10/11/2017 Olga Migunova 3 comments
Erythematous gastropathy is an endoscopic sign that is often detected during fibroesophagogastroduodenoscopy. Various factors can contribute to the appearance of this symptom, ranging from an unhealthy diet to stress.
Timely elimination of the causative factor and correct treatment tactics make it possible to quickly and completely eliminate erythematous gastropathy.
Therefore, in this topic we want to tell you in detail about the causes and signs of erythematous gastropathy, as well as how to deal with this problem.
General information
Erythematous gastropathy is inflammation, redness and swelling of the gastric mucosa, caused by the influence of a number of negative factors or bacterial damage.
Quite often, erythematous gastroduodenopathy associated with damage to the pylorus of the stomach and part of the duodenum is diagnosed in parallel. The above conditions are not considered an independent nosology; these symptoms are diagnosed during clinical examinations of the patient. If gastropathy is detected, it is recommended to review your lifestyle and diet as soon as possible in order to avoid the development of gastritis and subsequent peptic ulcer of the digestive tract.
Erythematous gastropathy and gastroduodenopathy can provoke the development of bulbopathy - an inflammatory process in the loop connecting the duodenum to the intestine. The pathologies described above can occur simultaneously or sequentially as a result of exposure to chemicals or pathogenic microorganisms.
Consequences
There are two most common complications of erythematous gastropathy: gastritis and peptic ulcer. Sometimes, if this pathology is not treated, the mucous layer of the stomach may atrophy. In turn, against the background of atrophy of the mucous membrane, a malignant tumor of the stomach may appear.
Having seen the diagnosis of erythematous gastropathy in the conclusion of FEGDS, you should not be afraid, but you also should not ignore it. In this case, it is recommended to consult a gastroeterologist or general practitioner. If necessary, specialists will conduct additional research and give treatment recommendations that will allow you to avoid the above complications.
Classification
Pathology is divided into 2 types:
- Focal erythematous gastropathy . Characteristically, only part of the mucous membrane is affected (pylorus, antrum). Small areas of inflammation appear on the mucous walls. Focal gastropathy is easier to treat than other forms. Diet therapy is effective.
- Common gastropathy . The inflammatory process and redness covers the entire gastric mucosa. In the absence of adequate, competent therapy, the pathology develops into acute gastritis with the subsequent development of peptic ulcer of the digestive tract.
Gastropathy is also divided into several forms:
- Erosive . The upper part of the stomach is affected. Concave erosions of small diameter (about 7 mm) form on the mucous wall. gastritis develops . The main difficulty in diagnosis is the lack of clinical symptoms that can help in diagnosis. Pathology is a random finding during examination.
- Stagnant . Small wounds appear on the mucous membranes. Patients complain of discomfort after eating, belching, and heartburn.
- Papular . It affects the lower part of the stomach in the form of small ulcers on the mucous wall. Develops against the background of increased acidity of gastric juice. It is practically asymptomatic.
- Antral gastropathy . Characteristically, the lower antrum of the stomach is affected, as a result of which the food bolus slowly moves towards the duodenum and is difficult to crush. Food stagnates and fermentation processes begin. In the absence of timely and competent therapy, gastritis develops with atrophic damage to the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract.
Erythematous-exudative gastropathy is a finding during gastroscopy. The exudative form involves the production of a small amount of exudate when damage occurs to the mucous membranes of the stomach.
Depending on the degree of damage to the epithelial layer, gastropathy is divided into:
- Erythematous gastropathy of the 1st degree of inflammation . Lesions of the epithelial layer in the digestive tract in grade 1 are minimal. The pathology is asymptomatic.
- Erythematous gastropathy of the 2nd degree of inflammation . Changes in the epithelial layer are minor, but noticeable. Grade 2 is characterized by a progressive course. The situation is aggravated when exposed to damaging factors. In adult patients, the disease becomes chronic.
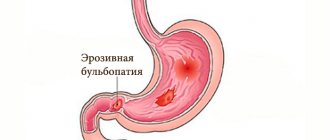
Erythematous bulbopathy
A chronic inflammatory process affects the duodenal bulb, or rather its initial section, which is located immediately behind the final section of the stomach. The mucous membrane takes on a swollen appearance and red oval spots form on it. When erosive defects appear, they speak of erosive bulbopathy , which is the most severe form of bulbitis .
