- To whom and why is the procedure prescribed?
- Preparation
- Carrying out a diagnostic procedure with and without anesthesia
- Rehabilitation
- Why is it better to do the procedure at the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences?
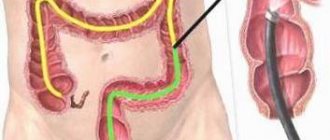
Translated from Greek, the term colonoscopy means “examination of the large intestine.” Using a diagnostic procedure, the doctor conducts a full examination of the condition of the intestines, identifying pathologies and neoplasms. For inspection, a flexible thin endoscope with a digital camera is used, with the help of which an enlarged image is transmitted to a monitor. During the study, it is possible to perform a biopsy and some therapeutic procedures: removal of polyps, stopping bleeding, and in some cases, administration of medications.
To whom and why is the procedure prescribed?
For diagnostic purposes, experts recommend regular colonoscopy under anesthesia at the age of 50+, even in the absence of symptoms, to exclude the possible presence of neoplasms. Indications for the procedure are also such manifestations as:
- discharge of blood, pus, mucus with feces;
- unexplained sudden decrease in body weight;
- constant constipation or alternating with diarrhea;
- pain in the abdomen and anus;
- discomfort, flatulence, feeling of incomplete bowel movement.
Indications for colonoscopy
Colonoscopy is prescribed in the following cases:
- frequent pain in the intestinal area
- bleeding
- purulent or mucous discharge from the rectal canal
- suspicion of inflammatory processes
- sudden, causeless weight loss
- the presence of cancer in the gastrointestinal tract in close relatives
- remove tumor or polyp
- remove foreign body
- stop the bleeding
- do a biopsy
- restore intestinal patency during narrowing (stenosis)
- eliminate adhesions
- identify the nature of hemorrhoids
Colonoscopy can be used to perform a number of medical procedures:
A referral for a colonoscopy is issued by a proctologist, gastroenterologist, or surgeon. The procedure itself is performed by an endoscopist. During the manipulation, he is assisted by a nurse and an anesthesiologist (if there is a need for general anesthesia).
Preparation
For a correct examination result, proper preparation for intestinal colonoscopy under anesthesia is important. It is necessary to free it as much as possible, for which cleansing enemas or special laxatives are used. 3-4 days before the procedure, fatty foods, gas-causing foods, flour products and milk should be excluded from the diet. You can have your last hearty lunch the day before, before 12 noon. The menu allows low-fat boiled fish, broth, semolina porridge, and scrambled eggs. Then only water without gas is allowed. You need to do an enema at night.
Given the significant pain of the examination, colonoscopy is best performed under anesthesia. Different types of anesthesia and anesthesia are used:
- local anesthesia involves lubricating the tip of the colonoscope with a gel that reduces sensitivity. However, this is an ineffective method that practically does not eliminate discomfort and pain;
- sedation is the process of putting the patient into a light sleep using intravenous administration of special drugs. The doctor begins the procedure only after he has completely fallen asleep, and awakening occurs after the end of the study. As long as the effect of the drug lasts, the patient is in a relaxed state, does not feel fear or pain, and awakening occurs easily and naturally.
Sometimes the procedure is done without anesthesia. Many people want to know what they will experience during the examination. However, it is impossible to answer unequivocally, because each person has his own, individual threshold of sensitivity. For some, the discomfort will be tolerable, but for others, the pain will not allow you to complete the procedure without the use of anesthetics. This issue is discussed with the attending physician, as well as how to prepare for a colonoscopy under anesthesia.
Ten years ago, colonoscopy was a fairly complicated procedure. Why?
The length of the human large intestine reaches 1.5-2 m (in some people 3 or more m), the intestine has several physiological bends along its length. During the examination, to ensure a good view, the intestine is inflated with air, which can cause intestinal spasms and severe pain. In addition, the very advancement of the probe through the intestine (especially in places of physiological bends) causes intestinal spasm and pain. The success of the procedure depends on the correct attitude of the patient, high-quality preparation for the procedure and the skill of the endoscopist.
Many patients undergo this procedure consciously, but during surveys, most of them note unpleasant (painful) sensations during the procedure, some of them are on the verge of tolerance. In some patients, the procedure causes severe pain, as a result of which it becomes impossible to move the probe through the intestines and the procedure has to be interrupted.
The modern approach in medicine is designed to ensure maximum safety and comfort during any therapeutic and diagnostic procedures. Unpleasant sensations during colonoscopy can be mitigated by performing the procedure while sleeping, i.e. under anesthesia.
