- Why is daily pH monitoring performed?
- Indications for the study
- Indications for gastroesophageal reflux
- Contraindications
- Equipment
- First appointment with a doctor
- How is the research going?
- Services of the gastroenterology center at SM-Clinic
Daily pH monitoring
is a method for studying the functional state of the upper gastrointestinal tract. It is based on long-term (over 24 hours) measurement of the level of acidity (pH) and impedance (resistance) directly in the esophagus and stomach using a special device. Normal acidity is ensured by sufficient production of hydrochloric acid, as well as timely and coordinated muscular work of the digestive organs. When these functions are disrupted, acid-dependent diseases occur, such as gastroesophageal reflux disease, peptic ulcer, and gastritis.
How to study the acidity of gastric juice
There are several methods to determine the acidity of the stomach. Thus, fractional intubation can be performed, during which part of the stomach contents is sucked out using a special tube and then examined in the laboratory. This method is considered not very reliable, since the process of such diagnostics, which is lengthy and quite unpleasant for the patient, disrupts the natural functioning of the stomach, as a result of which the results obtained are only partially trustworthy.
Another method is called “staining the stomach wall.” Its essence is that a special dye is injected through the endoscope channel during the gastroscopy procedure. The doctor then monitors how the color of the dye changes, based on which he draws conclusions about the acidity.
Experts are also wary of this method, since it is based solely on visual data and gives only very approximate results.
The method of studying acidity using ion exchange resins is quite uninformative, although not traumatic for the patient. The patient is asked to take a special reagent that contains pigment. This dye passes through the gastrointestinal tract and is then excreted in the urine. By assessing the degree of urine coloration, doctors draw a conclusion about the acidity of the stomach.
Finally, there is another, more informative method that allows you to obtain accurate data on the concentration of acid in the stomach. This is pH measurement, which involves measuring acidity in different areas of the gastrointestinal tract over a certain time. For this purpose, special devices are used - acidogastrometers, which are equipped with several pH sensors attached to probes.
Equipment
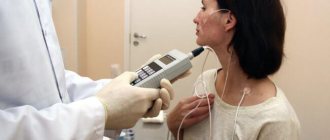
The SM-Clinic uses an ambulatory pH recorder for 24-hour pH/impedance measurements OHMEGA (Medical Measurement Systems, the Netherlands). It is a small and lightweight recorder that allows you to record pH and impedance values at the same time. Impedance measurement makes it possible to determine refluxes - acid, gas and mixed. The device detects refluxes and classifies them into acidic and non-acidic. This method is clinically convenient to evaluate the symptoms (causeless cough, hoarseness, etc.) of non-acid reflux during treatment with proton pump inhibitors.
Indications for pH testing
First of all, you should remember that you cannot “prescribe” this procedure to yourself. A gastroenterologist exclusively refers you for examination if he believes that problems in the digestive tract may be associated with acidity problems. There are also diseases for which this study is indicated. These are peptic ulcer disease, chronic gastritis and duodenitis, pancreatic adenoma, changes in the tissue of the epithelium of the esophageal mucosa, as well as GERD.
In addition, the doctor may prescribe pH testing to monitor the patient's condition after gastrectomy, as well as to monitor the effect of medications designed to reduce or increase the acidity of gastric juice.
Finally, this diagnostic method is indicated if it is not possible to accurately determine the etiology of the disease and doubts arise about the correctness of the therapy.
Why do you need pH testing of the esophagus?
Using pH-metry, you can assess the condition of the esophagus and identify dysfunction. The technique is based on measuring acidity (pH) and resistance (impedance) in the esophagus and stomach using a diagnostic device.
The acidity of the stomach depends on the production of hydrochloric acid in sufficient quantities, which, in turn, affects the functionality of the digestive organs. At the slightest deviation, acid-dependent pathologies develop: gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), Barrett's esophagus, gastritis, etc.
Therefore, in diseases associated with the reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus, it is important not only to confirm/exclude the presence of gastroesophageal reflux. It is also necessary to identify what happens in the esophagus, how long the mucous membrane is in contact with the acidic gastric contents, the effectiveness and duration of action of medications, etc.
Based on the results obtained, drugs and the regimen for their use are selected. With the advent of this technique, it became possible to select medications for a specific patient, abandoning those that are ineffective.