Erythematous colopathy
It is characterized by the appearance of erythematous spots on the walls of the small and large intestines. When exposed to unfavorable factors, erythema turns into erosion and ulcers.
Kinds
Erythematous gastroduodenopathy varies in forms of manifestation and in the degree of the inflammatory process. The first criterion evaluates the territorial distribution of the area of redness; they are of two types:
- the focal form implies local lesions occupying separate small parts of the upper layers of the stomach. This is the safest type of phenomenon. It occurs with minor deviations in the diet, and rarely results in an independent diagnosis of gastritis. May be caused by a reaction to medications;
- diffuse type (common) is characterized by damage to large areas of the stomach. Redness and swelling can simultaneously affect several parts of the organ. The advanced form progresses to gastritis and can cause additional stomach problems. There is a possibility that the resulting lesions appeared after consuming heavy irritating food or alcohol on the eve of the examination.
Treatment of focal erythematous gastropathy is much faster and does not pose any danger. The common form transforms when symptoms are ignored.
The disease is classified into two degrees of inflammation. The characteristic is determined by monitoring the condition of the surface layer of the mucosa and the stage of impact on the lining of the stomach. The first degree of inflammation is the primary manifestation of deformation of the integument of the organ under study. The second stage indicates the development of the process. This means that the stomach continues to be influenced by external, provoking factors.
Causes
Erythematous gastroduodenopathy and gastropathy develop under the influence of a number of unfavorable factors:
- Stress. Psychotraumatic factors stimulate the production of the hormone adrenaline , which enhances the production of hydrochloric acid. Prolonged exposure to high concentrations of gastric juice leads to irritation of the gastric mucosa, its redness, followed by the formation of ulcerative lesions and erosions.
- Unbalanced nutrition , diet . Long-term consumption of irritating and heavy foods causes inflammation in the gastric mucosa.
- Uncontrolled use of medications . Some medications have a negative effect on the functioning of the digestive tract, disrupting their normal functioning. Quite often, duodenopathy develops precisely while taking medications.
- Presence of Helicobacter pylori in the body . H. pylori is able to penetrate the gastric mucosa, triggering inflammatory processes in it.
- Heredity . The risk of developing erythematous gastropathy is very high if the pathology has ever been diagnosed in close relatives. In predisposed patients, the influence of even seemingly insignificant factors can trigger the development of a pathological process.
- Leading an unhealthy lifestyle . The lack of constant oxygen exchange, a sedentary lifestyle, and the presence of bad habits lead to stagnation in the body, which negatively affects the functioning of the digestive tract.
Treatment
In cases where erythema in the stomach appears as a result of taking medications, you must inform the doctor who prescribed them.
If possible, the drug will be discontinued or replaced with another that is safer for the stomach. But it happens that the treatment cannot be replaced by another, so the drug that caused gastropathy must be covered with a gastroprotector (Omeprazole, Rabeprazole, Pantoprazole) or an antacid (Phosphalugel, Almagel). You should definitely quit smoking or drinking alcoholic beverages, which negatively affect your stomach. It is also necessary to avoid psycho-emotional shocks, limit physical activity, and normalize sleep and rest patterns.
When the pH of gastric juice increases, patients are prescribed drugs that reduce acidity, namely:
- proton pump inhibitors (Omeprazole, Rabeprazole, Pantoprazole and others);
- antacids (Almagel, Phosphalugel);
- bismuth preparations (Vis-Nol, De-Nol).
Also included in the treatment regimen are gastroprotectors (Gastrocepin, Gastrofarm), which protect the gastric mucosa and accelerate its recovery.
If Helicobacter pylori is detected in the stomach, then patients are prescribed anti-Helicobacter drugs (Metronidazole, Amoxicillin).
All medications should be prescribed exclusively by the attending physician, since each medicine has a number of side effects and contraindications.
In difficult cases, when conservative therapy does not help, surgical intervention may be considered, during which the affected area of the stomach will be removed.
Very often, traditional therapy is supplemented with folk remedies, among which the most effective are decoctions and infusions of medicinal plants (chamomile, plantain, celandine, St. John's wort, nettle and others), vegetable oils (linseed, pumpkin, flaxseed, sea buckthorn) and flax seed products.
