The indirect toxic effect of antibiotics on the liver and biliary system is known through toxic products of the transformation of antibiotics in the body (metabolites). Some metabolites bind to liver substances (glutathione, etc.) and reduce the toxicity of antibiotic breakdown products and improve their excretion from the liver with bile. In this case, the bile may become viscous, and stagnation of bile in the gallbladder may be observed with the formation of suspension and flakes (i.e., bile sludge), which are risk factors and early signs of stone formation in the gallbladder.
Patient K., 40 years old, consulted a gastroenterologist about periodic aching pain in the right hypochondrium, heaviness after eating, and rarely bitterness in the mouth. The patient has been suffering from these sensations for several years; these sensations are provoked by long breaks in eating. Heredity is not burdened.
Prevalence of the disease
Every decade, the number of patients with cholelithiasis is steadily growing. Since the middle of the last century, the number has doubled every ten years. Currently, more than 10% of the world's population suffers from this pathology. In our country, the disease has been diagnosed in 15 million patients; in the United States, more than 30 million patients are registered. Most often, residents of developed countries are susceptible to the disease, and the risk of the disease increases with age. Among people over 45 years of age, every third person develops the disease. The number of operations performed for cholelithiasis in America in the 70s of the last century exceeded 250 thousand; in the 80s, over 400 thousand were performed. By the end of the century, the number of operated patients had already reached 500 thousand. As you can see, the incidence rate is steadily increasing and today in America the number of surgical interventions on the biliary tract and cholecystectomies reaches 1.5 million cases annually; this figure exceeds data for all other abdominal operations, including appendectomy.
Causes
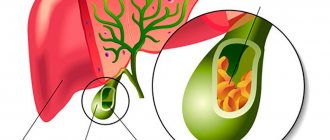
Rice. 1. Pathological anatomy of the biliary tract in cholelithiasis - stones in the gallbladder and obstruction of the cystic duct by one of them (diagram).
Rice. 2. Stages of laparoscopic cholecystectomy - clipping of the cystic duct and artery.
Rice. 3. Stage of laparoscopic cholecystectomy - intersection of the artery and duct and isolation of the gallbladder from the liver bed.
Rice. 4. View of the anterior abdominal wall during open cholecystectomy - suture after laparotomy.
Rice. 5. View of the anterior abdominal wall during laparoscopic cholecystectomy - 4 punctures.
Unfavorable factors that can provoke the appearance of gallstone disease include:
- age;
- overweight;
- pregnancy and childbirth;
- abuse of low-calorie diets, hunger, parenteral nutrition;
- use of certain medications (postmenopausal estrogens, contraceptive steroids, ceftriaxone, fibrate derivatives, octreotide and analogues, etc.)
- heredity (predominance of lithogenic genes, enzymatic defect in the synthesis of solubilizers, cholesterol excretion)
- Crohn's disease, diabetes mellitus, liver cirrhosis, duodenal, choledochal diverticula, infectious diseases of the biliary system, etc.
It should be noted that women are much more common among patients. In addition, there are so-called controllable factors: excess weight, the use of various low-calorie diets in order to reduce weight. For example, in obese individuals, the disease occurs in 33%. Studies conducted in the USA have confirmed that women whose body mass index (BMI) is 25-29 are more likely to get sick. The situation is aggravated by the presence of various diseases (diabetes, coronary heart disease, hypertension). As BMI increases, the likelihood of developing gallstone disease increases. So in women with a BMI above 35, the risk of developing cholelithiasis increases 20 times. It should be noted that low-calorie diets, as well as sudden weight loss (loss of body weight by 1.5 kg per week), weight loss of more than 24% of the initial weight, increase the risk of developing cholelithiasis.
In addition, the biochemical composition of bile is of great importance. Oversaturation with cholesterol, the state of the pronucleating and antinucleating systems, the formation of a crystallization nucleus, and other indicators are very important in the process of stone formation. In addition, a decrease in evacuation function and dysfunction of the enterohepatic circulation of bile acid should be taken into account. The formation of cholesterol stones is based on the hepatic secretion of vesicles that are enriched with cholesterol. However, neither the mechanism of vesicle development itself nor the factors that influence this process are currently not well understood.
