Pain in the right hypochondrium, causes and possible diseases
Pain in the right hypochondrium is a sign of many diseases, so even an experienced and qualified specialist cannot make an accurate diagnosis based only on this symptom.
Pain syndrome can be caused by completely harmless reasons, such as overeating or excessive physical activity. But more often, discomfort in the area of the right hypochondrium provokes an inflammatory process, acute and chronic diseases of the digestive, genitourinary system, internal organs (liver, kidneys), and biliary tract.
Why does the right hypochondrium hurt, in which cases is this symptom not dangerous, and in which cases does it require immediate medical attention? You will find answers to all questions in our material.
Pain under the right hypochondrium in healthy people
Pain in the right hypochondrium can be caused by a variety of reasons. In some situations, discomfort also appears in completely healthy people: in this case, we are talking about a variant of the physiological norm. However, often the problem lies in the development of pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract and other organs.
Physiological reasons why it hurts in the right hypochondrium:
- Pregnancy. In pregnant women in the third trimester, the uterus is enormously stretched and puts pressure on all the organs it comes into contact with, displacing the intestines, pressing on the stump and gall bladder. Therefore, for healthy pregnant women, stabbing or pressing pain in the right hypochondrium is not uncommon. In addition, progesterone, which maintains pregnancy in the later stages, expands the bile ducts and stimulates bile stagnation. And if you give physical activity to such a belly, then some discomfort can be felt with a high probability.
- Pain on exercise. Surely many have noticed how after intense physical activity there is pain in the right side. This occurs due to excessive stretching of the liver tissue, which, in turn, is caused by a sharp flow of blood to the organ. This happens especially often after a heavy meal. This condition does not pose any danger.
- Pain in women. At the end of the menstrual cycle, some women experience a sharp imbalance between low progesterone and high estrogens, which leads to spasm of the biliary tract and can also cause colic in the right hypochondrium. Taking hormonal contraceptives can worsen the course of premenstrual syndrome and increase the frequency of stabbing pain due to disruption of the passage of bile.
In pregnant women
In a pregnant woman, pain on the right under the costal area is associated with pathologies in the internal organs, and the cause may also be of a different nature. The expectant mother will experience pain due to the increased size of the organs, and they are displaced. In addition, pain may appear in the left hypochondrium from the back.
Pain in the back from the right hypochondrium may be dull
To exclude pathological processes, with frequent and long-lasting pain in the subcostal area of a pregnant woman, it is recommended:
- They undergo a medical examination.
- They donate urine and blood for laboratory analysis.
- They do an ultrasound.
Pathological causes of pain under the right rib
Anatomically, the upper right quadrant of the abdomen includes: liver, gall bladder, part of the diaphragm and small intestine, duodenum, right kidney, pancreas.
Diseases and injuries of these organs can intensify the occurrence of pain in the right side under the ribs:
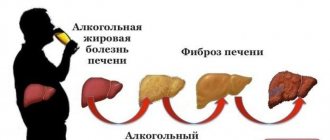
- The most obvious cause of pain is liver disease. This includes hepatitis, hepatosis and cirrhosis of the liver, parasitic lesions.
- Impaired patency of the biliary tract (cholecystitis). A sharp, acute pain that suddenly began, especially at night, is formed when the patency of the biliary tract is impaired and in acute cholecystitis. If the tone of the gallbladder increases, its tendency to contract increases, and the frequency and strength of its contractions also increases. Such processes are accompanied by sharp and short-term pain and are often provoked by nervous tension and stress.
- Urolithiasis disease. The cause of pain in the right hypochondrium may be urolithiasis, in which pain from the right kidney is felt acutely, but not clearly and can be felt in the back of the lower back, lower abdomen, as well as under the left or right side of the lower ribs. Urolithiasis is manifested by the detection of stones in the kidneys, bladder and urinary tract. There is a sharp pain that intensifies with every movement.
- Renal colic. It occurs when kidney stones begin to move and their sharp edges touch internal organs. The pain becomes very severe when the person moves. The stones block the urinary tract, causing the pain to shift to the groin.
- Peptic ulcer disease. Characteristic pain in the right hypochondrium anteriorly accompanies gastric and duodenal ulcers. The nature of the pain and its intensity depends on many factors. Discomfort occurs after eating, on an empty stomach or after exercise. The pain syndrome is accompanied by heartburn, sour belching, vomiting, loss of strength, alternating diarrhea and constipation, and rapid heartbeat. Often, peptic ulcer disease occurs in a latent form; in advanced cases, there is a threat of internal bleeding and peritonitis, which poses a danger to the patient’s life and requires urgent surgical intervention.