Symptoms
Erythematous gastropathy is characterized by a certain clinical picture. Main symptoms:
- discomfort in the epigastric region after eating;
- heartburn;
- belching;
- vomiting (rare);
- stool disorders (vomiting/diarrhea);
- nausea;
- a specific taste in the mouth with a putrefactive component;
- weight loss due to lack of appetite;
- decreased performance, deterioration in general well-being, lethargy and apathy.
Erythematous gastropathy is additionally manifested by the deposition of a white coating on the tongue, especially in the morning.
What is duodenopathy
Duodenopathy (duodenitis) is a common symptom complex, inflammation of the lining membranes of the duodenum of a chronic, recurrent nature . With combined inflammation with the lining of the stomach, they speak of gastroduodenopathy.
The inflammatory process is constantly progressing, despite the periodic occurrence of symptoms. The clinical picture of gastroduodenopathy resembles a stomach and duodenal ulcer, and with duodenopathy of the lower digestive tract - cholecystitis, acute pancreatitis. Patients complain of weakness, pain during meals or at long intervals between meals, sour belching, and flatulence.
Note! Gastroduodenopathy accounts for 34% of all diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and is a trigger for peptic ulcers, gastritis, and erosion. Inflammation of the duodenum is chronic in almost 90% of clinical cases.
The disease code according to ICD-10 is K29 - gastritis and duodenitis.
Classification
There are several classifications of the disease : according to the form, prevalence and type of duodenopathy.
are classified according to form , and limited and generalized inflammation according to prevalence.
, which is determined through endoscopic diagnosis, is also of great clinical importance
- Erythematous duodenopathy . The main feature is redness and slight swelling of the membranes of the duodenum. The erythematous form is often combined with other diseases and changes in the structure of the intestinal mucosa along its entire length.
- Hyperemic . Hyperemia is diagnosed if the membranes of the duodenum are swollen, the mucous membrane is loose, red, and there are bruises.
- Erosive . The formation of erosive foci on the lining membranes due to trauma, burns, stress, and severe metabolic disorders. Gastropathy with the formation of ulcerative-erosive foci is often combined with organ failure and becomes a consequence of the pathogenic activity of Helicobacter pylori infection and gastroesophageal reflux.
- Stagnant . The disease is accompanied by impaired motor function of the small intestine, and decreased peristalsis is observed. The bolus of food stagnates, and the gastric juice contained in it leads to inflammation. With chronic stagnation, duodenogastric reflux is formed - the reflux of chyme from the lumen of the duodenum back into the stomach. Congestion poses a danger to the function and integrity of the membranes of all parts of the digestive organs.
- Catarrhal . Inflammation is often caused by congestive duodenopathy. In the esophagus there is an alkaline environment, in the stomach there is an acidic environment, reflux and congestion contribute to an imbalance of microflora; in different parts of the intestine, enzymes characteristic of one organ negatively affect the membranes of other parts of the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms are often vague, and it is quite difficult to identify the disease at an early stage.
- Focal . One of the violations of the integrity of the membranes of the duodenum is focal (limited) erythematous duodenopathy. When multiple lesions appear, they speak of the development of a diffuse form of the disease. According to the results of endoscopy, the membranes are hyperemic and inflamed. The danger lies in the appearance of crater-shaped wounds, which, if left untreated, can transform into a peptic ulcer.
- Superficial . One of the common forms of the disease, the initial stage of pathological changes. Lack of treatment leads to chronic duodenopathy. The membranes thicken, and swelling of other parts of the gastrointestinal tract is observed.
- Atrophic . The disease becomes a consequence of tissue atrophy and impaired secretion of important digestive enzymes. This form is accompanied by the development of gastritis and gastric or duodenal ulcers.
We recommend: Signs of spastic colitis and how to treat it
According to morphology, duodenopathy is classified into follicular (lymphoid duodenopathy) and moderate type of changes in epithelial structures. This also includes erythematous proximal duodenopathy.
The key difference between all forms of gastroduodenopathy is the degree of damage to the membranes of the gastrointestinal tract; one type can transform into another and be complicated by an infectious process.
Why is it dangerous?
The main danger is associated with irreversible changes in the functions of the intestines and stomach , the spread of pathological changes throughout all parts of the digestive tract.
