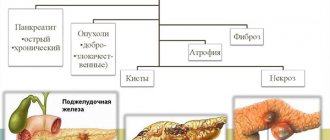
Catarrhal duodenitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the duodenum, not the most common disease of the gastrointestinal tract. Most often, men suffer from this disease, and often the disease becomes chronic and can haunt a person throughout his life.
What is gastric duodenitis?
Classification of duodenitis
There are two forms of duodenitis:
- Spicy. Symptoms of inflammation are pronounced. After therapy they disappear, leaving no changes in the structure of the mucosa.
- Chronic. Has a long relapsing course. Foci appear in the mucous membrane, contributing to changes in its structure.
In turn, gastroenterologists classify chronic duodenitis according to:
1. Localization of pathological foci of inflammation on:
- diffuse;
- local;
- bulbar;
- postbulbar.
2. By origin on:
- primary;
- secondary.
3. According to the degree of observed structural changes on
- atrophic;
- surface;
- interstitial.
4. According to the endoscopic picture on
- hemorrhagic;
- erythematous;
- nodular;
- erosive;
- atrophic.
There are also specific forms of duodenitis:
- fungal;
- immunodeficient;
- tuberculosis;
- with Crohn's disease;
- with Whipple's disease;
- with intestinal amylosis, etc.
In children, gastroduodenitis is more often diagnosed - simultaneous inflammation of the mucous membrane of the duodenum and stomach (a form of chronic gastritis).
pharmaceutical camomile
Another plant widely used for medicinal purposes is chamomile. Flower baskets are used in traditional pharmacology, as their medicinal properties have been proven by numerous studies. This plant has a variety of properties and is used both internally and externally. Preparations based on this plant have anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties, have a choleretic, hemostatic, antispasmodic and sedative effect. Treatment of duodenitis in adults can be combined with the use of decoctions or infusions of chamomile. The infusion is prepared from a tablespoon of dried inflorescences poured into 1 cup of boiling water. The medicine is infused in a closed bowl or saucepan for 20 minutes, then drained through a fine strainer or gauze and squeezed. Drink this infusion 1/3 of a glass 3 times a day.
Causes of duodenitis
The mechanism of development of inflammation of the duodenum is inextricably linked with damage to the mucous wall by hyperacid juice coming from the intestines. Reduced protective properties of the duodenal wall, along with increased acidity, lead to severe irritation of the mucous membrane. As a result, acute inflammation occurs.
If the disease does not have pronounced symptoms, over time it transforms into a chronic process and acquires a recurrent cyclic course. The intestinal wall begins to atrophy, and degenerative processes are observed in it.
Doctors include factors contributing to the development of duodenitis:
- alcohol abuse;
- frequent consumption of fatty, spicy and smoked foods;
- poisoning with toxins (poisonous mushrooms, berries), medications;
- the presence of helminthic diseases (opisthorchiasis, ascariasis, giardiasis, enterobiasis), leading to decreased immunity, the addition of secondary bacterial infections, and mechanical damage to tissues.
Also, the causes of severe duodenitis may lie in other gastrointestinal diseases. There is a high risk of encountering inflammation of the mucous membrane of the duodenum in people with:
- gastritis;
- peptic ulcer of the stomach, duodenum;
- cholecystitis;
- pathologies of the pancreas (pancreatitis, diabetes mellitus);
- cholelithiasis;
- postcholecystectomy syndrome (caused by removal of the gallbladder);
- Crohn's disease (all layers of the intestine are damaged);
- celiac disease;
- viral hepatitis A;
- Zollinger-Ellison syndrome (gastritis-secreting tumor of the pancreas);
- tumor of the stomach, esophagus, pancreas.
The bacterium Helicobacter pylori also has a negative effect on the condition of the mucous membrane of the duodenum.
