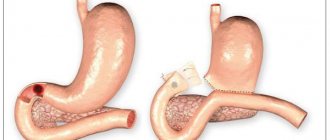
Causes
One of the most common causes of inflammation of the gastric mucosa can be considered food poisoning, which is often caused by poor-quality food, rotting products, bacteria, and the consumption of strong alcoholic beverages. The cause of inflammation can be irritation of the stomach wall with food, for example, eating excessive amounts of food. All kinds of poisons have a detrimental effect on the body - alkalis, acids, mercury preparations, prolonged use of a number of drugs, as well as the body’s high sensitivity to certain products (crayfish, eggs, strawberries, etc.). As a rule, only the gastric mucosa is affected, but in some cases muscle tissue can also be affected.
Major stomach diseases
10.10.2019
The hollow muscular organ that is located between the duodenum and esophagus is called the stomach. It is part of the digestive system (digestive tract). In terms of importance, the process of digesting food comes in second place. In this regard, any deviations in the activity of the duodenum, as well as the stomach, lead to the fact that other body systems begin to malfunction.
Symptoms of stomach diseases
Symptoms indicating problems with the stomach are divided into 3 categories:
- the appearance of pain in the epigastric region;
- discomfort in the stomach area;
- dyspepsia.
Most often, painful sensations appear after eating, on an empty stomach. You can reduce their manifestation by drinking a glass of milk. If you feel the stomach , a person may experience pain in the area under the stomach.
Heaviness in the stomach felt immediately after eating, even after a small portion of food, is called “gastric discomfort.” Heaviness in the area under the stomach appears even before a person has eaten enough.
Dyspepsia – disturbances in gastric activity. Such disorders include nausea , heartburn , bloating, vomiting and even belching . They appear after a person eats in cases where there are disturbances in the functioning of the stomach. After an attack of vomiting, a person usually feels much better.
Chronic gastritis
What is gastritis ? A disease in which the stomach lining becomes inflamed. Typically, the chronic form appears if it is long-term in nature, that is, it lasts for several years. Moreover, at this time there are attacks of both calm and exacerbation.
This disease is very common. Even if gastritis in a chronic form weakly or there are no manifestations at all, the process of inflammation continues. How dangerous is this disease? On its basis, other diseases develop, the severity and severity of which is much greater. These are tumors, various ulcers and various polyps. It is now customary to distinguish the following types of gastritis , which occurs in a chronic form:
- limited gastritis . In this case, only the exit area is affected by the inflammatory process;
- common gastritis . The body of the stomach itself becomes inflamed. Here are the glands that produce gastric juice.
Peptic ulcer
As a result of an increase in the amount of bile, as well as acid produced by the stomach, the walls begin to collapse. Persistent ulcers located on the mucous membrane, as well as the duodenum.
The causes of the disease include:
- alcohol;
- smoking;
- stress and shock to the nervous system ;
- lack of proper nutrition, that is, a diet without first courses, snacks;
- the labor regime is violated.
Stomach cancer
The exact causes are unknown, but it is assumed that they may be:
- genetics;
- constant smoking and alcoholism;
- toxic and chemical factors;
- some chronic diseases.
Functional stomach disorder
This is a disorder in which there are no changes in the anatomy of the mucous membrane. But the functions of the stomach are impaired.
There are quite a few reasons, here are some of them:
- physical factors;
- conditions in a person’s life change;
- stress, overstrain and conflicts;
- the diet is disrupted, the person abuses alcohol, smokes.
Erosion
Erosion of the stomach is a defect that is limited and does not penetrate deeply and heals. It differs from a regular ulcer in that in this case a scar does not form. Very often, erosions are accompanied by other gastric disorders.
There are internal and external reasons for the occurrence of erosion. Surgeries , burns, infections, and extensive injuries are classified as internal causes. And causes such as drugs, alcohol, drugs intended for chemotherapy, steroid drugs against inflammation are classified as external causes.
