Erosive bulbitis is a fairly serious pathology, which is characterized by inflammation of the duodenum. This disease is not very common, but can lead to negative health consequences. Therefore, the first signs of pathology should be a reason to visit a doctor. This disease is detected in 1-3% of people who have undergone gastroscopy due to pain in the upper abdomen.
What is the disease?
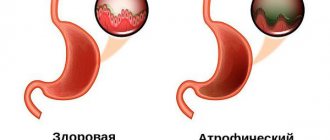
When the inflammatory process occurring in the area of the duodenum and stomach occurs and becomes chronic, doctors often diagnose erosive bulbitis (erosive gastritis).
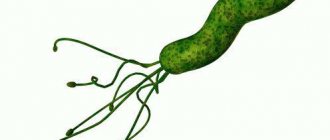
The disease often occurs against the background of ongoing duodenitis. The pathological process is formed as a result of the action of Helicobacter pylori bacteria on the mucous membrane. They initially affect the bile ducts, and then the digestive organs. In addition, superficial gastritis occurs quite often in patients; erosive bulbitis develops against the background of ongoing inflammatory processes due to improper or untimely treatment. Read more about this disease in this article: https://www.syl.ru/article/100464/chto -takoe-erozivnyiy-bulbit-i-kak-ego-lechit.
What forms are there?
Erosive bulbitis of the duodenum can occur for a variety of reasons, in particular, the process of its formation is influenced by: stress, poor heredity and irregular nutrition. There are several forms of this disease, each of which has its own specific characteristics. In particular, there are such forms of the disease as:
- focal;
- ulcerative;
- hemorrhagic.
Focal erosive bulbitis (erosive gastritis) differs from all other forms in that it has a certain localization of inflammation. In this case, the infection affects only the duodenum, without affecting the other digestive organs. Children and adults are equally susceptible to this disease. It has certain, quite characteristic features, including:
- heartburn and bitter taste in the mouth;
- nausea and vomiting;
- belching;
- white coating on the tongue;
- pain in the stomach area.
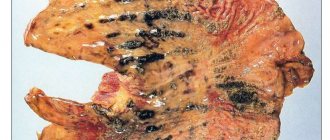
The ulcerative form of erosive bulbitis (gastritis) is characterized by the fact that the deep layers of the mucosa are affected. Inflammation also affects the muscle layer. For a long time, absolutely no signs are observed, which is very dangerous, since it is often possible to diagnose the disease in the later stages, which can lead to dangerous complications.
When pathological changes occur, gastric acid may be refluxed into the duodenum. As a result, erosive-hemorrhagic gastritis (bulbitis) develops, requiring immediate medical intervention. Basically, this form of the disease occurs when you have bad habits or take potent medications.
How is erosive bulbitis classified?
This disease can occur in several forms. Each of them requires emergency treatment prescribed by a specialist. Otherwise, internal bleeding may occur with serious consequences.
| Form of pathology | a brief description of |
| Erosive-focal | The disease manifests itself in the form of single lesions. The main blow falls on the mucous membrane. |
| Catarrhal-erosive | Pathological damage occurs at the cellular level (the epithelium is affected). |
| Erosive-ulcerative | The disease is so dangerous that the muscular structure of the organs is affected. |
| Erosive-hemorrhagic | The pathological process is so aggravated that the vascular system suffers. |
| Erosive drain | The lesions reunite, and a filmy coating forms on the mucous membrane. |
The disease has no gender differences; representatives of different genders and age groups are at risk.
Causes
There are a variety of reasons why erosive bulbitis (erosive gastritis) occurs, which include the following:
- violation of nutrition rules;
- prolonged stress;
- infectious processes in the digestive organs;
- genetic factor;
- deterioration of immunity.
Each of these factors in itself is very important and indicates a high risk of a pathological process. Among the main causes of the disease is the aggressiveness of one’s own immune system, which negatively affects pathogens and healthy cells of the body.
