the throat;
- lump in the throat, painful sensations from swallowing;
- nausea, less often vomiting.
Acute chest pain is often perceived as cardiac pain, but in fact it is a sign of a gastric ulcer or duodenal ulcer. But it appears against the background of gastrointestinal pathologies in direct connection with food intake - on an empty stomach for an ulcer, immediately after a meal - for gastritis, an hour after a meal - for duodenal problems.
During pregnancy, pain from gastrointestinal problems is accompanied by heaviness in the stomach and is almost always combined with severe heartburn.
Causes of chest pain
Angina pectoris
A painful attack of angina pectoris begins suddenly during fast walking, climbing stairs or other physical activity.
Severe pressing pain in the middle of the sternum makes a person stop and clutch his heart. Often, unpleasant symptoms radiate to the left arm or the collarbone area. Painful sensations compress the chest and prevent you from taking a deep breath. The skin turns pale and severe weakness appears. The pain disappears 5-20 minutes after resting or taking nitroglycerin tablets. The frequency of paroxysms ranges from a couple of times a month to several times a day, all of them are similar in duration and nature of the pain syndrome. Acute piercing pain behind the sternum, which is accompanied by cold sweat and lightheadedness, are more typical of myocardial infarction. In such a situation, it is necessary to call an ambulance.
Inflammatory heart diseases
Damage to the heart muscle is manifested by moderate pain, which is localized behind the sternum in the middle. The sensations are stabbing or squeezing in nature and occur at any time of the day, regardless of the level of physical activity. With endocarditis, the sternum hurts quite often. Soreness is combined with shortness of breath and palpitations. Increased pain occurs with exacerbation of the inflammatory process, as evidenced by fever and chills.
Dull pain in the center of the sternum and along the left surface of the chest is typical for myocarditis. Patients also complain of increased fatigue, a feeling of lack of air, and dizziness. Pericarditis causes severe pain and a feeling of fullness in the chest, leading to difficulty breathing. Due to ineffective heart function, symptoms worsen with minimal physical activity.
Respiratory diseases
When the sternum hurts in the center, this may indicate damage to the airways from the trachea to the middle bronchi. Viral and bacterial causes cause inflammation of the epithelial membranes, which is combined with irritation of nerve endings and a feeling of discomfort. With tracheitis and laryngotracheitis, chest pain is mild or moderate, scratching and sore throat are more disturbing.
Bronchitis is characterized by pain in the middle of the chest, which occurs at the height of the disease. There is a dull pressing pain, which intensifies during coughing attacks and significantly weakens at rest. The onset of unpleasant sensations is provoked by inhalation of cold air and dust entering the respiratory tract. The pain persists throughout the entire period of bronchitis - for 1-2 weeks.
There are also allergic causes of chest pain. Most often, the pain is caused by an attack of bronchial asthma, when, against the background of bronchospasm and suffocation, discomfort and a feeling of compression are felt in the middle of the chest. Pain of moderate intensity in the chest persists for several hours after the paroxysm. Similar clinical manifestations also occur in chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases.
Gastroesophageal reflux
With GERD, the sternum begins to hurt 15-20 minutes after finishing a meal, which is caused by the reflux of hydrochloric acid into the esophagus. The pain intensifies when bending the body forward, wearing tight belts, which contribute to compression of the stomach and reflex opening of the lower esophageal sphincter. The discomfort is localized exactly in the center of the chest; in addition to the pain syndrome, there is an intense retrosternal burning sensation and heartburn in the throat.
Painful sensations are provoked by errors in the diet - abuse of carbonated drinks, fried foods, strong meat broths. For GERD, morning pain in the chest immediately after waking up is typical, since in a horizontal position the acid passively flows into the esophagus. If symptoms are accompanied by repeated vomiting of bile or blood, emergency medical attention is needed.
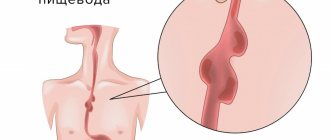
Pathology of the esophagus
Constant intense pain in the center of the sternum is usually associated with esophageal causes. In acute and chronic esophagitis, moderate cutting or burning pain is observed in the middle part of the chest, which intensifies after eating. For esophageal dyskinesia and esophagospasm, paroxysmal unbearable pain in the sternum exactly in the middle is typical, which usually lasts from 10 to 20 minutes.