Published in Gastroentorology Premium Clinic
Symptoms
Loss of appetite. Complete, partial loss or perversion of appetite. All these symptoms are characteristic of various diseases and arise due to damage to the walls of the stomach or disruption of its peristalsis.
White coating on the tongue. A consequence of excessive desquamation of the epithelium of the tongue. It is one of the first symptoms of stomach damage.
Belching. May occur when the stomach muscles contract while the cardiac opening is open. There are several types of belching:
- by air;
- with the smell of hydrogen sulfide;
- with a bitter aftertaste;
- sour;
- with a putrid odor;
- with the smell of rancid oil.
Heartburn. It is evidence of a violation of the tone of the lower part of the esophagus and the cardiac part of the stomach, because of this, the acidic contents of the stomach are thrown into the lumen of the esophagus.
Pain in the epigastric region. The pain can be different: pulling, cutting, squeezing, sharp, etc.
Nausea. This kind of sensation is associated with the antiperistaltic nature of stomach movements.
Vomit. Often, this symptom of stomach disease manifests itself when the stomach receptors are irritated by food of poor quality or due to a pathological disorder of their functioning.
Constipation. This symptom is characteristic of gastritis with high acidity of gastric juice, and is also a manifestation of gastric ulcer. The mechanism of their occurrence is a decrease in intestinal motility.
Diarrhea. They are often a sign of gastritis with low acidity. The mechanism of their occurrence is the opposite of constipation.
Loss of body weight. It occurs when, against the background of atrophic or inflammatory processes, disturbances in the digestion and absorption of substances develop.
Temperature increase. This symptom of stomach disease is characteristic of acute inflammatory processes in it.
Diseases of the stomach and duodenum
The most common chronic diseases of the stomach and duodenum are gastritis, duodenitis and peptic ulcer . With chronic gastritis, inflammation of the gastric mucosa is observed, with duodenitis - the mucous membrane of the duodenum. Peptic ulcer disease is manifested by the formation of a defect (ulcer) in the mucous membrane of the stomach or duodenum. The most characteristic symptom of these diseases is pain in the epigastric region. The connection between pain and food intake is noteworthy. Moreover, depending on the location of the pathological process, pain can be early, late, or hungry. With an ulcer of the gastric antrum and duodenal bulb, pain may occur at night, forcing the patient to wake up and eat. The nature of the pain can be different - dull aching, cutting, stabbing, cramping, of varying intensity. Less commonly, patients complain of belching, heaviness in the stomach, fullness of the stomach after eating, nausea, vomiting, which brings relief, loss of appetite, and body weight. Such manifestations can be alarming signs of pyloric stenosis (complications of peptic ulcers), as well as stomach cancer.
The causes of the development of chronic gastritis and peptic ulcer are similar. The bacterium Helicobacter pylori plays an important role. In 1994, WHO experts classified H. pylori as a carcinogen of the first risk group. When it enters the stomach, it can persist in it for a long time, multiply and damage the gastric mucosa, causing chronic inflammation, the appearance of erosions and ulcers, contributing to oncological pathology in a certain group of patients who have a hereditary predisposition, high acidity of gastric juice, disorders of local immunity, blood supply mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum, impaired gastric motility.
Treatment of diseases of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum
can be carried out using conservative (therapeutic) and surgical methods. Treatment tactics and duration should be determined by the attending physician.
Late treatment of diseases of the esophagus, stomach, duodenum, especially erosive gastritis, duodenitis, as well as peptic ulcers, and especially self-medication, can lead to the ineffectiveness of conservative therapy and the development of serious complications of the disease, which often requires immediate surgical treatment.
share information
0
Social buttons for Joomla
Diagnostics
Survey. Often, stomach diseases are chronic, develop gradually, and begin with minor symptoms. The patient is subjected to detailed questioning; first of all, the doctor seeks to find out what the patient’s diet is. Thus, the survey allows not only to correctly establish a diagnosis, but also to identify the cause of stomach disease.
