Hirschsprung's disease (HSCR, aganglionosis coli, congenital megacolon) is a congenital malformation of the lower digestive tract in which intramural nerve plexuses are absent, which leads to persistent impairment of intestinal function. The pathology was first identified in 1887 by the scientist G. Hirschsprung. After studying the structure of the intestinal wall in boys who died from chronic constipation, scientists identified aganglionic areas of the intestine and an enlarged colon cavity. Congenital megacolon is diagnosed in children from an early age. If a small area of the intestine is involved in the pathological process, Hirschsprung's disease is detected in later periods. The incidence of this disease is approximately 1 case in 5000 newborns. Idiopathic megacolon occurs 4 times more often in boys than in girls.
Pathogenesis
Ganglion (or ganglion) cells are the general name for certain types of large neurons that in the intestine are responsible for communication between nerve structures. During ontogenesis, ganglion cells migrate from the upper parts of the intestine to its distal part.
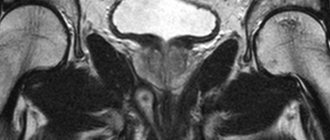
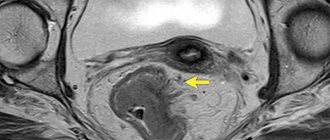
Violation of migration leads to the formation of an aganglionic section of the intestine (a zone of functional narrowing) with reduced or completely absent innervation (the ability to perform translational contractile movements). In some cases, the aganglionic region may become abnormally dilated, forming a megacolon, which is one of the serious complications of Hirschsprung's disease.
The location of the aganglionic site is usually the distal colon. In rare cases, there are forms of Hirschsprung's disease in which the aganglionic segment is formed in the area from the splenic column, or aganglionosis of the entire large intestine develops. With this form of the disease, patients experience total paralysis of peristalsis.
Forms
The locality of the lesion underlies the classification of the disease into forms.
- Rectal form. Damage to the rectum only, which may be partial.
- Rectosigmoid form. In this form, aganglionosis affects the rectum and sigmoid colon. The sigmoid colon may be partially or completely affected.
- Subtotal form. The transverse colon is affected along with the sigmoid and rectum.
- Total form. The most severe form in terms of clinical manifestations and treatment prognosis. The entire large intestine is affected.
The following forms are distinguished along the flow:
- Acute form. Occurs in the first month of a child’s life.
- Subacute form. Placed when the child is between 1 and 3 months old.
- Chronic form. Installed after 3 months.
Symptoms of Hirschsprung's disease
The severity of signs of Hirschsprung's disease depends on age, extent of the lesion and medical history.
Characteristic symptoms:
- Diarrhea appears periodically.
- Flatulence is observed. Gases accumulate in the intestines.
- Constipation. This is the most basic sign of the disease. Some children may not have bowel movements for several weeks. In severe cases of the disease, the process of defecation is generally impossible without an enema.
- In newborn babies, meconium (the first bowel movement) passes late (by 2-3 days) or does not pass at all.
- The baby experiences pain in the intestines. He is capricious, crying, pulling his knees to his tummy.
- The abdomen becomes bloated. The navel is flattened or turned outward. The abdomen takes on an asymmetrical shape.
- Intoxication of the body. The child refuses to eat and does not gain weight. An increase in temperature may occur.
- During the act of defecation, “fecal stones” (dense, hard stool) are passed out. Complete emptying does not occur. The stool has an unpleasant odor. They look like a thin ribbon.
If the anomaly does not cover the entire intestine, then the symptoms in newborns are quite vague. In a breastfed baby, stool has a semi-liquid consistency. They can be eliminated by the body without difficulty.
The first problems arise at the moment when complementary foods begin to be introduced into the baby’s diet. Adult food leads to compaction of stool. Intestinal obstruction appears, and symptoms of intoxication are observed. At first, an enema helps to cope with such a clinic. In the future, this event no longer brings relief.
Mother's diet
Source: Alexander Dummer: Pexels
Breastfeeding mothers often wonder how their diet affects the quality of their breast milk and how choosing foods for it can affect the baby's digestive system. However, most women do not need to restrict their diet while breastfeeding and should aim for a nutritious and varied diet.
In some cases, infants may seem to avoid feeding after the mother has taken certain foods. In this case, a woman can simply eliminate this food from her diet and return to it after stopping breastfeeding.