Is it correct to carry out the procedure under anesthesia? The question is debatable. On the one hand, anesthesia is a fairly serious procedure, on the other hand, keeping the patient in a state of sleep eliminates the emotional and painful component of the manipulation, which significantly reduces the time of the procedure and allows the endoscopist to qualitatively examine the entire colon.
The safety and possibility of anesthesia during colonoscopy is assessed by an anesthesiologist. Taking into account your individual characteristics (weight, gender, age, concomitant diseases), the safest composition of anesthetics is selected, which allows you to fall asleep gently and wake up quickly after the procedure. After the procedure, the patient is observed in a comfortable room for an hour, finally recovers from anesthesia and leaves the clinic.
Carrying out a diagnostic procedure with and without anesthesia
An endoscope for colonoscopy is a thin flexible probe made of hypoallergenic material, equipped with a backlit camera, which allows you to obtain a high-quality image and display it on the monitor. Before the procedure, the patient lies on the couch on his left side with his knees tucked and, with the help of safe medications, is immersed in a pleasantly relaxing sleep. Only then the guided endoscope is carefully inserted inside and the doctor begins to examine the intestines.
Gradually, a high-precision device moves through the colon, and its folds are straightened by an air stream for a better view. If necessary, the doctor carefully removes a piece of tissue for histological examination. The entire procedure lasts approximately 15-30 minutes. After it, the patient wakes up without experiencing any pain or discomfort. After assessing his condition, the doctor allows him to leave the clinic.
Colonoscopy performed without anesthesia cannot be called as comfortable. Although the tip of the endoscope is lubricated with a special substance, pain cannot be avoided. In addition, throughout the entire procedure there is discomfort from the introduction of air to straighten the folds of the colon. Another nuance is that in a moment of painful sensation or from anxiety and fear, the patient may twitch, and this is undesirable. After completing the study, you can leave the hospital. However, judging by the reviews, for the next examination many will prefer to opt for anesthesia.
Importance of the procedure, decision to use anesthesia
By performing this hardware examination, it is possible to determine the type of disease, the form of the pathological process, the degree of intestinal damage and the involvement of neighboring organs and tissues in the inflammatory process. About 10-15 years ago, this manipulation was considered painful. During the procedure, the endoscopist, directing the tube in the desired angle, could cause pain, because the intestines are equipped with an incredible number of nerve receptors. The painfulness of endoscopic examination forced many patients to refuse, agreeing to X-rays, ultrasound, MRI and computed tomography. But the disadvantage of such hardware manipulations is the inability to take biomaterial for examination for the presence of cancer, determining the infectious source + type of pathogenic flora. To eliminate the painful factor, doctors began to perform colonoscopy under local or general anesthesia.
Rehabilitation
After a colonoscopy, a hospital stay is not expected; the patient leaves the hospital. Drugs administered for anesthesia are eliminated from the body within several hours. For the first half hour or hour, sudden movements should be avoided, and the feeling of fullness in the intestines is a normal possible reaction, it passes quickly.
Main purpose of colonoscopy
The main task of endoscopy is the early diagnosis of any intestinal pathologies to prevent the development of dangerous complications:
- inflammatory diseases - Crohn's disease and colitis;
- ulcerative and erosive intestinal lesions;
- tumor and polypous formations;
- intestinal hemorrhages (bleeding).
During an endoscopic examination, our specialists can take a biopsy sample for research to establish an accurate diagnosis.
Why is it better to do the procedure at the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences?
When choosing a clinic for an informative, but not very pleasant (without anesthesia) examination, you should first of all focus not on the cost of the procedure, but on factors such as the experience and qualifications of doctors, hospital equipment, and patient reviews. The Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences offers many advantages:
- painlessness of the procedure;
- high-precision modern equipment;
- high level of qualification of specialists;
- professionalism of experienced doctors in making a diagnosis and prescribing effective treatment;
- affordable price of the procedure.
The clinic staff considers tactfulness, attention, willingness and ability to help to be a priority in relations with patients. Already at the first meeting, during the consultation, the doctor simply and clearly conveys important information about colonoscopy - how to prepare for it, how long the examination will last, what can and cannot be done the day before and on the day of the procedure. This creates a certain mood and inspires trust. This means that the result of a well-thought-out treatment method after an informative, most gentle diagnosis will be wonderful.
List of contraindications
The procedure for examining segments of the colon through an endoscope has become the number one tool in making the correct diagnosis. But despite the positive side of the diagnostic method, there are contraindications for its implementation.
Colonoscopy is not recommended if:
- increased reactivity of the body to anesthetics;
- pathologies of the central nervous system;
- epilepsy;
- pernicious anemia;
- cardiovascular failure;
- suffered a heart attack or stroke;
- mitral valve insufficiency;
- urolithiasis;
- peritonitis;
- pregnancy.
