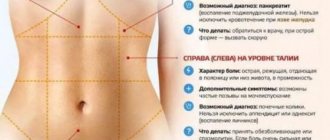
Copremesis, or fecal vomiting in humans, is a clinical symptom in which the vomit smells of feces or its impurities. Such symptoms usually occur against the background of distal intestinal obstruction or the presence of a gastrointestinal fistula in the abdominal cavity. In addition, vomiting of feces with blood can occur in cancer patients with cancer of the gastrointestinal tract. What to do and how to provide first aid to a person who is vomiting feces?
Fecal (fecaloid) vomiting - causes and symptoms
In medical practice, gastric vomiting most often occurs when a reflex eruption of stomach contents occurs. The precursors to the gag reflex are:
- nausea,
- rapid breathing,
- uncontrolled secretion of saliva,
- increased act of swallowing.
The most frequent urge to vomit occurs 30-40 minutes after eating, that is, at the very height of the digestive process. Vomit, in addition to the characteristic fermentative and/or putrefactive odor, contains remnants of undigested food. After such emptying of the stomach, a person usually feels significant relief.
When intestinal motility is disrupted, its contents enter the stomach, which also causes nausea in an adult or child.
Unlike the gastric gag reflex, intestinal or fecaloid vomiting has its own mechanism of occurrence - first vomiting of food occurs, which does not bring relief to the patient, then the person regurgitates bile, and only then fecal vomiting occurs, with black, white or green contents.
Causal factors for vomiting feces can be very different, for example:
- helminthic infestation,
- thrombosis of mesenteric vessels,
- intestinal obstruction in the distal area,
- inflammation of the abdominal cavity,
- kidney and/or liver damage.
However, clinicians believe that the causes of fecal vomiting are most common with intestinal obstruction. The main symptoms preceding vomiting of intestinal contents are also noted:
- long delay in defecation - 3-5 days,
- cardiopalmus,
- increased blood and intracranial pressure,
- irritability,
- general weakness,
- dyspeptic pain.
Read also: Proper nutrition for the stomach: eight simple rules
Also, a possible preceding factor for intestinal vomiting is an increase in a person’s body temperature to subfebrile values – 37-38 °C.
Causes of nausea and vomiting due to constipation
Stagnation of feces leads to the fact that toxins and waste products of microorganisms, which should have been excreted in the stool, begin to be absorbed from the intestines into the bloodstream. This is fraught with the appearance of intoxications of varying severity. One of the symptoms of poisoning is nausea, and in severe cases, vomiting.
But there are other mechanisms for the development of the symptom. So, when analyzing the possible causes of nausea and vomiting, you need to take into account the factors that led to constipation. Some of them can provoke nausea on their own.
For example, toxicosis during pregnancy can cause both constipation and nausea. These symptoms can develop even before the expectant mother finds out about her situation - during the first weeks of pregnancy.
In addition, constipation is often caused by an unbalanced, irregular diet and consumption of certain foods. Overeating can cause intestinal dysfunction, as well as nausea and vomiting.
Taking some medications can cause both constipation and nausea. Such side effects are common to many drugs. Researcher Rivkin V.L. in his scientific work lists the drugs that cause stool retention: “Beta-blockers, calcium antagonists, centrally acting antiadrenergic drugs, diuretics, antibiotics, tranquilizers, antidepressants, anticonvulsants” (Rivkin, 2013, p. 77) .
Another mechanism for the appearance of nausea is characteristic of chronic, prolonged constipation. Developing complications in the form of gastric dysfunction, intestinal dysbiosis, aggravation of the problem by proctological diseases lead to the fact that nausea can accompany constipation and be an independent symptom. A doctor can find out what complication has developed in a particular case. Many diseases are accompanied by other specific symptoms. For example, with dysbacteriosis, an unpleasant taste in the mouth and a coating on the tongue may occur. With the development of complications from the rectum, rectal bleeding and pain are observed.
It is important to remember that nausea and vomiting due to constipation can be a symptom of the development of diseases. The most common include the following:
- appendicitis;
- cholecystitis;
- gastritis, gastroduodenitis;
- intestinal obstruction;
- helminthic infestation;
- irritable bowel syndrome with a predominance of constipation;
- stomach ulcer, duodenal ulcer;
- neurological diseases, tumors, injuries;
- hypothyroidism, etc.
There are many reasons for the combination of constipation and nausea, so it is important to see a doctor for an accurate diagnosis.
First aid
Vomiting feces is a dangerous symptomatic sign of various disorders in the digestive system. Therefore, the only correct decision is to call an ambulance. Before the arrival of medical workers, it is advisable to provide first aid to the patient by following the following algorithm of actions:
- A person needs to be provided with complete rest and sufficient access to oxygen.