Important: Special recommendations include avoiding caffeine while breastfeeding. Caffeine is easily transmitted to the baby through milk. It reduces the amount of iron in milk, which can lead to iron deficiency anemia. It is recommended that a nursing mother consume no more than 400 milligrams of caffeine per day. The most caffeine is found in coffee and chocolate, and the least in tea.
A healthy diet while breastfeeding is essentially the same as a nutritious diet without breastfeeding. The main difference is that breastfeeding people need 450 to 500 extra calories per day. But if you want to lose weight after pregnancy, you can do without them, having first discussed this with your doctor.
A healthy diet for a pregnant woman includes:
- Fruits, especially rich in potassium and vitamin A (melon, banana, apricot, mango, oranges). Helps reduce the risk of constipation in both the child and the mother;
- Vegetables containing vitamin A and potassium (spinach, carrots, tomatoes, red peppers);
- Grain products, especially brown rice and whole grain bread;
- Protein-containing foods such as beans, peas, nuts, meat, fish, mussels.
Important: A nursing mother needs to drink a lot of water, especially in the first weeks after birth. Lack of fluid negatively affects milk production. A sufficient amount of water ensures the efficient functioning of the digestive system, helps food to be absorbed, which means breast milk will be well-balanced in nutrients. The higher the conditional quality of milk, the lower the likelihood of constipation in a child, since balanced milk improves peristalsis and fecal removal.
Stages of Hirschsprung's disease
Taking into account the dynamics of the disease and changing symptoms, doctors distinguish the following stages of the disease:
- Compensated - constipation has been noted since childhood, cleansing enemas can easily eliminate it for a long time
- Subcompensated - gradually enemas become less and less effective, the patient’s condition worsens: body weight decreases, heaviness and pain in the abdomen, shortness of breath; Severe anemia and metabolic disorders are noted. The state of subcompensation occurs in patients with decompensation during conservative treatment
- Decompensated - cleansing enemas and laxatives rarely lead to complete bowel movement. There remains a feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen and flatulence. Under the influence of various factors (sharp changes in diet, heavy physical activity), patients develop acute intestinal obstruction. In children, decompensation is often observed with subtotal and total forms of damage.
- The acute form of Hirschsprung's disease manifests itself in newborns in the form of low congenital intestinal obstruction.
Hirschsprung's disease, unlike other causes of constipation (tumor, atonic constipation in the elderly, with nonspecific ulcerative colitis), is characterized by the appearance of constipation from birth or early childhood.
Parents often note the presence of endocrine, mental and neurological abnormalities. The disease may be accompanied by other congenital anomalies: Down's disease, cleft palate.
Signs of the disease
Source: t.tomsickova / Depositphotos
Clinical manifestations of constipation are varied. They become most pronounced with prolonged constipation and are:
- Bowel movements less than 2 times a week;
- The stool comes out heavily, its substance is dry, hard, consisting of many pieces;
- Defecation is accompanied by pain;
- The child may feel that some of the contents have not come out;
- Abdominal pain and bloating;
- Traces of liquid stool on underwear.
You should immediately seek medical help if you have the following symptoms:
- Bleeding from the anus;
- Blood in the stool;
- Weight loss;
- Vomit.
If older children can talk about a problem with the intestines, then parents may not even be aware of the problem of a very young child.
Important: symptoms of constipation in an infant:
- Problems with sleep, the child often wakes up and cries.
- When changing the diaper and washing the baby, he behaves restlessly, fidgets, and begins to cry. This is associated with pain during bowel movements.
- The baby poops less frequently than usual and his or her stools are hard or pellet-like.
Chronic constipation is characterized by skin changes. It becomes pale, acquires an earthy tint, and loses elasticity. Becomes dry and flaky. There is a coated tongue and bad breath.
Complications
Congenital Hirschsprung anomaly often leads to the development of all kinds of complications. Their group includes:
- Anemia.
- "Fecal" intoxication. This complication is the result of poisoning of the body by accumulating toxic substances.
- Development of acute enterocolitis. With the rapid progression of such inflammation, death is possible.
- Formation of “fecal stones”. In this case, such solid masses are formed that they can disrupt the integrity of the intestinal walls.
It cannot be assumed that a congenital anomaly of intestinal development will go away on its own. The child’s further quality of life and the absence of changes in his entire body depends on timely treatment of the pathology.
Treatment of Hirschsprung's disease
Treatment of the disease with conservative methods is ineffective; such therapeutic measures are usually prescribed as preparation for surgery. The only effective treatment for Hirschsprung's disease is surgery. In each case, an individual approach is applied and three treatment options are considered:
- The use of conservative methods for the treatment of chronic constipation until the issue of the advisability of surgical intervention is resolved.