A sharp, dagger-like pain at one point occurs in the event of a serious disease - rupture of the esophagus. Against the background of an excruciating painful attack, vomiting of stomach contents and blood occurs, which does not bring relief. Subsequently, the pain is localized not only behind the sternum, but throughout the chest, in the epigastrium. The patient is in a state of shock, cold sweat appears on the forehead, and blood pressure drops sharply.
Neoplasms of the mediastinum
The mediastinum contains several organs: lymph nodes, thymus, thoracic duct, venous and arterial vessels. Most often, the sternum hurts when the lymph nodes are enlarged, which is caused by tumor causes - lymphogranulomatosis and non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. Moderate dull pain and a feeling of tightness in the chest are of concern; in the future, the symptoms intensify due to compression of the respiratory organs.
Thymoma initially manifests itself as discomfort in the chest area and periodic reflex cough. As the mass increases, the pain becomes stronger and radiates to the neck and shoulder blades. Patients also complain of sore throat and hoarseness caused by compression of the recurrent nerve. Similar symptoms occur with tuberculosis of the intrathoracic lymph nodes.
Complications of pharmacotherapy
Chest pain is a common side effect of taking sodium bicarbonate and other absorbable antacids. Although these drugs are used to reduce acidity, after 10-20 minutes of using them, the stomach expands and a new portion of acid is thrown into the esophagus (“rebound effect”). Other causes also lead to chest pain: long-term use of NSAIDs and corticosteroids.
Rare causes
- Granulomatous diseases
: sarcoidosis, silicosis. - Osteogenic processes
: costochondritis, osteosarcoma of the sternum, age-related changes in bone tissue. - Heart defects
: mitral disease, stenosis or insufficiency of the aortic valve. - Hiatal hernia
. - Gastrointestinal pathology
: hyperacid gastritis, peptic ulcer, Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. - Intercostal neuralgia
.
Chest pain - pulmonary pathologies are to blame
Since most of the chest is occupied by the lungs, their diseases may well cause discomfort. In women, chronic lung pathologies are more common with a long history of smoking, with autoimmune and allergic diseases, as well as with untreated inflammatory processes. Lung pathologies, each of which can cause pain in the middle of the chest, are as follows:
- pleurisy;
- pneumonia;
- whooping cough;
- tuberculosis;
- tracheitis;
- bronchitis.
Almost any pulmonary disease has a lot of other, more characteristic signs, and pain syndrome only accompanies them. The main component of the clinical picture is a cough - dry, wet, with or without sputum production
. Often there is an increase in body temperature, shortness of breath, wheezing in the lungs, and symptoms of general intoxication - if we are talking about an acute infectious disease. The pain in this case is associated with spasms that strain the intercostal muscles and the diaphragm.
Lung tumors cause pain inside the chest only in the later stages and are often accompanied by hemoptysis.
Acute heart-type pain can be characteristic of pleurisy, aching - for pneumonia, pain during exercise and on inspiration - for tracheitis.
Diseases of the spine and nervous system as a cause of pain
Cervical and thoracic osteochondrosis is a very “popular” cause of pain in women, which is localized in the chest. Why does discomfort appear in the chest area when the spine is damaged?
The fact is that pinched nerves lead to the development of intercostal neuralgia, which can cause pain in any part of the chest. Often such sensations even resemble a heart attack, or pain due to inflammation of the stomach.
Unpleasant signs may appear after sleep if a person with osteochondrosis sleeps in the wrong position and does not use orthopedic products. The pain may intensify when bending forward while inhaling. Osteochondrosis is accompanied by other symptoms:
- pain when pressing on the shoulder muscles;
- burning in the back;
- shootings under the shoulder blade.
Often, intercostal neuralgia is caused by scoliosis of the spine - its curvature in the thoracic region.
For women, such pathologies as cardiac neurosis and vegetative-vascular dystonia are very common, and they also cause pain in the chest in the middle.
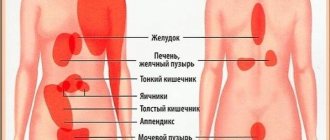
Causes of pain in the epigastric region
10.12.2021
Pain in the pit of the stomach is the popular name for epigastric pain or epigastralgia, which is a painful sensation that occurs in the upper abdomen just below the ribcage, in the area corresponding to where the stomach . In most cases, this pain is not cause for concern and may indicate a problem in the stomach , esophagus , or early intestines , such as reflux , gastritis , or indigestion , occurring in combination with other symptoms such as heartburn , dizziness , vomiting, gas , bloating or diarrhea .