- Biliary dyskinesia is a violation of the motor function of the organ. The main reasons for the development of the disease are stress, poor diet, and heavy physical activity. Usually, when examined for dyskinesia, the patient is diagnosed with diseases of the digestive system. The pathology occurs spontaneously, accompanied by heaviness, paroxysmal acute pain in the right side, nausea, stool upset (diarrhea or constipation), tachycardia, the appearance of a bitter taste in the mouth, and in rare cases, headache. Dyskinesia is accompanied by stagnation of bile in the gallbladder, which contributes to the formation of stones and the development of cholelithiasis.
- Pancreatitis. Throbbing pain indicates pancreatitis. The exact cause of inflammation of the pancreas has not been established. The pathology begins with throbbing, intense, girdling pain. If these symptoms occur, the patient requires immediate hospitalization and emergency surgical treatment. Pronounced pain in the right quadrant of the abdomen is observed during the transition of pancreatitis from the acute to the chronic stage and can be treated conservatively.
- Intercostal neuralgia. Pain in the hypochondrium is not always caused by pathology of the internal organs. Thus, pain in the rib area can occur due to skeletal diseases. Such a common disease as osteochondrosis occurs with degeneration of spinal cartilage. The altered cartilage puts pressure on the nerves, which leads to pain.
Neuralgia
If pain bothers a person between the ribs, then these are manifestations of neuralgia. This pathological condition is not only interconnected with vertebrogenic pathologies, but also with other underlying causes. Pain on the right side appears sharply and increases when the patient takes a deep breath. Also, the pain will spread not only from the front side, but also from the back.
If the pathological process is bilateral, then the pain will become encircling. A person feels “goosebumps” crawling longitudinally between the ribs, and the skin goes numb. During the examination, it is necessary to exclude cardiac pathology, in which pain syndrome may appear in the pericardial area.
Other reasons
Other diseases and pathologies, the symptoms of which may include painful sensations of various types in the area of the lower ribs on the right side of the body, are the following:
- From the nervous system: compression of the nerve endings that are located in the intercostal space (intercostal neuralgia), herpes zoster, characterized by acute pain, the appearance of rashes, itching;
- From the digestive system: gastritis, peptic ulcer, various inflammatory processes, intestinal obstruction, colitis, pancreatitis, spasms and pain simulating gynecological diseases, peritonitis, etc.;
- From the urinary system: pyelonephritis affecting predominantly the right kidney (otherwise the pain is localized on the left side, and not in the area of the lower ribs on the right), renal colic, stones;
- From the respiratory system: pneumonia (pneumonia) or bronchitis in acute or chronic course - cough provokes spasms of the respiratory system, which are felt as painful sensations in the right hypochondrium;
- inflammation of the uterine appendages, osteochondrosis, appendicitis, etc.
- From the liver: liver dystrophy, cirrhosis, abscess, hepatitis, hepatitis C and others, heart failure accompanied by stagnation of blood in the liver, and other chronic diseases and acute inflammatory processes.
Pain in the right hypochondrium behind
If the patient complains that there is pain in the back under the right shoulder blade, the causes of this phenomenon may be associated with injuries to the lower ribs, damage to the intercostal nerves. Pain appears from behind under the right shoulder blade from the back and with lesions of the right kidney and adrenal gland. The causes of back pain may also be associated with diseases of the inferior vena cava.
- Urolithiasis disease. Diseases of the right kidney and, first of all, urolithiasis can cause intense pain. A stone or sand that begins its journey from the renal pelvis scratches it, and then the ureter, so pain with renal colic will be not only in the projection of the lower ribs, but also in the lower back and lateral abdomen. The pain is paroxysmal and severe. It radiates to the thigh and genitals. When you tap the edge of your palm on the lower back, the pain intensifies and can radiate to the groin. In this case, traces of blood may appear in the urine. In some patients, renal colic is accompanied by vomiting.
- Pyelonephritis. The development of acute infectious inflammation of the kidney is accompanied by pain in the kidney area, intoxication, and fever. It also hurts when urinating, periodic false urges are noted, and swelling appears on the face.
- Necrosis of the renal papillae. It can result from oxygen starvation of the kidney tissue due to blockage of the vessels that feed it (infectious agents or diabetes mellitus). In this case, the pain is constant, combined with blood in the urine. The patient may die from septic shock.
- Kidney cancer. This condition may not appear for a long time. Mild pain and bleeding appear already in the last stages of the disease. Sometimes the tumor interferes with the flow of urine, and then there is acute pain. Pain in the hypochondrium also occurs with tumors of the right adrenal gland, provided that the tumor is large.