Inspection and feeling (palpation). During examination, the doctor may note a protrusion of the epigastric region due to excessive filling of the stomach or significant swelling. The main physical method of examining the stomach is palpation. Percussion and auscultation, as a rule, do not have diagnostic value in this case, due to the fact that the stomach and intestines usually produce the same tympanic sound.
Study of the secretory function of the stomach. In diseases of the stomach, there are cases of changes in its secretory function. There is increased secretion (acidity), normal, decreased, lack of acidity or absolute absence of gastric juice.
X-ray examination. X-ray scanning of the stomach (as well as the intestines and esophagus) with an X-ray machine allows one to obtain a large amount of information. The patient takes a contrast mass (barium salts), it fills the stomach, allowing you to determine its shape and evaluate peristalsis.
Stomach ulcer
print version- home
- >
- For patients
- >
- Gastrointestinal diseases
- >
- Stomach ulcer
Gastric ulcer
is a chronic relapsing disease that occurs with periods of exacerbation and remission. Its main symptom is the formation of a defect (ulcer) in the wall of the stomach. Often ulcers form not only in the stomach, but also in the duodenum (duodenal ulcer). Other organs of the digestive system may also be involved in the pathological process, with the development of complications that threaten the patient’s life.
Since the mechanisms of occurrence of stomach and duodenal ulcers are largely similar, in Russia it is customary to talk about gastric and duodenal ulcers
.
In the mechanism of development (pathogenesis) of gastric ulcers and duodenal ulcers (DU), a leading role is played by a complex of disorders that lead to an imbalance between aggressive factors of the gastric environment and the protective mechanisms of the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum.
Aggressive factors include hydrochloric acid, which is produced in the stomach, bile acids produced by the liver and entering the duodenum, and reflux of the contents of the duodenum into the stomach.
Protective factors include mucus, which is produced by mucosal cells, normal blood circulation, and timely restoration of mucosal cells.
| Stomach ulcer |
Another important cause of stomach ulcers is infection with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori.
There are, in addition, a number of factors that contribute to the development of the disease and its exacerbation:
- prolonged or frequently recurring neuro-emotional overstrain (stress);
- increased acidity of gastric juice;
- the presence of chronic gastritis, gastroduodenitis;
- eating disorder;
- smoking;
- consumption of strong alcoholic drinks;
- use of certain medications (acetylsalicylic acid, butadione, indomethacin, etc.);
- genetic predisposition.
Relatively rare causes of gastric ulcers include adenocarcinoma, carcinoid, penetration of tumors of neighboring organs, sarcoma, leiomyoma, diabetes mellitus, foreign bodies in the stomach, Crohn's disease, lymphoma, syphilis, tuberculosis, HIV infection.
| Clinical picture of the disease The main symptom of exacerbation of a gastric ulcer and duodenal ulcer is pain in the upper abdomen, which, depending on the location of the ulcer, can radiate to the left half of the chest, scapula, thoracic and lumbar spine, left and right hypochondrium, various sections belly. The time at which pain occurs also depends on the location of the ulcer. | Localization of pain in case of gastric ulcer |
Symptoms of a stomach ulcer.
With an ulcer of the cardial part of the stomach, i.e.
its upper part, pain occurs immediately after eating, with ulcers of the body of the stomach, i.e. in its middle part, 1 - 1.5 hours after eating. Symptoms of an ulcer of the pyloric canal
, i.e. the lower part of the stomach,
and an ulcer of the duodenal bulb
are characterized by the appearance of pain 2-3 hours after eating, “hungry” pain that occurs on an “empty stomach” and decreases or completely disappears after eating, as well as night pain. In addition to pain, during exacerbation of a peptic ulcer, dyspeptic symptoms are noted - heartburn, sour belching, nausea, vomiting at the height of pain, which brings relief, and a tendency to constipation. Peptic ulcer disease is characterized by a spring-autumn exacerbation.
| Complications of the disease may include gastric bleeding of varying intensity, perforation (perforation) of the stomach, cancerous degeneration, etc. | Perforation (perforation) of the stomach wall |
Diagnosis of gastric ulcers and duodenal ulcers
begins with a study of the medical history, complaints and results of a physical examination, and additional research methods are used to clarify the diagnosis:
- X-ray examination, which in most cases reveals an ulcerative niche.