It is important to remember that in some rare cases, pain in the stomach can indicate other more serious diseases, such as inflammation of the gallbladder , pancreatitis or even infarction , so if you experience severe pain that does not go away within a few hours or is accompanied by other symptoms symptoms such as shortness of breath, dizziness chest tightness , or fainting, seek emergency medical attention.
The main causes of pain in the stomach are:
Gastritis
Gastritis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane lining the inside of the stomach , which usually causes pain in the stomach , ranging in intensity from mild to moderate or even severe, causing a burning or squeezing sensation, especially after eating.
In addition to pain, gastritis causes other symptoms such as nausea , belching and increased gas production. This disease can be triggered by an unbalanced diet, excessive consumption of fried foods, caffeine or alcohol; stress; gastric mucosa , for example, anti-inflammatory drugs; infection with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, viral or bacterial gastroenteritis.
In some cases, gastritis can reach deeper layers of tissue, causing peptic ulcers . In these cases, the pain is usually intense and occurs on an empty stomach or after eating, and there is a risk of bleeding or perforation, which can cause severe inflammation of the abdominal cavity. A gastroenterologist is the most appropriate physician to make a diagnosis and recommend treatment, which may vary depending on the symptoms presented. In milder cases, for example, you can change your diet, and in more severe episodes, your doctor may prescribe medications that reduce stomach , and even the use of antibiotics.
Esophagitis
Esophagitis is an inflammation of the tissues of the esophagus , usually caused by gastroesophageal reflux or hiatal hernia . This disease causes pain in the stomach and burning in the chest , which is worse after eating and with certain foods, such as caffeine, alcohol and fried foods. In addition, the pain often occurs at night and does not improve with rest. Treatment is recommended by a gastroenterologist and includes the use of drugs to reduce stomach , drugs to improve gastrointestinal motility
Poor digestion
gastric mucosa , excessive gas formation, reflux and increased intestinal motility . The result is pain that may occur in the stomach or elsewhere in the abdomen and is accompanied by gas, diarrhea, or constipation .
In such cases, the pain goes away after a few hours, so it is recommended to take medications to relieve discomfort, such as antacids and painkillers, drink plenty of fluids and eat light foods. It is necessary to consult a doctor so that he can determine the causes and indicate the most appropriate treatment.
Gallstones
The presence of gallstones can cause colicky pain, which most often occurs in the right upper abdomen , but can also radiate to the stomach pit and back , and is accompanied by symptoms such as dizziness and vomiting. A gastroenterologist may prescribe medications to relieve symptoms, such as pain relievers and antiemetics, and consider the need for surgery to remove the gallbladder .
Acute pancreatitis
Pancreatitis is an inflammation of the pancreas , an organ located in the center of the abdominal cavity whose main function is to digest food and produce hormones . In this case, the pain almost always occurs suddenly and intensely and can radiate to the upper abdomen . The pain may be associated with vomiting, bloating , and constipation . Acute pancreatitis is a medical emergency, and treatment must be started quickly to prevent the disease from worsening and causing widespread inflammation in the body. Initial steps include fasting, intravenous hydration, and pain medications.
Published in Gastroentorology Premium Clinic
Other causes of chest pain in women
Having discovered pain in the chest, many women suspect problems with the mammary glands, in particular breast cancer. This disease, indeed, occurs frequently, but it causes pain only in the later stages, when there are a number of other signs (a formation noticeable when pressed and palpated, discharge from the nipples, etc.). Pain is more typical for mastopathy, although it is localized not in the center of the chest, but directly in the mammary gland.
Thyroid diseases are much more common in women. Hyperthyroidism, nodular goiter, diffuse goiter - all these diseases can cause pain radiating to the chest, as well as the following symptoms:
- heat in the throat;
- lump in the throat;
- pressure surges;
- weight changes;
- prolonged low-grade fever;
- weakness.
If you overuse training or undergo physical overexertion, pain in the chest muscles is also possible. This symptom is typical in women under stress, depression, nervous exhaustion, as well as bruise, blow, or any injury to this area.