Damage to the mucosa during gastroduodenitis (photo)
Lack of therapy and non-compliance with clinical recommendations often lead to ulceration of inflammatory foci , disruption of the integrity of the lining membranes and deeper submucosal layers. Atrophic processes can become a trigger for cell atypia and the occurrence of a cancerous tumor.
Tests and diagnostics
Based on the examination of the patient, the results of laboratory and instrumental studies, a diagnosis of “Erythematous gastropathy” is made.
Laboratory research methods:
- fecal analysis (presence of occult blood, assessment of quantitative/qualitative composition, identification of atypical impurities);
- blood analysis;
- Analysis of urine;
- pH-metry;
- examination of gastric juice .
Instrumental methods for studying erythematous gastropathy and duodenopathy:
- Manometry. Allows you to evaluate the evacuation capacity of the digestive tract by determining the speed of motility.
- Electrogastroenterography.
- Fibrogastroduodenoscopy.
- Colonoscopy.
- Ultrasound of the stomach and intestines.
In difficult situations, computed tomography, MRI and other radiation diagnostic methods are prescribed. It is very important to correctly differentiate duodenopathy from gastrointestinal ulcers, gastritis , ulcerative colitis and other gastrointestinal pathologies of inflammatory and non-inflammatory nature.
Most often, erythematous gastropathy is an incidental finding during examination of the digestive tract for other reasons. If necessary, a biopsy of material taken from the stomach wall is performed.
How to diagnose and detect the disease
The very first thing a doctor does with a patient is a general examination. May appear:
- paleness of the skin, visible mucous membranes (oral cavity, sclera),
- coating of the tongue from white to grayish shades;
- There may be an unpleasant odor from the oral cavity;
- the patient himself may notice increased dry mouth and constant thirst.
Then the doctor must evaluate the secretory function of the stomach using pH-metry manipulation. The secretory function at the beginning of the disease is a quantitative increase in gastric secretion and acidity (pH), then hypersecretion is replaced by inhibition of the functions of the gastric glands.
If necessary, an x-ray examination is prescribed. There are no characteristic radiological signs; a slowdown in motor and evacuation functions is detected due to hypotension, atony or spasm of the pylorus.
An important diagnostic method is gastroscopy. However, this method is not indicated for everyone for this pathology. If there is a suspicion that the disease is caused by mechanical damage or chemical exposure, then the procedure may further aggravate the course. Therefore, gastroscopy is performed only in the remission stage.
During the procedure, signs such as:
- redness and swelling of the mucous membrane;
- infiltration by the body’s protective cells – leukocytes;
- full-blooded vessels.
Treatment of erythematous gastropathy with folk remedies
Among folk remedies, they most often resort to herbal medicine, which helps suppress the severity of the inflammatory process and heal wounds.
- Honey . Take a teaspoon of candied honey into your mouth and hold until completely dissolved, gradually swallowing. The procedure must be carried out three times a day.
- A decoction of three herbs . Chamomile flowers have an anti-inflammatory effect, nettle leaves promote wound healing, and oak bark has an astringent effect. All dried components are mixed in equal proportions, brewed and taken as a solution, 1 tablespoon after each meal. Preparation of the solution: pour boiling water (250 ml) into three tablespoons of the herbal mixture, let it brew for 2 hours and strain.
Diet for erythematous gastropathy
Diet for erythematous gastropathy
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after 14 days
- Terms: 14-21 days
- Cost of products: 1500-1600 rubles. in Week
Drug treatment is not always sufficient to achieve maximum results in the treatment of erythematous gastropathy. Following a special diet can reduce treatment time and improve the prognosis.
All foods that irritate the gastric mucosa and cause congestion are completely excluded from the diet:
- fatty meats;
- cabbage and legumes;
- snacks;
- semi-finished products;
- fast food;
- smoked and pickled products;
- pickles and spicy dishes;
- mushrooms.
The diet must include fresh vegetables, herbs, dairy products, and fruits in moderate quantities.
Lifestyle correction involves proper distribution of diet. There should be at least three nutritious meals daily. It is advisable to eat small portions to avoid overeating. The food should be warm.
Playing light sports, which improve metabolic processes throughout the body, has a positive effect on the healing process.
