Intestinal microflora and the outside world
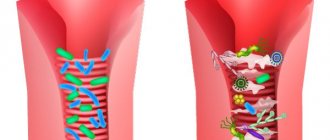
There are a huge number of microbes around us. These microbes are more ancient than us, than humanity. The task of this flora is to infiltrate each of us, live and reproduce at our expense. They are always looking for weak points. We are open to bacterial flora from the outside world, but we have our defenders everywhere: bifidobacteria, lactobacilli and typical E. coli.
Without bifidobacteria, lathobacteria and the typical E. coli, the immune system would not work! Bifidobacteria and lactobacilli are the body's natural defense against harmful bacteria, viruses, fungi, and protozoa. We must keep our flora in order, constantly feed it, give it a sufficient amount of carbohydrates, vitamins, microelements, and fluids.
How to restore intestinal microflora?
In healthy people in the absence of chronic diseases, the microflora is restored independently and does not require any additional measures.
The need for its correction may arise after suffering from acute gastrointestinal diseases and taking medications that affect the composition of the microflora due to flatulence, constipation, diarrhea, abdominal pain and food allergies.
Correction of the composition of microflora in the colon requires preliminary diagnosis and an integrated approach to treatment. Restoring the composition of intestinal microflora includes several stages:
- Treatment of the underlying disease that caused dysbiosis.
- Liberation of the gastrointestinal tract from pathogenic pathogens and their toxins.
- Correction of nutrition with the addition of foods that promote recovery.
- Restoration of impaired intestinal functions and the composition of the microflora itself using pre- and probiotics or synbiotics.
*Synbiotics are natural products or complex nutritional supplements with a combination of prebiotics and probiotics.
To date, the only scientifically proven means that can deliver microorganisms to the intestines to restore intestinal microflora is fecal transplantation.
Pre and probiotics are currently used as a means of promoting self-healing of the colon microflora. Their effect is not to add beneficial bacteria to the microflora, but to suppress pathogenic microorganisms, reduce the level of inflammation in the intestines and trigger the renewal of the intestinal microflora. There are scientific studies that confirm the improvement in well-being when taking such drugs.
If symptoms similar to those of dysbiosis appear, we recommend that you consult a gastroenterologist for examination and treatment. You can undergo the necessary examinations and get advice from specialists at the Gastroenterological Department. We also have a comprehensive “Check-up Intestinal Examination” at a special price, which includes all the necessary examinations and consultation with a gastroenterologist.
Inhibition of flora after antibiotics
Flora after antibiotics is especially vulnerable. By helping our microflora, we maintain health. If, after taking antibiotics, the microflora is somehow not restored, then due to the lack of a sufficient number of bifidobacteria and lactobacilli on the mucous membranes, the body’s immune defense is reduced, and pathogenic microorganisms from the external environment (or from the internal opportunistic microflora) provoke inflammatory processes in the body.
Among the consequences of suppressed intestinal microflora after antibiotics are:
- Intoxication of the body, diseases of vital organs (reproductive system, heart, liver, kidneys), suppression of local and general immunity, frequent acute respiratory viral infections, influenza, metabolic disorders (vitaminosis, anemia, atherosclerosis, diabetes, obesity),
- Development of inflammatory processes:
- Oral cavity – periodontitis, stomatitis, thrush in children, etc.
- Nasopharynx and ears - pharyngitis, tonsillitis, laryngitis, runny nose, adenoids, sinusitis, purulent otitis, etc.
- Gastrointestinal tract - colitis, gastritis, ulcers, constipation, diarrhea, pain, burning and heaviness in the abdomen, hemorrhoids, belching, flatulence, a sharp deterioration in food digestion and absorption.
- Liver - overload of toxins, cell destruction, hepatitis.
- Reproductive system – disorders of ovulation and spermatogenesis, infertility.
- Genital organs - inflammation, thrush, vaginosis, erosion, prostatitis, etc.
- Kidneys, bladder - cystitis, pyelonephritis, etc.
- Nervous system – insomnia, irritability, depression, chronic fatigue
- Heart, blood vessels – pericarditis, vegetative-vascular dystonia, etc.