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
In the event of an angina attack, the person must be seated, his collar unfastened and freed from clothing that is compressing the chest. It is important to provide a flow of fresh air. The sternum with ischemic heart disease stops hurting after taking nitroglycerin, which patients should always carry with them. If the pain does not subside within half an hour, emergency help should be called.
To reduce the pain of GERD, it is recommended to eat small, frequent meals, and avoid physical activity and bending immediately after eating. It is recommended to sleep on a high pillow. If you have respiratory diseases, it is undesirable to stay in dusty rooms or rooms with low air humidity, so as not to provoke coughing and chest pain. If you experience severe pain in the center of your chest, you should consult a specialist to find out and eliminate the cause.
Conservative therapy
Medical tactics depend on the pathology against which the pain syndrome arose. For chest pain, etiotropic drugs are predominantly prescribed; specific analgesics are indicated for unbearable sensations with the threat of developing painful shock. To eliminate the etiological factor of unpleasant symptoms, the following medications are used:
- Antianginal drugs
. In complex therapy of angina, calcium channel antagonists, beta blockers, and vasodilators are used. Medicines dilate coronary vessels and reduce myocardial oxygen demand. They are combined with lipid-lowering drugs. - Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
. Sharp pain in the chest caused by neuralgia or inflammation of the cartilage can be easily relieved with the help of selective COX-2 inhibitors. The drugs are taken in short courses during the acute period of inflammation to avoid side effects. - Antacids
. The drugs reduce the acidity of gastric juice and reduce its aggressive effect on the mucous membrane of the esophagus. If the sternum is very painful, antisecretory medications are additionally recommended, which provide a long-lasting effect. - Expectorants
. Effective in the treatment of bronchitis and tracheitis. They liquefy sputum and remove it along with pathogenic microorganisms, which reduces cough and chest pain and speeds up recovery.
Diagnosis and treatment of chest pain
The diagnostic algorithm will depend on the nature of the discomfort, its severity and other symptoms. Thus, in case of acute heart pain or serious injuries, diagnosis and treatment are carried out after hospitalization. For chronic pathologies with subacute symptoms, diagnostic methods may be as follows:
- X-ray of the lungs;
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy;
- general blood analysis;
- blood biochemistry;
- Ultrasound of the mammary glands, thyroid gland;
- radiography (CT) of the spine, etc.
Treatment will depend on the problem found. So, for neuralgia, you need to do massage, physiotherapy, and take painkillers. For angina pectoris, take a number of heart medications and follow a diet. Antibiotics and cough suppressants help treat lung diseases. For gastrointestinal pathologies, special medications and special nutrition are prescribed. It is not recommended to delay treatment - this is the only way to avoid complications.
First aid
Sharp pain in the middle of the chest can lead to painful shock and loss of consciousness. The patient's pulse quickens, the skin of the face and lips turns pale, and confusion or fear appears in the eyes. What to do if there is pain between the chest and spine:
- Urgently call an ambulance
- Place the patient in bed and raise his legs a little.
- Remove clothing that is constricting the neck and give a Nitroglycerin tablet. This drug has a vasodilating effect and normalizes the patient's condition.
- All unnecessary people should be removed from the room, since their presence will only irritate the patient.
- If the patient loses consciousness, it is necessary to give him a sniff of ammonia.
- You can use a reflexive technique: squeeze the little finger on your left hand in the nail area until painful sensations appear, then release. Repeat this 5-6 times.
What you should never do if your chest hurts when pressed:
- leave the patient alone;
- postpone calling an ambulance if the pain does not go away after taking appropriate medications;
- reduce bone fragments in case of injury;
- do warming compresses until the cause of the pain is determined.
For neuralgia, the compress helps, but for stomach ulcers it can cause harm.
Pain during pregnancy
Pain in the middle of the chest in women during pregnancy - what could be the reasons? During this period, a complete restructuring of the body occurs, which is associated with its preparation for the birth of a child. A woman’s hormonal levels change, internal organs shift, ligaments stretch and joints soften. This is why many expectant mothers experience discomfort and pain. The main factors of their occurrence are:
- Diseases of the heart and blood vessels - they can develop as a result of pregnancy and contribute to the appearance of pain in the sternum, even in those women who have not previously suffered from such diseases.
- Pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract - mainly heartburn, gastric ulcers.
- Neuralgia - appears due to compression of nerve endings and is associated with the growth of the uterus and abdomen.