How to treat pathology
To select the correct treatment regimen, it is necessary to establish the factors that provoked the onset of the disease. Another important point when prescribing treatment is the presence of concomitant pathologies, this could be erosive or chronic gastritis, gastroduodenitis.
When it is determined that the cause of gastropathy is the medications used, it is recommended to replace them. If this is not possible, medications are used that protect the stomach from the influence of negative factors.
Medicines prescribed for erythematous gastropathy:
- antisecretory agents - “Kvamatel”, “Nolpaza”, “Omeprazole”, “Pariet”. They reduce the synthesis of the main irritant of the mucous membrane - hydrochloric acid.
- gastroprotectors – “Vicair”, “De-Nol”, “Vikalin”. They protect the walls of the organ, have an astringent and anti-inflammatory effect.
- antacids - “Maalox”, “Almagel”, “Gastal”. These drugs help lower acidity, reduce the aggressiveness of the gastric environment, bind and remove pathogenic substances.
- regulating motor skills - “Itoprid”, “Ganaton”. They are prescribed in case of stagnation, fermentation and rotting in the stomach.
When the bacterium Helicobacter pylori is present, antibiotic therapy is prescribed.
In very rare cases, there is a need for surgical intervention. To do this, resection of the affected areas is performed.
Diet for erythematous gastropathy
Therapy for erythematous gastropathy will not be effective without diet correction.
Compliance with the following rules will help normalize nutrition and get rid of irritating effects on the organ:
- It is recommended to steam food;
- it is important to avoid eating irritating foods, such as: spices, smoked foods, spicy foods, pickles;
- It is prohibited to drink carbonated drinks, coffee, or alcoholic drinks. It is recommended to replace black tea with green, herbal infusion or plain water;
- The basis of nutrition consists of lean meats and fish, lean broths, liquid porridges, and jelly. It is allowed to eat jelly, cottage cheese, egg whites;
- All dishes should be eaten at room temperature. Too cold or hot dishes can cause irritation of the mucous membranes and lead to spasm of smooth muscles;
- It is recommended to eat at intervals of several hours;
- portions should be small - no more than 350 g. This helps to avoid increased stress on the digestive organs;
- you should not overeat. Excessive food volume contributes to the onset of rotting in the stomach. This causes a feeling of heaviness, nausea, and belching.
The presence of pronounced negative symptoms or deterioration of the patient’s condition requires adherence to a strict “Table No. 1” diet.
Only with a combination of drug therapy and dietary nutrition, as well as lifestyle correction, can you quickly get rid of the pathology.
Traditional methods of treatment
Folk remedies can be used as complementary to drug treatment.
Traditional methods of treatment include the use of herbal infusions, decoctions, freshly squeezed juices, etc. For example, oat decoction has an enveloping effect. For low acidity, it is good to drink fresh cabbage juice. You can use various herbs and medicinal plants: chamomile, fennel. The use of these remedies is aimed mainly at gently relieving inflammation and improving digestion.
Forecast
The pathology does not pose a serious danger to humans, however, in the absence of timely and competent therapy, the pathological process worsens, leading to the development of gastroduodenopathy, peptic ulcer of the digestive tract , and gastritis . If erythematous changes that are asymptomatic are accidentally detected, the patient is recommended to change their lifestyle and follow a special diet, which guarantees complete restoration of the stomach wall.
Pathology prognosis
Erythematous gastropathy is not considered a dangerous disease, but requires timely and adequate treatment, otherwise the pathology can lead to the development of gastritis, ulcers or gastroduodenopathy.
Erythematous gastropathy often indicates an unhealthy lifestyle and eating unhealthy foods. If initial symptoms occur, timely drug therapy and following a proper diet will help you quickly and completely get rid of the disease.
References: https://ilive.com.ua/health/eritematoznaya-gastropatiya-ochagovaya-diffuznaya-erozivnaya-antralnogo-otdela-zheludka_116745i15938.html https://gi-capsule.by/content/v-chem-opasnost- eritematoznoy-gastropatii https://womanadvice.ru/eritematoznaya-gastropatiya Nutrition for gastric diseases, Ilya Melnikov 2009 Notes from the author of the article, based on personal experience. This material is purely subjective and is not a guide to action. Only a qualified specialist can determine an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Last modified: 03/17/2020