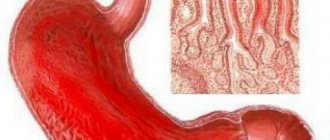
Megacolon
(
megacolon
; Greek megas large + Latin colon colon) - pathological expansion and hypertrophy of the walls of the colon in a larger or smaller area, or throughout its entire length (megadolichocolon). This concept unites diseases of different origins and pathological essence, the main symptom of which is persistent constipation (see). In 1886, the Danish pediatrician G. Hirschsprung spoke at a meeting of the Berlin Society of Children's Physicians with a report on an “unusual disease” of the colon. Having studied in detail the clinical picture and macroscopic changes in the intestine with this suffering, the author identified it from a number of previously described diseases with similar symptoms as an independent nosological unit.
Subsequently, this disease became known as “congenital megacolon” or “Hirschsprung’s disease.”
Classification of megacolon forms
Today in gastroenterology the following types of megacolon are distinguished:
- Congenital, also called Hirschsprung's disease. The disease often begins to manifest itself in early childhood, in the first weeks of a newborn’s life. This type of disease is one of the most common. Characteristic features of the pathology are aganglionosis (absence of nerve ganglia in the intestinal wall), difficult passage of the fecal bolus through the intestine, and lack of peristalsis.
- Idiopathic. This form of the disease accounts for about 35% of cases. The clinical picture of the idiopathic form of the disease is the same as that of Hirschsprung's disease. But the patient’s condition is not so serious. This pathology is characterized by an enlargement of the entire intestine, the absence of even small narrowed fragments, and the presence of a large amount of feces in the intestine.
- Endocrine. This disease occurs in no more than 1% of cases and develops against the background of endocrine diseases.
- Psychogenic. Occurs in 3-5% of cases and is a consequence of various incorrect habits of the patient. For example, such a habit could be regularly suppressing the reflex to defecate.
- Obstructive. The prevalence of this form of the disease ranges from 8-10% of all cases. The main causes of pathology are mechanical obstacles that accumulate in the distal colon, which include fistulas and scars.
- Neurogenic. Its appearance and development is caused in most cases by organic diseases of the central nervous system.
- Toxic. It occurs mainly due to taking medications or the influence of a viral infection.
Possible complications and consequences
- Intestinal obstruction is one of the most serious complications of megacolon; without medical intervention it can be fatal. In this case, intestinal rupture and the development of peritonitis are possible, in which it is extremely difficult to save the patient.
- Chronic constipation is systematic insufficient bowel movement.
- Intestinal inflammation is typical after a toxic form of the disease.
- Dysbacteriosis - a decrease in one’s intestinal microflora leads to a compensatory increase in the number of pathogenic bacteria, which, in turn, can lead to sepsis and death of the patient.
- Internal bleeding.
- Perforation (formation of a hole in the intestinal wall).
Causes and pathogenesis of megacolon
The main causes of this pathology in children are the congenital absence of peripheral nerve receptors, as well as conduction pathologies in the nerve pathways. In adults, the disease mainly occurs due to toxic damage to the wall of the large intestine, dystrophic damage to the central nervous system, and organic narrowing of the large intestine. As for acquired megacolon, it is often caused by fistulas, tumors, injuries, scars, hypothyroidism, collagenosis, and amyloidosis.
The formation of pathology is often carried out as follows: first, due to various disorders or mechanical obstacles, problems arise with the passage of feces through the narrowed part of the intestine, which then causes a significant increase in other parts of the intestine. Then, in the enlarged section of the intestine, muscle fibers begin to die and are replaced by connective tissue. All this negatively affects the normal functioning of the intestines, since the movement of feces gradually slows down, long-term constipation begins, when stool may be absent for more than 5-7 days, toxins are absorbed, fecal intoxication and dysbacteriosis develop.
Symptoms of megacolon
The clinical picture of the disease can manifest itself differently in adults and children. Namely, the following symptoms are characteristic of childhood megacolon:
- A significant increase in the size of the abdomen, which may appear in the first days of life. In babies, the stomach is usually rounded and slightly swollen downward.
- Continuous flatulence, in which gases are only partially expelled. Often a child experiences alternating constipation and diarrhea.
- Palpation of the abdomen helps to detect the accumulation of stool of dense consistency.
- When you press on the abdomen, in the area where the greatest accumulation of feces is observed, a small hole remains, similar to a pressure mark on a piece of clay.
- Vomiting and dehydration - as a result of the accumulation of large amounts of feces in the intestines.
- Regular long-term constipation, which begins to occur at 2-3 weeks of a child’s life.
In adult patients, the symptoms are similar, but differ in some specifics. These symptoms include the following:
- Bloating and gradual formation of a barrel-shaped chest.
- Tendency to regular constipation, which can last for quite a long time - for 5-7 days. With congenital megacolon, constipation can occur in childhood, but it becomes most severe and lasting between the ages of 20 and 30 years. Patients with acquired megacolon usually complain of constipation in later life.
- Flatulence.
- Stagnation of feces, which causes disorders such as headache, shortness of breath, weakness, nausea and vomiting, drowsiness, sudden weight loss, tachycardia and decreased performance.
- Severe intoxication of the body, which sooner or later leads to anemia, as well as swelling of the extremities.
