To obtain the most detailed and high-quality description of the results of an MRI, the radiologist must provide all available medical documentation: medical records, including after operations, images and conclusions of previous MRIs, ultrasound, MSCT. The more detailed information the radiologist has before the study, the clearer the task assigned to him. Also, previous results allow us to evaluate the dynamics of the disease and the success of the treatment.
In most cases, MRI does not require any special preparation.
However, when going for an MRI, you should wear clothes without metal fittings (no zippers, rivets, rhinestones, etc.). If there is metal on your clothing, you will need to change into a disposable shirt. Watches, glasses, jewelry, piercings will have to be removed. Also, on the day of an MRI, it is better for girls not to use cosmetics, because some cosmetics contain metal. Electrical appliances and plastic cards can be damaged by magnetic fields, so they should be left in storage rooms.
Some types of MRI should be prepared in advance.
General characteristics of the examination
The intestine is the longest organ and the most labor-intensive to examine. Various methods are used to diagnose intestinal diseases. It depends on the part of the intestine and the alleged illness. The most common method is colonoscopy. With its help, you can study the intestines literally centimeters at a time. However, this procedure is quite unpleasant, requires careful preparation and is not always possible. It is not able to cover areas of the small intestine and is contraindicated in a number of diseases. Due to its pain, many patients are looking for alternative methods of examination and ask the question: “Do they do MRI of the intestine and rectum?” Knowing about the safety and effectiveness of the study, it is often preferred. Intestinal MRI is also actively used as an additional diagnostic method.
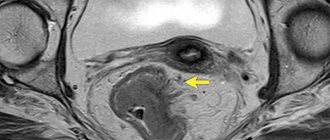
MRI diagnosis of primary rectal tumor
Possibilities of MRI in the diagnosis of rectal cancer (“gold standard”):
- visualization of the tumor, determination of its upper and lower boundaries, the degree of involvement of the intestinal wall, surrounding fiber and adjacent organs in the process;
- determining the relationship of the tumor to the structures of the pelvic floor and the sphincter apparatus;
- identification and assessment of the condition of lymph nodes and lymph drainage in the pelvic area;
- dynamic monitoring of the results of surgical treatment, radiation therapy and chemotherapy;
| Rectal cancer, coronal projection | Rectal cancer, axial projection |
Indications for intestinal MRI
Congenital anomalies
One of the most common pathologies of the digestive system. Occurs due to disruption of the intestinal tube in the fetus. The reasons may be: medications, radiation, viruses and infections, as well as bad habits of the mother. Since the intestines of a small child can be checked reliably and safely only with an MRI, it is prescribed precisely in these cases.
Bleeding
One of the indications for MRI. There can be many reasons and locations. It is the MRI of the stomach and intestines that shows what is the source of bleeding.
Intestinal obstruction
A disease in which food cannot move through the intestines due to a narrowing of its lumen. This can lead to serious consequences: from extensive necrosis to death. Therefore, the patient needs emergency care. The disease affects people of all ages, including infants. It can be either congenital or occur as a result of chronic inflammation, decreased peristalsis, or tumors. Obstruction shows that MRI of the intestine is the only method for diagnosing it.
Presence of stones
A disease in which stool accumulates in the intestines, becomes compacted and turns into stones. They are mainly localized in loops. The main reason is unstable bowel movements. They often accumulate for years. Depending on their size and location, the treatment method is chosen: from enemas to surgery. The disease is quite serious, as it leads to poisoning of the body, which is manifested by decreased immunity, allergic reactions, and constant fatigue. It can also develop into intestinal obstruction. Examination of the intestine using MRI can reveal the size and location of stagnant stones.
Benign tumors or tumors
An MRI of the intestine is done if neoplasms of any suspected nature are suspected. Only this diagnostic method determines the tumor in its early stages, its exact size and location.
MR enterography
MRI of the small intestine is currently the leading method for diagnosing patients with Crohn's disease, benign and malignant tumors of the small intestine. In patients with Crohn's disease, MRI not only detects the affected segments of the intestine, but also distinguishes between fibrous changes in the wall and active inflammation, which is important for proper treatment.
Magnetic resonance imaging room |
| Small intestine, coronal view |
MRI of different parts of the intestine
An MRI of both the small and large intestines is performed. More often, the technique is used in the diagnosis of tumors, bleeding and obstruction. If the patient has complaints about the state of the gastrointestinal tract, then a combined examination is possible - MRI of the stomach and intestines, which shows what caused the deterioration in well-being. Typically, MRI with contrast is used for diagnosis. One of the varieties is hydro-MRI, that is, a method of examining the small intestine. MRI of the large intestine is performed using the classical method.