- The position of the patient's head should be below chest level.
- The urge to vomit should not be stopped.
- Monitoring a person’s blood pressure and consciousness is mandatory.
- Consumption of food and any liquid is strictly prohibited.
Important! In case of vomiting of intestinal contents, the use of drugs with antiemetic and laxative activity, as well as any cleansing intestinal enemas, is prohibited.
After the doctors arrive, further treatment is carried out in a hospital setting.
Nutritional Features
You can fight and prevent constipation with the help of nutrition. It is important to include fiber-rich foods in your daily diet and drink enough fluids. Some doctors argue that only clean drinking water matters. But you can’t ignore the liquid you take in soups. The total volume should be at least 30 ml per 1 kg of weight - on average 1.5-2 liters.
Your daily diet should contain foods rich in plant fiber, vitamins, and minerals. You need to review your diet and include the following foods:
- fermented milk products (taking low-fat kefir or yogurt before bed will be especially useful);
- fresh vegetables, seasonal fruits and berries;
- cereals;
- low-fat varieties of fish, meat, poultry.
The use of dietary fiber allows you to increase the volume of intestinal contents, speed up its passage through the intestinal tract, and therefore serve as the prevention of constipation. If it is impossible to consume the required amount of fiber with food, the use of supplements containing it is allowed.
Diagnosis and treatment
Vomiting of feces or its impurities is a clinical symptom that requires urgent therapeutic action. However, any treatment begins with diagnosis, that is, with a visual examination, anamnesis and instrumental examination. Unpleasant fecal odor from the mouth may indicate various pathological abnormalities in the body. A gastroenterologist or surgeon palpates the patient’s abdomen, identifying painful localization of the obstruction in the intestinal tube, and after an X-ray and/or ultrasound examination, a decision is made on conservative therapy or surgical treatment.
The waste of bile, and then vomiting feces, may indicate both large and small intestinal obstruction, as well as the presence of an intestinal fistula. In addition, similar symptoms occur during colonic volvulus, when fecal vomiting is a late symptom requiring urgent surgical intervention. In this case, we are talking about saving minutes of the patient’s life. If the evacuation of intestinal contents, according to experts, does not pose a threat to human life, then therapeutic treatment with various pharmacological agents is possible.
It is important to know that fecal vomiting is a clinical symptom of acute intestinal damage that requires a serious medical approach. Treatment with folk remedies in this case is absolutely ineffective.
Treatment of intestinal obstruction
In the absence of peritonitis, decompression of the gastrointestinal tract is carried out by aspiration of its contents through a nasogastric tube and siphon enema. Severe antiperistalsis and painful contractions are eliminated by antispasmodic drugs - Drotaverine® , Atropine® , Platyfillin® , etc. Perinephric or novocaine blockade will help stimulate intestinal motor functions. The water-electrolyte balance is restored with the help of intravenous administration of saline solutions.
Read also: Herbs for stomach and duodenal ulcers
Fecal stones blocking the intestines contribute to the development of mechanical ileus, that is, restriction of the movement of the food bolus. In this case, having determined the localization site, urgent surgical intervention is required.
What to do for constipation and nausea
The first priority is to identify the causes of constipation and the accompanying symptoms. If a disease is detected during diagnostic procedures, the doctor will prescribe specific treatment. In many cases, eliminating the cause of the condition normalizes bowel function.
If medications become the source of unpleasant symptoms, do not stop taking them yourself. Contact your doctor for dosage adjustments or alternative treatment options.
In case of prolonged absence of stool, you need to pay attention to the accompanying symptoms - a detailed description of the complaints will help the doctor determine the tactics for diagnosis and treatment. If you are sure that nausea arose precisely due to prolonged constipation, it is important to take measures to empty your bowels.
If you are not sure that there are no possible serious pathologies - intestinal obstruction, appendicitis, etc. - do not take any measures on your own, seek emergency help.
Get rid of intestinal problems
The natural British drug is not addictive and works immediately
Find Phytomucil with benefits
Prognosis and prevention
The outcome of clinical pathology depends entirely on timely treatment. Bile and fecal vomiting, as symptoms of colonic or small intestinal obstruction, should be eliminated no later than 4-6 hours after the start of the eruption of gastrointestinal contents. Otherwise, the situation is complicated by inflammation of the parietal and visceral layers of the abdominal cavity - peritonitis, systemic blood infection, and the person will face death.
How to cleanse the intestines (video):
To avoid an acute clinical condition, it is necessary to promptly pay attention to bowel function. Therapeutic prevention will include an annual ultrasound examination of the intestines, physical activity of a person and the exclusion of spicy, too salty and fried foods from the diet.