Diagnosis of megacolon
When making a diagnosis, the doctor is based on data obtained during a patient interview, symptoms of the disease, as well as additional special studies. The key symptoms that confirm the presence of megacolon in a patient are constipation, lack of stool, the presence of a narrowed part of the colon and bloating. In the practice of diagnosing megacolon, the following methods are used:
- X-ray examination (performed after bowel cleansing). On a plain X-ray of the patient, such manifestations of the disease as the presence of dilated and swollen loops of the colon, as well as a rather high position of the dome of the diaphragm, are noted.
- X-ray contrast techniques. This diagnostic method involves injecting barium into the rectum and examining it under x-ray in different projections. During this study, four radiographs are taken from different angles: one each in the direct and lateral positions, as well as two after bowel movement. In this case, the first two radiographs are taken with the intestine full in order to accurately determine the degree of expansion of the area near the expanded part of the intestine.
- Rectal biopsy. It is one of the most important and reliable diagnostic techniques. Used to confirm the absence of nerve nodes in the muscular and submucosal parts of the rectum. A biopsy is performed in the area of the muscle sphincter - above the internal sphincter.
- Rectal manometry. Using this technique, the functional state of the rectoanal zone is assessed. Namely, the technique makes it possible to identify such symptoms of the disease as the absence of the rectoanal reflex, a significant increase in muscle sphincter, as well as an increase in the maximum tolerated volume.
- Irrigoscopy. Necessary to determine areas of narrowing of the colon, lack of folding, and presence of smooth contours.
- Colonoscopy and sigmoidoscopy are used for a thorough examination of the large intestine.
- Differential diagnosis is carried out in the case of colon tumors, irritable bowel syndrome, chronic colitis, constipation, diverticular disease.
Treatment of megacolon
The choice of treatment method depends on the severity of the disease. If the patient has been diagnosed with a mild degree of megacolon, then conservative treatment is chosen: suppositories, Vaseline oil, enemas, therapeutic exercises, restorative treatment, diet.
For patients with severe forms of the disease, surgical intervention is the only option. But at the same time, in the preoperative preparatory period it is necessary to strictly adhere to the principles of conservative treatment. First of all, the patient must follow a diet - eat mainly those foods that enhance peristalsis. Such products include oatmeal, beets, prunes, apples, carrots.
Prevention
Intestinal megacolon is quite difficult to cure. Even with a surgical operation, serious complications remain, which then accompany the patient throughout his life. Therefore, it is better to prevent the occurrence of pathology. To do this, it is very important to follow the rules that will help avoid constipation. The main thing is to eat right.
The diet should be rich in fresh vegetables and fruits, dietary fiber, and dairy products. You need to get rid of bad habits, try not to drink alcohol and fast food. It is also important to avoid stress and a sedentary lifestyle. And to prevent organic damage to the intestines, undergo regular examination by a doctor.
Postoperative measures
After the operation, the patient is also required to follow a certain regimen. In particular, it is recommended to continue physical therapy exercises, as well as diet. In addition, during the rehabilitation period it is worth doing enemas at the same time, and also regularly resort to electrical stimulation of the rectum. The patient may be additionally prescribed drug therapy.
As for surgical intervention, for the treatment of megacolon, the technique of resection of the extended part of the colon and the aganglionic zone is used. In the case of a congenital disease, it is recommended to carry out such an operation already at 2-3 years of the child’s life. The extent of bowel resection depends on how severely it was affected. Usually, the colostomy is closed immediately after the operation is completed.
In some cases, treatment of megacolon comes down only to eliminating the causes that caused it. Such reasons may be mechanical obstructions in the colon such as fistulas, scars or adhesions, inflammation of the intestines, chronic constipation. It is worth noting that in the case of early diagnosis of the disease, as well as effective and timely treatment, the prognosis for the patient is usually favorable.
Varieties
The main classification of the disease takes into account the time of its onset. There are congenital or acquired megacolon. When intestinal formation is disrupted during the fetal development of a child, congenital megacolon develops. It is often diagnosed with Hirschsprung's disease. It is characterized by the fact that at birth the child has no nerve plexuses on the walls of the colon or part thereof. In this place, intestinal motility is disrupted, so the passage of feces is difficult. In addition, congenital megacolon can develop in the presence of an organic obstruction in the lower rectum, for example, its stenosis or atresia. As a result, the colon increases in size. If the sigmoid colon undergoes changes, it usually lengthens, this is dolichosigma.
This pathology can also develop in adults. There are many causes of acquired megacolon, about a third of them are idiopathic, that is, uncertain. In addition, according to the etiology of the development of the disease, toxic megacolon, traumatic, psychogenic and endocrine are distinguished. Pathology can develop due to injuries, mechanical obstructions in the intestines, nerve damage, inflammatory processes or intoxications.
There are several types of megacolon also based on the location of the pathology. Most often, the sigmoid colon enlarges - megasigma, but if the changes concern the colon, a diagnosis of megadolichocolon is made. In addition, the rectal form of the pathology is often detected, when the rectum in the perineal area is affected. The changes can affect part of the intestine, sometimes they are segmental, that is, between the enlarged areas there is a normal-sized intestine.
Particularly severe cases are observed in the total form of megacolon, when the entire colon and rectum are enlarged.