Contrast-enhanced X-rays of the stomach and esophagus can detect diseases such as hiatal hernia, ulcers or cancer. To increase the information content of an X-ray examination of the gastrointestinal tract, a polypositional study is used in the vertical, horizontal and lateral position of the patient.
For the diagnosis of paraesophageal (near the esophagus) hiatal hernia, the Trendelenburg position is important, since it increases intra-abdominal pressure.
What it is?
The method is based on the use of X-ray radiation. It is carried out due to the ability of rays to penetrate the tissues of the body and, reflecting from their contour, leave an imprint of the image on the film. Usually the study is prescribed by a therapist or gastroenterologist.
Thanks to X-ray methods for examining the gastrointestinal tract, you can see both the internal and external surface of the stomach, as well as identify a wide range of disorders. To examine the stomach, a contrast agent based on a barium mixture is used. Its peculiarity is that it is not capable of transmitting X-rays. Thanks to this, the doctor not only sees the condition of the internal organs, but also evaluates their function.
Contrast with two substances
X-ray of the esophagus with contrast is quite effective. It can be performed using double contrast. In this case, barium and gas are used. The bottom line is that the barium mixture is drunk using a straw. At the same time, air is swallowed. To ensure proper and uniform delivery of contrast, a massage is performed in the abdominal area. The air, in turn, plays the role of a straightener of folds in the esophagus and stomach.
Additionally,
antispasmodics .
They also affect the muscles, which promotes the straightening of organs. This method is aimed at a thorough study of the esophagus. With its help, you can recognize a tumor in the early stages. After this method, constipation and nausea may develop. It is also recommended to drink more water.
Indications
List of indications for radiography of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum:
- gastric ulcer or gastritis (it is necessary to visualize the mucous membrane and evaluate its integrity);
- tumor process (it does not matter what nature the neoplasm is);
- hiatal hernia;
- stricture (consequence of scar changes) of the gastric mucosa;
- disturbances in the passage of the food bolus through the gastrointestinal tract.
Signs that pathology may be lurking in the stomach are unexplained weight loss, nausea and vomiting, and pain of varying intensity in the epigastric region . Pain may occur before and after eating, or may not depend on it at all. One of the symptoms of the disease is also dysphagia (swallowing disorder), appetite disturbances, belching and heartburn.
Preparing for an x-ray of the esophagus
Before a barium x-ray of the esophagus, certain preparations should be made.
Stop eating and drinking 8 hours before the procedure
It is advisable to avoid eating any food in preparation for a barium x-ray of the esophagus for at least 8 hours before the procedure. This will provide a more accurate picture of the condition of the esophageal walls and prevent distortions that could be caused by food remaining in the esophagus. This will also help to avoid difficulties when barium suspension flows around the walls of the esophagus.
Exclusion from the diet of foods that stimulate gas formation in the gastrointestinal tract
Also, when preparing a patient for an X-ray of the esophagus with barium, it is worth excluding from the diet foods that contribute to gas formation in the organs of the gastrointestinal tract. It is necessary to understand that air masses interfere with obtaining informative images, which can cause difficulties in making a diagnosis.
Contraindications
X-rays in a certain dose are relatively safe for humans, and the method itself is quite informative. But in some cases, it is better to refuse x-rays in favor of other diagnostic methods.
X-ray is contraindicated for:
- ongoing bleeding from the upper gastrointestinal tract
- the presence of pregnancy in a woman, as well as during breastfeeding;
- an existing allergic reaction to the administered contrast;
- serious condition of the patient with decompensation of vital organs and systems.
Radiography is justified if the proposed diagnostic value is greater than the possible harm.
Important: Radiation used in X-rays in high doses is harmful to the body. Modern devices reduce radiation exposure as much as possible, which makes it possible to carry out the procedure 3-4 times a year without negative effects.
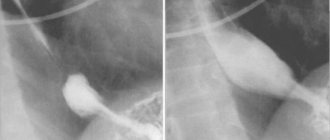
What does the doctor see on x-rays?
At the same time, when conducting an examination of the esophagus, an examination of the stomach is also carried out. This allows for a comprehensive assessment of the condition and functioning of these organs. Pictures are taken in several positions. There is a lateral, upright, supine and Trendelenburg .
