general description
Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum is a chronic seasonal recurrent disease of the stomach and duodenum, manifested by a defect in the mucous membrane (ulcers).
These disorders occur against the background of destabilization of the nervous and humoral mechanisms in the human body, which regulate secretory-reparative processes in the stomach and duodenum. Peptic ulcer disease is characterized by periods of exacerbation (spring and autumn) and remission. The result of ulcer healing is the formation of a scar. The prevalence of the disease in all countries is about 4-6% of the adult population. With full medical screening of patients, this percentage increases to 20-25%.
The peak incidence occurs at the age of 30-45 years. Mostly in men aged 35-50 years, peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum is 3-4 times more common.
Duodenal ulcer - symptoms and treatment
Mandatory measures in the treatment of gastric and duodenal ulcers include:
- following a gentle diet (mechanical and chemical sparing);
- exclusion of such factors of aggression as smoking, alcohol;
- reducing the dose or limiting the intake of certain medications (NSAIDs).
Drug treatment
Drug treatment is aimed at reducing the level of hydrochloric acid, protecting and increasing the regeneration of the duodenal mucosa. To reduce acidity, proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) are used as the “gold” standard of treatment and H2-histamine blockers.[6] To increase the protective properties of the mucous membrane, coating agents and antacids are used. To increase mucosal regeneration, bismuth and sucralfate preparations are used. If Helicobacter pylori infection is present, first-line or subsequent line eradication therapy is performed.[6] To a lesser extent they are used:
- drugs that regulate the motor-evacuation function of the stomach and intestines - prescribed for peptic ulcer disease combined with reflux and insufficiency of the pyloric sphincter;
- psychotropic drugs - used to relieve depression and stress factors when the disease lasts a very long time and a psychosomatic component is added.
In case of complications, endoscopic or surgical treatment methods are used.
Surgery
Surgical methods are limited to the treatment of complications such as:
- perforation - the ulcer is sutured or the damaged area of the intestine and stomach is removed with anastomosis;
- penetration—damaged tissue and part of the intestine are removed with anastomosis;
- cicatricial stenosis - resection (partial removal) with anastomosis is performed.
Endoscopic methods primarily include endoscopic hemostasis. This method allows, in most cases, to stop bleeding from an ulcer and prevent its relapse (if the bleeding has stopped).[4] In case of cicatricial stenosis and narrowing of the duodenal lumen, stenting can sometimes be used (if abdominal surgery is contraindicated).
In general, the course of drug treatment for exacerbation of a peptic ulcer or for a newly diagnosed ulcer lasts 1-2 months. Surgical and endoscopic methods are resorted to only when relevant complications develop.
Emergency help during a seizure
Emergency care is provided for complications of a peptic ulcer (bleeding, perforation, stenosis of the duodenal lumen). If these complications develop, you must contact the clinic for a consultation with a surgeon. If there is severe pain, a drop in blood pressure, weakness and other signs of internal bleeding, you must call an ambulance to provide emergency medical care.
To reduce pain, alginates and antacids and/or fast-acting drugs from the group of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) - rabeprazole - are used as emergency medications.
Diet for peptic ulcers
During the period of exacerbation of duodenal ulcer, a gentle diet with pureed cooking is used. The diet is based on the following principles:
• Mechanical sparing is ensured by choosing food products with a low content of coarse fiber, short stay of food in the stomach and special culinary processing of products (stewing, steaming, grinding food to a puree consistency).
• Chemical sparing is based on increasing the content of fats of plant origin and proteins of animal origin (cottage cheese, cheese, eggs, boiled meat and fish) against the background of the physiological norm of carbohydrates, vitamins, microelements, since fats inhibit gastric secretion, and proteins inactivate hydrochloric acid.
• Thermal sparing is achieved by excluding too cold and hot foods, which injure the gastric mucosa; the optimal temperature for hot foods is +30-40 °C.
• Limiting the volume of food taken at the same time in order to prevent overstretching of the stomach: food is taken 5-6 times a day and in small portions. Eating should correspond to the rhythm of gastric secretion and should be carried out at intervals of 3.5-4.5 hours.
Avoid foods that greatly increase the production of hydrochloric acid by the stomach. Such as: salty seasonings, strong meat, fish or vegetable broths, brown bread, soft bread and pastries, carbonated drinks, strong tea, coffee.
We recommend products that have a medium level of stimulation of hydrochloric acid production: boiled meat, fish, most berries and fruits, and a weak level: soft-boiled eggs, white crackers or dried bread (made from fine flour), cereals, sweet fruits and vegetables.
In a gentle diet with pureed food, the range of dishes includes:
• unleavened cottage cheese, mild and low-fat cheese, pureed;
• pureed soups from prefabricated vegetables (except for cabbage soup and borscht), vegetable and cereal soups, milk cereal soups, with noodles or chopped pasta;
• boiled pureed vegetables - zucchini, cauliflower and Brussels sprouts, tomatoes, carrots, beets (the obligatory exception of white cabbage, turnips, radishes, radishes and legumes, which are rich in plant fibers and essential oils);
• ripe fruits and sweet berries (after heat treatment);
• compotes with pureed dried fruits;
• dried wheat bread.
Dishes are steamed, boiled, boiled until soft, pureed, chopped, and served warm.
The recommended dishes for a gentle diet with unprocessed food are the same as for the option described above. Dishes are steamed, boiled, crushed until soft, but not crushed, served warm 5-6 times a day.