Fennel fruit
A plant such as fennel has been used for many centuries as a flavoring additive in the confectionery and perfume industries. But in addition to the pleasant aroma, the fruits of the plant have diuretic, antispasmodic, and antimicrobial properties. Fennel infusion is prepared from its fruits as follows: pour a teaspoon of seeds with 1 glass of boiling water and leave, covering the container with a lid, for 10 minutes. Then it is poured into a glass, passed through several layers of gauze, and squeezed out. You should take half a glass of fennel infusion 2-3 times a day, best before meals.
Symptoms of duodenitis
The severity of the pain syndrome is determined by the form of damage to the duodenum.
- With superficial duodenitis, when the mucous membrane is slightly damaged, the patient feels discomfort in the navel area (usually in the upper abdomen).
- With atrophic duodenitis (the mucous membrane is thinned, the duodenal glands of the intestine are damaged, the process of secretion of digestive juices is disrupted), pain may be completely absent. In this case, the patient feels irritability, weakness, increased fatigue, headaches, and dizziness.
Common symptoms of all forms of duodenitis include:
- decreased appetite;
- vomiting (can be single or multiple, relieves the condition);
- nausea (occurs immediately after eating);
- heartburn, bloating;
- abdominal muscle tension;
- prolonged hiccups (about half an hour);
- bitter belching;
- increased body temperature;
- bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract caused by damage to the intestinal walls.
Clinical forms of duodenitis:
- gastritis-like (stomach pain occurs 15-20 minutes after eating, vomiting, nausea, belching, flatulence, diarrhea, loss of appetite are observed);
- ulcer-like (the stomach hurts at night and when the patient wants to eat, there may be a bitter belch);
- pancreatic-like/cholecyst-like (acute severe pain localized in the left or right hypochondrium is observed, there are signs of dyspeptic disorder, cholestasis);
- neurovegetative (asthenoneurotic autonomic disorders are clearly expressed);
- mixed (symptoms of different clinical forms of duodenitis are present);
- asymptomatic (more often observed in older people).
If you experience similar symptoms, consult your doctor
. It is easier to prevent a disease than to deal with the consequences.
Advantages of SM-Clinic
Our medical center employs some of the best pediatric gastroenterologists in St. Petersburg. The clinic has advanced diagnostic equipment and its own laboratory. With us, your child will be able to undergo the necessary examination without queues and in a comfortable environment. If hospitalization is necessary, we provide comfortable rooms and provide nutritious and tasty meals.
Call us to make an appointment and ask any questions you may have.
Sources:
- M.N. Repetskaya, O.M. Burdina. Modern features of the course of chronic gastroduodenitis in children // Perm Medical Journal, 2022, vol. XXXIV, No. 3.
- A.A. Baranov, P.L. Shcherbakov. Current issues in pediatric gastroenterology // Issues of modern pediatrics. 2002, vol. 1, no. 1, p. 12-16.
- M.Yu. Denisov. Practical gastroenterology for pediatricians: reference book. manual // M.: Publisher Mokeev, 2000. 296 p.
Grek Elena Anatolyevna Clinic
Author of the article
Grek Elena Anatolyevna
Doctor of the highest qualification category
Specialty: gastroenterologist
Experience: 24 years
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.
Diagnosis of duodenitis
Diagnosis of duodenitis includes:
1. Assessment of patient complaints. The doctor clarifies when stomach pain appears and whether it worsens depending on the season. Finds out whether the patient has suffered from intestinal infections, poisoning, or other gastrointestinal diseases.
2. Analysis of family history. Allows you to determine hereditary predisposition to a particular disease.
3. Inspection. Abdominal tenderness on palpation is determined.
4. Laboratory research:
- biochemical and clinical blood tests (show whether there is an inflammatory reaction, what is the level of hemoglobin, red blood cells, whether there are diseases of the pancreas, liver, kidneys, etc.);
- general urine analysis;
- stool analysis to exclude bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract;
- coprogram.
5. Instrumental research methods:
— Ultrasound of the abdominal organs. Makes it possible to study the condition of the bile ducts, gallbladder, kidneys, pancreas, and intestines.