With a direct projection, the doctor evaluates the relief of the entire mucous membrane of the esophagus and the adjacent part of the stomach. It is in this projection that the position and condition of the grooves and folding in the organs are assessed. Information about the state of the transition between the esophagus and stomach is especially important during direct projection.
In the lateral projection, the degree of organ movement is assessed. That is, in this case it is clearly visible whether the patient has neoplasms. In this case, the tumor may be located in neighboring organs. This phenomenon will be visible in the photographs as a change in the localization and displacement of the organ. In the lateral projection, it is also possible to assess the condition of the esophagogastric sphincter and determine reflux .
Lying on your back allows you to assess the condition of the gastric mucosa. In the image, the doctor clearly sees the lesser curvature of the stomach. The condition of folds and grooves is assessed.
The Trendelenburg position allows you to assess the condition of the esophageal opening in the diaphragm. Using this body position, a hernia is detected.
How do they do it?
X-ray of the stomach consists of three successive stages:
- Performing a plain radiography of the abdominal organs. It is performed with the patient standing. In the picture, the doctor excludes possible gross violations of the digestive system.
- Introduction of contrast into the body. The patient drinks the barium mixture while standing (about 200 ml).
- The X-ray of the stomach itself. In order to get really high-quality images, in which the contours of the stomach will be clearly visible, the examinee is asked to change his body position: first stand, then lie on his back, on his stomach and on both sides.
The duration usually does not exceed 20-30 minutes. X-ray examination of the gastrointestinal tract is painless, well tolerated and does not require further patient care.
In Trendelenburg position
An X-ray in the Trendelenburg position is done if a diaphragmatic hiatal hernia is suspected. The patient is positioned so that his pelvis is elevated relative to the rest of the body by 45 degrees. The intestines are moved to the upper abdomen, allowing a better view of the stomach.
The Trendelenburg position is not used if there is purulent or bloody discharge in the patient’s abdominal cavity, as well as any other accumulations of fluid, as this can cause them to flow into the pockets of the liver or spleen.
Trendelenburg position
Indications for X-ray examination with barium
There are a number of indications that require an X-ray examination of the esophagus with barium. If there are suspicions regarding the disease and diagnosis, this type of diagnosis can also be performed. We list some conditions in which it is recommended to take an X-ray of the esophagus with barium.
Swallowing disorders: feeling of retention of a bolus of food, pain when swallowing food
Various disturbances in the act of swallowing, the appearance of a lump in the throat, pain when swallowing food may indicate an obstacle to the natural flow of food during the act of swallowing. The cause of this pathological condition may be the presence of a foreign body in the esophagus, thickening of its walls, or the growth of neoplasms of various origins.
An X-ray of the esophagus with barium will clearly show the location of the obstruction in a certain part of the esophagus, and will also make it possible to assess its size and shape, which will help specialists in making a reliable diagnosis and selecting rational treatment.
Chest pain not associated with pathology of the respiratory system and cardiovascular system
If there is a history of pain in the chest and, with the help of differential diagnosis, it was found that they are in no way related to the cardiovascular and respiratory systems, then it is possible to assume a pathology of the esophagus. Since the esophagus is located directly behind the trachea and descends all the way to the diaphragm and stomach, the cause of pain can very likely be localized there.
Diseases such as hiatal hernia, esophagitis and peptic ulcers can be accompanied by pain and are detected using contrast-enhanced radiography of the esophagus.
Repeated vomiting, heartburn, belching
If the clinical picture contains symptoms such as repeated heartburn, vomiting and belching, then this may indicate a violation of the motor function of the esophagus, as well as its anatomical sphincters or the presence of various pathologies of the walls. Thus, this symptomatology can occur with diverticula of the esophagus, dyskinesia and achalasia. All these diseases can be detected using a barium X-ray of the esophagus.
Other methods
X-ray examination is not the only procedure prescribed for diagnosing diseases of the stomach and duodenum. If there are contraindications, it is advisable to use other diagnostic methods that have their own advantages and disadvantages.
| Procedure name | pros | Minuses |
| Radiography |
|
|
| FGDS |
|
|
| Ultrasound |
|
|
|
| |
| Capsule endoscopy |
|
|
Along with X-ray, the leader in the reliability of the results obtained is FGDS. Our article will help you choose one of these two studies, where we identify the pros and cons of both methods.