- Acute upper paranephritis. This is an inflammation of the fatty tissue at the top of the kidney due to infection from the tonsils, carious teeth or other foci of inflammation. First, there is a temperature of up to 38, moderate pain in the lower back on the affected side. After 2-3 days, the pain moves to the right hypochondrium and intensifies with a deep breath. Lower back pain increases with sudden straightening of the body and when walking.
- Intercostal neuralgia. The reason that a person’s right side feels tight and numb in the hypochondrium area may be intercostal neuralgia. In this state, sometimes there is a pulling from the back, the ribs hurt on both sides in front. With neuralgia, there is a strong tingling sensation in different areas, even to the point of limited mobility. The pain becomes stronger when bending or turning. Also, the cause of a sudden tingling sensation in the pit of the stomach or twitching on both sides can be myositis, when a person’s muscles are inflamed.
- Osteochondrosis of the lumbar region. It produces pain of varying intensity, which is accompanied by limited mobility, muscle tightness and tension symptoms. The pain can range from aching to shooting of varying degrees of intensity.
- Shingles. In this case, herpetic eruptions appear along the nerve in the form of bubbles with cloudy liquid, and the skin turns red. Itching, burning, and pain develop at the site of the lesion. This means that you need to see a dermatologist.
- Thrombosis of the vena cava. A rare variant of thrombosis of the inferior vena cava (when a blood clot comes from the iliac veins and clogs the main trunk of the vein) causes pain in the lower back (right hypochondrium from the back) and a clinical picture similar to the late stage of kidney tumors. If the liver segment is thrombosed, then intense pain will occur in the right hypochondrium in front and will radiate under the right shoulder blade. This will cause fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity and jaundice.
Drowsiness
Severe pain on the left, as well as in the solar plexus area, can be eliminated by ascorbic acid. It will allow you to establish metabolic processes in the body and tone the tissues. You can replace ascorbic acid with rosehip or half a glass of orange juice.
Pain in the side after drinking alcohol is not a random symptom. They can be a manifestation of a number of serious diseases or alcohol poisoning. When you experience pain under the ribs, weakness and nausea after drinking alcohol, you need to:
- try to intoxicate using absorbents,
- orange juice,
- mineral water
- or drink a glass of weak and not hot green tea with a slice of lemon.
But these measures can only be tried once. If pain in the side is observed after each use of alcohol-containing products, you should urgently seek help from a doctor.
If there is pain in the right hypochondrium in front
Tingling or sharp pain in the right side occurs due to diseases of the organs that are adjacent to this area. Some conditions are accompanied by pain from the back, sometimes it radiates to the leg, shoulder blade, kidney, etc. There may also be pain in the lungs when taking a deep breath. With some diagnoses, pain may be periodic, appearing when walking or coughing. With others, unpleasant sensations bother you constantly.
- Hepatitis. Viral, alcoholic or toxic hepatitis gives a picture of intoxication (weakness, lethargy, loss of ability to work) and dyspepsia (nausea, loss of appetite, vomiting). At the height of the disease, jaundice occurs with a lemon tint to the skin and whites of the eyes. During the same period, urine becomes the color of beer, and feces - the color of clay due to disturbances in the exchange of bile pigments.
- Cirrhosis of the liver. In patients with cirrhosis, liver cell death and changes in its structure are observed. People with this diagnosis have pain in the right side at the waist level, sometimes the pain is felt in the back. With cirrhosis, a person may notice pain in the right side below the ribs, already at the very beginning of the disease. At the same time, the burning sensation in the right side is persistent. In the later stages of cirrhosis, the liver becomes smaller, its performance decreases, the patient develops hepatic coma, and death is likely.
- Echinococcosis. These are cysts with liquid contents, which are caused by the worm Echinococcus. Cysts are most often located in the right lobe of the liver and, as they grow, they compress the capillaries and intrahepatic bile ducts, causing severe heaviness in the hypochondrium and uneven enlargement of the liver. If the cyst festeres, a cavity filled with pus develops - a liver abscess. In this case, the pain intensifies, the body temperature rises and inflammation of the peritoneum or even blood poisoning may develop.
- Congestive heart failure. Why discomfort in the right hypochondrium in this case is bothersome is explained by the patient’s condition. Initially, his blood circulation deteriorates, as a result, the liver enlarges, and fluid accumulates in the abdominal cavity. A nagging pain appears in the right side, a feeling of heaviness. A nagging pain is disturbing as the disease progresses. With abdominal myocardial infarction, the patient experiences severe, burning pain in the lower right hypochondrium. Sometimes the patient complains that there is pressure in the side. But in some cases, the onset of pain is sometimes very sharp, similar to the blow of a knife; the pain appears in the shoulder blade and sternum. As a rule, this happens with the development of infarctions of the posterior wall of the heart muscle. Sometimes it seems to the patient that this painful sensation manifests itself in waves: periodically it decreases and intensifies. In this case, pallor, heart rate disturbances, and a drop in pressure may be noted.