What antibiotics are needed for cholecystitis?
The following drugs are most effective for cholecystitis. Erythromycin is a pharmacological group of macrolides, its action is close to penicillins, it slows down the proliferation of streptococci and staphylococci.
Gives a cross-allergic reaction with other drugs of the group (Oleandomycin), intensified by tetracyclines. The disadvantage is that they are produced only in tablet form; patients drink them only with a mild form of inflammation.
Ampicillin - from the group of semi-synthetic penicillins, kills bacteria by destroying their cell membrane. Effective against staphylococci, streptococci, enterococci, salmonella, and E. coli. Quickly penetrates the gallbladder and intestines. Suitable for intravenous and intramuscular administration. When used together, it enhances the properties of aminoglycosides and anticoagulants. It is necessary to monitor blood clotting tests.
Levomycetin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic, but for cholecystitis it makes sense to prescribe only if the pathogen is identified (typhoid and paratyphoid bacillus, salmonella, dysentery bacteria). Has weak activity against clostridia, protozoa, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Used in tablets and injections.
The drug is poorly compatible with anti-inflammatory drugs such as:
- sulfonamides;
- cytostatics;
- anticoagulant medications;
- barbiturates (sleeping pills).
Joint use enhances the inhibitory effect on hematopoiesis.
Amoxiclav - as a penicillin drug, is enhanced with clavulanic acid, therefore it has a wide spectrum of action. It is used even when Ampicillin-resistant strains are identified. Destroys bacteria by binding the cell receptor apparatus and blocking enzymes.
Available in the form of tablets and suspensions for internal use. Cannot be used together with tetracycline antibiotics and macrolides, with sulfonamides due to a decrease in the effectiveness of the drug.
The group of “protected” penicillins (clavulanic acid and tazobactam, which inhibit the enzymes of microorganisms) includes:
- Timentin (Ticarcillin + clavulanic acid);
- Tazocin (Piperocillin + tazobactam).
Ampiox is a combined type of antibiotic, available in capsules and solution for injection, and is a liquid mixture of Ampicillin and Oxacillin salts in a 2:1 ratio. Suitable for intravenous administration. Quickly enters the gallbladder. Effective on a wide range of infections.
Gentamicin - belongs to the group of aminoglycosides, destroys pathogenic microorganisms by destroying protein synthesis, is effective in cases of cholecystitis etiology caused by:
- coli;
- staphylococci;
- Proteus;
- klebsiella;
- Shigella and others.
The drug is poorly absorbed through the intestines, the main use is in injection form
It does not create sufficient concentration in bile, so it is used in combinations. Has a negative effect on the kidneys and nervous system. All antibiotics are contraindicated:
- during pregnancy and lactation;
- in case of damage to the liver, kidneys;
- require caution in case of blood diseases.
Clinical picture and symptoms of the disease
Most often, the first sign that forces the patient to see a doctor is pain in the right hypochondrium, of varying intensity. Cutting or stabbing in nature, the pain is most often constant, often radiating to the right shoulder blade, lower back, and forearm. In some cases (with cholecystocoronary Botkin's symptom), it can radiate beyond the sternum, resembling an attack of angina. It should be borne in mind that the intensity of pain is in no way an indicator of the severity of the process. For example, in some cases, severe pain may disappear, but mild pain does not mean a mild form of the disease.
Often the patient’s condition worsens after eating spicy or fatty foods; their consumption increases the need for bile to process food, which leads to contraction of the gallbladder. In any form of the disease, there is an increase in body temperature. In the form of short rises, the temperature rises to 37-38°C, and the patient often experiences pain. However, during an acute attack accompanied by chills, the temperature can rise to 38-40°C.
What complications should I be wary of when treated with antibiotics?
Each organism has individual sensitivity and characteristics of drug absorption, which cannot be foreseen in advance. While using the required doses of antibiotics and after a course of treatment, the following undesirable complications may occur:
- allergic manifestations of varying severity, from urticaria (skin rash) to anaphylactic shock;
- attacks of bronchospasm with suffocation;
- significant decrease in immunity;
- addition of a fungal infection;
- intestinal dysbiosis, manifested by unstable stools and constant bloating.
