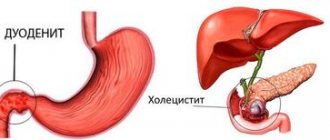
Biliary dyskinesia is a disease as a result of which the flow of bile into the duodenum is stopped or significantly reduced due to uncoordinated work (contractions) of the ducts, gallbladder and sphincter of Oddi. Bile is a special liquid that is produced by the liver and promotes the breakdown of fats and the movement of food through the intestines. Before bile enters the intestines, it passes through the bile ducts - the hepatic and bile ducts, the gallbladder, and the sphincter of Oddi. The latter, due to its contractions, ensures its entry into the duodenum.
Dyskinesia is often observed in children, which is expressed by pain in the right hypochondrium and disturbances in the functioning of the digestive tract. As a result of the disorder, the child experiences a deficiency of bile in the intestines, which entails disruptions in the digestive tract and a deterioration in the general condition of the body. The latter is caused by insufficient absorption of many nutrients and vitamins K, E, A and D, which significantly worsens if bile does not participate in the process.
Symptoms
The symptoms of the disease depend on its type. However, it is possible to identify common features that are characteristic of all types of ADHD:
- dull or sharp pain in the right hypochondrium, radiating to the scapular region and shoulder (occurs mainly after meals and physical activity);
- feeling of abdominal distension, heaviness;
- bitterness in the mouth;
- flatulence;
- nausea or vomiting;
- constipation, loose stools;
- heart rhythm disturbances, changes in the tone of blood vessels and other vasomotor pathologies;
- headache (migraine), insomnia;
- increased sweating;
- general weakness, mood swings, irritability.
The disease is accompanied by a deterioration in the process of bile outflow into the duodenum with subsequent disturbances in digestive function. If you do not consult a doctor in a timely manner and do not begin quality treatment for dyskinesia, the risk of developing serious complications increases significantly.
Types of dyskinesia
According to the nature of the motor dysfunction, the gallbladder is divided into hyperkinetic (contractions of the gallbladder are increased) and hypokinetic (the walls relax, the outflow of bile is slowed). In the first case, symptoms of dyskinesia are observed, such as intense pain radiating to the scapula and manifesting itself in paroxysms, as well as nausea (in rare cases, vomiting).
Characteristic signs of hypokinetic disease:
- feeling of fullness, heaviness in the stomach;
- mild pain in the right hypochondrium;
- problems with stool (diarrhea, constipation);
- change in color of stool;
- an increase in bilirubin, cholesterol in the blood, the formation of clots, gallstones.
Dyskinesia can also be classified according to the mechanism of etiology into primary and secondary. For example, in the first case we are talking about an incorrect lifestyle, in the second the disease is provoked by concomitant pathological processes.
Surgery
In the absence of long-awaited relief after adequate and comprehensive conservative therapy, doctors use surgical techniques. They can be:
- minimally invasive (usually using endoscopic equipment);
- radical.
In case of identified dysfunction of the sphincter of Oddi, the following is carried out:
- injections directly into this sphincter of botulinum toxin (it significantly reduces spasm and pressure, but the effect is temporary);
- balloon dilatation of this sphincter;
- placement of a special catheter-stent in the bile duct;
- endoscopic sphincterotomy (its excision together with the duodenal nipple) followed (if necessary) by surgical sphincteroplasty.
An extreme measure to combat severe hypotonic-hypokinetic variant of biliary dysfunction is cholecystectomy (complete removal of the atonic gallbladder). It is carried out laparoscopically (instead of an incision on the abdominal wall, several punctures are made for equipment and instruments) or laparotomy (with a traditional incision) by way. But the effectiveness of this serious surgical intervention is not always felt by patients. Often after this, the resumption of complaints is associated with the developed postcholecystectomy syndrome. Rarely done.
Diagnostics
If suspicious symptoms occur, it is recommended to consult a gastroenterologist. The specialist interviews patients to establish the clinical picture, studies the anamnesis and conducts an initial examination with palpation of the abdominal area to identify foci of pathology. Then the doctor must prescribe a list of necessary studies that are carried out to further make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe effective therapy.
Standard list of laboratory tests for diagnosing dyskinesia in children and adults:
- general, biochemical blood test;
- general urine analysis;
- stool analysis for Giardia, coprogram;
- liver tests, etc.
Instrumental diagnostic techniques:
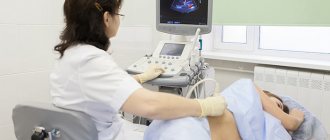
- Ultrasound of the biliary system;
- duodenal intubation;
- radiography (including cholangiography and cholecystography);
- MRI of the liver (if necessary);
- gastric, intestinal intubation with bile sampling.
All of the above studies make it possible to determine the structure and assess the functional state of internal organs and identify possible disorders.
The main task that doctors set for themselves when treating dyskinesia is to normalize the outflow of bile and prevent its stagnation in the gallbladder. General recommendations for patients regarding lifestyle during an exacerbation of the disease:
- a full night's sleep of at least 8 hours a day;
- alternating physical exercise and intellectual activities;
- going to bed no later than 23:00;
- regular walks in the fresh air.
During the treatment of biliary dyskinesia in adults and children, special attention is paid to nutrition. A few important rules:
- eat at least 5-6 times a day in small portions to stimulate the excretion of bile;
- exclusion from the diet of smoked meats, fatty, fried foods, spicy, canned products;
- drinking mineral water;
- minimizing the amount of salt in prepared dishes to prevent the accumulation of fluid in the body.
Treatment in adults
Drugs that are prescribed to adults as part of the conservative treatment of the disease, depending on the type of disease:
- Cholespasmolytics;
- choleretics;
- enzymes;
- neurotropic medications (as prescribed by a psychotherapist, if indicated).