Causes and forms of the disease
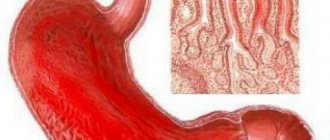
Bulbitis occurs in the duodenum according to a certain algorithm. Initially, catarrhal changes occur in the mucosa, which, as they progress, lead to the development of erosions on the surface of the intestinal lining. After this, the eroded surfaces deepen, and in their place deeper lesions - ulcers - form.
Therefore, we can consider that the erosive type of pathology is an intermediate stage between superficial and ulcerative bulbitis.
Acute erosive bulbitis in most cases is associated with the penetration of pathogenic microflora into the duodenum. The greatest role in the appearance of the focal form of the disease is played by Helicobacter pylori infection - invasion of a special pathogen that leads to damage to the mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines.
The occurrence of manifestations of the disease, including focal erosive-hemorrhagic bulbitis, can also be provoked by chemical damage to the mucous membrane. Intestinal trauma occurs when certain toxic substances, including alcohol, enter it. The development of erosive-ulcerative bulbitis can be caused by medications that are part of the group of anti-inflammatory drugs (indomethacin, aspirin, ibuprofen).
Chronic erosive bulbitis often occurs in the absence of proper treatment for the acute form. If a person does not undergo eradication therapy with antibacterial drugs or does not fully comply with the doctor's recommendations, bacteria in his intestines may persist even after symptoms have disappeared.
Due to the persistence of microorganisms in the digestive system, a person develops a chronic disease, which is characterized by constant alternation of periods of exacerbations and remissions. It is much more difficult to treat a pathology with a protracted course, so patients are advised to promptly contact a gastroenterologist when the first symptoms of an acute form of the disease appear.
Symptoms of the disease
At the initial stages of the disease, there are no symptoms of erosive gastritis (bulbit), but over time they become more and more pronounced. The danger of this pathology is that the symptoms are similar to many other diseases. Mostly painful sensations are observed before eating food, as well as heartburn. If treatment is not started in a timely manner and is not carried out comprehensively, this can provoke serious complications, for example, transition to a chronic form. Among the main signs of the disease it is also necessary to highlight:
- frequent nausea and vomiting with bile;
- the presence of a bitter aftertaste;
- bitter belching and heartburn;
- presence of blood clots during vomiting;
- pain during long breaks between meals;
- general deterioration of health.
If treatment is not carried out in a timely manner, the disease from the acute stage can become chronic. To prevent this, you need to undergo regular examinations and, if necessary, carry out treatment, as well as prevention.
Varieties of bulbit
There are many varieties of bulbit
Bulbitis can occur in different ways and have different shapes. In this regard, several types of disease are distinguished:
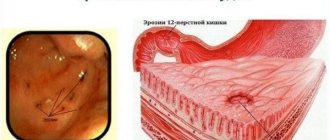
- Erosive. The erosive form of bulbitis is dangerous because it can easily turn into an ulcer. A small erosion forms on the duodenal mucosa, which can grow and bleed. In this case, the patient experiences abdominal pain with prolonged absence of food and heartburn after eating. The pain may be accompanied by dizziness, weakness, and chills. Erosive bulbitis can be caused by alcoholic drinks, mechanical damage to the gastrointestinal tract, infections, and severe poisoning.
- Surface. With superficial bulbitis, the upper part of the mucous membrane becomes inflamed. It can be called the initial stage of the disease. There is usually no severe pain and vomiting, but heartburn, heaviness and minor pain may be present. Most often, this form of bulbitis occurs due to poor diet, smoking, and alcohol abuse. If left untreated, the disease will progress.
- Catarrhal. In fact, such a disease does not exist in nature. Catarrhal bulbitis is the next stage after the superficial one. Indigestion and increased acidity are observed. The patient may have pain after eating, heartburn, general weakness, and belching with a bitter taste.
- Focal. Focal bulbitis is similar to erosive bulbitis, but in this case there is an accumulation of several ulcers in the intestine. Pain almost always occurs in the pit of the stomach, nausea and vomiting are possible. The causes still remain alcohol, smoking, poor diet, and infections.