- Skin, hair, nails - rashes, acne, dermatitis, hair loss, brittle nails.
- Skeleton, bones – osteoporosis, spinal dysfunction.
What to drink with antibiotics to normalize microflora
In order to restore normal intestinal flora after taking antibiotics, specialists from the Moscow Research Institute of Experimental Medicine named after. G.N. Gabrichevsky recommend using probiotic preparations with a high content of bacteria (more than 10 * 9 CFU/ml), i.e. with an equal or greater amount than in the human body.
The leaders among liquid probiotics in terms of concentration (titer) of bacteria are Bifidum BAG and Trilact. 1 ml of the drug contains 10 billion (10*10 CFU/ml) cells of beneficial bacteria. Note that normally, 1 g of feces in an adult contains 10*9-10*10 cells of bifidobacteria and 10*7-10*8 lactobacilli.
To enhance the effect of drugs with bifidobacteria and lactobacilli, in order to ensure complete restoration of the microflora after antibiotics, it is necessary to take a sorbent. Ecoflor is a unique sorbent with selective sorption that absorbs and removes toxins and waste from the body. Ecoflor is capable of adsorbing up to 77% of Staphylococcus aureus and up to 43% of Escherichia coli. It has been proven that taking the drugs in combination increases immunity by 65%.
Scheme for restoring microflora after antibiotics:
Course duration 40 days adults
| Stages of treatment | Duration | Time and dosage of medications | Need for the course |
| 1st stage | 1-10 day | In the morning – dose Ecoflor 2 packets 25 minutes before meals In the evening - dose of Bifidum BAG 6 ml 1 hour after dinner Morning and evening Bifidum nasal drops 3-4 drops in each nasal passage (1 part Bifidum 3 parts saline solution) course 10 days | Bifidum BAG 20 bottles Trilact 15 fl Ecoflor 20 pack |
| 2nd stage | 11-40 day | In the morning – dose of Trilact 6 ml 1 hour after breakfast In the evening - dose of Bifidum BAG 6 ml 1 hour after dinner |
The effectiveness of restoration of intestinal microflora after antibiotics using the Bifidum BAG, Trilact, Ecoflor complex reaches 98%. In other words, taking liquid probiotics eliminates symptoms of intestinal dysbiosis by 98%, such as:
- bloating and increased gas formation;
- constipation and diarrhea
- allergic skin rashes, dry skin and mucous membranes;
- nausea and vomiting;
- increased fatigue, weakness, sleep disturbance, anxiety and depression.
If the intestinal microflora needs help
Often the gastrointestinal tract works overtime. Especially on holidays and during vacations. Overeating, lack of diet and, for those who are especially lucky, intestinal infections are all the other side of the excesses that we allow ourselves at the table.
Winter and the intestines: what is the connection?
It is important to arrange rehabilitation of your gastrointestinal tract after gastronomic exploits. After all, we need his strength so much now. The cold season is a period during which all the body’s immune forces are activated, and the intestines are one of the most important immune organs.
The totality of intestinal microorganisms (microbiota) is directly involved in the activation of the body's immune systems. The intestinal microflora for the most part consists of bifidobacteria and lactobacilli, which perform functions that are very important for our immunity:
- prevent the emergence of pathogenic microflora;
- produce enzymes to digest food;
- participate in the synthesis and absorption of vitamins and many other important elements;
- are responsible for the production of lymphoid cells, which subsequently perform their defensive function in other organs;
- participate in the formation of the immune response to foreign bacteria and microorganisms;
- support the intestinal immune system, which produces IgA immunoglobulins.
That is why, only if the microflora is normal, the intestines are able to perform their protective functions and it is easier for the body to resist viral diseases.
Do I have problems with microflora?
Signs of dysbiosis are difficult to miss. Everyone has encountered these symptoms at least once in their life:
- dyspepsia (nausea, flatulence, heartburn, heaviness in the stomach);
- stool disorders (diarrhea, constipation);
- the occurrence of food allergies;
- increased fatigue, decreased mood, signs of depression, lethargy;
- deterioration of skin and hair condition;
- rapid weight gain or loss.
If you find yourself with the listed symptoms, then you should think about how to support your body during the difficult autumn-winter period.