Hydro-MRI
A procedure before which the patient needs to drink a special solution. When it enters the small intestine, it stretches it a little and colors it, making MRI more informative.
MRI diagnosis of rectal fistulas
(cryptogenic fistulas and perianal complications of Crohn's disease)
MRI is the method of choice for the preoperative assessment of rectal fistulas due to its high accuracy and non-invasiveness. MRI provides an accurate picture of the course of the fistula, its relationship with the pelvic structures, the presence of secondary fistula tracts and abscesses. New techniques make it possible not only to identify rectal fistulas, but also to assess the degree of activity of the inflammatory process in them.
Magnetic resonance imaging room |
| Rectal fistula, coronal projection |
Preparation for the procedure
- Preparation for an MRI study of the intestines begins several days in advance with a gentle diet, excluding foods that lead to bloating.
- As with any other examination of the large intestine, before an MRI it must be cleansed using laxatives or enemas (unless there is an obstruction).
- The examination is carried out only on an empty stomach.
- During an MRI of the intestine with contrast, a preliminary test is done to determine the tolerance of the contrast agent.
- Before the procedure itself, metal objects are removed from the body.
MR defecography
With MR defecography, it is possible to record the position of the pelvic organs at rest and during functional tests, which makes it possible to identify and evaluate both anatomical and functional disorders of the rectum, bladder, uterus (perineal prolapse, rectocele, rectal prolapse, cystocele, prolapse cervix). The advantages of MRI defecography are the possibility of non-invasive comprehensive diagnosis of pathological conditions of the pelvic organs, the absence of ionizing radiation, good image quality of the soft tissues of the pelvic floor, the ability to obtain images in any plane, high resolution, and good tissue contrast. MRI defecography is indicated primarily for patients with rectal defecation disorders.
Defecography.
How is an MRI of the intestine done?
MRI of the intestine is done both with and without contrast.
Time of examination
Depends on the intestinal MRI method. Hydro-MRI is the most labor-intensive and time-consuming process and can last up to an hour.
Contrast enhancement
In most cases, an MRI of the intestine is performed. With the help of a contrast agent introduced into the patient's body, the area being studied becomes clearer and brighter on the tomograph screen, which improves its diagnosis.
MRI diagnosis of rectal tumor recurrence
MRI is the method of choice for the preoperative assessment of rectal tumor recurrence due to its high accuracy, rapidity and non-invasiveness. MRI provides an accurate picture of the localization of the process and its extent, as well as the involvement of pelvic structures.
Magnetic resonance imaging room |
| Recurrence of rectal cancer, sagittal projection |
MRI or colonoscopy of the intestines?
When problems with the intestines arise, the patient is faced with a difficult choice - which diagnostic method to prefer? The standard procedure for examining the intestines is colonoscopy, which many patients are afraid to do due to its excessive pain. The question inevitably arises: should I prefer an MRI of the intestine or a colonoscopy and which will better identify the causes of gastrointestinal disease? The choice in each specific case is best left to the attending physician, who, after an examination, study of the medical history and analysis of other factors, will give his recommendations.
* Crohn's disease on MRI of the small intestine in a series of sequences *
When is an MRI recommended over a colonoscopy?
- an increased level of safety and comfort for the examinee is required - MRI is clearly the leader here, and intestinal colonoscopy can cause spasms and pain;
- For diseases of the small intestine, areas inaccessible to endoscopy are clearly visible on hydro MRI with the introduction of double contrast: intravenous and orally.
- if endoscopic examination is impossible: bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract;
- hernias;
- diverticulosis of the colon or sigmoid colon;
Speed and painlessness - this is why intestinal MRI over colonoscopy with comparable diagnostic capabilities.
Remember that endoscopy is the main method of examining the intestines, but the safety, speed and absence of pain make it possible to choose MR imaging of the intestine .
What does an abdominal MRI show?
The study allows you to evaluate such anatomical structures as:
|
|
MRI of the retroperitoneal organs shows:
|
|
Abdominal scanning, unlike other types of MRI, requires the most sensitive equipment. For some organs, a low magnetic field with a power of 0.3-1.5 Tesla is sufficient, for others a medium and high one is needed - 1.5-9 Tesla. In our clinic in St. Petersburg you can undergo an inexpensive MRI of the abdominal cavity using the latest American device SIGNA Architect 3.0. It gives the most accurate results.
ABSOLUTE CONTRAINDICATIONS FOR MRI
- The presence in the body of metal foreign bodies of any origin (bullets, fragments, shavings, shot, etc.)