Even with such contraindications, if there is a critical need, this procedure is performed. All stages are discussed in advance, and when it is performed, in addition to the endoscopist, several doctors are present (anesthesiologist, resuscitator, oncologist, surgeon). Considering the risks of the procedure, doctors are ready to provide specialized assistance in case of unforeseen circumstances such as bleeding, respiratory arrest, heart rhythm disturbances, perforation of the intestine due to ulcers, polyps or tumors. Before the procedure, the patient must be prepared according to a special scheme, which determines the results of the study and the patient’s condition before and after the investment.
Diet recommended before the study
The basis of the standard method of preparing the colon for endoscopic examination is diet. It involves switching to refined, easily digestible foods that do not contain difficult-to-digest components. A diet is required for 3 or 4 days before the procedure, with a transition to clear drinking the day before the examination.
Can:
- chicken eggs;
- varieties of meat with low fat content, soups made from them without vegetables;
- low fat fish varieties;
- products made from low-fat milk - skim milk (no more than 500 ml), low-fat kefir, cheese, curd products, natural yogurt;
- drinking - juices without pulp of a transparent consistency, tea and low-strength coffee;
- sweets - various syrups, bee honey, jelly, regular sugar.
In small quantities, it is permissible to use margarine, natural vegetable and butter, and mayonnaise as part of dishes and separately.
It is forbidden:
- pasta, flour and bakery products;
- cereal porridge, coconut flakes, any nuts, muesli, poppy seeds, grains;
- various greens, all berries, fresh or cooked fruits and vegetables;
- white cabbage, fresh or cooked;
- okroshka, various milk or cream soups;
- poultry and meat with a high fat content;
- smoked meats, sausages and various pickles;
- any homemade and store-bought canned goods;
- river and sea fish with excess fat content;
- seaweed and dishes made from it;
- mushrooms in brine or marinade;
- fatty cottage cheese, ice cream and dairy products with the addition of pieces of fruit;
- seasonings with herbs and spicy ingredients;
- alcohol, compote, kvass, soda;
- beans, peas, lentils;
- sweet foods are not from the permitted list.
The day before the examination, you should drink and eat only clear water. We recommend drinking or mineral non-carbonated water, clear fruit ice or jelly, juices without pulp, tea and coffee without the addition of milk and cream, clear meat broths. The amount of liquid is not limited.
It is important to remember that you should not consume drinks and jellies with a red tint, milk, jelly, juices and fruit drinks with pulp and small seeds.
Preparation rules
Survey results
The results of the examination depend on what changes in the intestinal cavity the doctor finds:
- Inflammatory diseases of the colon (pseudomembranous colitis, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease) are characterized by the presence of an abundance of bloody or mucous exudate in the intestinal lumen, swelling and hyperemia of the intestinal walls, ulcerative lesions and the application of non-globular protein (fibrin).
- Tumor neoplasms. They can form directly on the mucous membrane or grow into the intestine from the outside. In this case, at the affected area, a change in tissue color, bleeding and smoothness of the folds are noted.
- Polyps are pale pink growths sitting on a thin or thick stalk. There may be single or multiple formations (polyposis). They stand out well on the mucous membrane. They are usually removed during the examination.
In addition, endocoloscopy allows you to identify inflammatory processes and diagnose diverticulosis.
The doctor describes in detail all detected changes in the intestines, their size and location in the medical report. A quarter of an hour after the procedure, the patient receives the result in his hands. You can immediately make an appointment with a doctor for a final diagnosis and prescription of the necessary treatment. If a biopsy was performed during the examination, the research results will be ready after a week.
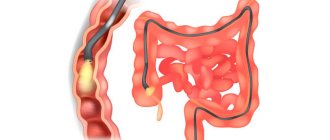
Colonoscopy with polyp removal
When malfunctions occur in the intestines, growths appear on the mucous membrane - polyps.
They are benign and grow without symptoms, but can become malignant, that is, degenerate into malignant neoplasms. In order not to miss the growth of the tumor, colonoscopy is performed regularly - for men and women over fifty, once every 5 years or as indicated. Polyps can be removed immediately if it is safe for the patient. When the polyps are large or there are too many of them, the tumors are removed during a separate procedure. Removing polyps is called a polypectomy. Together with the endoscope, forceps or a loop are inserted into the intestine. The forceps pinch off a piece of the tumor, and the loop excises it. The material is placed in a container and sent for analysis to the laboratory.
Polyps do not disappear or dissolve. The only way to get rid of tumors is to remove them.