- EGDS - examination of the condition of the inner surface of the esophagus, duodenum, stomach using an endoscope (a biopsy must be taken).
— Determination of the presence of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori in the gastric material, which damages the walls of the duodenum and stomach.
— Colonoscopy (examination of the inner surface of the colon using an endoscope).
— Test of stomach acid production (if the acidity is below 2.0, the patient can be assumed to have duodenitis or gastroduodenitis).
— X-ray of the stomach with double contrast. It is carried out if the patient turns out to have an endoscopy.
— CT scan of the abdominal organs. Allows you to assess in detail the condition of internal organs, to exclude the presence of a tumor or damage to the intestine.
Complex structure
The gastrointestinal tract is a complex system in its structure, consisting of several departments and organs that perform certain functions, without which the normal process of digestion is difficult to imagine. One of the components of the gastrointestinal tract is the duodenum - a fairly short section that starts immediately from the stomach and is the structure of the small intestine. It performs several important functions:
- the contents of the stomach entering the intestine are brought to an alkaline pH in the duodenum, which will not irritate the following sections of the gastrointestinal tract;
- here the process of digestion of food begins;
- the duodenum takes part in activating the secretion of bile enzymes;
- maintaining the required level of acidity, the chemical composition of the food mass moving from the stomach to the intestines;
- implementation of feedback with the stomach: reflex interaction with the pylorus of the stomach, which depends on the acidity and chemistry of the incoming food mass.
The duodenum is an important element of the gastrointestinal tract; the functioning of the entire digestive system, the absorption of nutrients, and therefore the general well-being of a person depend on its functionality. There are many diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and duodenum. One of them is duodenitis.
Gastric duodenitis, the treatment of which requires a long time and compliance with many conditions for quality therapy, is a common diagnosis in modern medicine.
How to treat duodenitis
Treatment of duodenitis includes the use of:
- antibiotics if the bacterium Helicobacter pylori has been diagnosed;
- antiparasitic drugs if helminthic infestations are detected;
- proton pump inhibitors (medicines that reduce stomach acidity, minimizing its negative effects on the mucous membrane);
- painkillers and antispasmodics for severe pain and spasms.
Properly selected treatment for duodenitis allows:
- destroy Helicobacter, if any;
- protect the duodenal mucosa;
- restore normal digestion.
If duodenitis has led to the formation of adhesions and functional obstruction, which cannot be eliminated with conservative therapeutic treatment, surgery is performed.
If you plan to treat duodenitis with folk remedies, it is important to consult your doctor first so as not to worsen the situation.
Simple tips
Traditional medicine is the centuries-old experience of generations of therapy with the help of plants, products of plant or animal origin for many diseases. One of the fairly common diseases is duodenitis. Treatment with folk remedies for such a disease can be of auxiliary value in traditional therapy. Here are some simple recommendations:
- Sea buckthorn oil prepared at home should be taken in the morning on an empty stomach, one large spoon. It is prepared like this: half a kilogram of sea buckthorn berries in a ceramic or glass bowl is ground using a wooden masher. The resulting slurry is poured with olive oil, taken in the amount of half a liter. Mix everything and pour it into a jar or bottle, seal it and leave it for 2 weeks in a place protected from sunlight. Then the oil is filtered and squeezed out. The remaining mass is rubbed through a sieve to obtain a homogeneous paste, which is added to the drained oil. Everything is mixed again, the mixture is taken as medicine. The course lasts 2 weeks, then you need to take a week break and repeat the treatment.
- It is necessary to include a variety of jelly in the diet, which, with the help of their mucous structure, will protect the walls of the stomach and intestines from irritation.
- Ordinary potato decoction has the same protective properties - it should be poured into a glass, do not add salt, and drink warm when pain occurs.