- Atrophic. Atrophic bulbitis is accompanied by thinning of the lining of the duodenum. In this case, abdominal pain occurs, sour belching, frequent heartburn, constipation alternates with diarrhea. Vitamins and other beneficial substances are poorly absorbed in the intestines, so the body’s condition worsens and weight quickly decreases.
- Chronic. The symptoms of chronic bulbitis are the same as those of other forms. But in this case, immunity is further reduced, headaches and muscle weakness occur. Lesions of the intestinal lining may be microscopic. At first there is no severe pain. The presence of ulcers is excluded.
All types of disease are treatable, and if you start it on time, you can avoid serious complications. Chronic disease most often occurs due to a careless attitude to doctor's recommendations.
Carrying out diagnostics
Before starting treatment, it is imperative to conduct a comprehensive diagnosis. Its main method is endoscopic examination of the gastric mucosa. A special probe, which is a hollow tube with a light bulb and a camera at the end, is inserted through the mouth and esophagus. Tissue is collected from the affected area, which is then examined for the presence of pathogens.
X-rays are also used to identify the disease. First, the patient must drink a barium solution, which will stain the inner surface of the digestive organs, making it possible to examine the pathological process.
Additionally, laboratory tests of blood and stool are prescribed. The detection of red blood cells in the stool indicates the presence of gastric bleeding. In addition, blood tests may reveal anemia.
Features of treatment
Treatment of erosive gastritis (bulbit) implies an integrated approach to therapy. You definitely need to change your usual work routine and give up bad habits. During an exacerbation, a strict diet is required.
For treatment, medications are used to help normalize acidity and intestinal function. In addition, taking medications that promote healing of the affected gastric mucosa is indicated. The patient needs a lot of time to recover, so treatment is carried out in specialized sanatoriums.
In addition, good results can be obtained by using traditional medicine. If traditional methods of therapy are ineffective, surgical intervention is performed to help eliminate the pathological process.
Medications
When erosive bulbitis occurs, treatment is carried out in stages. First of all, therapeutic measures are aimed at eliminating the causes that provoked the onset of the disease. If Helicobacter pylori bacteria are detected, antibiotics are prescribed and taken for a long time.
Antimicrobial agents are also prescribed, in particular Metronidazole. If too strong antibiotics are used for a long time, then the biological additive “Rioflora balance” is additionally used. Antispasmodics are also required that eliminate spasms of the stomach muscles and relieve pain, in particular, such as “Spazmolgon” or “No-shpa”.
When carrying out treatment, it is necessary to normalize the acidity of gastric juice, and even change its chemical composition, as this will help protect the affected mucosa from aggressive influences. For this purpose, antacid drugs are used that can block hydrochloric acid. Improved digestion is achieved by prescribing the medications Mezim and Digestal.
Restoration of the gastric mucosa is required. This requires medications that can enrich the affected areas with oxygen. Drugs such as Trental and Iberogast will help speed up recovery.
During an exacerbation of the chronic form of the disease, doctors recommend bed rest.
Reasons for the development of erosive bulbitis
In addition to the negative impact of the Helicobacter pylori bacterium on the stomach and duodenum, the cause of the disease is the concentration of hydrochloric acid in the gastric juice, which entails a negative effect on the gastric mucosa. There are a number of other reasons that entail the occurrence of erosive bulbitis:
- problems with the nervous system (stress, fatigue, etc.);
- endocrine system problems;
- all kinds of poisoning;
- waste products of various harmful bacteria;
- food tract parasites;
- Giardia and helminths, etc.;
- Crohn's disease.
- the presence of similar diseases in close relatives (mother, father, brothers, sisters).
ethnoscience
When erosive bulbitis occurs, folk remedies and methods for treatment are widely used. They are used as an adjunct to drug therapy. Good means are:
- propolis tincture;
- wheat sprouts;
- sea buckthorn oil;
- green apples.