X-ray of the esophagus and stomach: how to do it
There are several ways to conduct research. Traditional method:
- It is carried out in the morning on an empty stomach. The patient is in a lying position on a special table.
- The patient is asked to drink a contrast agent. Barium suspension is used as it .
- The patient takes a couple of sips of barium solution . Then the mixture moves along the esophagus, and at this moment transillumination is performed. When the mixture reaches the sphincter, a picture is taken.
- During the entire procedure, the patient changes the position of his body. The position on your back with your pelvis elevated is especially important. This allows you to examine other parts of the gastrointestinal tract.
X-ray of the esophagus and stomach lasts no more than 40 minutes. It is possible that after the manipulation you will feel a little nausea. The contrast agent will be released in your stool. In this case, the color of the stool will be gray. Sometimes constipation may occur. This is due to the fact that the substance has astringent properties. To quickly evacuate barium, it is recommended to drink 1.5 liters of distilled water.
Price
The cost of X-ray examination of the stomach and duodenum in Moscow and St. Petersburg is approximately the same. The price range starts from 1.2 thousand rubles and ends at 4 thousand rubles.
The price depends on the clinic where the patient wants to be examined, on the number of images and the contrast administered. In the Sverdlovsk, Novosibirsk, and Tula regions, prices are slightly cheaper - from 870 rubles.
Help The procedure is included in the list of studies that are carried out under the compulsory medical insurance policy. Therefore, in public medical institutions, if indicated, stomach X-rays can be taken free of charge with a doctor’s referral.
What are the indications for the procedure?
Fluoroscopy is performed to make a diagnosis and to monitor treatment. Therefore, there are some indications for this. Firstly, it is a long-term inflammation of the mucous membrane of the esophageal canal and stomach. A patient with GERD .
Carry out to assess the degree of narrowing of the esophageal tube. In this case, the indication will be the appearance of scar tissue in this organ. The method is used to detect and monitor the treatment of hiatal hernias .
The indication is any disease in the esophageal canal and stomach, with the exception of the special cases described above.
Contraindications
An absolute contraindication is pregnancy. X-rays are not performed for symptoms of esophageal and gastric bleeding. They also do not resort to it when the patient is in serious condition. In these cases, more suitable examination methods are used.
In what cases is the study indicated?
The method allows you to visualize the area of the esophagus, assess its internal state and find most anomalies and pathologies. Thanks to what an x-ray of the esophagus shows, a specialist can make a diagnosis for almost any disease. Therefore, examination is prescribed for a large number of different symptoms.
Unmotivated, repeated vomiting
In most cases, vomiting is of visceral origin (caused by irritation of stomach receptors). However, the symptom can also appear with a malignant neoplasm in the esophagus. Then vomiting will recur for no apparent reason. Blood clots may appear in it.
To diagnose a tumor, the patient is sent for a contrast-enhanced x-ray of the esophagus. The method allows you to detect a tumor, localize it and make an assumption about its nature.
Belching that accompanies the patient constantly
Belching often occurs when swallowing function or esophageal motility is impaired. The patient complains of a lump in the throat and heartburn, vomiting and other symptoms. The problem may lie in achalasia cardia, scleroderma or other diseases.
It is almost impossible to make an accurate diagnosis without a detailed examination of the esophagus. Therefore, in diagnosis, the specialist relies on what an x-ray of the esophagus shows.
Suspicion of reflux
Reflux is the reflux of stomach contents up the gastrointestinal tract into the esophagus. This occurs due to insufficiency or damage to the lower esophageal sphincter, which is supposed to act as a valve.
With reflux, stomach contents rich in hydrochloric acid and pepsin (a protein-breaking enzyme) enter the esophagus. In this case, the patient experiences heartburn and discomfort. If reflux occurs regularly, erosion and peptic ulcers will appear in the lower part of the organ. If the disease is not detected in time by X-ray of the esophagus and not treated, severe bleeding caused by perforation of the esophageal wall and other dangerous complications are possible.
Pain syndrome behind the sternum
The pain is caused by stretching of the walls when food passes through. Often the sensation is spasmodic in nature, pain radiates to the jaw, ear, neck and back.
Pain may appear due to irritation of the mucous membrane of the organ due to esophagitis, reflux or malignant neoplasm. To make an accurate diagnosis, a specialist needs to conduct a series of examinations, including an x-ray of the esophagus.