- Gallbladder diseases. They give the greatest percentage of intense and sharp (cutting or stabbing pains), which are characteristic of acute inflammation. In this case, a displaced stone that closes the lumen of the bladder neck or bile duct or bacterial flora may be to blame for the inflammation. Pain during acute inflammation occurs at the point between the rectus abdominis muscle on the right and the costal arch. They are cramping, strong, and radiate to the right shoulder or left hypochondrium. There may be a bitter taste in the mouth, belching of air, nausea and vomiting of bile. Sometimes the body temperature rises. For calculous cholecystitis, the development of obstructive jaundice with a yellow-green tint to the skin and mucous membranes is typical.
Nature of pain
The pain reaction in the right side and back can differ in intensity, character and duration.
Depending on the intensity of the pain syndrome, there are 2 main types: acute and chronic pain. Epicritic (acute or primary) pain reaction can be burning, cutting, stabbing. It has a clear localization, but can change intensity when moving or changing the position of the body. With an exacerbation of the disease that caused this syndrome, the patient cannot fixate in one position. Acute pain is often caused by spinal injuries, radiculitis (pinched spinal roots), myositis (inflammation of skeletal muscles), and cancer.
Protopathic (secondary or chronic) pain reaction can be aching, pulling and dull. It spreads from the primary focus higher or lower, so its exact localization cannot be established. Despite the fact that the pain is moderate, it is impossible to get used to it. In most cases, it is caused by diseases of the heart and blood vessels, gastrointestinal tract, genitourinary system, and other abdominal organs. Another cause of chronic pain syndrome is pregnancy.
Pain after eating
Eating accelerates the secretion and movement of bile, increases blood flow to the liver and stimulates intestinal peristalsis. Therefore, food provokes pain in pathologies of the liver, gall bladder, and intestines.
In this case, the nature of the pain can be different: nausea and dull pain are characteristic of cholecystitis, sharp pain of a spastic nature accompanies colitis and intestinal dysbiosis, stabbing pain accompanies biliary dyskinesia or cholelithiasis.
After load
Unpleasant sensations in the form of nagging or stabbing pain occur after physical exertion in people with hepatitis, cirrhosis, or congestive liver. After shaking or physical exertion, an attack of calculous cholecystitis may occur. Also, periodic pain during exercise appears in patients with myositis, intercostal neuralgia, osteochondrosis, rib fractures, and vena cava thrombosis.
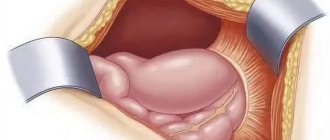
Pain in acute appendicitis
The appendix is a lymphoid organ that takes part in the immune defense of the digestive system. It is located in the area of the right ilium, but its position is quite variable. This causes difficulties in diagnosing inflammation of the appendix. Appendicitis has its own distinct stages of development, which only a surgeon can diagnose.
Signs of appendicitis are:
- Diffuse pain in the navel and stomach;
- The pain is localized in the right half of the abdomen for three hours;
- Reducing pain when lying on the right side;
- Increased pain when walking and lying on the left side;
- Against the background of pain, general health worsens, body temperature rises, vomiting and diarrhea occur.
In such cases, emergency surgical treatment is performed in a surgical hospital.
Localization of pain
Depending on the location, local, referred, and radiating pain is distinguished in the right side and back. Local pain reaction can be acute, dull, aching or diffuse. Its intensity does not change with movements. Referred pain is projected from internal organs, for example, liver, pancreas, kidneys. Radiating pain is highly intense and is accompanied by sensory disturbances. It occurs as a result of damage to the spinal nerve roots.
Pain in the side and back on the right can be located below or above. This is an important diagnostic sign that will help determine the cause of discomfort.
Pain in the lower part (under the ribs) indicates damage to the spleen, liver or pancreas. By the nature of the pain you can understand which organ is affected.
For example, a stabbing pain reaction indicates inflammation of the gallbladder. In this case, a fever appears (about 39°). Aching pain that spreads to the back indicates liver problems.
If pain in the right side and back extends to the lumbar region, then problems with the spine or genitourinary system are possible. In the first case, the pain intensifies with changes in body position, and in the second, it is constant and spreads to the groin area. Acute pain syndrome indicates kidney disease or inflammation of the appendix.