To begin with, it is worth noting that in order to normalize the functioning of the intestines, it is necessary first of all to eliminate factors that negatively affect its functioning: stress, poor diet, alcohol, smoking. As soon as you return to a healthy lifestyle, the body will begin to restore the normal functionality of the intestinal tract. Also, some medications have a destructive effect on the state of microflora: antibiotics, antidepressants, hormonal and others.
Of course, for most of us it is quite difficult to suddenly give up bad habits and start eating only healthy foods. Yes, and stopping taking a drug prescribed by a doctor is also a bad idea. For such cases, there are drugs that normalize the intestinal microflora, namely, probiotics and prebiotics.
Pro- or pre-: what's the difference?
Probiotics are live microorganisms that are normally present in the intestines of every healthy person and, when administered in adequate quantities, provide benefits. These include:
- lactobacilli (L. casei, L. acidophilus, etc.);
- bifidobacteria (B. bifidum, B. infantis, B. longum, etc.);
- lactic acid streptococcus;
- non-pathogenic varieties of enterococcus;
- non-pathogenic varieties of Escherichia coli.
Manufacturers produce a wide variety of dietary supplements and over-the-counter medications containing one (single-component) or several (multicomponent) probiotics. The range of these drugs is presented in different forms of release: powders in sachet, capsules with lyophilisates of bacteria, liquid forms, tablets and others.
Unfortunately, there is no universal probiotic for all diseases, so the most effective drug will be one prescribed by a doctor depending on the causes of dysbiosis.
Prebiotics are substances that are not absorbed and partially or completely not digested by our body. Their consumption has a beneficial effect on the growth and reproduction of the intestinal’s own beneficial bacteria. That is, this is the food that probiotics need for normal functioning.
Based on their origin, they can be divided into substances:
- carbohydrate nature (monosaccharides, oligosaccharides, polysaccharides, sugar alcohols);
- protein nature (peptides);
- others (lactobionic acid, polyphenols).
The most commonly used prebiotics are lactulose, inulin, oligofructose and dietary fiber. All these substances are included in medications and dietary supplements, the mechanism of action of which is based on maintaining the balance and constancy of the intestinal microflora.
Without being digested in the previous sections of the gastrointestinal tract, they enter the large intestine in transit and there create comfortable conditions for the life of “native” microflora bacteria.
Together or apart?
Depending on the individual characteristics of the body, the causes, form and nature of dysbiosis, the prescribed dosage forms and rules for taking probiotics and prebiotics will differ. They can be used together, in turn, or in the form of synbiotics (preparations containing beneficial bacteria and a nutrient medium for them). Therefore, it is better to coordinate their choice with your doctor.
But there are general recommendations that are relevant for any drug regimen to normalize the microflora:
- Prepare the body with enterosorbent. This helps remove all toxins from the body before taking medications to normalize the microflora.
- Adjust your diet. Reduce your consumption of sugar and foods containing it, eat more complex carbohydrates, fiber and greens.
With the right preparation and regular use of probiotics and prebiotics, you will very soon feel light and energetic, and your intestines, in gratitude, will help your immune system resist all the adversities of the autumn-winter season.
Be healthy!
Sources:
- Kaibysheva, V. O. Probiotics from the position of evidence-based medicine / V. O. Kaibysheva, E. L. Nikonov // Evidence-based gastroenterology. - 2022. - 8 (3). — P. 45–54.
- Khramtsov, A. G. Prebiotics as functional food ingredients: terminology, criteria for selection and comparative evaluation, classification / A. G. Khramtsov, S. A. Ryabtseva, R. O. Budkevich [and others] // Nutrition Issues. - T. 87. - No. 1. - 2022. - P. 5–17.
- Bovbel, I. E. Modern ideas about the intestinal microbiota and the possibility of effective use of probiotics in the practice of a pediatrician / I. E. Bovbel // Medical news. — 2022. — No. 2. — P. 25–31.
- Microbiota / ed. E. L. Nikonova and E. L. Popova // Media Sphere. — 2022. — pp. 20–30.
Anna Gorobets, pharmacist, medical journalist
Photo depositphotos.com The author’s opinion may not coincide with the opinion of the editors