A general allergic reaction is one of the possible complications
To prevent possible negative effects, patients should follow the doctor's recommendations. If unusual symptoms appear, be sure to inform your doctor. Under no circumstances should such phenomena be tolerated.
Nystatin helps get rid of fungi. Sometimes it is prescribed in parallel with antibiotics. Probiotics and diet help restore intestinal flora after the acute symptoms of cholecystitis are eliminated.
Antibiotic therapy is subject to careful comparison of indications and the mechanism of action of the drugs. Therefore, it requires special knowledge and experience. Self-administration is not only ineffective, but also causes significant harm to human health.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is based on the results of instrumental studies and anamnesis data.
- Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the upper abdominal cavity is performed to diagnose cholelithiasis and calculous cholecystitis. During the study, in addition to stones in the gall bladder or ducts, the size of the gallbladder, the condition of its walls, and pathology of the liver or pancreas are determined.
- gastroduodenoscopy - allows you to determine diseases of the stomach, esophagus and duodenum.
- retrograde cholangiography (x-ray examination using a contrast agent) is performed in the presence of complications.
- transgastric ultrasound of the ducts is necessary when diagnosing choledocholithiasis.
Use of combination treatment
Even modern drugs of the II and III generation cephalosporin class are not always sufficiently effective for severe cholecystitis. The threat of the formation of empyema (ulcer) in the gallbladder, peritonitis with a breakthrough into the abdominal cavity necessitates the use of combinations of antibiotics with other anti-inflammatory drugs or two drugs from different groups.
Thus, cephalosporins form active combinations with Metronidazole:
- Cefoperazone;
- Ceftriaxone;
- Cefotaxime;
- Cefuroxime;
- Ciprofloxacin.
Another option: Ampicillin + Gentamicin + Metronidazole. In this case, some drugs are administered intravenously, others intramuscularly. Instead of Gentamicin, Sizomycin is used, since nosocomial strains of microorganisms provide up to 90% resistance to Gentamicin.
In order to eliminate the side effects of aminoglycosides, combinations of third generation cephalosporins and the newest penicillins are recommended:
- Ceftazidime (can be replaced with Fortum or Tasicef) + Flucloxacillin.
- Cefipime (belongs to the IV generation of cephalosporins) can be replaced with Maximim and used in combination with Metronidazole.
Conservative methods of therapy
To identify cholelithiasis, determine the degree of inflammation in the wall of the gallbladder, as well as select the correct individual tactics for surgical treatment, you can send me a complete description of an ultrasound of the abdominal organs, preferably a gastroscopy, to my personal email address, you must indicate your age and main complaints. In rare cases, if stones in the ducts are suspected, it is necessary to perform an endoscopic ultrasound examination of the ducts and pancreas. If I provide the above research, I will be able to advise you by email.
In the absence of pronounced manifestations, or in case of a single attack of biliary colic, conservative treatment is carried out aimed at reducing inflammation, improving the motility of the bile ducts and bladder, and the outflow of bile. In addition, it is necessary to correct metabolic processes, as well as eliminate concomitant diseases. However, the tactics of therapy depend on the phase of the process, whether it is an exacerbation, biliary colic or remission. The patient can receive treatment either on an outpatient basis or in a hospital (therapeutic department or surgery). During the period of remission, patients are recommended drug therapy, diet, physiotherapy, and sanatorium-resort treatment is also indicated.
For repeated attacks of biliary colic, which are accompanied by pain, surgical methods for the treatment of cholelithiasis are recommended - only in this way can the development of complications be prevented: peritonitis when the gallbladder ruptures, the development of obstructive jaundice and biliary pancreatitis when the stone enters the hepatic duct, which will lead to obstruction of the biliary tract .