- A sprain is caused by a natural process that causes the hips to widen and all joints to soften. It is because of this that some women may complain of discomfort in the chest.
Depending on the nature and type of pain, the expectant mother is recommended to visit a cardiologist, neurologist, therapist or other doctor. You should not resort to self-medication, as you can harm yourself and the child.
Necessary examinations
If there is pain in the middle of the sternum, the patient’s condition is assessed on an outpatient or inpatient basis. Depending on the expected phenomenon. A minimum program is required against the background of a likely urgent process. It includes:
- Blood pressure measurement
. Heart rates. - Electrocardiography
. Used to assess the functional position of cardiac structures. Shows arrhythmias and typical features of a heart attack. - Echocardiography
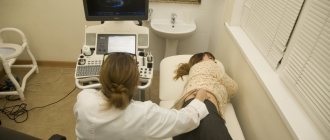
. Study of the anatomical state of the heart and surrounding tissues. The method involves visualization of areas. It is possible to identify the extent of the violation.
In particularly difficult situations, they do not wait for results; they stabilize the condition, and only then think about long-term therapy. In other cases, there is time for a thorough examination. Additional measures: 24-hour monitoring, cardiac MRI, stress tests (with caution), coronography and blood tests.
Also, chest X-ray, FGDS (endoscopic technique for assessing the condition of the mucous membrane of the stomach and esophagus), visualization of vertebral structures. As necessary, third-party specialists are involved, most often a neurologist. In the absence of evidence for organic defects, they speak of idiopathic cardialgia.
Diagnostics
Complaints of pain in the sternum are grounds for visiting a general practitioner. The specialist carries out a primary examination to determine the cause of chest pain: collecting data on the time of onset and dynamics of development of the disorder, conducting standard laboratory and clarifying instrumental methods. The greatest diagnostic value is:
- Electrocardiography
. An ECG is necessary to confirm or exclude an ischemic cause of chest pain. Disturbances in the functioning of the heart are indicated by expansion and deformation of the ventricular complexes, changes in the length of intervals, and their shift relative to the isoelectric axis. To exclude pathology of the heart valve apparatus, echocardiography is prescribed. - Radiography
. On a standard x-ray, the OGK looks for signs of widening of the mediastinum and displacement of organs from the center of the sternum. An indirect sign of bronchitis is increased bronchial pattern and deformation of the roots of the lungs. For a detailed study of the identified tumor or granulomatous neoplasm, spiral CT of the chest cavity is used. - Gastroscopy
. Pain that is felt in the middle of the sternum after eating is an indication for endoscopic examination of the esophagus and stomach. In the case of GERD, upon examination, a specialist notices hyperemia and swelling of the esophageal mucosa, erosion or ulcer of the esophagus. The EGDS method is informative for diagnosing destructive processes and ruptures of the esophagus. - Lab tests
. To exclude myocardial infarction, a troponin test is recommended to determine the level of creatine phosphokinase. Multiple bacteriological culture of sputum is necessary if tuberculous lesions of the mediastinal organs are suspected. A standard clinical blood test can detect leukocytosis and the presence of immature cells.
Electrocardiography is a method of differential diagnosis of chest pain
Preventing chest pain
In order to prevent heart disease as the most serious and common cause of chest pain, it is necessary:
- stop smoking;
- control blood pressure, cholesterol and blood glucose levels;
- reduce the risks of stressful situations, learn to relax (breathing exercises, meditation, yoga), take natural-based sedatives (Novo-Passit, Persen, Sedafiton);
- reduce body weight in case of obesity; set aside time every day for physical exercise and walks in the fresh air;
- change your diet - give up fatty and fried foods, limit meat, replacing it with fish, legumes, reduce the proportion of sweets, flour, eat more fresh and boiled vegetables, whole grain cereals, berries, fruits, herbs, nuts, fermented milk drinks.
Pain in the middle of the sternum is most often associated with heart disease - angina pectoris, myocardial infarction. The attack causes inflammation (myocarditis, pericarditis), aortic dissection, pulmonary embolism.
All of these conditions are extremely dangerous. Diseases of the digestive and respiratory system, osteochondrosis, and vegetative-vascular dystonia are similar in their manifestations. With injuries and physical strain, there is also pain in the chest. When an attack occurs for the first time, sedatives, Aspirin, Nitroglycerin are used, if they do not produce an effect, an ambulance must be called.