- Intracranial vascular clamps, clamps on vessels of the extremities, abdominal cavity, pelvic cavity, large metal implants (joint prostheses). Except in cases where the patient provides documentary evidence of the MRI compatibility of the object installed to him (see below)
- Electrical, magnetic or mechanical active implants (pacemakers, implanted drug dispensers, artificial heart valves, etc.)
- Pregnancy in the first 12 weeks
- The patient has electronic middle ear implants
- Body mass ? 110 kg (limitation of tomograph table load capacity)
- Waist circumference >180 cm (limitation of MRI machine aperture diameter)
- State of drug or alcohol intoxication
- Inability to remain still during the study (for example, due to severe pain or depressed consciousness).
- Presence of tattoos made with dyes containing metallic compounds (or the examination time should be significantly reduced)
- If you have a stent or prosthesis in your body, have with you a document confirming the MRI compatibility of the implant: an extract, an operation report, a certificate with permission to conduct MRI, a passport of the metal structure, an implantation certificate, etc.
- It is necessary to bring for examination all the results of previous CT and MRI of the abdominal and pelvic organs: radiologist’s reports, films and discs.
PREGNANCY AND MRI
If you are pregnant, be sure to inform your doctor before the test. Pregnancy is not a contraindication to MRI, but it is not entirely clear what effect the magnetic field has on the fetus in the 1st trimester. MRI is not recommended in the first 3 months of pregnancy - it is better to postpone the examination or choose an alternative method. In the 3rd trimester, it is possible to undergo an MRI examination of the fetus, which is a more accurate alternative to an ultrasound examination, and also allows you to measure the size of the pelvis (pelviometry) and decide on the possibility of spontaneous childbirth.
Features of MRI in children and people with claustrophobia
SIGNA Architect 3.0 is the largest tomograph model in the world, so there is no feeling of enclosed space inside. Parents can be with the child to support him. The doctor may also prescribe sedatives before the procedure. Patients with hypermobility and severe claustrophobia are diagnosed under general anesthesia. This applies to any examination at the Center for Precision Diagnostics: if indicated, anesthesia can be used to undergo a CT scan of the chest organs, MRI of soft tissues, as well as during other examinations on a computer or magnetic resonance imaging scanner.
Bibliography:
- Konovalov R.N., Krotenkova M.V., Kremneva E.I. Functional magnetic resonance imaging [Electronic resource] // Journal “Annals of Clinical and Experimental Neurology”, 2011. https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/funktsionalnaya-magnitno-rezonansnaya-tomografiya
- Kukhtevich I.I., Goryunova T.I., Goryunova V.V. Practice and safety of MRI studies [Electronic resource] // Journal “International Student Scientific Bulletin” - 2022. https://eduherald.ru/ru/article/view?id=18294
- Ternovoy S.K., Sinitsyn V.E., Belichenko O.I., Stukalova O.V. Clinical application of magnetic resonance imaging [Electronic resource] // Regular issues of “RMZh” No. 7, 1996. https://www.rmj.ru/articles/obshchie-stati/KLINIChESKOE_PRIMENENIE_MAGNITNO-REZONANSNOY_TOMOGRAFII/
When is testing recommended?
The abdominal MRI procedure is a simple and painless alternative to surgical diagnostic methods. She is prescribed:
- for abdominal pain of unknown cause;
- damage to internal organs;
- inflammatory processes: pancreatitis, hepatitis, cholecystitis, etc.;
- abnormalities in the development of internal organs;
- accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity;
- liver diseases: cirrhosis, dystrophy, necrosis, fibrosis;
- the appearance of benign neoplasms: cysts, lipomas, adenomas.
An examination is also prescribed before surgery to adjust the intervention tactics, and after - to assess the results of further treatment.
Preparing the patient for an abdominal MRI
Before the procedure, the body must be properly prepared:
- Diet For 2-3 days, we recommend sticking to a low-carbohydrate diet: excluding fresh vegetables and fruits, pasta, legumes, rye bread, fermented milk products, carbonated and alcoholic drinks, tea, coffee from the diet.
- Taking special medications If you suffer from severe constipation or flatulence, take medications that relieve these symptoms (laxative, espumizan, etc.) 2-3 days before the procedure.
- Restriction in food and liquid The last meal should be at least 6-8 hours before the scan. The liquid should not be drunk 4 hours before the appointed time.
- Preparation for MR enterography On the eve of the study, the last meal is at 13.00. Preparation with Fortrans or Moviprep in accordance with the instructions for the drug. On the day of the study, do not eat anything: you can drink water or broth.