Some categories of patients use traditional medicine methods in the treatment of cholelithiasis. As a result, according to the patients themselves, stones come out of the gallbladder with feces. However, the opening of the sphincter of Oddi, which separates the small intestine from the common bile duct, is no more than 3 mm in diameter. In this case, stones visible to the naked eye simply cannot enter the intestinal lumen. In fact, the patient may find “stones,” which are nothing more than clots of bile that enter the intestines in large quantities. Stone-like formations the size of a walnut, greenish-yellow in color can come out under the influence of various choleretic agents: decoctions and infusions of St. John's wort, flaxseed, immortelle flowers, dandelion root, stelina, peppermint, trefoil, etc. Thus, folk remedies have only a choleretic effect, but the stones are still in the patient’s gall bladder. It should be borne in mind that uncontrolled use of folk remedies can lead to undesirable consequences. Thus, as a result of increased peristalsis, stones in the gallbladder can move, blocking the duct, which will lead to edema, the development of an attack of acute cholecystitis, which, in turn, will cause obstructive jaundice and the development of acute pancreatitis.
In cases where the inflammatory process is pronounced, as well as with long-term stones, with the development of reactive changes in organs located nearby (duodenitis, pancreatitis, cholangitis, hepatitis), as well as with stone obstruction of the neck of the gallbladder, conservative treatment may be useless.
What pathogens will antibiotics “fight”?
Studies of the contents of the gallbladder in patients with clinical manifestations of cholecystitis show the presence of growth of bacterial microflora in 1/3 of patients on the first day of the disease or exacerbation, and after three days - in 80%.
The most common causative agents of cholecystitis when infected from the intestines are:
- enterococcus;
- coli.
If there is a distant chronic focus, then from it through the lymph and bloodstream the following enter the gallbladder:
- staphylococci;
- streptococci;
- Klebsiella
Less common:
- bacteroides;
- clostridia.
Very rare pathogens include:
- Proteus;
- typhoid and paratyphoid bacillus;
- Candida fungi.
In 1/10 of patients, chronic cholecystitis is caused by hepatitis B and C viruses against the background or after an active process in the liver. When choosing a drug, it should be taken into account that in non-calculous chronic inflammation in the gallbladder, a mixed flora is often found.
In the occurrence of chronic cholecystitis, importance is given to parasitic infection:
- opisthorchiasis;
- roundworms.
They penetrate the bile ducts and bladder, causing stagnation of bile in the liver ducts with subsequent reactive inflammation.
Giardia is currently considered as a means of attack:
- 5 times enhances the infectious properties of E. coli;
- reduces immunity;
- causing dysfunction of the biliary tract.
But they are not considered causative agents of cholecystitis, because:
- Giardia cannot live for a long time in the bladder, they die in the bile;
- it is very likely that they come from the duodenum;
- no morphological results were obtained to prove penetration into the gallbladder wall.
The role of Giardia is to support inflammation
The best antibiotic should be considered the one that:
- maximally sensitive to the identified flora;
- upon entry into the body, it is able to penetrate into the bladder and accumulate in bile.
Surgical methods of treatment
Today there are two main methods of surgical treatment for cholelithiasis:
- Laparoscopic cholecystectomy
- with this method, the intervention is performed using laparoscopic equipment through small incisions on the anterior wall of the peritoneum, through a puncture in the umbilical area or transvaginally. Today, laparoscopy is recognized as the “gold” standard in abdominal surgery. Among the advantages of this method, it is worth noting the excellent cosmetic result: only small incisions remain on the skin. The rehabilitation period is much shorter than with traditional surgical treatment. The patient begins to walk on the first day, and on the second day he is allowed to take liquid food. The operated patient usually leaves the clinic on the 2nd or 3rd day after the operation. A person can usually start work within 10-14 days. - Traditional cholecystectomy
is an open operation, performed manually, with a 15-20cm incision made on the anterior abdominal wall. Currently, surgical intervention using this method is performed only for complications of cholelithiasis (peritonitis, gallbladder perforation).
These operations are performed under general anesthesia, and the gallbladder is removed along with the stones according to the same procedure. If there is a single large or several small stones, the gallbladder is completely removed. Some patients ask about the possibility of removing only stones while preserving the gallbladder. It is possible to perform such surgical intervention. However, at this time there is no definite guarantee that the stones will not reappear. Today, specialists from all over the world are working on this problem, but stones often reappear within six months.