Pain in the side and back at the top right can be a consequence of damage to the respiratory organs or spinal nerves in the thoracic spine. Often discomfort is caused by gastrointestinal organs, for example, the gallbladder.
Pain differentiation
Depending on the pain felt by the patient who consults a doctor with this problem, it is possible to identify which organ disease is associated with certain painful sensations.
So, pain in the right hypochondrium, what could it be:
- Burning pain in the right hypochondrium is often the cause of acute cholecystitis.
- Acute pain in the right hypochondrium is most likely associated with diseases of the gallbladder.
- Severe pain in the right hypochondrium is usually felt by patients suffering from hepatitis.
- Dull pain may be a consequence of inflammatory processes in the gallbladder.
- Aching or pressing pain can be classified as symptoms that occur with biliary dyskinesia.
- Nagging pain is characteristic of chronic hepatitis.
- The bursting type of pain can be caused by chronic diseases of the pancreas.
- Throbbing pain is typical for patients diagnosed with pancreatitis.
- Stitching pain is observed in patients with problems with the right kidney.
Also, pain in the right hypochondrium can only occur in the evening or at night. As medical practice shows, constant night pain in this area is often the first sign of a duodenal ulcer.
Osteochondrosis
With osteochondrosis changes, dystrophy occurs with degeneration of the discs located between the vertebrae. Back pain on the left side under the ribs behind or on the right side behind the back can be nagging and lasts a long time. Often, over time, a person’s back always hurts under the ribs, and the lower back is also painful. Symptomatic manifestations are extensive. The affected spine is characterized by stiffness of movement, the spinal column loses flexibility.
How to diagnose and treat?
Treatment is carried out by a neurologist. The specialist collects anamnesis and examines the patient. Additionally, X-ray examination, CT, and MRI are indicated. Therapy is aimed at reducing inflammation and pain. As a rule, they treat:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Chondroprotectors.
- Muscle relaxants.
- Vitamins and macroelements.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures.
How to relieve pain?
In order to relieve pain, you can drink no-spa, but you should not abuse the painkiller - this will not make it possible to correctly determine the cause of the discomfort.
It is necessary to immediately call an ambulance if the patient exhibits the following symptoms:
- incessant vomiting;
- fainting and presyncope;
- delay or complete inability to urinate;
- the pain is acute, unbearable, lasts more than a few minutes (not attacks - spasms, characterized by cramping pain, but constant significant discomfort);
- uterine bleeding;
- blood in vomit, feces, urine;
- significant increase in body temperature (above 38.5°C);
- diarrhea or constipation lasting several days.
If there is pain in the right hypochondrium and the causes have been clarified, the question remains of what to do. The main thing that the patient should know is that under no circumstances should you self-medicate. Taking antispasmodics, analgesics and similar drugs significantly blurs the picture and complicates the doctor’s work.
First aid recipes widely circulated on the Internet are also ineffective, but also dangerous. Under no circumstances should you take alcohol tinctures, place heating pads on your stomach, etc.: for unknown reasons, this can cause death. The main thing the patient should do is consult a doctor. In this case, it is not necessary to go to the local police officer. In case of intense pain, you should contact an ambulance.
Treatment is almost always medicinal and includes taking analgesics, antispasmodics, diuretics, choleretic drugs, etc. These medications are prescribed exclusively by a doctor. Surgical assistance is required in extreme, urgent cases, such as intestinal obstruction, perforated ulcers, etc. In all other cases, conservative therapy is indicated.
How to help, who will help?
Since pain on the right side, in the back area, is a symptomatic manifestation of dangerous pathologies, self-medication is contraindicated. The person must take a horizontal position and drink a tablet pain reliever. When pain appears, you should contact a specialist in the field of therapy. If necessary, he will refer you to other specialists involved in:
- Surgery.
- Gastroenterology.
- Cardiology.
- Gynecology.
- Traumatology.
- Infectious diseases.
- Endocrinology.
If the pill does not help, you need to urgently call an ambulance. Analgesics should not be taken in large doses, since the clinical picture of the disease will be distorted and it will be difficult to establish a diagnosis. Only qualified medical care will restore not only health, but also save lives.
Prevention
Preventive measures to prevent pain in the right hypochondrium boil down to following the following recommendations:
- taking medications only as prescribed by a doctor;
- avoidance of stressful situations;
- compliance with personal hygiene rules;
- healthy and active lifestyle;
- rejection of bad habits;
- proper and nutritious nutrition;
- use of barrier contraceptives during sexual intercourse, refusal of casual relationships.
Regular medical examination (once a year) will allow you to prevent or promptly detect any health problems and receive the necessary treatment.