Types of pH measurement
Today, there are several types of pH measurements that can solve various diagnostic problems.
The simplest method is endoscopic pH measurement. This procedure only takes about five minutes. It is performed during fibrogastroscopy. A special pH probe is inserted into the instrumental channel of the endoscope, with the help of which the acidity level is established at nine points in the stomach and duodenum. The procedure is carried out under visual control. When interpreting the results, doctors take into account the fact that endoscopy itself stimulates the production of acid in the stomach.
Express research, which takes at least half an hour. In this case, the level of acidity is determined exclusively by the pH level in the so-called body of the stomach.
Short-term intragastric pH-metry. This procedure involves determining the initial indicators of stomach acidity, as well as its stimulation with special substances. Doctors analyze the average indicators in different departments, on the basis of which they make a general conclusion.
A daily study lasting 24 hours. At the same time, the patient is not in the hospital or in the doctor’s office all the time, but must continue his normal lifestyle and be in a familiar environment. The patient is asked to take food in the mode in which he is used to taking it, and also to record his feelings and details of his well-being in a special diary.
Which particular technique is used in each specific case depends, first of all, on the individual characteristics of the patient, as well as on the disease. All types of diagnostics, with the exception of daily diagnostics, are carried out in a hospital, patients are under the supervision of medical personnel.
Decoding the results
With this procedure:
- determine the acidity level;
- establish a period during which the stomach is exposed to the negative effects of hydrochloric acid;
- determine the effectiveness of esophageal clearance.
The readings obtained from PH measurements are interpreted by a specialist. The stomach environment can be alkaline, normal, slightly acidic or simply acidic. The norm depends on the study area. Based on this information, the doctor makes a diagnosis and determines the severity of the disease. The cost of the procedure is calculated taking into account the type of pH measurement, the price of the medicines and equipment used.
Methodology and preparation for the study
As noted above, the devices used for pH measurement are called acidogastrometers. These are flexible probes equipped with special measuring electrodes, which are inserted through the mouth or nose into certain parts of the gastrointestinal tract.
The probe is inserted exclusively in the morning, on an empty stomach. In this case, at least twelve hours must pass since the last meal. Smoking is also prohibited during this time. Please note that you can drink water for the last time no later than four hours before the procedure - otherwise the risk of complications when inserting the probe increases (the patient will feel nauseated and may vomit). In addition, water can change the acidity of the stomach, which will distort the study data, as a result of which the reliability of the results will decrease.
Before diagnosis, you should inform your doctor about what medications you are taking. Some medications should be stopped at least three days before the procedure, others should be stopped twenty-four hours before the test.
It is recommended that a few days before the procedure, you avoid taking foods that can distort the data by changing the pH of the stomach. So, it is necessary to completely exclude black coffee, strong tea, fruit juices and yoghurts from the diet, or at least reduce the presence of these products on the menu as much as possible. Alcohol and carbonated drinks, as well as mineral water, should be completely excluded.
Express and short-term pH measurements are carried out in a medical office, under the constant supervision of a doctor. The patient is in a sitting position. For these studies, oral pH probes are usually used - in other words, those that are administered through the mouth. Such probes are thicker than transnasal ones, but the risk of them getting wrapped up in the stomach is an order of magnitude less.
The most frightening thing for many patients is the daily diagnosis. Typically, people are concerned about the fact that they will not have a medical professional nearby and the probe will be inside for a long time. A qualified doctor should treat such experiences with understanding and explain to the patient in detail the essence of the procedure and his behavior during the study.
The probe for daily research is inserted through the nasopharynx, so the patient will be able to eat as usual. The recorder is attached to the belt. To make the research data more accurate and complete, the patient is asked to keep notes in a special diary. Most often, it is necessary to note the time of meals and medications, as well as indicate the periods of staying in a horizontal position. It is also necessary to record any negative sensations associated with the gastrointestinal tract - heartburn, nausea, discomfort. It is the daily diagnosis that is considered the most informative and complete and provides the maximum amount of information necessary to analyze the patient’s condition.
How is daily pH measurement performed?