During the period of remission, it is recommended to adhere to the basic principles of a healthy diet. This excludes strong meat and fish broths, mushroom broth, spices, spicy dishes, pickled and smoked foods, which have an irritating effect on the mucous membrane and can increase the formation of hydrochloric acid in the stomach. Limits on pastries, pies, pancakes, coffee, mineral waters and drinks containing large quantities of carbon dioxide. Long-term (more than 10-15 minutes) use of chewing gum is harmful.
Physiotherapy and therapeutic exercises for peptic ulcers
The effectiveness of physiotherapy methods for duodenal ulcers has not been proven, as well as therapeutic exercises. Therefore, these methods are not used in the treatment of peptic ulcer.
Causes of peptic ulcer
- The presence of Helicobacter pylori in the stomach and duodenum, which is the main etiological factor in the occurrence of ulcers. The influence of other bacteria has not been proven
- Eating disorder
- Alcohol and tobacco abuse
- Long-term use of drugs that affect the gastric mucosa, the main ones: NSAIDs and glucocorticosteroids (prednisolone)
- Emotional overstrain, stress
- Genetic predisposition
- Metabolic disorders
- Hypovitaminosis
General information
About 10% of the population worldwide is affected by peptic ulcers, with men 2 times more likely than women. Medical statistics show that in the duodenum, compared to the stomach, ulcers form 4 times more often. Ulcers found in both the duodenum and stomach are called combined.
Pain and dyspeptic syndromes are the main manifestations of peptic ulcer disease. Up to 75% of patients experience pain in the upper half of the abdomen, manifestations of pain of minor intensity - in approximately 50% of patients, and severe pain - in about a third of patients.
Symptoms of peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum
- Aching or cramping pain, low intensity in the epigastric region, often occurs on an empty stomach or immediately after eating
- Constant heartburn, especially at night and in the morning, sour belching
- Nausea
- Belching with air, sour or bitter taste
- Heaviness in the epigastric region after eating, a feeling of rapid filling of the stomach
- Decreased appetite
- When bleeding from ulcers, vomiting appears like “coffee grounds”, dark stools (melena)
- With perforation of ulcers - severe, dagger-like pain in the epigastric region, nausea, vomiting, painful tension in the abdominal muscles
Causes
One of the main causes of the development of this disease is the bacterium Helicobacter pylory. The microorganism is resistant to the acidic environment of the stomach, so an effective medicine for stomach ulcers must cause the death of the bacterium.
Other predisposing factors for the development of gastric ulcers include:
- Regular exposure to stress factors on the body. Neuroses, depressive disorders and neurasthenia can provoke the development of gastric ulcers.
- Poor nutrition, predominance of fried and fatty foods in the diet.
- Abuse of alcohol and caffeinated drinks.
- Tobacco smoking.
- Inhibition of the body's defenses.
- Long-term use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
Diagnostics
- General clinical analysis of blood and urine
- Analysis of stool for coprogram
- Fecal occult blood test
- Biochemical blood test (liver tests, cholesterol, alkaline phosphatase)
- ECG
- X-ray of the chest organs in 2 projections and X-ray of the abdominal organs (to exclude perforation of ulcers)
- X-ray of the esophagus, stomach with barium mixture
- Ultrasound of the hepatobiliary system
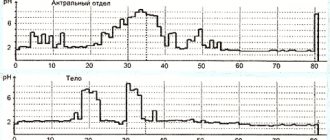
- 24-hour pH monitoring in the lower esophagus and stomach
- EGDS
- Non-invasive tests for the determination of Helicobacter pylori (respiratory)
Why do gastritis, duodenitis and gastroduodenitis occur?
A healthy stomach produces juice, the acidity of which the mucous membrane of the organ can withstand. If the protective functions of the mucous membrane weaken, or acidity increases, then inflammation of the gastric mucosa occurs. Further development of the process leads to erosions and then to an ulcer (or several) of the gastric mucosa and/or duodenal wall (which, being a continuation of the gastric outlet, suffers no less from the effects of gastric acid).
Erosion is an ulceration of the gastric mucosa, but less deep than with an ulcer. With erosion, the mucous membrane is never affected to its entire thickness. As soon as the lesion begins to affect the entire mucous membrane, right down to the muscular layer, we are talking about a peptic ulcer.
It is customary to distinguish erosive (erosive) gastritis, in which the surface of the mucous membrane is affected by multiple erosions, which causes the patient severe pain in the epigastrium and other unpleasant symptoms. This stomach disease is difficult to treat and can lead to serious complications, so timely, high-quality diagnosis is very important. The treatment regimen for the stomach is always prescribed strictly based on the results of the examination and necessarily includes a special diet.
The appearance and development of gastric and duodenal ulcers, chronic gastritis and duodenitis are also influenced by other factors. Stress, unbalanced diet, frequent use of medications, infection with the bacterium Helicobater pylori are the most common causes of these diseases.
You can learn about the dangers of Helicobacter and how to fight it from the animated films on our website.
You need to consult a gastroenterologist if you have:
- pain (often pain on an empty stomach, in the morning) in the epigastric region;
- heartburn;
- unpleasant sour taste in the mouth;
- nausea (sometimes vomiting);
- bad breath, etc.
1 Consultation with a gastroenterologist in MedicCity
2 Consultation with a gastroenterologist in MedicCity
Our clinic diagnoses and treats various types of gastritis and other diseases of the stomach, duodenum, and other gastrointestinal organs. Experienced gastroenterologists, using gastroscopy, will determine the presence, localization, stage of development of the inflammatory process (erosion, ulcers), make a diagnosis and prescribe an adequate treatment regimen. Gastroscopy of the stomach and colonoscopy of the intestines in our center is performed using modern equipment, without pain and discomfort, with sedation.