To remove the contents of the duodenum after using drugs that stimulate the release of bile, duodenal intubation is used.
Closed gallbladder tubes are also shown. Physiotherapeutic techniques (electrophoresis, diadynamic therapy) show good results. Some experts advise taking a course of massage with influence on certain points of the body responsible for the functioning of the biliary system. Non-traditional methods are also used, for example, acupuncture (acupuncture).
Folk remedies will not help get rid of dyskinesia, but they can be used as part of complex therapy in addition to medications. Medicinal herbal infusions are prescribed in courses every six months. Which plants should be used depends on the type of pathology.
Radiation in children
When an inflammatory process is detected, small patients diagnosed with VSD are prescribed antibacterial drugs. If the provoking factor is parasites, anthelmintics are indicated. Treatment tactics directly depend on the type of disease and its causes. If hypokinetic dyskinesia is diagnosed, a complex of drugs from various groups is selected (for example, prokinetics, choleretics, medications to support liver function, etc.).
Well-known pediatrician Evgeny Komarovsky recommends physiotherapeutic methods such as electrophoresis and galvanization. Also, sinusoidal modulated currents and diadynamic Bernard currents will help in positive dynamics.
Hyperkinetic dyskinesia in children is treated with the following drugs:
- sedatives;
- hepatoprotectors;
- enzymes;
- Cholespasmolytics.
In this case, it is also worth resorting to physiotherapy. Effective methods:
- Microwave;
- paraffin applications;
- electrophoresis;
- radon, pine baths.
The child must adhere to a healthy diet. The patient is fed according to the principle of table No. 5, and sometimes fasting days with kefir and cottage cheese or fruit should be arranged. Meals should be frequent and portioned.
Why does JVP occur?
Possible causes of biliary dyskinesia include the following factors:
- irregular nutrition, predominance of fatty, salty, spicy foods, foods with flavor enhancers;
- cardiopsychoneurosis;
- food allergies;
- chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- parasitosis;
- stress, increased neuro-emotional excitability;
- increased physical and intellectual stress.
Exacerbating factors may be excess weight in the child, a sedentary lifestyle, and functional intestinal disorders.
Prevention
Preventive measures that help prevent the occurrence of the disease:
- compliance with the work and rest regime;
- a complete balanced diet with a limit on fried, fatty foods, smoked foods, salty foods and the inclusion of fresh vegetables and fruits;
- quitting smoking and other bad habits;
- dosing of physical activity;
- good sleep, regular walks in the fresh air;
- timely treatment of pathologies (both acute and chronic);
- exclusion of stressful, traumatic situations.
It is worth highlighting separately secondary prevention, which is indicated after diagnosing the pathological process in the patient. It consists of conducting regular preventive examinations to identify characteristic signs of the disease at the earliest stages.
Despite the fact that the pathology is chronic, if the measures listed above are observed, the disease will proceed without exacerbations. If you refuse to take preventive measures, serious complications from the liver, gallbladder, and bile ducts are possible.
Mineral water
Mineral waters should be drunk regularly, 1/2 - 1 glass 20 - 30 minutes before meals, warm, choosing the required variety depending on the form of dyskinesia. Thus, for hypomotor dyskinesia, it is recommended to drink water of high mineralization (for example, Essentuki 17, Batalinskaya, Borjomi, Mashuk, etc.), and for hypermotor dyskinesia, it is recommended to drink water of low mineralization (for example, Darasun, Karachinskaya, Lipetskaya, Narzan, Smirnovskaya, etc.) .
You can and should drink mineral waters, as well as follow a diet, for a long period of time, that is, at least 3–4 months. However, if mineral waters cannot be included in complex therapy of the disease, then it is quite possible to refuse their use.
Question answer
Women get sick 10 times more often than men.
The primary type most often occurs in individuals with autonomic dysfunctions, nervous disorders, poor diet and sleep disorders. Secondary pathology develops against the background of diseases of the digestive system, hepatitis, after removal of the gallbladder. The likelihood of getting sick is influenced by hormonal levels and the presence of certain chronic diseases in the anamnesis.
If treated incorrectly, the risk of gallstones formation, acute or chronic pancreatitis, cholecystitis, and reflux gastritis increases. All this is difficult to treat and seriously affects the patient’s health.
Causes of biliary tract diseases in children
Biliary dyskinesia does not manifest itself in structural changes in internal organs - liver, gall bladder, ducts. Its cause is a violation of their function, which is caused by malfunctions in the central nervous system and the autonomic system of the body. The causes of the disease should be sought much deeper than it might seem at first glance - in the vast majority of cases, in the emotional state of the child.
Stressful situations, increased emotionality, nervous breakdowns - all this affects the state of the child’s body and leads to excessive involuntary contractions of the gallbladder. Because of this, excess bile accumulates in the area of the bile ducts, which begins to thicken, losing its antibacterial properties and functionality. At the same time, the formation of stones and blood clots begins inside the biliary tract, which interferes with the natural movement of bile to the duodenum. As a result, the disease itself develops and its complications become probable.
Additional factors of psychosomatic causes of the development of the disease may be:
- irregular meals;
- excess fat in food;
- a large amount of spicy, salty, smoked foods in the diet;
- consumption of junk food - nuts, crackers, soda;
- food allergies;
- intestinal parasites. Giardia is especially dangerous;
- side effects of certain pharmacological drugs;
- intestinal diseases and poisoning.
Frequency of meals and healthy foods are very important for children. This should be given the closest attention to anti-parasitic prevention. A specialist will help you adjust your child’s diet.