The procedure begins in the first half of the day; for examination, it is recommended to hospitalize the patient in the clinic for a day. The study consists of inserting a thin probe with a diameter of 2.2 mm into the esophagus and/or stomach transnasally - through the nasal passage. To eliminate unpleasant sensations, anesthesia of the nose and throat is possible.
To ensure that the probe is installed correctly, its position is monitored using a pressure gauge or x-ray equipment. To obtain information related to the examination, a portable recording device is attached to the probe equipped with sensors, which is attached to a belt. During the entire examination, which lasts 24 hours, the patient engages in usual activities, takes food, medications, etc.
At the end of the examination, usually after 1-2 days, the patient receives a result that indicates the quantity and quality of the contents entering the esophagus, contains graphs, a data block and a doctor’s conclusion.
Contraindications to the procedure
Like any medical procedure, pH measurement has a fairly impressive list of contraindications. Therefore, if the doctor talks about the need for this diagnosis, it is necessary to clarify exactly what diseases you suffer from and what medications you are taking.
Contraindications to the study include not only diseases for which insertion of a gastric tube is not recommended, but also health problems for which the use of certain bioactive stimulant substances is not permitted.
Thus, a pH probe must not be inserted during gastric bleeding, as well as for ten days after its cessation. Patients with an aortic aneurysm, as well as those who have been diagnosed with coronary insufficiency and severe hypertension, should refrain from performing the procedure.
The probe should not be inserted in case of any injuries or burns of the esophageal mucosa, as well as in case of serious bleeding disorders. Reasons for refusing the procedure are also maxillofacial injuries and nasopharyngeal obstruction. Difficulties when inserting a probe may occur in patients suffering from diseases of the thyroid gland, in particular, nodular goiter.
The psychological factor is also of great importance. People with an overly labile nervous system are often simply unable to properly tune in to the procedure, as a result of which they may experience asthma attacks or panic attacks.
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
As a rule, such phenomena can be avoided if the doctor explains the essence of the manipulations.
Purpose of the study
Daily pH impedance monitoring of the esophagus and stomach with acidity monitoring sets the following objectives:
- Assessment of the process of daily production of gastric juice under normal operating conditions of the body, taking into account the influence of external factors (smoking, physical activity, body position, medication) on acidity;
- Diagnosis of gastroesophageal or duodenogastric reflux, the frequency and severity of their manifestation, as well as the degree of aggressiveness of the influence of the contents thrown from the duodenum and stomach onto the mucous membranes of the stomach and esophagus, respectively;
- Detection of factors that provoke the formation of reflux;
- Assessing the effectiveness of prescribed therapy;
- Assessment of the condition of the stomach and esophagus during periods of preparation for surgery and after surgical treatment;
- Designing a schedule of individual acidity rhythms and adjusting the patient’s daily diet taking into account the data obtained;
- Selection of long-acting medications to reduce and control acidity levels.
Indications for intragastric pH measurement:
- apnea;
- heartburn;
- chest pain;
- cough;
- hoarseness and hoarseness of voice;
- widespread recurrent caries;
- bad breath, subject to regular hygiene procedures.
Indications for GERD:
- nonerosive type of disease;
- extraesophageal symptoms (hoarseness of voice, sore throat, chest pain, paroxysmal shortness of breath, dental diseases, association with bronchial asthma);
- refractory form of GERD;
- functional heartburn;
- esophageal hypersensitivity;
- individual selection of antisecretory treatment;
- the period before and after surgery, for example, during gastric resection or elimination of hiatal hernia (hiatal hernia), a disease in which the lower part of the esophagus or stomach is displaced relative to the diaphragm.
Is there a risk of complications?
Theoretically, when performing daily pH-metry of the stomach, there is a possibility of complications developing: damage to the mucosa, bleeding, bronchospasm, vomiting, rhinorrhea. A serious complication is perforation of the esophagus or stomach. To eliminate the risk of undesirable consequences, it is better to carry out the procedure in specialized clinics equipped with modern equipment.
If there are various diagnostic methods to identify pathology of the esophageal mucosa (gastroscopy, tomography), then the functioning of the esophagus can only be assessed using pH-metry. Therefore, patients with gastric diseases are recommended to use the method of esophageal daily pH impedansometry, which today is considered the “gold” standard in the examination of patients with pathologies of the digestive system.
Sign up for a consultation: +7 (495) 782-50-10