- Gastroduodenoscopy is the most reliable diagnostic method, allowing you to detect an ulcer, determine its nature, and take a biopsy (for stomach ulcers).
- Intragastric pH-metry
allows you to determine gastric secretion levels depending on the location of the ulcer.
pH-grams of a patient with gastric ulcer obtained using the Gastroscan-5 device (basal study 30 min, basal alkaline test 5 min, pentagastrin stimulation 45 min, alkaline test after stimulation 2 min) Treatment of gastric ulcers and duodenal ulcers
is necessary carry out only under medical supervision!
For peptic ulcers, drugs that reduce the acidity of gastric juice are almost always prescribed - most often proton pump inhibitors. Treatment of peptic ulcer associated with Helicobacter pylori requires the use of antibacterial agents.
Drug treatment is naturally necessary, but to a greater extent the outcome of the disease depends on the patient himself. He needs to adjust his lifestyle - diet, daily routine. It is necessary to reconsider the attitude towards bad habits - smoking and alcohol. You will find more detailed information in the section Advice for patients.
Doctors classify stomach ulcers as K25
in the International Classification of Diseases ICD-10.
Resources for healthcare professionals regarding gastric and duodenal ulcers
Printed materials
- Firsova L.D., Masharova A.A., Bordin D.S., Yanova O.B. Diseases of the stomach and duodenum // – M: Planida. – 2011. – 52 S.
- Skvortsov V.V., Odintsov V.V. Current issues in the diagnosis and treatment of gastric and duodenal ulcers // Medical alphabet. Hospital. - 2010 - No. 4. P. 13-17.
- Methods for diagnosing gastric and duodenal ulcers. Website "Medicine of Rostov".
- Narezkin D.V., Belkov A.V., Stupin V.A., Siluyanov S.V., Smirnova G.O. Variants of the course of duodenal ulcer in patients of different ages. Department of Hospital Surgery No. 1, Russian State Medical University.
- Stupin V.A., Siluyanov S.V., Afanasyev V.V., Baglaenko M.V., Sabirov M.A., Smirnova G.O. Features of conservative therapy of patients with bleeding ulcers of the stomach and duodenum // Farmateka. – 2011. No. 2(215). pp. 58-63.
- Kolesnikova I.Yu., Volkov V.S. Diagnosis and treatment of acid-related diseases of the digestive tract. Guide for doctors / M.: Publishing House “Medical Information Agency”, 2014. - 432 p.
- Peptic ulcer of the stomach and/or duodenum. Clinical recommendations. Age category: Children. Ministry of Health of Russia. 2022
On the website GastroScan.ru in the “Literature” section there is a subsection “Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum”, containing publications for healthcare professionals.
Video for medical students
Filippova M.P. Peptic ulcer disease. Lecture for the 2nd year of the FKP MGMSU named after. A.I. Evdokimova (video)
Tsukanov Yu.T. Ulcers of the stomach and duodenum. Lecture for medical university students (video)
Lebedeva A.V. Acid-dependent diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Lecture for IVGMA students (video)
Serebrovskaya N.B. Department of Pediatrics MGMSU named after. A.I. Evdokimov. Diseases of the digestive system in children. Lecture for students (video). Lecture for 3rd year students of St. Petersburg State University
Alexandrov M.V. Acid-dependent diseases of the digestive system in the practice of a clinic physician. Lecture for sixth year students of the Faculty of Medicine of the Ivanovo State Medical Academy (IvSMA)
Video for pediatricians
Still from video: Volynets G.V. Functional and inflammatory diseases of the upper digestive tract in children
On the website in the “Video” section there is a subsection for patients “Popular Gastroenterology” and a subsection “For Doctors”, containing video recordings of reports, lectures, webinars in various areas of gastroenterology for healthcare professionals.