- Postponement of surgery, for which the method of applying a temporary colostomy is used
- Emergency surgery
Based on many years of experience, surgeons believe that the optimal age for such an operation is 12-18 months. But if a persistent compensation process is observed during conservative treatment, intervention can be postponed until 2-4 years of age.
It is also worth considering that if you undergo surgery and delay its implementation, unfavorable secondary changes begin in the patient’s body: the threat of developing enterocolitis, dysbacteriosis, and protein metabolism disorders increases. Therefore, it is important for the doctor to grasp the line when the optimal age limit for surgery has reached, and there are no clear manifestations of secondary changes.
Minimizing negative consequences
To minimize constipation, diarrhea and other undesirable effects after surgery, patients are recommended to adhere to a special diet, which is based on the consumption of foods rich in plant fiber.
The risks of postoperative complications include the development of enterocolitis due to intestinal infection, therefore, if there is an increase in body temperature, vomiting, diarrhea, or signs of intestinal bleeding, you should immediately consult a doctor.
In mild cases of Hirschsprung's disease, surgical interventions can be abandoned and symptomatic treatment can be performed using siphon enemas.
Conservative treatment
The main goal of this therapy is the constant cleansing of the intestines. To do this, doctors recommend taking the following measures:
- Diet. It is prescribed only by a doctor. The choice is made on foods that have a laxative effect: vegetables (carrots, beets), fruits (plums, apples), cereals (oatmeal, buckwheat), dairy products (ryazhenka, kefir).
- Physical exercise. The doctor will recommend special therapeutic exercises. It stimulates peristalsis and helps strengthen the abs.
- Massage. The lower abdominal area is massaged daily. It stimulates natural peristalsis and bowel cleansing.
- Vitamins. Strengthen the body and protect against the negative effects of toxic substances.
- Cleansing enemas. The child needs constant bowel cleansing.
- Probiotics. Medicines stimulate the functioning of the intestines and saturate it with beneficial microflora.
- Protein preparations. Electrolyte solutions are administered intravenously. They are recommended for pronounced symptoms of malnutrition.
In cases where conservative treatment methods do not produce the desired effect or the disease is in an advanced stage, the patient is prescribed surgical treatment.
Surgery
After a series of examinations, the surgeon decides when and how to perform the operation. It should be carried out during the most favorable period, and not during exacerbations. What is the essence of the surgical method? The affected segment is removed, after which healthy sections of the large intestine are connected. The operation can be of two types:
- One-step. The aganglionic zone of the colon is truncated. The healthy part of the large intestine immediately connects to the rectum.
- Two-stage. First, a truncation is performed, then a colostomy (a section of intestine is brought to the surface of the abdomen). Feces are discharged into a special container - a colostomy bag. After the adaptation period, the second part of the operation is carried out: healthy sections of the truncated intestine are connected.
All patients who have undergone surgery should undergo clinical observation to assess the functional results of treatment and identify and correct late complications caused by the operation. It is recommended to undergo a medical examination and consultation with a doctor every week for a month after surgery. Then, throughout the year, examinations can be carried out once every 3 months.
Hirschsprung's disease in children has a fairly favorable prognosis. Most operations to remove a defective area of the colon occur without further complications, but only if the parents or the child himself follow the doctor’s recommendations and undergo periodic examinations.
Causes of pathology
Although this disease was described back in 1887, it took many years to identify the causes and development of this disease.
Doctors cite several sources that provoke the development of such an unpleasant pathology as Hirschsprung's disease in children.
Causes of the disease:
- As a result of the studies, it was found that the formation of pathology occurs during intrauterine development. Nerve clusters that will perform the necessary functions in digestion are formed in the fetus from 5 to 12 weeks of pregnancy. In rare cases, nerve cells in a baby's digestive system do not fully develop. They are not formed in the large intestine. The causes of this pathology have not yet been clarified. It is believed that this is how mutations in DNA manifest themselves.
- Heredity is also noted in the occurrence of this disease. If there are cases of this disease in the family, then the likelihood that a sick child will be born is quite high. Especially if the fetus is male, since boys suffer from this disease 4-5 times more often than girls.
- In areas where there is increased radiation, children with Hirschsprung's disease are more often born.
- A factor influencing the occurrence of this disease is Down syndrome.
- Pathology can develop as a result of endocrine disorders in the mother.