For prolonged pain, propolis tincture helps to cope with the problem. Another good way to get rid of inflammation and soreness is sea buckthorn oil. You can purchase it ready-made or prepare it yourself.
Before carrying out treatment with traditional methods, you must first consult with your doctor, as they may have certain contraindications.
Diet
When erosive gastritis (bulbit) occurs, a diet is mandatory. It implies the exclusion of certain products from the usual menu. Allowed for consumption:
- lean varieties of fish and meat;
- eggs;
- cereals;
- vegetables and fruits.
Food must be chewed thoroughly and must be at an optimal temperature. Throughout the entire period of treatment, you must follow a strict diet, and then you are allowed to gradually switch to a more gentle diet.
It is prohibited to consume various pickles, smoked foods, spicy, fatty foods, chocolate, and alcoholic beverages. Meals should be taken in small portions and at strictly defined times. Dishes are best stewed or cooked using the boiling method.
Therapeutic diet for illness
In the acute course of erosive bulbitis, a therapeutic diet is the main method of treatment and implies a balanced diet in compliance with certain rules:
- Taking liquid and pureed food in fractional portions (5–6 times a day every 2–3 hours);
- Puree soups with rice, oatmeal with the addition of a small amount of butter;
- Kissel or warm milk;
- Soft-boiled eggs.
The above dishes are the established diet for exacerbation of erosive bulbitis. After the body has been relatively restored, white crackers, milk porridge, and lean steamed meat in crushed form can be gradually introduced into the daily diet. After 1.5 months of following the diet and positive changes, doctors allow the consumption of soups with vegetables, white bread, stewed vegetables, cottage cheese, sour cream, and porridge with a viscous consistency. The duration of limited nutrition is about 6 months, since during this period the resulting erosion should heal.
Erosive bulbitis is an inflammatory disease of the duodenum. The pathology is quite rare, but has serious consequences for the body. For diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct a number of specific studies when suspicious symptoms are identified.
Prevention
To prevent the occurrence of the disease, it is imperative to carry out prevention. You need to watch your diet, it should be healthy and balanced. It is necessary to prevent chemical, mechanical and thermal injuries to the mucous membrane.
Treatment of any inflammatory processes must be carried out in a timely manner, as they are dangerous due to their complications. It is important to prevent and treat worms.
Reviews and results
Compared to the strict restriction of foods in Diets No. 1A and No. 1B , this table provides for a significant expansion of the list of permitted foods. In addition, an additional type of cooking (baking) also allows you to diversify your diet. The exclusion of baked goods and sweets is poorly tolerated by patients, so many patients reduce the time spent on a strict diet if their health allows this.
- “... The first time erosion was discovered, there was severe pain and nausea. He refused hospitalization. At home I followed a diet and took pills. After two weeks everything returned to normal, but I continued to do all this, and to make sure everything healed, I went for an examination only a month later. The treatment result was good, but there was still a month of diet and pills. Now I eat everything, but I try to avoid smoked and spicy foods, and, of course, alcohol”;
- “... I had everything: pyloritis and gurgling. Compliance with the diet, diet plus peace of mind is what is needed for treatment. And of course the pills prescribed by the doctor. At first, while I followed the diet from time to time (only when there was an exacerbation), and even my restless character, there were continuous relapses. Then I was treated in a hospital and decided to take charge of my health and monitor my diet. So a year passed without exacerbations, which made me very happy and inspired. Now I try not to eat fried foods, smoked sausages, I have forever given up vinegar, marinades, hot seasonings and spices. I feel good";
- “... I came to the conclusion that I personally need to constantly follow a diet. As soon as you relax a little and switch to a normal diet, belching, heartburn or stomach pain immediately appears. And this worries me almost constantly. The last time I was examined, they prescribed treatment for me and told me to improve my diet. I followed this diet for 3 months - I lost weight, there was no pain or heartburn. Of course, I’m tired of everything steamed and vegetables without seasoning to taste, but I have no other choice. Now I’m expanding my diet, but I’ll still leave the dishes boiled or baked in foil so there’s no crust.”