- An ancient helper for many human health problems is aloe. This plant has high biological activity. Treatment of duodenitis with the help of such a plant implies the following: from a plant that has reached the age of 3 years, cut off the leaves so that it weighs half a kilogram. They need to be washed and dried with a napkin. Then the aloe leaves are crushed and their juice is squeezed out. The resulting amount of juice is mixed with 0.5 liters of red wine and 500 g of honey. Mix everything and keep in a dark place for 10 days. Take the strained medicine as follows: 1 week - 1 teaspoon per day, the next 14 days - 1 tablespoon 3 times a day, 4 week - 1 teaspoon 3 times a day. Take the medicine before meals.
Folk treatment for duodenitis undoubtedly receives very different reviews. Many note positive dynamics in the treatment of this disease. The effectiveness of herbal medicine is especially noticeable in combination with drug treatment. When deciding to take a decoction or infusion, even one or more components, you should consult your doctor. Some plants may have undesirable effects on the body of a particular person, some products have contraindications for use under certain circumstances.
Diet for duodenitis
It is impossible to get rid of duodenitis by ignoring the principles of a healthy diet. It is important to avoid smoked, fried, canned and too hot foods. Patients with acute form should follow Table No. 1. They are allowed:
- weak tea, cocoa;
- low-fat cottage cheese;
- wheat bread (yesterday's);
- eggs (1-2 pieces per day);
- semolina, oatmeal, buckwheat porridge;
- puree soups.
- Prohibited:
- fresh baked goods;
- smoked meats, pickles;
- sorrel;
- salo;
- spinach;
- black coffee;
- alcoholic drinks;
- chocolate, ice cream;
- fatty fish and meats.
When treating chronic duodenitis, you must follow Table No. 5. Allowed to eat:
- lean beef, chicken;
- non-acidic fruits;
- crumbly porridge;
- soups prepared with vegetable broth;
- skim cheese;
- wheat bread.
Drink weak tea and compotes. The same products are prohibited as when following Table No. 1.
Wild strawberry
An inconspicuous plant hiding in the grass - wild strawberry - in addition to the amazing aroma and sweet taste that its berries give people, has long given people medicine in the form of carved leaves. Strawberry leaves are a universal remedy that has many medicinal properties, and they optimally correspond to the problems of duodenitis:
- anthelmintics;
- antiviral;
- choleretic;
- diuretics;
- wound healing.
Strawberry leaves are used additionally in the treatment of duodenitis in children. You can use not only strawberry leaves, but also fresh berries, which have been used for centuries as a vitamin and medicine that has a positive effect on digestion. It should be remembered that the berries should not be eaten by those who suffer from an allergy to strawberries. You should also not overeat them, as diarrhea and vomiting may develop. The infusion is prepared as follows: a tablespoon of crushed dry wild berry leaves is poured into a glass of boiling water. The medicine needs to be infused for 2 hours, then it should be drained through gauze or a bandage and squeezed out. It is necessary to take an infusion of wild strawberry leaves 3-4 times a day, half a glass.
Why is duodenitis dangerous?
The prognosis for acute and chronic duodenitis is favorable. However, in some cases, patients develop serious complications:
- stomach bleeding;
- periduodenitis (the outer membrane of the duodenum becomes inflamed);
- peptic ulcer of the duodenum and stomach;
- duodenal hormonal insufficiency (little hormones are released);
- stenosis of the pylorus of the stomach (at the site of transition to the duodenum, the stomach narrows greatly);
- malignant tumor of the stomach;
- intestinal obstruction;
- phlegmonosis (purulent inflammation of the tissues surrounding the duodenum).
Len - assistant
One of the medicinal plants used for many diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, not excluding duodenitis, is flax, or more precisely, flax seeds. The medicine is prepared from them like this: a teaspoon of this substance must be crushed into a paste, and then poured with one glass of boiling water. Cover the container with a lid and a towel to allow the medicine to infuse for 20-30 minutes. Then the infusion is squeezed out and drunk all at once. This must be done before meals, approximately 1 hour. Therapy with flax seeds is continued for at least 1 month.