Watch a video of operations performed by Professor K.V. Puchkov. You can visit the website “Video of operations of the best surgeons in the world.”
Transvaginal laparoscopic cholecystectomy using the NOTES method
Rice. 6. Scheme of laparoscopic transvaginal cholecystectomy using NOTES technology
Rice. 7. View of the anterior abdominal wall during laparoscopic cholecystectomy using SILS technology.
Since 2007 in France, and since 2008 in the Russian Federation, a unique method of removing the gallbladder has been practiced - transvaginal cholecystectomy using NOTES technology. The operation is performed without any punctures of the abdominal wall, therefore, there are no postoperative scars. The essence of the surgical intervention is access to the affected organ through a small puncture (1 cm) of the posterior vaginal fornix. The intervention is performed using laparoscopic instruments and optics introduced into the peritoneal cavity through this access. After removing the gallbladder through the same access, one suture is placed on the puncture. The synthetic suture material used in this case dissolves within 3-4 weeks.
The advantages of this method are:
- in the absence of pain after surgery;
- the patient's motor activity is not impaired;
- short rehabilitation period, patient hospitalization lasts only one day;
- excellent cosmetic effect;
After 7-10 days after surgery, a person can begin to work, and they can play sports on the 14th day. Among the restrictions in the postoperative period should be the need to exclude intimate relationships for a month. At the same time, the genital organs (uterus, appendages, etc.) are not affected during transvaginal cholecystectomy, so their functionality remains unchanged.
Rules for antibiotic treatment
In his choice, the doctor is guided by certain requirements for antibiotic treatment.
- It is best to prescribe a drug with proven sensitivity to the identified causative agent of cholecystitis. If there is no time or opportunity to wait for the results, tank. analysis, use broad-spectrum antibiotics, then, upon receipt of a conclusion and the ineffectiveness of the previous therapy, replace with another.
- The dose is calculated based on the severity of the patient's condition, age and weight.
- The intravenous and intramuscular route of administration is preferred. You should not take pills against the background of vomiting and dyspepsia.
- The course of treatment should be at least 7–10 days. Interruption and extension are equally harmful and threaten the development of resistant forms of pathogens.
- During antibiotic therapy, it is imperative to prescribe vitamins (groups B, C). Being coenzymes in many biochemical processes of the body, these agents have a supportive anti-inflammatory effect.
- In the presence of mixed flora and concomitant chronic diseases, it is possible to prescribe combinations of antibiotics with other drugs. In this case, contraindications and compatibility should be taken into account.
Before starting antibiotic therapy, it is imperative to perform an intradermal test to detect increased sensitivity of the body.
Single-port laparoscopic cholecystectomy SILS
The use of the NOSE technique is technically impossible in cases where patients have undergone many surgical interventions on the pelvic organs in the past. Therefore, an equally effective method of minimally invasive cholecystectomy was developed, which has been used in America since 2008, and since 2009 such operations have been performed by domestic surgeons. We are talking about removing the gallbladder through a puncture in the navel area (SILS technology).
Single-port laparoscopic cholecystectomy
consists of performing an operation using a special device (port), which is a soft plastic apparatus that is inserted into the abdominal cavity through a puncture. Port diameter 23-24 mm. It is through this that laparoscopic instruments are inserted; the diameter of the laparoscope does not exceed 5 mm. Upon completion of the operation, a cosmetic suture is applied to the small wound. Surgical intervention using SILS technology (single-port surgery), in contrast to conventional laparoscopic access (multi-puncture), has a number of advantages:
- fewer punctures on the abdominal wall;
- less pain after surgery;
- shorter rehabilitation period;
- better cosmetic effect;
The advantages of this method of surgery are especially noticeable when there are multiple stones in the gallbladder - with the usual method, the surgeon must increase the puncture to remove stones and the diseased organ.
The choice of the appropriate surgical treatment method depends on the individual characteristics and health status of the patient. Visiting a clinic with qualified and experienced specialists guarantees the highest possible treatment results.